Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
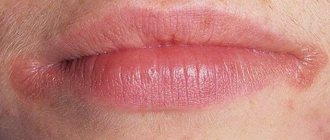
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is a chronic pathology characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa. Its main symptom is a rash of aphthae or ulcers, which are noticeably painful. Aphthae usually appear periodically in the following areas:
- Language;
- Cheeks;
- Hard and soft palate;
- Mucous membrane of the lips.
If ulcers are periodically injured, they can develop into full-fledged, difficult-to-heal wounds, in place of which noticeable scars remain. The normal healing time for aphthae is no more than a week from the moment of its appearance.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis are as follows:
- Chronic colitis;
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Chronic stress;
- Injury to the mucous membrane;
- Hormonal imbalance during menstruation.
With a normally functioning immune system, ulcers heal on their own in one, or in extreme cases, two weeks. If healing does not occur, you must visit a doctor to prescribe the correct treatment. As a rule, the basis of therapy is taking vitamin C, which has a positive effect on the immune system.
Trophic ulcer - treatment in Moscow
Do you have a trophic ulcer? Treatment in Moscow or in any other city is quite lengthy and involves a whole range of measures to ensure that the trophic ulcer disappears. Conservative treatment, the same as drug treatment, is aimed at reducing the symptoms of the underlying disease that caused a violation of tissue trophism, treating the ulcerative lesion itself and fighting secondary infection.
Excellent results in laser treatment of trophic ulcers
Depending on the stage, the trophic ulcer is removed in different ways. Treatment (Moscow offers many methods) depends on the stage of development of the trophic ulcer and is carried out in the following areas:
- local treatment;
- elastic compression;
- drug treatment;
- hemosorption - removal of toxic tissue breakdown products from the blood;
- physiotherapy;
- autoirradiation of blood with laser or ultraviolet rays;
- surgical intervention if indicated;
- visiting sanatoriums.
What to do if you have deep trophic ulcers of the lower extremities? What to do if a large trophic ulcer, treatment (photo, results you have already assessed) which you have not carried out, increases?
Herpetiform stomatitis
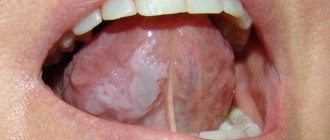
Herpertiform stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of numerous ulcers on the oral mucosa, which in appearance resemble ordinary herpes. Girls under 30 are at risk - they are the ones who suffer from pathology more than others. Locations of the disease:
- Underside of tongue;
- Floor of the oral cavity.
Ulcers heal in no more than 10 days from the moment they appear, leaving no scars. Treatment, as in the case of the previous type of stomatitis, is based on the use of vitamin C. The dosage and regimen of medications is prescribed by the attending physician.
Trophic ulcer - treatment at home
The attending physician decides about the possibility of treating the disease at home. With the prescribed set of medications, the patient can do dressings at home, while regularly visiting the doctor. It is desirable, of course, that this doctor be a good specialist in the treatment of trophic ulcers. There are few such doctors in Moscow.
Leading specialist of our center for the treatment of trophic ulcers Malakhov A.M.
Our leading surgeon-phlebologist Alexey Mikhailovich Malakhov deals with this problem.
Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis
Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis is also called Setton's aphthae. Its symptoms are:
- Seals appear in the submucosa of the oral cavity;
- Instead of compactions, ulcers with raised edges develop over time;
- The ulcers become inflamed, causing blood and lymphatic discharge.
Places where such afts accumulate are the upper and lower lips, cheeks and sides of the tongue. The pathology is characterized by extremely severe pain. Patients find it so difficult to eat that many give up eating completely. Difficulties also arise during conversation. The healing process of aphthae lasts a long time - sometimes up to several months, and the pathology itself persists for up to several years.
Trophic ulcer - symptoms
Trophic ulcers do not form spontaneously. Initially, swelling appears, accompanied by severe itching. The skin becomes thinner. Pigmentation or cyanosis appears.
Multiple trophic ulcers on the leg
The appearance of a trophic ulcer is often accompanied by chills and night cramps of the calf muscles. Due to stagnation in the lymphatic vessels, droplets of liquid begin to appear on the glassy surface of the skin. Next, the foci of exfoliated epidermis merge, and an ulcer with ragged, compacted edges is formed, causing severe pain at the slightest touch. As a rule, the ulcer surface is quickly colonized by bacteria, and the bleeding ulcer begins to fester.
Afty Bednar
Bednar's aphthae is the appearance of small wounds on the oral mucosa. The pathology manifests itself exclusively in children due to poor hygiene or accidental injury.
The location of the ulcers is the palate. They have a slightly yellowish coating and heal quite quickly - up to 5 days. For the pathology to go away, it is enough to normalize oral hygiene.
The gums become inflamed due to insufficient oral hygiene and lack of regular visits to the dentist. The result is an excessive accumulation of plaque on the teeth and pathogenic microorganisms. Pathogenic microorganisms trigger a process in which their own toxins and inflammatory mediators are generated. Treatment of diseases of the mucous membranes and gums with the Vector device
Material and methods
We studied the incidence of traumatic lesions of the oral mucosa (traumatic stomatitis - TS) in children 12-17 years old and young adults (18-32 years old) when using brace systems. Frequency T.S. assessed in 52 children and 43 adults for up to 1.5 months immediately after installation of the brace system, as well as in 136 children and 256 adults during orthodontic treatment, from 1.5 months to 1.5 years from the start of using fixed orthodontic equipment .
To evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, 4 groups of patients were formed, taking into account age and the drug used for local treatment of traumatic injuries of the oral mucosa caused by the use of fixed orthodontic appliances (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Distribution of patients into study groups.
The 1st group included children who used vinylin for internal use for the treatment of traumatic injuries of the oral mucosa (JSC ", Moscow region, Staraya Kupavna, Russia), in the 2nd group, children used a gum gel with propolis (JSC "VERTEX" ", Saint-Petersburg, Russia). The following groups included adult patients whose TS was treated with topical vinylin (group 3) or gum gel with propolis (group 4). All observed patients (children and adults) underwent orthodontic treatment using vestibular brace systems with correction in order to prevent re-injury of the oral mucosa during treatment.
Control examinations of patients of all groups suffering from TS were carried out on the 3rd, 5th and 10th day from the start of treatment using these drugs. Their local application in children was carried out by parents, and in young people - by the patients themselves, 3 times a day after meals. Along with this, all patients during dynamic observation for up to 10 days before local use of the drug for the treatment of TS, in order to increase the effectiveness of treatment, used the ASEPTA parodontal active mouth rinse (JSC VERTEX, St. Petersburg, Russia).
To ensure the comparability of the results obtained and their reliability, a developed semi-quantitative method was used, which consisted of a visual assessment of various clinical symptoms of TS, each of which was assigned one of three symbols indicating the absence or severity of a specific clinical symptom. Thus, based on an analysis of the symptoms of TS, an index method was proposed for assessing the severity of this pathology, taking into account the following clinical symptoms and their assessment in points:
1. Pathological sensations (pain): absent - 0; moderately expressed - 1; pronounced - 5.
2. The area of the focus of traumatic lesions of the oral mucosa (determined taking into account the damaged organs and
fabrics): TC is not determined - 0; lesion on the mucous membrane in the area of the brace system on one of the jaws - 1; lesion on the mucous membrane in the area of braces on both jaws - 5.
3. Localization of traumatic lesions
: the lesion is not determined - 0; visualized in the lips or cheeks - 1; visualized in the area of lips and cheeks - 5.
4. Presence of hyperemia and edema of the mucous membranes
: no hyperemia, mucous membranes are pale pink, no swelling - 0; moderate (mild) hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes - 1; pronounced hyperemia (bright red) and swelling of the mucous membranes - 5.
5. Clinical and morphological characteristics of the focus of traumatic lesions of the oral mucosa
: the lesion is not determined - 0; erosion or erosions are visualized - 1; erosive and ulcerative lesions are diagnosed - 5.
To establish the severity of the clinical picture of TS, the listed clinical symptoms are first diagnosed. After registering the symptoms of the pathology, the sum of points is calculated and the severity of TS is assessed based on the obtained sum of points as follows: 0 - no pathology; 1-4 points - mild severity of the vehicle; 5-9 points - average degree; 10-25 points - severe degree. The data obtained in each group of patients according to symptoms were arithmetically added, and the resulting average values were used for further statistical processing (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. An erosive-ulcerative traumatic lesion in the area of the mucous membrane of the lower lip on the right of moderate severity, caused by wearing a brace system, in a 14-year-old patient (group 1, subgroup 1). Clinical manifestations: pathological sensations (pain): moderate - 1; area of the focus of traumatic lesion of the oral mucosa (determined taking into account damaged organs and tissues: lesion on the mucous membrane in the area of the brace system on one of the jaws) - 1; localization of traumatic lesions: visualized in the area of the lower lip - 1; presence of hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes: moderate (mild) hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes - 1; clinical and morphological characteristics of the focus of traumatic lesion of the oral mucosa: erosive and ulcerative lesion was diagnosed - 5 (total 9 points).
To objectify the result of treatment for TS, a method was used that involved determining the effectiveness of the therapy for the specified pathology of the oral mucosa, which was carried out according to the formula:
Efficiency (%)=100·(A–B):A,
where A is the sum of points in the clinical assessment of the severity of TS before the start of therapeutic measures; B - the sum of points for clinical assessment of the severity of the pathology in question on the 3rd, 5th and 10th day from the start of treatment.
The reliability of differences in the average values of independent samples was assessed using the parametric Student's test for normal distribution and the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test for differences from the normal distribution of indicators. Normality of distribution was checked using the Shapiro-Wilk test. For statistical comparison of proportions with an assessment of the significance of differences, the Pearson χ2 test was used, taking into account the Mantel-Haenszel likelihood correction. In all statistical analysis procedures, the achieved level of significance was considered ( p
), the critical significance level was equal to 0.05.
Traumatic mouth ulcers
The name of traumatic ulcers speaks for itself. This is the appearance of wounds in the oral cavity due to injury to the mucous membrane. The causes of injury may be:
- Bite of the mucous membrane;
- Accidental contact with a toothbrush;
- Inaccurate dental treatment.
One of the types of traumatic ulcers are prosthetic ulcers - wounds formed due to incorrect sizes of removable dentures. They are localized precisely under the dentures.
Healing of traumatic ulcers lasts 1-2 weeks. As a rule, this is a one-time pathology that goes away on its own without additional treatment. Such aphthae are painless and small in size.
If a complication of the disease nevertheless begins, it is necessary to visit a doctor so that he can prescribe anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications to completely eliminate the pathology.
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the development of this pathology is the penetration of infection into the body due to constant microtrauma. The most easily infected wounds are those caused by carious teeth.
The second most common reason is dentures. Although many of them fit quite tightly, some put too much pressure on the gums. As a result, the process of self-cleaning of teeth is hampered and the natural balance of microflora is disrupted.
Crowns and dentures irritate the lining of the gums and can create small wounds that are a gateway to infection.
Additional factors in the development of ulcers are bad habits, stress, insufficient and unhealthy nutrition, as well as seasonal vitamin deficiency.
Quite often, ulcers develop in patients with malocclusion due to uneven pressure exerted on the gums.
Tuberculosis of the oral mucosa
Tuberculosis of the oral mucosa is a complication of standard pulmonary tuberculosis. The cause of the pathology is the penetration of bacteria into the oral cavity through damaged soft tissues. Localization of ulcers occurs in the following places:
- Cheeks;
- Language;
- Floor of the oral cavity.
At the affected sites, standard tuberculous tubercles first form, and then ulcers appear in their place. They do not heal and gradually increase in size. Aphthae are shallow, but very loose with slight bleeding. Their edges are soft, but despite this, the ulcers are noticeably painful.
Usually, along with the appearance of tuberculous ulcers, the patient feels a general deterioration of his condition, which manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- Loss of appetite and weight;
- The appearance of a white coating on the tongue;
- Sweating;
- High body temperature.
Treatment of such a pathology involves staying in a special closed dispensary. As a rule, during the period of weakening of the symptoms of the disease, sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out, as well as treatment with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
Trophic ulcer - treatment without surgery
If the cause of the ulcer is not venous pathology, then conservative measures are sufficient. A portable laser device is a great help in home treatment of the initial stages of ulcerative skin lesions up to 50 cm2 in size. A laser injected into a vein helps reduce blood viscosity, significantly reduces the risk of blood clots, and increases blood flow in problem areas. In addition, the laser beam effectively reduces pain and trophic ulcers. Laser treatment (reviews below) in combination with conservative treatment allows you to avoid surgical intervention.
Laser therapy is carried out in courses of 10-15 procedures. With the correct individual selection of treatment parameters, this treatment method does not cause complications, patients note good tolerability of the procedures, and the trophic ulcer is quickly eliminated. Laser treatment, the price of which is not too high, is very popular.
Syphilis
Syphilis is an infectious pathology caused by Treponema pallidum. Mouth ulcers are a typical symptom of syphilis that appears throughout the entire period of the disease. Moreover, the ulcers themselves undergo a certain development process:
- The ulcers are round in shape and have dense edges. They are painless and have a white coating.
- Over time, the ulcers begin to bleed slightly.
- After about 1-3 months, the ulcers heal, and in their place strong scars form, around which dense bluish edges are concentrated.
After defeating syphilis, dense scars still remain in the oral cavity. They are the most eloquent sign of a recent illness.
Treatment of syphilis is carried out in a closed venereology clinic. During remission, the oral cavity is treated with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
Trophic ulcer, stages or course options
The size of the trophic ulcer directly depends on the lack of blood supply and the duration of the pathological process. Usually the ulcerative surface occupies no more than 35 cm2. If left untreated, it can cover the entire lower leg and reach 100 cm2. Treatment methods for trophic ulcers must be correct, competent and qualified: no poultices or tinctures!
Stages of appearance of a trophic ulcer
The initial stage (small bleeding ulcer) is complicated by the addition of a bacterial and fungal infection. Purulent contents with an unpleasant odor begin to separate from the ulcer. The longer the process, the deeper the layers are subject to inflammation and rotting. The ulcerative lesion spreads to the calf muscles, involving the ankle joint in the inflammatory process. In advanced cases, the development of pyoderma, phlegmon and sepsis is possible.
It is worth distinguishing between venous and arterial trophic ulcers. The former occur in patients of any age, while arterial ulcers are a disease that occurs exclusively in old age, caused by atherosclerosis of the artery walls.
Acute necrotizing gingivostomatitis
Acute necrotizing gingivostomatitis is a viral infectious pathology in which ulcers form on the surface of the entire oral mucosa, including the tonsils. The prerequisites for this disease are:
- Deterioration of the immune system;
- Injury to the oral mucosa;
- Lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- Chronic severe fatigue;
- Sudden hypothermia;
- Complication of ordinary stomatitis or viral pathologies.
The risk group is mainly men under 30 years of age. Ulcers are wounds with a loose bottom, uneven edges and a dirty green coating, which has an unpleasant odor and can be easily removed if desired. All the soft tissues around them are swollen and inflamed, and the wounds themselves bleed slightly. As a rule, the appearance of such ulcers is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Acute pain while eating and talking;
- Very bad breath;
- Heavy secretion of saliva;
- A sharp increase in body temperature;
- Swelling and soreness of the gums;
- Bleeding gums;
- Yellowish plaque on the surface of the gums.
Treatment of the disease should be carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician. The treatment regimen depends on how poorly the patient feels and at what stage the disease is. Typically treatment involves the use of:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- Antiallergic drugs;
- Vitamins C and R.
Additionally, the inclusion of high-calorie food and drink in the diet is prescribed. Sometimes, if necessary, heart medications are added to the treatment regimen.
Local treatment of pathology is also carried out by surgical removal of damaged tissue under anesthesia. After this, the oral cavity is treated with anti-inflammatory, antiseptic drugs, as well as a solution of white clay. When a positive result is achieved, professional oral hygiene is performed.
Vacuum cleaning of wounds
Vacuum therapy or negative pressure therapy is a method of removing serous fluid and dead tissue from a wound or surgical site. Currently, vacuum ulcer debridement can be used on all types of wounds: acute, subacute or chronic. It reduces swelling, promotes rapid healing and the formation of young connective tissue.
The essence of the method is that a piece of porous sponge with silver ions is inserted into the wound, then the whole thing is covered with a transparent membrane. A hole is made in it and a drainage tube is inserted, which is connected to a vacuum source. The fluid is drawn from the wound through the sponge into a reservoir for subsequent disposal.
The membrane prevents air from entering and allows a vacuum to form inside the wound, reducing its volume and making it easier to remove fluid. Before starting the procedure, the ulcer should be washed.
The duration of treatment depends on the size and depth of the wound. The dressing is changed every 24-48 hours.
HIV infection
Oral ulcers are a common symptom of HIV infection and occur in approximately 30% of patients. In this case, their treatment is very specific. An infectious disease doctor selects a treatment regimen and medications for each patient individually. Sometimes ulcers are considered normal and do not require treatment, but this happens extremely rarely and only in advanced stages of the disease.
The patient can also go to any public dental clinic for surgical removal of ulcers. But before that, you need to make sure that there are no negative consequences after such surgery. If removal is justified, it is carried out in accordance with all precautions.
Trophic ulcer, diagnosis
When diagnosing a trophic ulcer and identifying the causes of its occurrence, the following laboratory tests are used:
- determination of blood sugar levels
- Wasserman reaction
- cytological analysis
- bacteriological examination
The doctor also prescribes a number of necessary studies:
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower extremities
- angiography (x-ray examination of blood vessels with a contrast agent)
- rheovasography
- infrared thermography
- spiral computed tomography
Diagnosis of a trophic ulcer is a key stage in proper treatment
To select an effective treatment, consultation with a phlebologist surgeon specializing in vascular diseases of the lower extremities is necessary.
Prevention of oral ulcers
Prevention of any type of ulcers is always the elimination of the root cause of their appearance. If ulcers are a symptom of infectious diseases, it is necessary to prevent the pathogen from entering the body. If this is the result of poor oral hygiene, you need to pay more attention to it. It is also worth visiting your dentist for advice on proper hygiene.
At least once a year, experts recommend visiting a dental clinic for professional oral hygiene. So, mouth ulcers can be a sign of many diseases. To determine the reason for their appearance in more detail, it is necessary to pay attention to the location of the ulcers and their appearance. To treat diseases, it is better to consult a doctor. Self-medication may not only not lead to the desired results, but also aggravate the situation due to the lack of correct therapy.
Trophic ulcer with varicose veins
More than 70% of cases of trophic ulcers are caused by severe cases of varicose veins. Even minor damage to the integrity of the skin with varicose veins can lead to the formation of ulcers on the ankles and legs.
Large trophic ulcer on the leg
Trophic ulcers located on the lower leg indicate serious changes in larger venous vessels and the spread of an area with impaired innervation and poor blood supply. A trophic ulcer of the leg usually causes severe pain.
Trophic ulcer - laser treatment (EVLO, EVLK)
A more radical method of treating trophic ulcers is surgery using laser coagulation (Endovasal laser coagulation). We have been using the EVLT technique for many years. This treatment method consists of “burning out” the vein, which is located in the area of the trophic ulcer. The results are very good: the ulcers heal almost before our eyes. Scarring occurs over several weeks. At the same time, patients do not fall out of their normal routine of life.
Treatment of trophic ulcers with laser in
Laser treatment of trophic ulcers in Moscow has a number of advantages:
- low morbidity - the phlebologist does not make additional incisions in the ulcerated area;
- the ability to avoid long-term conservative treatment before surgery;
- high efficiency - scarring of the ulcer goes away quite quickly;
- positive cosmetic effect - low tissue trauma eliminates the formation of rough scars when the trophic ulcer disappears. Laser treatment, the cost of which can be discussed upon admission, will help you.
Trophic ulcer - treatment. Reviews from our patients.
Patient's review of laser treatment for trophic ulcers in our center.
Victor Petrovich, 65 years old.
I am a pensioner with a whole cartload of all sorts of ailments. My legs had been hurting and swollen for a long time, but I, like many, put off going to the doctor until later. I took some pills on the advice of a neighbor nurse, although I didn’t notice any particular improvement. In general, I lived to the point where I had a huge ulcer on my leg. God bless your doctors, I already thought that I would be left without a leg. They gave me laser treatment. I didn’t particularly delve into the nuances of this case; the doctors guaranteed a good result. Everything went without pain, literally after a few days my trophic ulcer began to disappear before my eyes, and after two weeks only a small scar remained. Of course, various medications were prescribed, then I went to a sanatorium and forgot about this terrible disease. Thanks to all the doctors of the Medical Center for Phlebology, especially Dr. Malakhov Alexey Mikhailovich.
A patient's review of the treatment of trophic ulcers using the EVLO method in our center.
Komissarova L.I.
Our patient with surgeon-phlebologist A.M. Malakhov. after treatment
My leg ached constantly, there was a buzzing sensation in it at the end of the day, and then a trophic ulcer formed, which became larger and larger. I didn’t dare to have surgery using the classical method, because I was afraid after reading reviews online and all sorts of complications. Well, my daughter is in the know, she found me an experienced doctor in Moscow, Alexey Mikhailovich Malakhov. Before the operation, and this is endovasal laser coagulation, at the medical center in Moscow, where I decided to have it, they did an ultrasound, donated blood and that’s it. After the operation, I was forced to get up from the table and walk for about an hour. After 3 weeks I saw my doctor. I didn’t worry about scars, the main thing was that the ulcer healed faster. It's been 3 months since the laser procedure on my leg. Everything is fine, the ulcer has become very small, but I hope it will heal completely soon.
I'm very glad that everything went well. Thanks for all. Komissarova Lyudmila Ivanovna, December 7, 2016
Is a diet necessary when treating a trophic ulcer?
What should be avoided if there is a trophic ulcer? Photos of complications will help you control yourself when dieting. Diet for trophic ulcers excludes salty foods and spices. It is necessary to saturate the body with nutrients, vitamins and Omega-3 acids. Vegetables (carrots, tomatoes, cabbage), fruits, nuts, milk, cheeses, vegetable and butter, and fish are especially useful. You should eat small portions to avoid a sharp increase in blood sugar. A radical change in diet is not required; a small adjustment will have a beneficial effect on the healing process.
Trophic ulcer - radiofrequency treatment (RFA, RFO)
The radiofrequency treatment method is considered the most modern and safe if you have a trophic ulcer. RFA treatment in Moscow involves heating the walls of the vein with microwaves, it “closes”, and the trophic ulcer gradually shrinks. RFO treatment - and after a few months the problem vein is a connective tissue cord, and the entire load is transferred to neighboring, healthy vessels. This is how the trophic ulcer gradually heals.
Treatment of trophic ulcers with radiofrequency (RFA, RFO) in our center
RFO treatment in Moscow is carried out quite quickly; the patient goes home 10 minutes after the intervention. The radio frequency method provides the following advantages:
- short duration of the procedure - 30-40 minutes;
- exposure parameters are selected automatically and without the participation of a doctor;
- cosmetic effect - the absence of additional trauma promotes the formation of a less rough scar where there was a trophic ulcer. RFA treatment is very positive in this regard.
- the procedure is completely painless and easily tolerated;
- Hospitalization is not required, the patient can lead a normal life, limiting activity only after the procedure.
Frequently asked questions from our patients on the Internet about trophic ulcers
How to treat non-healing wounds on the legs?
To effectively treat non-healing leg wounds, it is necessary to understand how such wounds appeared. Long-term non-healing wounds on the legs can form as a result of a number of completely different pathologies, and each requires its own specific treatment.
How to treat non-healing wounds at home?
Before you begin to treat long-term non-healing wounds at home, you need to find out the cause of such wounds. Most often this is:
- Diabetes.
- Obliterating atherosclerosis.
- Chronic venous insufficiency.
If you want to cure long-term non-healing wounds, then in addition to the local use of ointments, it is necessary to deal with the underlying pathology that caused the problem.
How to treat a deep wound?
How to treat a deep wound should be asked to the doctor during an in-person consultation. Treating such wounds on your own, using the Internet, can be fraught with progression of the process and the development of a life-threatening condition.
My father developed sores on his legs six months ago, how can I get rid of them?
If “sores” on your legs appear and do not go away for a long time, as a rule, only a doctor will help you get rid of them. Long-term non-healing wounds are often a sign of a serious pathology that requires specific treatment.