Content
hide
1 Pulp - structure, functions, features
2 Why is a tooth without pulp considered dead?
3 How long does a tooth live without pulp?
4 What can lead to the need to remove a “dead” tooth: 4.1 There are several rules by adhering to which patients can prolong the use of the tooth:
Inflammation of the “nerve” of the tooth (pulpitis) is not always accompanied by severe toothache. A chronic infectious process can occur in a tooth unnoticed, leading to significant tooth destruction, the formation of a cyst on the root of the tooth, and even tooth loss. This pathology is an indication for tooth depulpation—removal of its “nerve.” Sometimes such news can come as a surprise to a patient if he did not suspect the presence of chronic pulpitis. At the same time, we are often asked - what will happen to the tooth later, after pulp removal? How long will the tooth live after this procedure, how will its condition change? We'll talk about this in the article.
Tooth removal
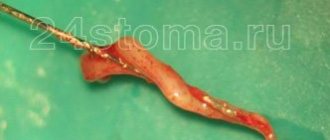
Depulpation (depulpation of a tooth) is the removal of pulp, connective tissue consisting of blood vessels and nerve endings. Removing the tooth nerve and cleaning the canals is designed to relieve the patient from pain, inflammation and further complications. However, the tooth, having lost its blood supply, becomes dead and, therefore, more fragile.
Dental treatment and nerve removal is one of the most common dental procedures. This is partly because patients turn to the dentist only in case of unbearable pain, when it is no longer possible to do without depulpation. Removing the nerve of the tooth and filling the canals allows you to preserve the natural tooth, which is a priority for endodontic treatment.
Indications for depulpation:
- extensive caries
- classic pulpitis and infectious pulpitis (bacteria penetrate through the root apex)
- trauma and damage to the tooth affecting the pulp
- if it is necessary to install crowns or classic bridges
Many patients who come to the dentist's office with toothache are interested in the question: is it possible to save the pulp? Today, there are methods of biological treatment (preservation of the entire pulp) and vital amputation (preservation of the root pulp), but many favorable factors must converge for them to be carried out. For example, biological treatment is not carried out after 25 years.
What can lead to the need to remove a “dead” tooth:
- damage to the tooth root by caries;
- the occurrence of longitudinal fractures and root cracks (below the gum level);
- the presence of a cyst or granuloma on the root of the tooth, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth, the treatment of which is not possible.
There are several rules that patients can follow to prolong the life of their teeth:
- cover the tooth with a ceramic inlay or crown;
- visit the dentist once every 6 months for a check-up, hygienic cleaning and, if necessary, a control X-ray of the tooth;
- do not chew hard food (nuts, seeds, crackers, etc.);
- Avoid temperature changes when eating (for example, hot coffee with cold ice cream).
As we see, a patient can do a lot for his health. But in order for the tooth to last longer, it is much more important to choose a specialized clinic that uses modern technologies, high-quality equipment and materials. An experienced and knowledgeable doctor will ensure the vital activity of a pulpless tooth for a long time.
Removal of tooth nerve with arsenic
Removing pulp using arsenic is considered an outdated treatment method, which is almost never used today. The procedure was quite simple: the tooth was prepared using a drill, then the root canals were expanded, medicine was applied to remove the nerve in the tooth, after which a temporary filling was installed for 2 - 3 days. The negative side of such treatment is that arsenic is a strong poison that has a detrimental effect on both the tooth and the tissues surrounding it. With the advent of new safe techniques, the need for arsenic has disappeared.
Pulp - structure, functions, features
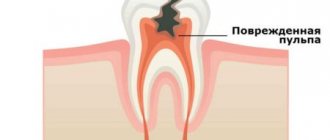
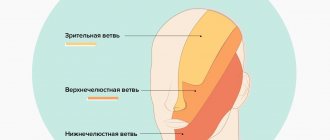
The pulp is also called the dental nerve. This is a soft connective tissue that contains a collection of nerve fibers, lymphatic and blood vessels. It is located in the tooth cavity (pulp chamber of the crown part of the tooth and in the root canals). Along the edge of the pulp there are cells, the processes of which are immersed in the dentin of the tooth. Thus, the pulp is closely connected with the hard tissues of the tooth. Through these connections, the trophic function is carried out; the pulp “nourishes” the walls of the tooth. Pain and mechanical sensitivity are also provided by the processes of pulp cells.
The blood supply to each tooth is provided by the common arteries and veins of the maxillofacial area. Small capillaries extend from them and enter the pulp, feeding the tooth. This structure protects the tooth from inflammation, proliferation of pathogens and other pathological processes.
The rich blood supply to the tooth also causes pain during inflammation. When the pulp becomes infected, a massive rush of blood occurs to its capillaries to provide a protective reaction, and swelling occurs inside the tooth. Enlarged vessels and soft tissues compress the nerve endings of the pulp, causing pain.
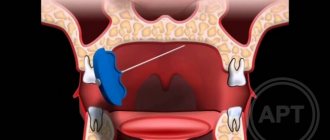
Modern method of depulpation
Today, depulpation is carried out using a pulp extractor - a thin metal rod with teeth that can penetrate even remote areas of the root canals. The apex locator device helps determine the depth of the canal to reduce the risk of injury. After the procedure, a temporary filling is usually installed, but a permanent one can also be installed if the doctor does not see the risks of complications and has high-precision instruments on hand, for example, a dental microscope.
Symptoms of tooth pulpitis -
Pain with pulpitis can be of varying degrees of severity - from minor pain, which is provoked by thermal irritants, to acute paroxysmal spontaneous pain, which makes you want to climb the wall. Given the difference in symptoms, it is customary to distinguish 2 forms of this disease. Below we have described what pulpitis symptoms and treatment will have in each of these cases.
- Acute form of pulpitis – this form is characterized by acute paroxysmal pain that occurs especially at night.
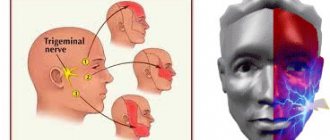
It is typical that the pain increases, while pain-free intervals become shorter and shorter. As a rule, pain occurs spontaneously, i.e. without the participation, for example, of thermal stimuli. However, during the pain-free interval, in some cases it can be provoked by cold or hot water. With pulpitis, it is typical that after the removal of the irritant, the pain persists for about 10-15 minutes (this makes it possible to distinguish pain with pulpitis from pain with deep caries). With the latter, the pain stops immediately after the cessation of exposure to the stimulus. Very often, patients cannot even indicate which tooth exactly hurts, which is due to the irradiation of pain along the nerve trunks. The pain increases due to the gradual transition of inflammation from serous to purulent. With the development of purulent inflammation in the pulp, the pain becomes pulsating, shooting, and pain-free intervals almost completely disappear.
- Chronic form of pulpitis - in this form the inflammation is unexpressed. Patients usually complain of slight aching pain, most often arising from exposure to heat and cold irritants. Sometimes, by the way, with this form of pain there may be no pain at all. Keep in mind that the chronic form of pulpitis can periodically worsen, and during periods of exacerbation of inflammation, the symptoms will be exactly the same as in the acute form.
Tooth after depulpation - complications
A fragment of the instrument remained in the dental canal
A common complication associated with negligence or inexperience of the doctor. Repeated treatment involves removing instrument fragments and refilling the canals. Due to a number of factors, removal of a foreign body can be very difficult. Pain after removal of a nerve in a tooth does not occur very often, so in some cases the doctor recommends leaving everything as it is if the complication does not manifest itself.
Incompletely removed nerve or insufficient filling of dental canals
The most common reason for pain after depulpation. In such a situation, an inflammatory process develops that spreads to the root apex, provoking the formation of periodontitis, gumboil and cysts. If your tooth aches after nerve removal (several days or more), then you need to consult a doctor who can check the quality of the tooth canal filling.
Resealing
Extraction of filling material beyond the root apex. In mild cases (with a small amount), the tooth hurts when pressed for some time after the nerve is removed, after which the pain goes away. If the excess material is large, then surgical intervention is necessary to avoid the development of complications.
Perforation of the wall or root
Mechanical damage that leads to the formation of a perforation (hole) in the wall, floor of the tooth cavity or root. After the nerves are removed, the tooth continues to hurt. The pain is usually aching and paroxysmal.
Darkened tooth after nerve removal
If the tooth darkens after removal of the nerve, this may be caused by poor filling material or poorly performed depulpation. Also, over time, a dead tooth can become cracked and more vulnerable to dyes. This is partly why the front tooth, after removing the nerve, is subsequently covered with a crown or veneer.
Questions and answers on: tooth hurts under a filling
The most common questions patients ask after tooth filling concern pain.
- Question : “A month ago, I had a tooth healed using paste to kill the nerve and installing a temporary filling, but it hurts when pressed. Also, the gums on the cheek side were swollen. After the temporary filling fell out, I did not install a new one. What to do? Is it related to the root or the nerves?” Answer : “Most likely, the periosteum became inflamed because the canals were not treated in time. It was necessary to treat them and put a permanent filling. In your case, the tooth needs to be removed, but if you consult a doctor urgently, there is a small chance of saving it.”
- Question : “Can a tooth hurt after filling? It’s been 2 hours since the filling was placed, but I feel a little pain.” Answer : “Mild pain in a filled tooth is a natural physiological reaction to surgical intervention in the dental cavity. Periodic painful sensations may be felt for 2 months until complete healing. They will pass unless the pain becomes more severe and increasing.”
- Question : “Yesterday we got a filling, but the tooth still hurts. A small rash and itching appeared near him. I can’t stand it any longer, what should I do?” Answer : “You need to see a doctor to replace the filling. You have developed an allergic reaction to it. This is quite a rare occurrence."
- Question : “A week ago I was treated for caries and a filling was placed at the 6th unit below. But the tooth did not stop hurting. It especially bothers me at night; I can’t sleep due to the throbbing pain. Should a tooth hurt after filling?” Answer : “Most likely, the dentist treated you for deep caries due to periodontitis or chronic pulpitis and made a mistake, guided only by a visual examination of the oral cavity. In any case, it was necessary to take an x-ray of the tooth affected by caries. We urgently need to remove the filling and treat the canals.”
- Question : “2 weeks ago a permanent filling was placed without removing the nerve, but it still hurts me to chew. In addition, the tooth reacts to cold and hot food and at times there is aching pain.” Answer : “Such symptoms may indicate the development of chronic pulpitis or the development of an abscess inside the tooth.”
If various pains appear in the tooth after the filling procedure, then the only recommendation is to contact a qualified specialist. After all, the reasons can be completely different.
When is dental nerve removal required?
Depulpation is carried out in cases of severe damage to tooth tissue, advanced forms of caries, pulpitis, or benign formations near the root system. In addition, pulp removal is required during prosthetics and in case of medical error during root canal treatment.
Symptoms that you should contact your dentist for:
- constant aching or throbbing pain that does not go away even after taking painkillers;
- increased tooth sensitivity - a reaction to cold or heat, as well as sour, salty, sweet foods;
- pain while chewing food.
Such symptoms indicate the development of some pathology, so if they appear, you should immediately consult a dentist. The initial stages of dental diseases are treated quickly, and sometimes it is even possible to do without depulpation. The main condition is timely diagnosis and adoption of therapeutic measures.
Reference! Many patients are afraid to undergo depulpation, thinking that after it the tooth will begin to quickly decay. In fact, with proper care, it retains its functions for several years, then it is advisable to cover it with a crown. In some cases, pulp removal is the only sure way to preserve the tooth and avoid severe inflammatory processes.
Stages of depulpation
Modern techniques make it possible to remove the dental nerve in just one visit to the dental office. The process of depulpation begins in the same way as in the treatment of caries.
- Anesthesia. The doctor treats the soft tissue with a freezing agent, then injects an anesthetic and waits about 15 minutes.
- Preparation for pulp removal. The affected tissue is removed to provide access to the dental nerve.
- Depulpation. To remove the pulp, special instruments are used to quickly and painlessly remove it from the root canal and crown part of the tooth.
- Filling. Safe composites, dental cement and other materials are used for filling. In case of difficult removal, the doctor can place a temporary filling, and at a follow-up appointment, if there are no complications, he will install a permanent one.
Removal can be complete or partial. The second method is used in case of an inflammatory process that has affected only the coronal part of the dental nerve. In this case, after anesthesia and removal of dead tissue, only the affected coronal pulp is cut off, while the root pulp remains completely.
Most often, this technique is used in the treatment of teeth in childhood, when there is a need to preserve the root part, since it is the part that is responsible for the correct formation of the root system.
Complications and consequences that will not keep you waiting if your teeth are not treated
A far-fetched fear is extremely harmful: because of it, patients often take the situation to extremes and go to the doctor only when the disease spreads to neighboring teeth and gums, and serious intervention is required.
Deterioration of the general condition of the body
There is a misconception that bad teeth have no effect on the body as a whole. And that “one day the moment will come...” - the teeth will be cured, and there can be no complications. The immune system actually copes with the infection up to a certain point, and the problem is localized in the oral cavity. But one day the strength of the immune system weakens, because... he receives no help from outside. General intoxication of the body develops, which is poorly diagnosed, but manifests itself very clearly.
Intoxication is expressed in constant fatigue, fluctuations in body temperature, etc. The prolonged presence of rotten teeth leads to the following consequences:
- 1. Cardiac dysfunction. Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, which can only be treated surgically;
- 2. Loss of appetite. Impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to the entry of harmful microorganisms into it with saliva. Development of gastritis, food intoxication;
- 3. Frequent headaches due to tooth decay at the base of the root;
- 4. Many doctors are sure that bad teeth can cause problems with bone tissue and harm the musculoskeletal system. Arthrosis and polyarthritis often develop;
- 5. It has been scientifically proven that rotting of large chewing teeth leads to hair loss on the back of the head; destruction of small chewing units leads to baldness of the temporal part;
- 6. Rotting of any bone in the skull leads to brain damage;
- 7. Hearing impairment;
- 8. Poor condition of the skin;
- 9. An advanced putrefactive process spreads to the sinuses and can provoke chronic tonsillitis, hyperplasia of nasopharyngeal tissue, etc.
Pulpitis is a consequence of caries
The most common complication of caries is pulpitis. In fact, it is a natural consequence of caries and does not threaten a healthy tooth. With pulpitis, the dental nerve becomes inflamed; the disease is characterized by particularly severe pain when pressing on a tooth (biting on food).
A person can determine for himself when caries turns into pulpitis. With caries, pain appears only if a certain irritant acts on the diseased tooth. The unpleasant sensations disappear as soon as the irritant is eliminated. With pulpitis, pain can occur on its own. It can only be eliminated by the intervention of a doctor. A pain reliever will also help, but this is a short-term measure that loses effectiveness with frequent use. Taking painkillers is allowed only when it is not possible to visit the dentist. Their effect is only to relieve or weaken the pain syndrome; they do not have a therapeutic effect.
Periodontitis
If for some reason pulpitis has not been cured, the disease develops further. The ligaments that attach the tooth to the bone are affected.
Periodontitis has 2 phases:
- 1. Acute, characterized by severe pain;
- 2. Chronic – this phase may practically not appear.
How long does pulp removal take?
On average, it takes about 40-50 minutes for pain relief, nerve removal, and root canal treatment. If the doctor administers high-quality anesthesia, it will take effect almost immediately, and the patient will not feel pain throughout the entire process. If the effect of anesthesia weakens during depulpation, an additional injection is given.
Reference! Before administering an injection with anesthesia, the doctor treats the soft tissue with a special freezing agent. That is, the patient will not experience pain either when inserting a needle into the tissue or during the process of removing the dental nerve.
Surgery
It is possible to understand what dental pulpitis is and how to treat the pathology in question, including through a detailed analysis of the techniques that require the use of any types of surgical interventions. The main indication for the use of such instructions is the presence in a person of a diffuse, focal and chronic inflammatory process of the fibrous and hypertrophic type. All activities are carried out according to strictly defined instructions:
- Anesthesia by introducing local, conduction anesthesia into the body.
- Isolate the affected area with sterile pads and pads.
- Opening the carious plane and treating the lesions with an antiseptic.
- Excision of the coronal part of the pulp extractor.
- Expanding the canals and treating them with antiseptic agents.
- Preliminary and final filling performed after x-rays.
It is not difficult to guess that only an experienced doctor with a variety of different skills can cope with a series of such procedures at the highest quality level. These are the specialists who work in dentistry.
Treatment of pulpitis with removal of the dental nerve
Another event characterized by a fairly high complexity. As a rule, all medical interventions are performed in two stages. During the first of them, the specialist:
- Removes the carious plane.
- Removes damaged tissue from the pulp itself.
- Treats the excision site with an antiseptic.
- Carrying out work on installing a temporary filling.
After approximately one to two weeks, the patient necessarily comes for the second session. As part of the additional (finishing) procedure, the following actions are carried out:
- Short-term filling is removed.
- Inspection and cleaning activities are carried out.
- The oral cavity is exposed to antiseptic agents.
- A permanent material is installed to fill the voids in the tooth process.
The main advantage of all processes is the possibility of preserving a healthy dental element. In addition, the person subsequently feels positive effects due to the regeneration of vitality and sensitivity of the pulp itself.
Treatment of pulpitis of a multi-rooted tooth
A devital technique, in which the doctor initially kills the problem area using a special necrotizing paste. In the past, doctors involved in such work used ordinary arsenic, placed in the carious plane for several days.
Today, modern medicine has stepped forward, providing craftsmen with a much wider range of tools. Dental staff use the most gentle drugs that do not kill nerve tissue in the oral cavity. It is not difficult to guess that the use of such substances is a completely safe operation.
Extirpation of pulpitis
Probably the most radical treatment method, which includes a whole complex of processes to remove the inflamed neurovascular bundle, followed by sanitation and filling. The doctor can undertake its implementation only in the case when any other methods of therapy clearly do not lead to success. As in previous cases, the procedure is carried out in a vital and non-vital format: under the influence of local anesthesia or using a necrotizing paste-like drug. Depending on how complex the disease is, the specialist may need from 3 to 4 sessions, the result of which, of course, will be a complete cure of the patient from the specified range of problems.