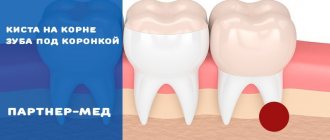
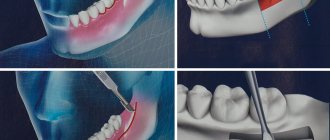
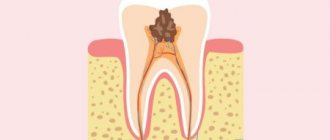
Methods of modern dentistry are aimed at preserving the dental unit. Removal is resorted to as a last resort if gentle treatment techniques are ineffective. Resection of the apex of the tooth root (apicoectomy) is a microsurgical intervention for excision of tissue affected by infection with part of the injured tooth root. The operation is performed if the inflammation has taken the form of a cyst or granuloma. The main condition for the success of such a surgical intervention is the timeliness of the patient’s visit to the dentist. If the pathological process spreads to most of the root, the tooth will have to be removed.
Briefly about the treatment method
Bowel resection is an operation to remove part of the small or large intestine. This is a fairly traumatic procedure, so it is not performed without very compelling reasons.
Types of bowel resection
Different types of resections are performed to remove different parts of the intestine. Each type of bowel resection is named based on what it removes: Segmental small bowel resection: A portion of the small bowel is removed. The surgeon may also remove part of the mesentery (the fold of tissue that supports the small intestine) and lymph nodes in the area. This type is used to remove tumors in the lower duodenum (upper part of the small intestine), jejunum (middle part of the small intestine), or ileum (lower part of the small intestine). Right hemicolectomy: removes part of the ileum, cecum (part of the large intestine), ascending colon (part of the large intestine), hepatic flexure (flexure of the colon), first part of the transverse colon (middle of the large intestine), appendix. Transverse colectomy: the transverse colon, hepatic and splenic flexures are removed. This surgery may be used to remove a tumor in the middle of the colon when the cancer has not spread to other parts of the colon. Left hemicolectomy: Part of the transverse and descending colon, the splenic flexure (the curve in the colon near the spleen), and part or all of the sigmoid colon are removed. Sigmoid colectomy: The sigmoid colon is removed. Low anterior resection: the sigmoid colon and part of the rectum are removed. Proctocomectomy with ileoanal anastomosis: the entire rectum and part of the sigmoid colon are removed. An ileoanal anastomosis is a procedure that a surgeon does to attach the lower portion of the small intestine to the anus. Abdominoperineal resection: The rectum, anus, anal sphincter and muscles around the anus are removed. The surgeon makes one cut or incision in the abdomen and another in the perineum (the area between the anus and vulva in women or between the anus and scrotum in men). This procedure requires a permanent colostomy (taking a section of the colon out) because the anal sphincter is removed. Partial and total colectomy: Surgery to remove part or all of the colon (including the cecum).
Do I need to do a resection or still remove the tooth?
Tooth root resection is a tooth-preserving operation. The dentist will recommend it to you when there is at least the slightest opportunity to save the tooth. If the dentist does not see this possibility, then the conversation will immediately focus on removal.
When will the tooth have to be removed?
- You have a large cyst that affects more than a third of the tooth or several teeth.
- The root of the tooth is destroyed.
- There is severe inflammation of the tissues adjacent to the diseased tooth.
- The tooth is movable.
- Subsequent prosthetic replacement of a diseased, destroyed tooth with a crown is impossible.
Indications and contraindications for the treatment method
Bowel resection is performed to treat the following diseases:
- Cancer in the small intestine, colon, rectum, or anus;
- Cancer that has spread to the intestines (treatment and symptom relief);
- Blockage in the intestines (intestinal obstruction);
- Precancerous polyps before they become cancer (called preventative surgery);
- Inflammatory bowel disease or diverticulitis;
- Ulcerative colitis (characterized by chronic inflammation of the colon and rectum, resulting in bloody diarrhea). Surgery may be indicated when drug therapy does not improve the condition.
- Mesenteric thrombosis or abdominal ischemia;
- Intestinal necrosis.
In addition, surgery is used for intestinal trauma, bleeding, and to close a hole in the intestine (intestinal perforation). The reasons for resection are always carefully assessed by the attending physician. There are a number of contraindications for the operation:
- critical condition of the patient, leading to the inappropriateness of resection,
- coma or unconsciousness of the patient,
- pathology of the heart, kidneys or respiratory system, which can lead to serious complications during or after surgery,
- inoperable tumor.
When surgery is not performed
Like any other surgical intervention, apicoectomy has limitations and contraindications. These include:
- Mobility of teeth II-IV degrees;
- destruction of the crown part of the tooth (more than 50%);
- the presence of cracks in the affected root;
- severe curvature of the root canal (impossible to fill);
- crowding of teeth, which does not allow identifying the affected root;
- acute infectious, viral disease;
- severe bleeding disorders;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- severe immunodeficiency;
- oncology in the active stage.
Some of the limitations to root resection are the indication for removal of the affected unit. The second part refers to general contraindications to any surgical intervention. The risk of surgery for the patient is assessed individually.
The specialists at the Ilatan Clinic make every effort to save the dental unit, if possible. But if there are direct indications for removal, for example, extensive damage to dental tissue, the doctor will not suggest apicoectomy.
Preparing for treatment
Before surgery, diagnostic tests are usually performed to check your general health and ensure that the surgery can be performed. This may include blood sampling, chest x-ray, electrocardiogram (ECG), angiography, CT or ultrasound, or endoscopy. You should follow a diet that excludes legumes, baked goods, alcohol, fresh fruits and vegetables. A liquid diet is administered at least the day before surgery, with nothing taken on the day of surgery. Depending on the type of bowel resection, it may be necessary to cleanse the bowel. This usually involves taking a laxative 1-2 days before surgery. Cleansing enemas may also be given in the hospital. Immediately before the procedure, antibiotics are prescribed to help prevent infection. You should also tell your doctor about all the medications, supplements, and herbal products you take.
Reviews
- Review by Anton Nikolaevich Logvin
The operation was performed 6 years ago. Weight was 175. My knees started to hurt. It was impossible to find clothes. Constant feeling of hunger. Now I weigh 110. The weight suits me. I don't want to lose weight anymore. Boris Yurievich Tsvetkov is a surgeon from God, a very decent person and a wizard, an architect of human bodies. I'll say this.
Photos and interviews
- Review by Olga Vladimirovna Ryabokon
Before the operation, the weight was 154 kg and there were a million concomitant diseases. Now 87-88. I’m no longer treating diabetes, it doesn’t bother me, my blood pressure is very rare. At 64 years old, I don’t walk, I run. Before, I couldn’t walk through the kitchen; I was out of breath.
And after me, my daughter also had the same operation. All the best that I can, I know, all the good words, I dedicate everything...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Irina Sergeevna
Thank you very much to Boris Yuryevich for the gift of a new happy life, with all my heart. I say that I celebrate the day of the operation as my second birthday. My life has changed, my mind has brightened, my soul has brightened, I don’t know, it’s as if I’ve actually become younger. I was 44, now I’m 45, a new life has begun. Thanks to him for his golden hands, thanks to the whole team...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Marina Konstantinovna and Nate Donelson
I would like to express my deep gratitude to Boris Yuryevich and his entire team. The man who changed my life, who changed my husband's life, who saved my husband's life. I am very grateful to him. We are now planning a second child. He may have saved another life. We will have a second child, and at my former weight I could not give birth.
This is a surgeon...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Alexander Semchev
Friends! Previously, some time ago, it was difficult for me to live because the moment of my “promiscuity” played a bad joke on me. But, thank God, Dr. Tsvetkov and his clinic appeared in my life. Thanks to his efforts, his attention, I began to live differently. Of course, with a plus sign.
Photos and interviews
- Anna's review
I would like to say a huge thank you to Boris Yuryevich. He told me everything about the operations competently and in a language that I could understand, where there were any pros and cons. He gave me comprehensive answers to all my questions. He is a professional with extensive experience whom I trusted. I can say one thing. That this is a person who tells patients it like it is, in simple language accessible to...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Tatiana
Boris Yuryevich is a great guy, of course. Attentive, he told me everything that interested me. I walked differently from Marina, for example. Marina probably teased him for a very long time; he probably told a lot of things for a long time. I flew on wings. Everything would have been done faster for me. But what interested me, for example, the same operation, what to do...
Photos and interviews
- Alina's review
Boris Yurievich Tsvetkov is truly a doctor of the highest category, who is adapted for people. All people are different. Some work for their own personal gain. And Boris Yuryevich works for the people. It is available 24/7, which was very important to me. That I could call him at night and say: “Boris Yuryevich, I’m not feeling very well.” He always…
Photos and interviews
- Olga's review
Thanks to Boris Yuryevich for making people beautiful and happy. I already told him that I really have become more beautiful, younger, and much happier. I would like to wish him long life, even more career growth, newer modern technologies.
It's too bad he doesn't do breasts. It does the stomach, but he says I don’t do the chest now. And that’s what I would do...
Photos and interviews
- Valeria's review
I had gastric resection surgery and I am very pleased. What happened before and what happened after is noticeable in life, in health, in everything. A person changes - this is a new life. There is no need to be afraid of this operation, you need to go and do it. Boris Tsvetkov is a worthy, high-quality surgeon who will care for and guide his patient from beginning to end. In the hospital…
Photos and interviews
- Feedback from Natalya Anatolyevna Kukshina
I am a person who, at the age of 26 (at the time of the operation), has experienced a lot - various cleansing programs, nutritionists, fitness programs for losing weight, buying and consuming tons of products, as advertising aimed at weight loss instills in us, I can only say one thing. If you have problems with excess weight, diseases caused by excess...
Photos and interviews
- Alexey's review
What Boris Yuryevich Tsvetkov did... I want to say frankly. Without praising him, nothing, simply, what Tsvetkov did - he simply did what is impossible to do, you know? Tell someone else. I talked with other doctors, with endocrinologists, with therapists, there are a lot of people we know in medicine. Even people who are in this profession…
Photos and interviews
How the treatment method works
The surgeon may use open or laparoscopic techniques. With an open technique (laparotomy), the surgeon makes a large longitudinal incision to reach the intestine. In the laparoscopic technique, small holes are made in the abdomen, and then an endoscope (a thin, tubular instrument with a light and lens) and instruments are inserted to perform the operation. The laparoscopic technique tends to result in shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, fewer complications, and less pain during incisions. However, not all patients can undergo laparoscopic bowel resection due to the location and stage of the disease or other factors. In addition, surgeons require specialized training, skills, and equipment to use laparoscopic techniques. The surgeon examines the cavity and removes the diseased or damaged part of the intestine within healthy tissue. However, some healthy tissue on either side of the affected part may also be removed.
Anastasmosis
When part of the intestine is removed, the surgeon connects the remaining ends of the intestine together using stitches or staples. This procedure is called anastomosis. When the entire large intestine is removed and the anastomosis is between the small intestine and the anus, it is called an ileoanal anastomosis. When it is between the sigmoid colon and the anus, it is called a coloanal anastomosis. For any of these procedures, the surgeon may create a pocket before attaching the intestine to the anus. The pocket creates a place for stool when the rectum is removed. It helps reduce the number of bowel movements a person has and manage incontinence (the inability to control bowel movements).
In some cases, the surgeon does not connect the ends of the intestine together. Instead, it attaches one or both ends of the intestines to an opening in the abdomen. This procedure is called a colostomy or ileostomy (depending on the part of the intestine used) and is an artificial anus. A colostomy can be temporary or permanent.
Advantages of the Clinical Hospital on Yauza
The clinic on Yauza successfully performs surgical interventions of any complexity using laparoscopic and open methods. Hospital treatment has many benefits. The main ones include:
- the latest diagnostic devices;
- modern rehabilitation wards;
- highly qualified personnel;
- individual approach to each patient;
- affordable prices.
You can book an appointment with a surgeon using the hotline number or on the clinic’s website.
Sign up for the procedure
Possible complications during treatment
The side effects that may occur depend mainly on the type of bowel resection and your overall health. They include:
- obstruction (obstruction) of the intestine,
- paralyzed or inactive bowel
- damage to nearby organs such as the bladder, ureter or spleen, anastomotic leak associated with infectious problems,
- excessive bleeding wound infection,
- hernia,
- thrombophlebitis,
- inability to control urination.
The attending physician should be informed of any of the following problems after surgery: severe pain, swelling, redness, drainage or bleeding in the incision area, muscle pain, dizziness or fever, constipation, nausea or vomiting, rectal bleeding or black, tarry stools.
Prognosis after treatment method
The period of time required for recovery varies depending on the initial condition, type of resection, the patient's general health prior to surgery, and the length of bowel removed. The prognosis of bowel resection depends on the severity of the disease. For example, in the case of patients with ulcerative colitis, the disease is cured and most people go on to live normal, active lives. Patients with cancer will have a less positive prognosis (due to possible relapses). Alternatives to bowel resection depend on the specific medical condition being treated.
Why is it better to perform anterior rectal resection at the Swiss University Hospital?
- The clinic was among the first to perform sphincter-preserving operations; to date, the number of surgical interventions on the intestines has exceeded 3,000 operations.
- We employ specialists of the highest category, many of whom, being authorities in surgery, are known not only in domestic but also in foreign clinics. Each of our specialists is fluent in all techniques and can perform more than 100 types of operations within their specific area.
- Every year we consult about 5 thousand people, including patients with proctological pathologies referred from other clinics.
- For diagnostics, our Center carries out almost all necessary studies: from laboratory tests to complex examinations using video endoscopic or computer technology. Thanks to the presence of a histological laboratory, the time for examining patients is minimal, which is extremely important for patients with cancer.
- If necessary, doctors of other specializations can be involved in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with concomitant diseases: endocrinologists, gynecologists, vascular surgeons, etc.
- We were one of the first to carry out simultaneous operations: during one anesthesia, the patient can get rid of other pathologies of the abdominal cavity or pelvic organs.
Observation program after treatment method
After your bowel resection you will need to stay in the hospital for several days. The patient should be given warm, liquid food for 1-2 days after surgery. Solid foods and meals will be introduced gradually. If a colostomy or ileostomy has been performed, a specially trained health care professional will teach the patient how to care for themselves. Temporary ostomies usually remain in place for several months. After the rest of the colon has healed, another operation, an anastomosis, will be performed. The hole in the stomach will be closed. A nasogastric tube is inserted through the nose into the stomach during surgery and may be left in place for 24 to 48 hours after surgery. This eliminates stomach secretions and prevents nausea and vomiting. It will remain until bowel activity resumes. Postoperative patient care also includes monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, respiration and temperature. Fluid intake and output are measured, and the color and amount of drainage from the wound is observed at the incision site. The patient can get out of bed approximately 8-24 hours after surgery. Most patients will stay in the hospital for 5-7 days, although laparoscopic surgery can reduce this stay to 2-3 days. Postoperative weight loss accompanies almost all bowel resections. Weight and strength are slowly restored over several months. You will need to follow a diet prescribed by your doctor. Full recovery from surgery may take two months. Laparoscopic surgery can reduce this time to one to two weeks.