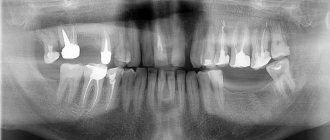
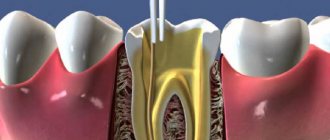
Canal unsealing is a dental procedure that is aimed at removing a previously installed filling. Another name for it is “disobturation”. The process requires expansion of the canals in the direction from the crown to the apex of the root for the purpose of high-quality cleaning of dental cavities. The procedure is resorted to after endodontic treatment carried out with violations of technology. It must be carried out on time, since infectious agents that have penetrated the dental tissues will provoke the development of inflammatory processes, which, in turn, can cause the loss of the entire tooth.
The therapeutic department of dentistry CELT invites you to undergo root canal retreatment in Moscow. Our clinic is multidisciplinary and has been offering paid medical services for more than two decades. Our dental therapists have a modern diagnostic and treatment base in their arsenal, thanks to which they are able to accurately and promptly make diagnoses and carry out treatment in accordance with international standards. You can find out the approximate price for unsealing canals by going to the “Services and Prices” tab. We regularly update the price list, but in order to avoid misunderstandings, we recommend that you check the exact numbers with our operators or at a doctor’s appointment.
Consultation with a dentist-therapist - 1,000 rubles.
Unsealing a previously obstructed canal (1 canal) - RUB 3,000.
Unsealing the canal under the stump tab - 1,700 rubles.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a consultation with a dentist-therapist is 1,000
Make an appointment
Indications and contraindications for root canal filling
Indications
- Painful symptoms, inflammatory processes and swelling of the gum tissue in a patient who some time ago underwent endodontic treatment;
- Insufficient quality of the filling is its depressurization or poor fit at the edges, which makes it difficult to remove food debris and provokes the development of a carious process;
- Inflammatory or infectious processes of the dental canals under the filling;
- The need for retreatment of root canals for pulpitis, periodontitis, cystic formation, granuloma;
- The need to install an intracanal pin;
- Violations of the previously performed root canal obturation technology.
Contraindications
- Serious damage to the periodontal tissues surrounding the unit, which is not an obstacle to saving the tooth;
- The unit is unsuitable for restoration;
- Impossibility of intervention on its closed part;
- Neoplasm of malignant etiology in the area of the affected unit;
- A purulent-necrotic process that affects bone tissue;
- General serious condition of the patient.
Possible complications
Unfilling the canal is associated with the risk of tooth perforation. This is the formation of an artificial hole between the root or crown of the tooth and the periodontal ligament. Occurs due to medical error at the stage of creating endodontic access without root canal topography.
Another possible complication is the presence of broken parts of dental instruments. In this case, it is necessary to remove the foreign body, since the metal corrodes and irritates the walls of the dental canal, which can lead to the formation of cracks in the tooth root or its premature loss.
Complications are also possible with late opening of the tooth cavity into the root canal. Advanced caries, periodontitis, and low-grade inflammation increase the risk of tooth loosening and loss. Therefore, it is important to unseal the canal as soon as possible if there are indications.
Features and stages of unfilling root canals using medication
Chemical deobturation is carried out using one of two methods:
- Moderate complexity - performed in one visit and indicated if you need to remove hardening pastes. The latter dissolve well with organic solvents and are easily removed using endodontic instruments. In this case, canal retreatment under a microscope is carried out in one visit to the dentist;
- High complexity - indicated if the canals were filled with cement or resorcinol-formalin paste, rarely required when treating patients with old fillings. A dissolving gel is instilled into the canal, and after the filling has softened, a special tool is inserted into it, which allows it to be removed by turning it clockwise and counterclockwise. The dentist must work very carefully so as not to damage the integrity of the canal walls or break the instrument. This type of filling requires two visits to the doctor.
Stages of chemical unsealing:
- Removing a surface filling with a dental bur;
- Applying solvent to old material;
- Careful removal of the filling material after it has softened;
- Removal of tissue affected by caries, treatment of other diseases;
- Re-filling of canals.
Situations requiring disobturation
The dentist will learn about the need for repeated endodontic treatment by a variety of symptoms. One of these symptoms is the presence of pain in the treated tooth. We are not talking about temporary pain, which often accompanies the patient in the first 2-3 days after treatment, but about permanent pain.
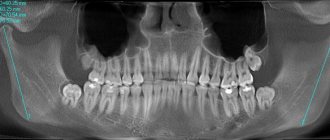
The need for repeated intervention is also indicated by the appearance of infectious and inflammatory processes in the tooth. This is established during a delayed X-ray examination or when the patient complains. Similar diseases include caries, periodontitis, inflammation under the crown.
Swelling of the gum tissue at the location of the tooth is also considered a symptom. Poor condition of the filling that covers the root canals and its loosening. This happens when the edge fit of the material is unstable.
The same procedure may be required if it is necessary to install a channel pin. Depressurization of the filling material and darkening of the tooth lead to repeated intervention. Poor quality work by the dentist when applying the filling for the first time, as well as incomplete filling of the canals with it, is also considered an indication.
Reviews of doctors providing the service - root canal unfilling
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
Words cannot express my gratitude to Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva. This is the best doctor in the world. I got an appointment after many years of being ignored by the dentist’s office and with a bitter experience of treatment in another paid clinic, the mistakes of which had to be corrected in the first visits. Thank you for this... Read full review
Roman Stanislavovich Sh
25.07.2020
Modern technologies in the field of tooth refilling
Dental treatment under a microscope is one of the newest services that has appeared in dentistry. High-tech equipment allows specialists to fill the dental canal with better quality, more accuracy and efficiency. Thanks to the use of such a device, the likelihood of causing harm to healthy tissue is close to zero. In addition, the treatment is carried out very delicately. Microscope glasses allow you to view the tooth at multiple zooms. This will allow you to see all the affected areas that may simply not be visible during normal examination.
A microscope allows dentists to perform root canal treatment faster and safer for the patient.
Why is the procedure so effective?
With the right approach, the procedure allows you to save the tooth due to:
- removal of tissue affected by caries;
- no need for anesthesia;
- eliminating the symptoms of diseases that developed under the filling
The use of a microscope in the process significantly improves its quality, since it allows you to correctly assess the features of the anatomical structure and the condition of the root canals. It is worth noting that the cost of canal retreatment with their use is higher, however, the effectiveness of the procedure increases significantly.
Modern techniques
Unsealing root canals provides for the possibility of using two techniques:
- Chemical desobturation is a procedure during which a layer of paste or a special solution is applied to the filling material, softening its structure;
- Mechanical filling removal involves the use of dental equipment to remove material from the crown and root.
A prerequisite is antiseptic prophylaxis of the oral cavity, as well as, if necessary, treatment of the tooth with a drill or root reamer.
Reviews
Diseased teeth can cause very serious pathologies not only in the oral cavity, but in almost any organ.
Timely filling and re-treatment of teeth can save you from major health problems.
If you have had to use canal deobturation, share your impressions of this procedure with our specialists and patients, please leave a comment at the bottom of this page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags seals unsealing channels
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
Closing Methods
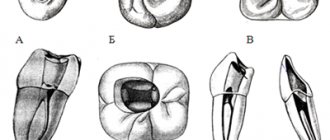
There are many methods of root canal obturation; the choice of a specific one is determined by the clinical situation. The most common technologies include the following:
- filling with gutta-percha (vertical and lateral condensation, obturation from a syringe, etc.);
- one paste;
- with installation of a central pin;
- on a carrier (thermophile system).
Gutta-percha filling
There are 2 methods of obturation with gutta-percha resin.
- Lateral (side) condensation . It is a sequential introduction of several (usually 4-5 pieces) cold gutta-percha pins with each one pressed into the wall with a spreader.
- Vertical condensation . The method involves pressing gutta-percha pins in the axial direction using hot instruments (pluggers), which heat the gutta-percha and press it into the canal, ensuring that all cavities are filled.
Both methods are considered effective and reliable.
The following advantages of gutta-percha as a filling material are noted:
- predictability of obturation;
- gutta-percha is indifferent and non-allergenic (does not irritate tooth and gum tissue);
- preservation of properties for an indefinitely long time;
- radiopacity, which allows you to control the quality of filling using fluoroscopy;
- ease of removal from the canal (if necessary).
Gutta-percha also has disadvantages:
- the material does not have an antibacterial effect;
- requires high professionalism of the dentist.
Filling with one paste
Typically, hardening pastes based on zinc oxide eugenol or resorcinol-formaldehyde resin are used. The cavities are filled using a channel filler or manually.
In the latter case, the following technology is most often used:
- the walls of the prepared channel are lubricated with the solvent on which the paste was mixed.
- a portion of material is introduced at the tip of the endotool.
- The paste is compacted with a turunda wound around the instrument.
- the next portion is introduced with compaction - and so on until the channel is completely filled.
- Excess paste above the mouth is removed.
The advantages of filling with one paste are:
- technological simplicity;
- comparative cheapness;
- Possibility of use in narrow and curved passages.
There is only one drawback, but a serious one - the lack of guarantee of reliable obturation.
Indications for conduction anesthesia in dentistry and procedure techniques.
In this publication we will announce the price of a panoramic dental photograph.
Here https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/zubyi/plombyi/kakie-problemyi-reshayut-svetovyie-na-perednih.html read about the benefits of using light fillings on the front teeth.
Filling with installation of an intracanal pin
The method is recommended for channels that are round in shape, ensuring a tight fit of the pin to the shades. Sequence of work:
- selection of a pin with dimensions corresponding to the standard size of the master file (the tool used to make the last pass during cleaning);
- adjusting the pin - fitting, trimming, bending, if necessary, in accordance with the shape of the channel;
- inserting a portion of paste into the cavity using endoinstruments;
- coating the pin with sealing paste and inserting it into the stock;
- removing air by slow back-and-forth movements of the pin.
Filling using the Thermofil system
The technology is based on the use of an obturator - a plastic carrier filled with gutta-percha, which is sometimes called the same as the system itself - “Thermophile”.
The set of materials and equipment includes:
- obturator;
- verifier (plastic carrier without gutta-percha, used for selecting an obturator).
- thermophile heating oven;
- sealant (thermostable materials like Tseal, H-Plus, etc.).
Filling technology
Obturation is performed under anesthesia due to the possibility of pain caused by the peculiarities of the technology.
- Calibration of the channel by the verifier and selection of a thermophile based on it.
- Injection of sealant into the cavity on a paper pin or thin file of sealant.
- Heating the obturator in the oven (the plastic state is maintained for about 15 seconds).
- Injection of thermophile into the channel.
- Pause 2-4 minutes for gutta-percha to cool.
- Trimming the obturator handle to ensure that the tip is raised by 1-2 mm (needed to remove the thermophile if the filling is unsuccessful).
- If necessary, thermophile obturation can be supplemented with lateral condensation.
- Installation of a temporary filling.
But complete curing of thermophile requires 1-3 days.
Advantages of the “thermophile” system:
- efficiency and reliability (the method is considered one of the most advanced):
- allows you to fill all narrow branches from the main canal with gutta-percha.
- Flaws:
- not recommended for canals with a taper of less than 04 and without an apical stop.
Removing the seal under the anchor pin
Obturation of the tooth root canal is done in parallel using anchor pins. If the filling in the lower part of the root is placed correctly and hermetically, then it is left to install the pin structure. This procedure is carried out over two trips to the dental office.
On the first day, the doctor treats the dental canal mechanically, softens the filling with medications and cleans the passage with an endo-instrument. The doctor then soaks a cotton swab in the medicine and inserts it into the canal. The patient takes the medicine for a couple of days and then makes another visit to the doctor, during which the cotton swab is removed and the canal is refilled.