Causes of pulpitis
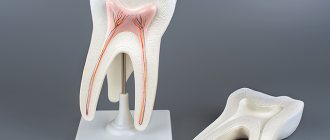
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp, the inner tissue of the tooth . In simpler terms, this is an inflammation of the nerves that are located in the root canals of the tooth.
It occurs as a result of the development of ordinary caries, when it penetrates deeper, moving from the crown to the roots of the teeth.
Diagnosing it yourself, or at least assuming its existence, is quite simple: if a tooth reacts very sharply to cold or hot, sour or salty, then it is the nerve that is reacting , and accordingly, it is the nerve that is inflamed.
Despite the fact that the cause of such sensitivity is often depleted enamel, in any case it is worth contacting a dentist.
Considering the fact that pulpitis is mainly treated using local anesthesia, the occurrence of pain after its treatment is a normal situation, and you should not immediately think that the tooth was poorly cured. Within one or two days, the pain goes away, and the person can again allow himself to eat hard apples, nibble carrots or nuts.
Pulpitis most often occurs due to the lack of timely treatment of deep caries.
The treatment of pulpitis, depending on its stage, is carried out by therapeutic (for mild forms) and surgical dentistry (for severe forms).
If pulpitis is not treated in a timely manner, the tooth may be completely destroyed, which may lead to its removal. More details here: .
However, approximately two thirds of cases of pain after pulpitis treatment are not due to the fact that there was intervention in the inflamed area of the tooth. Very often, a treated tooth begins to ache due to the fact that its treatment did not comply with all the necessary rules.
Signs that the tooth is filled incorrectly include, in addition to pain, swelling of the gums. Although sometimes inflammation can only be diagnosed on an x-ray.
One of the root canals was not processed
This is one of the rarest complications, since before starting endodontic treatment the doctor will definitely prescribe an x-ray diagnosis. It allows you to reliably determine the number of channels and evaluate their structure. But there are cases of abnormal location of root canals or their extremely small sizes, which makes them unnoticed in the image.
This leads to the following situation: the doctor removes the pulp in each canal, but one remains unattended - the inflamed pulp continues to hurt, and pathogenic bacteria continue to multiply. Such pain is difficult to confuse with other complications - the patient simply does not receive relief after treatment, and the pain characteristic of pulpitis itself remains. The sensations are pulsating in nature, the pain intensifies when eating, exposure to temperature on the tooth, and becomes unbearable at night.
The same symptoms can be observed with incomplete removal of the pulp in the diagnosed canal. In both cases, other symptoms may be observed:
- headache, sensations “radiate” to the ear, temple - depending on the specific tooth;
- increased body temperature;
- symptoms of general malaise.
Most complications are related to the complexity of the canal structure, and the following is no exception.
How long does a tooth usually hurt after pulpitis treatment?
What to do if, after treatment of pulpitis, a tooth hurts, and the pain does not go away for several days or even lasts more than a week after the procedure?
Of course, it is best to immediately consult a doctor and treat it. The sooner this happens, the less painful it will be for the patient. It is not recommended to use painkillers, especially strong analgesics. They can cause a powerful blow to the entire body.
It is also not recommended to endure pain, since this will also be stressful for the body. In general, there is only one way out - visiting a doctor. The only case when pulpitis cannot be treated immediately is pregnancy .
Here, as they say, there is a double-edged sword: X-rays, which are mandatory for pulpitis, are strictly prohibited, anesthesia cannot be used, it is also not advisable to endure it, but it is better to choose the lesser of two evils.
Allergy
This complication of pulpitis treatment is easier to differentiate - an allergic reaction is often accompanied by tissue swelling. If it is a consequence of material moving outside the root canal, there may be swelling of the gums around the treated tooth. In some cases, it spreads to other areas - cheek, lip, depending on the specific tooth.
When pressure is applied, the pain becomes stronger, it is difficult to relieve with painkillers, and over time it only intensifies.
What are the causes of pain
The occurrence of pain after treatment of pulpitis after removing nerves and cleaning root canals can be caused by two main reasons. The first is damage to the tissues of the apex of the tooth root, the second is poor-quality filling.
The first reason is quite understandable: when instruments intervene in the internal areas of the tooth, part of the nerve is torn off, and until this place heals, some time must pass. If the tooth itself was treated efficiently, then in a maximum of 3 days the wound inside will heal and the pain will disappear.
But with the second option the situation is more complicated.
There are several options for poor-quality filling of a tooth with pulpitis:
- The dental canal is not completely sealed;
- The canal is sealed too deeply;
- The filling material has gone beyond the root;
- When filling, a piece of the instrument remained inside;
- During the procedure, a perforation of the root canal occurred during cleaning.
It should be noted that the vast majority of such cases occur through the fault of the dentist. I don’t want to talk badly about doctors, but the statistics speak for themselves. In part, such misfires among doctors stem from a lack of experience; it is much worse when their poor-quality work is associated with ordinary negligence.
However, the dentist cannot be blamed if the patient’s root canals are not completely straight: in this case, even an experienced dentist, no matter how hard he tries, can accidentally damage the canal or fill it not to the top. Therefore, in such cases, it is always better to take an X-ray of the tooth.
Let's look at the most common causes of pain after pulpitis treatment.
An incompletely sealed canal
If the canal is not completely sealed, it means that there is free space left in it or the filling material is not placed tightly, and bacteria will continue to develop in this space, even if the canal itself has been well cleaned. They'll get there anyway. The development of this process often smoothly flows into periodontitis (aka abscess).
To prevent infection from entering the space surrounding the treated tooth, it needs to be treated, and, if possible, as quickly as possible.
Otherwise, this may result in tooth loss, and then either prosthetics or empty space. The first is much more expensive and takes longer than treating pulpitis, the second is constant inconvenience and not the most aesthetic appearance.
The filling material has gone beyond the root
The situation opposite to the above is not so critical. Excess filling material is less dangerous. The tooth may hurt for a long time, although not severely.
But, in any case, before retreatment, it is better to take an x-ray. If the doctor did not go too far with the filling, the pain will go away in about a month; if there is a lot of excess material, you can do a simple operation to remove it.
A piece of the instrument remained inside
The third option, a fragment of an instrument in the root canal, is practically the same as an incompletely sealed canal, only there is also a foreign body in addition. The consequences are the same as an abscess, so the tooth must be immediately treated, foreign objects removed, the canal thoroughly cleaned and properly sealed.
Root perforation during the procedure
The most dangerous of all the undesirable consequences of pulpitis treatment is root perforation. This happens mainly when the canals are severely curved, and even if the doctor works carefully, he may accidentally damage it.
The treatment is carried out with special preparations, it can be performed from the inside of the tooth and from the outside, but in general the procedure is quite complicated.
Brief conclusions
The main consequences of poor treatment of pulpitis are as follows:
- flux, formation of cysts in cases where the canals are not completely filled, periodontitis;
- prolonged pain and neuralgia during repeated canal filling.
One of the most unpleasant consequences for the patient is tooth extraction. It cannot be avoided if:
- the doctor during the treatment broke the root or caused a perforation, which was not eliminated as soon as possible;
- A periodontal abscess formed at the root apex, and the patient delayed its treatment.
Recovery period
Once treatment for pulpitis is completed, the patient will need some more time to fully recover - from one week to a month. During this period, physical therapy is indicated, for example laser therapy using a helium-neon apparatus. This is necessary to speed up the healing process and consolidate the therapeutic effect.
Since pulpitis is an inflammatory disease, after treatment in the clinic it is necessary to take a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs at home, such as: Ibuprofen, Ketanov, Naproxen-Acri. However, it should be remembered that all anti-inflammatory and painkillers have their contraindications, so the choice of a specific medication must be agreed with your doctor.
SYMPTOMATICS
SUBJECTIVE
Complaints of tearing, wave-like pain, which becomes continuous: periodically weakens, but does not disappear. The pain intensifies even more when trying to drink a hot liquid and weakens when drinking a cold one (“bottle symptom”). There is irradiation of pain along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. Increased body temperature and deterioration of health. A positive percussion reaction is possible.
OBJECTIVE
The softened pigmented dentin at the bottom of a deep carious cavity is easily removed in layers using a dental excavator. This opens the exposed pulp chamber. Painless superficial and painful deep probing, painful percussion. It is possible to relieve pain after the pus is released. Mucous with a whitish coating. The gums are swollen, and the tooth is mobile. Electrical excitability of the pulp is 40-60 μA.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSTICS
Purulent pulpitis should be differentiated from:
- Acute diffuse pulpitis It is characterized by long pain-free intervals, as well as increased pain from the action of any irritating factors.
- Acute periodontitis or chronic periodontitis in the acute stage. Pain occurs when biting, there are no pathological changes on the radiograph.
- Trigeminal neuralgia Pain begins in the form of an electric shock and lasts for a certain time with a short interval between them. They are provoked by touching certain areas of the face.
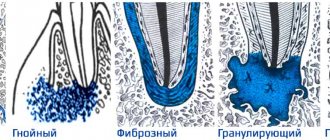
Forms of purulent pulpitis
Acute purulent pulpitis
there are two types:
- Focal purulent-serous - characterized by damage to part of the dental nerve and the release of exudate in the form of a clear liquid;
- Diffuse - characterized by damage to the entire pulp and its death. The exudate that is released has a yellowish-greenish tint and smells of rot.
It is worth noting that under favorable conditions, focal purulent pulpitis can become diffuse within 24 hours.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Why does purulent pulpitis occur?
Precursor of purulent pulpitis in children
and adults is acute pulpitis. The formation of pus occurs from the serous exudate that is present in the nerve. Due to an increase in its volume, metabolic processes occurring in the nerve suffer, which stimulates the accumulation of lactic acid and, as a result of this process, a decrease in the protective function of cells. It is accompanied by tissue breakdown and abscess. The infection that provokes the development of purulent pulpitis penetrates the pulp in different ways:
- from a carious cavity in the absence of treatment;
- during the treatment of periodontitis with dissection of the gums;
- through blood and lymph in infectious diseases.
Pulpitis in a child
Pulpitis in a child
It is a mistake to believe that treatment of baby teeth is not necessary. Without adequate treatment, caries of a baby tooth in a child, just like caries in an adult, can very quickly turn into pulpitis with all its complications. There are known cases of death after complications of pulpitis due to the development of sepsis, when no more than two days passed from the first pulpitis pain to the development of facial edema and subsequent death.
To avoid any kind of complications, caries of primary teeth in children must be treated on time. And if the moment is missed and pulpitis has already developed, you need to contact the dentist immediately. A competent doctor will do everything possible to ensure that the treatment of a small patient is as painless, comfortable and, most importantly, effective.