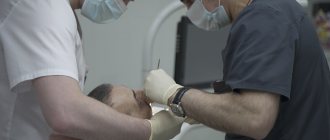
Bone grafting is prescribed to patients before dental implantation in cases where insufficient bone tissue is diagnosed, which is a contraindication for implantation and subsequent prosthetics. Dental implantation involves the introduction of an artificial root into the jaw bone and then, after its engraftment, fixation of a prosthesis on the implant. When there is not enough bone tissue, which occurs as a result of atrophy due to insufficient chewing loads, the implant cannot be securely fixed in the bone. An operation to increase bone tissue is prescribed - bone grafting of teeth.
More about the procedure
The periosteum is a connective film consisting of two layers. The upper one includes blood vessels and nerve fibers that supply the upper jaw and transmit impulses to the brain. The lower one contains osteoblast cells. During the inflammatory process, the upper layer is the first to be affected, which leads to acute pain. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the lower layer and bone tissue are affected.
Periostotomy is a tooth-saving operation. During its implementation, a free outflow of pus from the inflamed area is created.
What is a periostomy?
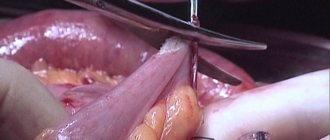
Periostomy, otherwise called periosteotomy, is a surgical procedure that involves cutting the periosteum (periosteum) to open the subperiosteal abscess or as a way to gain access to the bone. This operation is tooth-saving.
In addition to the function of periostomy, which is to gain access to the jaw bone, it is also necessary for flux. If it causes inflammation of the periosteum with the typical formation of a purulent tumor, periostomy is done to be able to separate pus from the inflamed area.
It should be noted that periostitis (flux) is a fairly serious disease with a lot of negative consequences if it is treated incorrectly or ignored altogether. If there is the slightest sign of flux, you should not self-medicate, you should immediately contact a specialist. Incorrectly chosen treatment will not only aggravate periostitis, but can also provoke the spread of purulent discharge throughout the body (for example, if a purulent tumor ruptures due to overheating with compresses).
Healthy teeth and good health
FDC will be a pleasant find for you and your family on the path to impeccable aesthetics and good health.
The main symptoms of periostitis are:
- swelling and hyperemia of the area of the diseased tooth;
- increased body temperature, especially during exacerbation;
- pain in the area of the affected tooth;
- pain in the area of the affected tooth;
- separation of pus;
- malaise, feeling of weakness, loss of appetite.
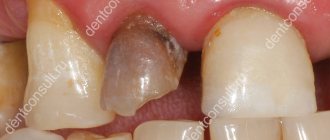
A lump on the gum is the most obvious symptom of periostitis. It is formed by pus that forms in the area of the tooth root and penetrates out through the bone tissue. It must be said that sometimes symptoms disappear without treatment. This happens when a purulent formation breaks out on its own. Inflammatory processes in the tooth area continue to occur, and external relief does not at all indicate that they have passed.
How is periostomy performed?
The surgeon administers a local anesthetic and opens the abscess, freeing the site of inflammation from pus discharge, then he leaves a drainage at the incision site for complete drainage of purulent discharge for two or three days. The drainage is represented in this case by a piece of rubber strip. This design allows the pus accumulated in the periosteum to escape without being deposited or retained in the soft tissues.
Postoperative recommendations are simple: temporary rest and antibiotic therapy. For speedy healing and rapid disappearance of swelling, the dentist will prescribe antiseptic solutions for rinsing the mouth.
After periostomy, the patient is advised to maintain temperature, oral hygiene and avoid unnecessary physical activity. Specialists of the French Dental Clinic will perform periostomy, if necessary, using modern anesthesia methods and unique equipment.
Indications
Surgical intervention is required in case of inflammation and flux. When the gum tissue swells, pus concentrates inside. Periostotomy is performed in the following conditions:
- abscess (or purulent preriostitis) - an incision for the outflow of pus;
- actinomycosis of the jaw - overgrown bone is eliminated;
- periostitis of the serous type - reducing the tension of dental tissues and eliminating suppuration;
- inflammation after canal filling - an incision to relieve swelling.
In addition, the operation can be a stage of complex treatment during extensive surgery for sinus lifting, bone grafting, radicular cyst, as well as prosthetics on implants.
When is surgery indicated?
Purposes of periostotomy:
- gaining access to the jaw bones;
- ensuring free outflow of purulent contents from the source of inflammation.
As a rule, the need for surgery arises in the presence of inflammatory processes developing in the periosteum (periosteum), accompanied by flux. Flux is a swelling of the gums surrounded by a diseased tooth with an accumulation of pus.
In addition, the operation is advisable in the following clinical cases:
- treatment of actinomycosis of the jaw or periosteum for primary treatment of the source of inflammation. The essence of the manipulation is to remove overgrown bone tissue;
- treatment of jaw periostitis. The doctor opens the periosteum to reduce the degree of tension in the dental tissues and prevent the development of a purulent process;
- elimination of the inflammatory process after filling the tooth canals. The essence of the manipulation is to make an incision on the periosteum, which helps prevent swelling;
- with purulent periostitis (abscess). Gaining access to the periosteum is necessary to ensure the outflow of pus exudate;
- during resection of the apex of the tooth root. The surgical procedure is the initial stage of treatment and is performed to gain access to the root apex. After cutting the periosteum, the bone material is cut out.
Also periostotomy when performing other surgical interventions, if indicated.
Preparation
Before periostotomy, the doctor performs X-ray diagnostics to assess the anatomy of the periosteum, its condition, and the location of inflammation. After receiving the data and analyzing it, the patient is recommended to undergo surgery. To perform it, it is necessary to pass a number of tests standard for any surgical intervention.
The process takes place under local anesthesia. If the inflammation is in the upper jaw, then pain relief is done bilaterally. If the lower jaw is affected, mandibular or torusal anesthesia is performed (in the area of the lower jaw ridge).
How is bone grafting surgery performed?
The technique of bone tissue augmentation (bone grafting) through directed tissue regeneration is used more often because it is less traumatic for the patient. In most cases, after growing bone tissue in this way, it is possible to immediately install implants. The operation of bone tissue augmentation through directed tissue regeneration allows you to increase both the height and width of the bone. When performing tissue regeneration techniques, it is necessary to provide conditions for its implementation. The material for grafting can be either synthetic or natural; it can be natural bone material of foreign origin (bovine), granules of synthetic hydroxyapatite, autogenous bone chips (bone tissue is collected from the person himself). Autogenous bone chips are considered to be the most effective material, since in this case the risk of material rejection is minimal. However, there are also disadvantages, which include an additional operation to harvest the bone.
In the case of using materials made from natural bovine bone, there is a risk of infection with a virus; as for synthetic materials, absolute safety for humans is guaranteed, but the effect of the operation is much lower. Further, to perform bone tissue augmentation by directed tissue regeneration, the use of a special membrane is required, which is applied on top of the bone material being grafted and the pieces of the mucous membrane located above it are sutured. The membrane is necessary to provide isolation of the bone material from the surrounding soft tissue, in addition, the membrane prevents the bone material from being washed out of the wound through the incision line. Membranes used for guided tissue regeneration can be self-absorbable or non-absorbable, requiring removal through repeated surgery. Failure to use a membrane is fraught with ineffective growth, when the bone tissue either does not increase at all, or increases, but in insufficient sizes.
The use of a combined method together with the method of directed tissue regeneration and subsequent implantation ensures an increase in the width of the narrow alveolar process. To do this, the doctor performs a vertical splitting of the alveolar process, then, using a special tool, widens the cut, screws the implant into it and replants the bone tissue. Afterwards, a membrane is applied and the mucous membrane is sutured.
If we talk about the method of grafting a bone block, then in this case an autogenous bone block is used, taken from the patient from other parts of the jaw. Osteosynthesis screws are used to secure the bone block to the bone. Then, bone chips or synthetic hydroxyapatite granules are applied on top and covered with a membrane, and the mucous membrane is sutured. The bone block grafting method is considered traumatic for the patient, since an additional operation is required to remove the material, and in addition, simultaneous implantation is impossible in this case.
Progress of the operation
The duration depends on the complexity of the condition; on average, the operation takes 30-40 minutes. Stages:
- anesthesia;
- treatment of the cavity with antiseptics;
- tissue dissection by 1-2 cm;
- peeling of the periosteum;
- cleaning and treating the cavity with antiseptics (“Furacilin”, potassium permanganate solution);
- installation of drainage to prevent wound healing.
A few days after the cavity is completely cleansed, the drainage is removed and an application with anti-inflammatory and regenerating drugs is applied. If the wound is too large, stitches are applied.
The process of periostotomy
The algorithm for performing periostotomy in standard clinical cases includes the following steps:
- Administration of local anesthesia.
- Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity.
- Making an incision followed by tissue dissection. If the operation is performed in the area of the vestibule of the oral cavity, then the incision is made horizontally, along the fold. The optimal length of the incision should be at least 2 cm. This will ensure normal outflow of pus and complete closure of the infiltrate.
- If the manipulation is carried out in the mandibular region, then the incision is made along the surface of the mucous membrane in the places of maximum protrusions of the seals.
- If the source of inflammation is localized in the palate, the doctor makes a dissection parallel to the central line of the palate. In this case, the area of maximum swelling is selected.
- Next, the periosteum is moved back and peeled off using a special smoother, which is a blunt instrument.
- Treating the site of inflammation with antiseptic drugs. As a rule, potassium permanganate and furatsilin are used for these purposes.
- At the final stage, drainage is installed, which is a rubber plate. It prevents the wound from sticking together and ensures the drainage of pus.
The duration of the manipulation depends on the severity of the pathological process and the clinical picture as a whole. In most cases it takes 30-40 minutes.
The risk of complications is associated with incorrect surgical intervention, in particular:
- improper installation of drainage prevents the normal outflow of exudate;
- making an incision in the wrong place or over-cutting can also lead to negative consequences.
To avoid all sorts of consequences, it is important to ensure that the operation is performed by an experienced dental surgeon.
Rehabilitation
It is recommended to limit food intake for several hours after surgery. In the first days, it is recommended to avoid solid foods and eat only grated and chopped food.
To reduce the likelihood of complications, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics and analgesics. During the wound healing period, you need to rinse your mouth with special compounds and herbal decoctions (for example, chamomile, sage, calendula).
After healing, a course of physiotherapeutic procedures (for example, heating, UHF) and laser therapy may be prescribed.
Rehabilitation
For the first two hours, eating and drinking (except water) is not recommended. In the future, food should be soft, preferably pureed. All food and drinks should be at room temperature.
The doctor also prescribes painkillers and antibiotics. Rinse only when indicated. If the process was difficult and the healing process is difficult, physiotherapy is prescribed.
If you conscientiously follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the recovery period takes 4-6 days.
Cost of services
Surgery Price
Periostotomy of the tooth: indications and features of the operation from 1500 rub.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
You may also be interested in:
Wisdom tooth removal Tooth extraction Removal of the dental nerve Complex tooth extraction Resection of the apex of the tooth root Removal of an impacted tooth Removal of the tooth root Removal of a dystopic tooth
Show more