From this article you will learn:
- why is my cheek swollen after removal,
- How long does swelling of the cheek or gum last?
- What does the temperature say after tooth extraction?
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
If your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction, this in most cases is an unfavorable symptom of the development of inflammation, for example, this may indicate the development of alveolitis (suppuration of a blood clot in the socket of the extracted tooth). Swelling of the cheek can also be caused by the formation of a hematoma along the transitional fold, the formation of a purulent abscess on the gum in the area of the extracted tooth, and other reasons.
However, in some cases, swelling after tooth extraction may be natural, without requiring a second visit to the doctor. As you probably know, swelling of the soft tissues after an injury or surgery is the norm, and therefore it is logical after a complex tooth extraction (for example, when the extraction was carried out with an incision in the gums and sawing out the roots of the tooth with a drill).
Swelling of the cheek after wisdom tooth removal –
Moreover, some patients complain only that their gums are swollen after tooth extraction, and they do not have visible swelling of the cheek. The appearance of swelling of the gums has the same reasons (as with swelling of the cheeks), it’s just that there are features of the course of the inflammatory process - depending on the location of the inflammatory focus. For example, if the inflammatory focus is located closer to the transitional fold (i.e., the place where the mucous membrane of the gums enters the cheek), then this is more likely to lead to swelling of the soft tissues of the face.
Below we will examine in detail the cases - when the appearance of edema is quite natural and does not pose a danger, as well as situations in which you urgently need to contact a dental surgeon for a re-examination.
Why did gumboil appear after dental treatment?
Swelling of the gums indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process, which caused the complication. If painful sensations are observed against the background of the tumor, the main reasons for this may be:
- Periodontal inflammation. The tumor is observed on both cheeks, but pronounced swelling occurs only on the infected side.
- Neglected teeth, improper placement of fillings. Before swelling occurs, pain occurs. After 2-3 days, a flux with pus may form.
- Incorrect development of wisdom teeth. A hood forms from the mucous membrane, in which food particles accumulate and become inflamed.
- Removal of a tooth. Due to mechanical damage to the tissue, swelling can be considered normal.
- Cyst. The inflammatory process lasts for 1.5-2 years and injures the periosteum. The pathology occurs against a background of severe pain.
Attention! Swelling of the cheek after dental treatment can develop due to infection in the socket, which not only causes discomfort and swelling, but can also lead to more serious consequences.
If there is no pain during swelling, the reasons for this are as follows:
- allergic reaction to anesthesia, dental materials (swelling sometimes affects the entire face);
- removal of the nerve: part of the nerve may remain in the canals; after installation of the filling, flux appears;
- dissection of the gums, extracted tooth (in these cases, swelling is normal);
- infectious inflammation of the lymph in children, accompanied by aches and fever;
- neurological diseases accompanied by swelling, congestion in the ears, sore throat, weakness.
Important! In the case of severe pathologies of internal organs, the drainage of fluid is often disrupted; as a result, it accumulates in the nose, cheeks, neck, cheekbones and near the eyes.
Other causes of cheek swelling
If you have a tooth removed and your gums are swollen, the cause does not necessarily lie in soft tissue damage. Swelling is possible due to the following:
- performing an operation if the patient has a flux;
- complex course of the operation - due to tooth growth in the wrong direction, strong inclination, removal of large teeth with large, intertwined roots;
- inflammation and infection of soft tissues or tooth roots before surgery;
- allergies or other forms of individual intolerance to anesthesia and medications used during removal - therefore it is important to know exactly what components you are allergic to before removal;
- poor antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and mistakes made by the doctor during tooth extraction;
- chronic diseases leading to complicated recovery - neuralgia, hypertension, as well as a general decline in the body’s immune functions;
- ignoring prescriptions received from the dentist - for example, independently adjusting the dosage or deciding not to take antibiotics.
Most often, patients' swelling does not subside after tooth extraction due to lack of normal care - skipping medications, complete absence or insufficiently frequent disinfection treatment.
Possible complications
Patients face complications due to incorrect care, complex or incorrect removal. Dentistry distinguishes 5 types of complications:
- Alveolitis - to put it simply, this is dryness of the socket. A blood clot always forms in the latter. It does not need to be removed, since the clot protects soft tissues from the penetration of bacteria and infection. If it is accidentally removed, the mucous membrane becomes susceptible to the pathogenic influence of bacteria, and suppuration may develop. Sometimes the inflammation shifts and spreads - a large area of the jaw, cheekbones and eyes become inflamed.
- Osteomyelitis is bone inflammation. With osteomyelitis, acute pain is felt in the upper and lower jaw, and swelling only increases.
- An abscess is suppuration inside the gum. Can move, leading to loosening of the tooth root.
- Flux is a severe inflammation of the jaw, in which the temperature rises and acute pain appears in the area of the jaw and temples.
- Neuritis is an inflammation in which the motor activity of the facial nerve is disrupted. Neuritis is indicated by swelling of the cheek, palate, tongue and larynx.
What does flux look like?
It is of infectious origin, the process occurs against the background of inflammation of the body of the jaw or in the periosteum. Flux is formed not only after dental surgery, but also after furunculosis or tonsillitis. If the cheek and gums are swollen, there is throbbing or mild pain, in advanced stages pus may appear and the temperature may rise. On the upper jaw, the flux covers the lip, cheek, gum and nasolabial area. In addition to the face, the infection often spreads to the neck.
Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. After using topical medications, you should not eat or drink liquids for 2 hours.
Reasons for the development of abscesses after an injection
Any intramuscular injection is an invasive procedure. Such an intervention violates the integrity of the skin and triggers a whole chain of pathological changes. As a rule, the cause of an abscess is incorrect administration of injections in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. Often such complications occur if the injection was given at home.
Predisposing factors for the development of an abscess are decreased immunity and a sharp weakening of the body.
The correct way to administer the injection is to insert a needle into the upper outer quadrant of the buttock. It is permissible to inject the medicine into the muscle layer of the shoulder or thigh. If the syringe needle enters a large blood vessel, hemorrhage occurs into the soft tissue, which can lead to the development of an abscess. A number of drugs can have an irritating effect on tissue; when administered not into the muscle, but into the subcutaneous fat, it can also lead to the formation of an abscess.
If the wound at the injection site was scratched, this could serve as an entry point for infection and cause a suppurative process.
What symptoms do you see a surgeon for:
- Presence of hernial protrusion
- Daggering pains in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Bitterness in the mouth
- Nausea
- Presence of neoplasms on the skin
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Bone fractures and bruises
- Wounds of any location
- Vomit
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes
Swelling on the inside of the cheek
Anesthesia makes tooth extraction easier. But, if after treatment of a tooth your cheek is swollen, you should find out the origin of the pathology. You may need treatment for your gums. Discomfort appears in many patients after depulpation. Pain and swelling on the inside of the cheek can be observed from 2 hours to 7 days. If discomfort intensifies or occurs 2 days after surgery, you should immediately consult a dentist.
If, after removing the nerve, in addition to painful sensations, the gums become inflamed, purulent discharge appears, and the temperature rises, you should visit a dentist. He will find out why the cheek is swollen and how to remove the gumboil.
Attention! You cannot take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs before consulting a doctor; this will complicate the diagnosis, which will not allow you to prescribe adequate treatment.
How to reduce swelling after implantation
The main thing you need to do after implantation is to rest well and expect the outcome to be favorable. Your doctor performed the operation successfully, so now how the rehabilitation period goes depends only on you. Read our useful guide after dental implantation, which details what you need to prepare at home in advance and how to solve any problems that arise.
How to apply compresses? This is the most basic method that allows you to relieve tissue swelling. It is especially effective in the first day and even in the first hours after installation of implants.
Proceed as follows: use ice, a heating pad with ice water, or any food from the freezer. But don't overdo it, i.e. do not cause frostbite and tissue necrosis. The procedure is as follows: wrap ice in a towel or 2-3 layers of gauze/thin fabric, apply to the cheek on the side of the surgical intervention, hold for 5-10 minutes. The duration of the compress is 5-10 minutes, breaks are 3-5 minutes. The number of approaches is 7-10 times, for approximately 1.5-2 hours. Such courses can be repeated periodically during the first day.
How to eat properly to avoid swelling? In addition to solid foods (for any implantation protocols, even if the prosthesis was installed immediately), you must exclude excessively hot, spicy and salty foods, coffee, and spices from your diet. Caffeine, for example, increases blood pressure, which contributes to an even greater rush of blood to the head and, accordingly, increased tissue swelling.
Hot foods and drinks are prohibited, as they can lead to increased swelling. Hard - because they can injure the operated area and displace the installed implants. All of the above restrictions are in effect for a week.
Andrey Nikolaevich, 45 years old
“The operation went quickly for me, under anesthesia. I went home fully conscious and without much pain. I expected that when the anesthesia wore off, the pain would be unbearable, there would be severe swelling... Having covered myself with the recommended pills, I waited while I made compresses. The tablets were bought in vain. At night I slept as usual. In the morning I also didn’t experience anything special, there was almost no swelling. On the evening of the first day I came for my first fitting. On the third day, the prosthesis was installed - everything went perfectly!”
“If the doctor is a professional, then rehabilitation will take place very quickly, without pain and without swelling. Tested for myself! "
watch a video with the patient
How should you sleep after implantation? It is necessary to ensure the outflow of blood from the head; it is better to sleep with your head elevated. You can place several pillows under or on the mattress, thus increasing the angle of inclination. Many patients note that after surgery there is a feeling of pulsation in the head. Such a measure will also relieve such a symptom.
Is it possible to visit swimming pools and saunas? To relieve swelling, you need cold. Therefore, not only saunas and swimming pools are prohibited in the first week after installation of implants, but also long stays in a hot bath. It is better to limit yourself to a warm shower.
What medications will help against tissue swelling? After installation of the implants, the patient is prescribed drug therapy. We deliberately do not indicate the names of medications, because in each specific case medications are prescribed individually. But the complex necessarily contains anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs, which help reduce tissue swelling. Patients who have problems with the heart and blood vessels, high blood pressure, are also recommended to take appropriate medications.
On the 3rd day after implantation, the patient is scheduled for a preventive examination: the doctor will assess the condition of the tissues, the dynamics of healing and give the necessary recommendations. If you have doubts earlier, you should not wait for a scheduled visit; you can see a doctor earlier.
What to do if swelling appears after treatment at the dentist
If after tooth extraction your cheek is swollen from the tooth, there is no need to worry - this is a normal reaction. You can take a pain reliever that your dentist recommends. When a pathological condition is accompanied by pain and weakness, the temperature should be measured.
Edema does not always indicate a complication; it is worth distinguishing a simple reaction of the body from a pathological condition. Don't worry if:
- the flux disappears 3 days after surgery;
- the swelling is not pronounced and does not increase in size;
- no temperature or it does not exceed 37.5 degrees;
- the pain is aching, slight, gradually goes away, eliminated with analgesics;
- in the hole there is a bloody dense clot, which is covered with fibrous tissue within 2-3 days.
On a note! Do not apply hot lotions to the injured area, release pus yourself, or massage the gums. This will provoke further development of the infection, which will lead to serious consequences.
The following symptoms indicate complications:
- the flux grows;
- there is severe pain that cannot be relieved with analgesics;
- tension together with surgery;
- temperature over 37.5-37.6 degrees;
- it hurts to swallow, speak, open your mouth;
- there is no blood clot in the hole or it is covered with a green, gray or yellow coating;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- itching, hyperemia, shortness of breath - indicate an allergic reaction.
Attention! If you have any of the symptoms, you should consult your doctor. Such signs indicate infection. If an operation was performed, the treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon or an endodontist if the root canals were cleaned.
What can lead to severe swelling
Some diseases and complications lead to similar non-standard reactions of the body to tooth extraction. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Systemic chronic diseases. These include diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and low immunity. All these diseases impair the body’s ability to recover after surgical procedures.
- Alveolitis is an inflammation of the alveolus (socket) that remains after tooth extraction. The cause of inflammation can be general diseases, smoking, mechanical damage, or non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations. As a result, a blood clot does not form in the socket, severe pain, a gray coating and an unpleasant odor occur. If alveolitis is not cured in time, dangerous purulent diseases such as phlegmon and osteomyelitis may develop.
- Difficult tooth extraction. The presence of dental anomalies associated with incorrect tooth position (dystopia, retention) almost always complicates the extraction process. Often these deviations lead to greater trauma and, as a result, more pronounced swelling. The same can be said for third molar extractions. If the operation was performed professionally and the patient followed the dentist’s instructions, then there is no reason to worry.
- Incorrect tooth extraction. Doctor's mistakes include: incomplete root removal, removal of the interradicular septum, leaving fragments in the alveolus, infection. A more rare cause of inflammation is the presence of a cyst that was not detected during surgery: its growth is accompanied by an increase in edema.
To speed up healing and eliminate any unpleasant symptoms that may arise, do not delay your visit to the dentist. It is advisable to contact the surgeon who performed the tooth extraction procedure.
When does swelling of the cheek go away?
How long the swelling lasts after tooth treatment depends on the degree of damage. Swelling causes injury to tissues, ligaments, and blood vessels during surgery or root removal. After such an intervention, swelling is normal. It can last from 2 hours and last for 7 days or the first day after surgery. There are no painful sensations.
Swelling after surgery on a wisdom tooth can last 4 days longer and persists for 11 days. If the surgery was serious, a bruise may form on the cheek. Pronounced swelling, increasing every day, pain is a reason to urgently consult a dentist.
When is it necessary to contact a specialist?
We kindly ask you not to self-medicate and not to leave things to chance. Severe swelling may be a variant of the norm, your individual reaction to the intervention, but if you are unsure about something, be sure to contact your doctor. Complications are always easier to prevent than to treat.
In rare cases, swelling may occur after implantation as a symptom of complications. Occurs with reduced immunity, wound infection, and improper care. You can read more about what to do if your face is swollen after tooth implantation and what to do in the postoperative period. If you experience the following symptoms of the disease, you should visit a doctor:
- Tissue swelling, which increases from 3-4 days after surgery.
- Throbbing pain that gets worse.
- Discharge of pus.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- General symptoms include weakness, headache, malaise.
- Increased body temperature.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
How to treat gumboil on the cheek
Once a tumor develops, antibiotics are often indispensable. The dentist selects them taking into account the stage of the pathology and the characteristics of the body. Antibiotic therapy should be completed to the end, otherwise further treatment will be greatly complicated.
If surgery is required, all activities are carried out in a dental clinic. For any complication, the patient is given local or general anesthesia. The gum is incised and the accumulated pus is completely pumped out. A drainage is placed to quickly remove fluid. The patient is prescribed antibiotics to allow the soft tissues to recover faster. In case of severe damage, the gum is sutured. In the absence of complications, this is not required.
How to remove swelling from the gums through surgery:
- In case of complicated flux, urgent hospitalization in a dental clinic and an operation performed by a dental surgeon are necessary.
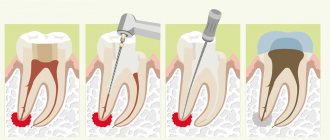
- If an inflammatory process is diagnosed due to dental problems, endodontic therapy (cleaning and filling the canals) or root removal will be required.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed to treat infection in many situations. In case of serious complications, combination drugs are used to treat severe swelling, selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogens.
- Surgical treatment - incision of the abscess (on the face and oral cavity - the incision is made in both areas), removal of purulent discharge, treatment with disinfectants, installation of drainage. In severe cases, general anesthesia is used.
- Additional therapy - analgesics to eliminate discomfort, antipyretic drugs, large amounts of fluid (if necessary, fluid is introduced into the body by infusion during hospitalization).
Chronic pathology often occurs without pronounced symptoms, pus appears gradually. In this situation, the dentist uses a therapeutic approach, both surgical and conservative. Surgery can be replaced with herbs or antibiotics, or used as an additional treatment after consultation with a specialist.
Swelling of the cheek does not always indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
A tumor after depulpation is normal and does not require serious treatment. When the gumboil gradually grows, pain is observed against this background, and the help of a dentist is required. In case of serious complications, surgical intervention while taking antibiotics is indicated. The doctor's consultation
Diagnosis and treatment
To make a diagnosis, the doctor only needs to examine the oral cavity and study an X-ray of the jaw. The flux treatment regimen is compiled individually for each patient. This may include:
- complex treatment of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis,
- taking antibacterial drugs,
- opening the abscess and draining the contents,
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions,
- physiotherapy - UHF, laser therapy, electrophoresis.