Causes What to do about pain?
Home Remedies Dental Care Prevention Having completed treatment, we leave the dentist's office with a feeling of relief. Then the effect of local anesthesia ends and it is discovered that the tooth hurts after the filling. There is no reason to panic and immediately make an appointment. Pain is a natural reaction to medical intervention:
- To prepare a tooth, it is drilled. Nerve endings in hard tissue react to this process by sending pain signals to the brain. The deeper the drill went, the more painful it was.
- When the pulp (nerve) is removed, adjacent vessels and nerve endings are injured.
- The antiseptic used to treat the cavity has a strong irritant effect. It can get into surrounding tissues, causing discomfort.
This kind of pain goes away on its own within up to 2 weeks.
. The main feature: the unpleasant sensations gradually subside and disappear.
What else causes toothache under a filling?
Sometimes, the tooth continues to hurt or causes discomfort. This may be caused by medical error:
- The dentist overdried the dentin, causing a burn. The tooth reacts to temperature stimuli and tapping.
- Dentin was not dried enough. An air gap with negative pressure appears between the filling and the wall, which causes pain.
- When treating deep caries, the doctor damaged the pulp chamber, pathogens penetrated into the pulp and caused inflammation - pulpitis.
- The filling was placed incorrectly; it irritates the gums, causing swelling, redness, and pain.
A broken instrument, too much or too little filling material, allergic reactions to its composition also lead to unpleasant sensations.
Toothache after filling
4383 March 25
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Toothache: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
After filling a cavity or canal of a tooth, pressing or bursting pain may occur. Sometimes pain occurs when biting, chewing and tapping a tooth; in some cases, the pain becomes acute with the development of swelling of the gums in the area of the causative tooth.
Types of toothache after filling
Depending on the cause of the appearance, local or diffuse toothache after filling is distinguished. More often it is transient and goes away on its own after a short time (no more than a day).
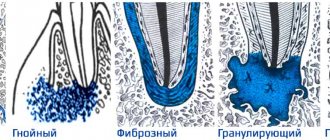
In some patients, after filling a carious cavity with deep caries or a canal with pulpitis, the intensity of pain gradually increases, it can be paroxysmal in nature, intensify under the influence of cold, and radiate along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. If left untreated, such pain becomes throbbing, the tooth may react to hot food, and swelling and redness of the gums develop. An infiltrate may form on the gum, from which pus or an abscess flows out when opened.
Possible causes of toothache after filling
Impact of irritants on the pulp.
First of all, you need to understand the location, intensity of pain and under what circumstances it occurs. If pain appears immediately after installation of a filling, this may be a consequence of the reaction of the nerves of the tooth and periapical tissues (tissues surrounding the root of the tooth) to mechanical, thermal and chemical influences.
Pain after the cessation of anesthesia indicates restoration of tissue sensitivity. As a rule, discomfort disappears within 24 hours after treatment.
Sometimes strong drugs placed into the tooth cavity lead to overdrying of dentin (the main solid substance of the tooth surrounding the pulp) and even to chemical burns of the pulp. This complication is accompanied by an acute pain reaction to cold and hot foods and sweets.
Incorrect installation of the seal
. If the upper border of the filling protrudes above the chewing surface of the tooth, then all the pressure of the opposite jaw during chewing falls on one tooth. This leads to overload of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, injury to the periapical tissues and the occurrence of dull local pain during chewing. To prevent such a complication, the doctor, after installing the filling, conducts a test with carbon paper. The paper is placed on the tooth with a filling and the patient is asked to close the jaws and make lateral and anteroposterior movements. The cusps of the tooth, which are marked with carbon paper, are ground off.
It is a mistake to think that excess filling material will wear off on its own over time.
The process of natural grinding lasts for years, during which time the patient experiences pain when chewing and, ultimately, this leads to traumatic periodontitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth). Inflammation of the periapical tissues
and the appearance of pain may be a consequence of pushing the filling material beyond the apex of the root canal. Together with the filling mass, infected tissues from the tooth canal enter the periodontium, which cause periodontitis. In this case, prolonged aching pain occurs, which intensifies when pressing on the diseased tooth. Tapping on a tooth is painful. Nearby lymph nodes (for example, submandibular) may enlarge. There is a risk of accumulation of purulent exudate in the area of the root apex and the formation of an abscess. The gums near the diseased tooth swell and turn red. Sometimes pus breaks through the gum, in these cases the swelling, redness and pain decrease. However, without treatment, this process constantly recurs.
Pain after filling can also occur in cases where one of the canals extending from the pulp chamber remains untraversed.
The number and location of canals in multi-rooted teeth varies from person to person.
If during tooth sanitation one of the canals remains unnoticed, the infection from it penetrates into the periodontium with the development of chronic periodontitis.
Close location of the carious cavity to the dental pulp
. In some cases, the bottom of the cavity is located too close to the pulp. The thin intermediate layer of dentin is penetrated by short tubes, through which infection from the carious cavity can enter the pulp and cause its inflammation (pulpitis). In these cases, hyperemia of the pulp develops (the initial stage of pulpitis), which, if left untreated, turns into acute pulpitis. There is no pain when tapping on the causative tooth.
A characteristic sign of initial pulpitis is pain that occurs upon contact with irritants (temperature and chemical) and goes away a few minutes after the cessation of their influence.
In other cases, the doctor may not recognize the initial stage of pulpitis when filling a tooth. In this case, sealing the infected pulp leads to acute pulpitis, which is accompanied by sharp, paroxysmal pain, intensifying at night and radiating along the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Which doctors should I contact for toothache after filling?
If pain occurs immediately after dental treatment, you should contact your dentist. However, in some cases, when there are no signs of malocclusion and periodontitis and pulpitis are not observed on radiographs, the patient may be referred for consultation to an otolaryngologist (if sinusitis is suspected) or (if inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is suspected).
Diagnosis and examination for toothache after filling
The connection between the occurrence of pain and previous dental treatment helps to make a preliminary diagnosis. The presence of an inflammatory process is confirmed by redness and swelling of the gums.
However, accurate diagnosis is only possible after radiography.
In the absence of clear radiological signs of periodontitis, they resort to electroodontodiagnostics (a method for assessing the condition of the pulp, in which its reaction to a weak electric current is checked), it allows one to assess the degree of damage to the pulp.
What to do if you have toothache after filling
Mild, aching pain after tooth treatment may continue for 1-2 days, and this is normal.
However, if the pain does not subside or intensifies, a consultation with a dentist is necessary to diagnose possible complications.
Treatment of toothache after filling
If the pain is caused by malocclusion due to excess filling material, it should be sanded off.
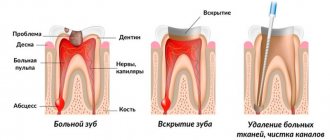
Pain due to the development of pulpitis requires opening the pulp chamber and depulping the tooth. Acute and chronic periodontitis also indicates the need for unfilling of root canals and their mechanical and medicinal treatment. After treating the cavity and canals, the doctor can apply therapeutic and insulating linings, covering the tooth with a temporary filling, then another visit will be required so that the doctor can re-treat the cavity and place a permanent filling.
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of periapical tissue disease // Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after. A.I. Evdokimov of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. – 2014.
- Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook / ed. Borovsky E.V. – M.: Medical Information Agency. 2004. - 400 p.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
What to do if your tooth hurts after installing a filling?
You should pay attention to the nature of the pain. If it is aching, tolerable, and is not associated with food intake, then the chances are high that everything will work out on its own.
You should worry if:
- The pain is throbbing, increases towards night, the sealed tooth with the nerve hurts - this indicates inflammation of the pulp.
- Unpleasant sensations appear only when biting or pressing on the filling - most likely, the filling technology is broken.
- There is a feeling that the tooth is sticking out, there is discomfort when chewing - the filling is too large.
- The mouth burns, the gums hurt, the mucous membrane turns red and swells - signs of an allergic reaction.
- The pain does not decrease, but may intensify. The gums swell, general malaise appears, and the temperature rises. These symptoms indicate that periodontitis is developing.
What symptoms after treatment require urgent consultation with a doctor?
How can you understand in the first days after dental treatment whether the pain is physiological or the process is already pathological? There are some signs that indicate that you need to see a doctor without delay.
The following symptoms are considered abnormal after dental treatment:
- the pain in the filled tooth pulsates, it is sharp and sharp, and there is no tendency to decrease it;
- pain radiates to neighboring teeth, ear, temple, neck;
- body temperature rises;
- headaches appeared;
- cheek swollen;
- suppuration in the tooth area;
- inflammation of the gums;
- there is a feeling that the filling is in the way in the mouth.
If you have a headache or fever, you need to see a doctor
Possible pain after dental treatment
| Norm | Pathology |
| It hurts to press, press, or bite on a tooth for 2-3 days (maximum – a week) | Increased body temperature |
| Slight lifting of the gums | Pain radiates to the ear, temple, neck |
| Slight pain after the anesthesia wears off | Headache |
| Increased sensitivity and pain when exposed to cold food and liquid, as well as hot, spicy, sweet, sour | Severe swelling of the gums and/or cheeks |
Even if the required two days have not passed after therapy, during which the pain should go away, do not hesitate to visit the dentist. It is necessary to stop the inflammatory process and treat the tooth. Even if the alarm is false, you need to make sure that everything is in order. In this case, the patient’s increased suspiciousness is even encouraged.
Dental filling is not the most complicated process; it is not a surgical intervention. But often this work can be compared to jewelry. Therefore, unfortunately, some problems cannot be ruled out - the doctor may make a mistake. It is good if the patient is treated in a proven clinic with a good reputation, perhaps with the same doctor.
It is best to have your teeth treated in a good clinic
Happy treatment!
How to help yourself at home
All home remedies that are recommended for use if a tooth aches under a filling reduce the symptoms, but do not eliminate the cause. These measures are temporary and are applied until you see a doctor. The only exception is natural pain after a filling has been placed.
Pharmacy painkillers will help you relax and sleep. Rinsing with salt or soda relieves irritation. Infusions of herbs, calendula, chamomile, and sage have a disinfectant and anti-inflammatory effect.
Modern dentistry has a negative attitude towards such traditional medicine as a hot compress. This can increase inflammation, cause bleeding and a purulent process.
When there is no need to see a doctor
Why does a tooth hurt after pulpitis? The appearance of pain is due to the increased trauma of the entire procedure, which consists of opening the tooth, removing pulp from the root canal and filling the empty space with artificial material - a filling.
How long does a tooth hurt after pulpitis in normal condition? Without pathologies, the pain persists for 5-10 days, and it gradually subsides. It is considered normal when:
- after pulpitis, the tooth hurts without increasing pain;
- there is no bleeding, swelling, swelling or redness, general weakness, or fever.
Treatment in dentistry
If you experience severe, increasing pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. Also, you should make an appointment if your tooth ache after filling, although about 2 weeks have passed. The dentist will conduct an examination and order an x-ray examination. An examination will determine whether the filling is in the way. If so, the doctor will simply sand the surface.
The picture will show what causes discomfort:
- periodontal inflammation;
- pulpitis;
- tool fragment.
In this case, the tooth will have to be refilled. The old filling is removed and the reason why the filled tooth aches is eliminated. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the defect. A piece of the tool can be removed in one go. Severe inflammatory processes will require several visits and endodontic intervention when the canals are re-treated.
If, after installing a filling, a tooth hurts as a result of an allergy to the material, it is replaced using a different composition.
Why else can a tooth hurt after visiting a doctor?
There are several other reasons that explain toothache after a visit to the doctor. These are only possible options; you should not make diagnoses on your own. As a rule, the doctor gives a guarantee on the filling, and if pain occurs, he is obliged to see you, and this visit will be free.
Why else can a tooth hurt?
- Partial removal of pulp tissue. May cause re-inflammation.
- The caries has not been completely removed. If the tooth is seriously damaged, a temporary filling may be necessary. If for some reason the doctor underestimated this measure, the toothache may become even worse due to incorrect therapy. The fact is that in a completely closed area the inflammatory process will be more severe than in an open one. And secondary inflammation in an already clean area can no longer lead to caries, but to a more serious process - pulpitis.
Pulpitis
- Allergy. A rare case, but it cannot be ruled out. Increased sensitivity to the filling material can cause inflammation and pain in the tooth area.
- Failure to comply with medical recommendations. For example, the doctor told him to abstain from food for some time (usually no more than two hours), but the patient ignored the recommendations.
Violating medical orders can be dangerous
So, pain in the treated tooth, which can occur periodically at certain points, should go away within 2-3 days. If the pain lasts more than a week or two, you need to go to the doctor and find out what went wrong.
Memo for patients
- Do not delay visiting your doctor if there are signs of an allergic reaction.
- If the pain increases, swelling, redness, or fever appears, make an emergency appointment
- Do not relieve pain with antibiotics unless prescribed by a doctor.
- Do not use alcohol or garlic applications, as they can burn the mucous membrane.
- Never heat your tooth
- Follow all dentist recommendations
A qualified doctor, a clinic with modern digital equipment and following the recommendations will help you avoid situations where a tooth hurts after installing a filling.
Expert of the article Bolshakova Evgenia Vladimirovna Dentist-hygienist
More than 11 years of experience
Causes of pain
After pulpitis, a tooth hurts for several reasons - damage to the tissues surrounding the tooth root (periodontal) or an inflammatory process.
Tissue damage can be caused by the following circumstances:
- formation of a wound surface during removal of the neurovascular bundle of a tooth;
- treatment of root canals with antiseptic agents if the antiseptic leaves the canal.
Can a tooth hurt after pulpitis due to the dentist’s dishonest work? The inflammatory process can occur due to poor quality work by the doctor. Signs of poor treatment of pulpitis on an x-ray are:
- incomplete filling of root canals, when there is still free space left to the apex;
- excessive filling of root canals, when the filling material extends beyond the apex of the root canal;
- extra holes in the root canals.
Classic filling
The conventional filling procedure does not imply penetration into the tooth pulp and depulpation of the root canals. This manipulation is much simpler compared to endodontic intervention, however, not everything is so obvious here. First, conventional therapeutic procedures are performed more frequently. Secondly, the quality of materials and the level of specialists in Russia are often low, so severe pain after filling a tooth and other complications are by no means uncommon even with the simplest manipulations. Below is a table that describes the most common causes of complications and pain after filling.
| Type of complication | Description | Pain symptoms |
| Mechanical trauma to the pulp during filling (pulp perforation) | It occurs when the bur is used roughly and carelessly, when the partition between the pulp and dentin is destroyed. Modern dentistry offers conservative ways to eliminate such complications, but often only a depulpation procedure can help. | With this problem, the tooth “pulsates” after filling and reacts sharply to cold and hot. The pain is severe and practically does not subside. |
| Burn of dentin or pulp (tooth overheating) | Usually occurs when the cooling system of the drill malfunctions, when the tooth tissue gets burned during the operation of the drill. In the most severe cases, the patient develops pulpitis and periodontitis. | If your tooth ache after filling and the pain does not go away for a long time, it is quite possible that you have a dentin burn. If, after filling, the tooth reacts sharply to hot and cold or there is throbbing pain, then most likely the pulp was affected. |
| Incorrectly installed seal | Overbite and overhanging filling edges are among the most common causes of pain. Incorrect closure of the dentition provokes very unpleasant sensations. | Does your tooth hurt when you bite it after filling? Perhaps the problem is an incorrectly installed seal. If the cause is not eliminated in time, the tooth reacts painfully even with gentle pressure. |
| Error when choosing material | There are more than a dozen filling materials on the market, many of which are not suitable for everyone due to their properties and components. | Acrylic composite and silicate cement fillings can cause allergies and inflammation. Amalgams and some light fillings can shrink, which is why the tooth hurts quite noticeably when bitten after filling. |
| Gum injuries | Damage to soft tissue is a very common occurrence during therapeutic manipulations (especially in the treatment of cervical caries). Serious injuries may require gum grafting. | Aching or cutting pain at the site of gum damage. |
If your tooth hurts after root canal filling
Unlike classic filling, root canal treatment is a procedure that essentially kills the tooth and its tissues. Of course, after such manipulations, pain in the first few days is quite common (this is related to the question of whether a tooth should hurt after root canal filling). However, if a tooth hurts a week after filling, then this is a good enough reason to start worrying. Pain after root canal filling can be caused by a number of reasons, but in any case you should not think that everything will go away on its own. Negligence in relation to one's own health can lead to periodontitis, damage to bone tissue and even death caused by infection of the body. So, in popular parlance, when your nerve hurts after filling a tooth, you have serious cause for concern.
Pain after REMOVAL of a “NERVE” from a tooth (after treatment for PULPTIS).
Quite often, so-called “post-filling” pain occurs after tooth depulpation. Mild pain when pressing on a tooth is considered normal.
and tapping on it, lasting no longer than 4–8 weeks. This is due to the fact that during the treatment process the doctor performs mechanical treatment of the root canals with metal instruments and rinses the canals with powerful antiseptics. All this can irritate the tissue surrounding the root. The reaction to such influences is different for all patients.
If the pain when biting on a tooth is sharp, severe, there is a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth, swelling of the gums or cheeks around the tooth appears, general health worsens or body temperature rises - this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. Complications of endodontic treatment may have arisen that need to be addressed.
Pain after treatment of PERIODONTITIS.
Sometimes it happens that the tooth never hurt, but the doctor diagnosed periodontitis and treated it, after which the tooth began to bother. In such a situation, do not rush to blame the doctor and believe that he provided poor-quality treatment.
Treatment of periodontitis is a very complex process that cannot promise guaranteed success. After all, periodontitis is an accumulation of microbes outside the tooth root (in the bone tissue). If before treatment microbes moved freely from the oral cavity to the tooth root and back, then after filling the canals, the bacteria remaining in the bone tissue are “immured.” Normally, this manipulation allows you to localize the source of infection, after which it is easier for the body to cope with it and “defeat” the microbes.
However, with a weakened immune system, due to the individual characteristics of the body, inflammation and a pain reaction may occur in response to sealing of the channels. Even if the tooth did not bother you before, now it can react to pressure and touching it; there may be pain when biting, throbbing, or a slight aching pain in the tooth.
Abnormalities include sharp, paroxysmal pain, the inability to close teeth due to pain, swelling of the gums or cheeks around the tooth, the appearance of tooth mobility, deterioration in general health, or a significant increase in body temperature.
In any case, if pain occurs, it is better to consult a doctor. Additional manipulations or the prescription of certain medications may be required. However, don't panic! Sometimes this kind of pain goes away on its own after some time.
Why does a healthy tooth hurt?
A seemingly healthy tooth without any damage or caries can also hurt when biting.
The reasons for this are increased sensitivity of the enamel. Pain occurs both from mechanical stress and when eating hot, hungry or sour foods. The discomfort is short-term and goes away immediately after the irritant is eliminated.
2 ways to get rid of enamel hypersensitivity:
- Do-it-yourself is the home use of gels and pastes based on fluoride, calcium and other useful minerals (ROCS, SPLAT Biocalcium, Colgate Sensitive, Elmex, etc.).
- Turning to the dentist means professional fluoridation of enamel, remineralizing therapy, as well as enamel extension with filling material.
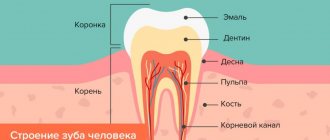
What can hurt a tooth?
A tooth consists of a root and a crown. It is covered as a frame with dentin and cement in the root area, dentin and enamel in the crown area. These are hard tissues that lack nerve endings, so they cannot hurt. Inside the tooth there is a space filled with tissue penetrated by branches of nerves. This is pulp. The pulp is also contained in the canals that connect the tooth cavity to the root. Any diseases (for example, inflammation - pulpitis) and injuries to the pulp are very painful.
Periodontitis is also a very painful disease - inflammation of the periodontium - the ligament that holds the root in the socket, since there are also many branches of nerves in the periodontium.
Caries
If after treatment the tooth hurts when pressing or eating, this is considered normal and can persist for up to two months. This is explained by the fact that with deep caries, a very thin layer of dentin remains between the pulp and the filling, so when pressing or biting, pressure is transferred to the nervous tissue and causes pain.
In addition, the patient may experience dull pain for 14 days. This is also considered normal and is explained by a reaction to the use of boron, as well as various medications. But, if even after two weeks the discomfort does not go away, you need to contact your dentist.
Acute or throbbing pain is a reason to visit the dentist immediately: perhaps a carious infection has penetrated into the pulp, causing pulpitis. The sooner you do this, the higher the chance of avoiding the removal procedure and the subsequent need for prosthetics. You can learn how to avoid caries from the article “Prevention of caries.”
Periodontitis
A slight aching pain or pain when pressing on a tooth, which occurs after the end of the periodontitis treatment procedure, is considered normal and goes away on its own over time. If your gums or cheeks are swollen, you have paroxysmal pain, or your body temperature has risen, you should go to the hospital as soon as possible.
In our dental center in Brest you will receive qualified dental care both for caries, pulpitis and periodontitis, and for pain after dental intervention.