Questions and answers on: tooth hurts under a filling
The most common questions patients ask after tooth filling concern pain.
- Question : “A month ago, I had a tooth healed using paste to kill the nerve and installing a temporary filling, but it hurts when pressed. Also, the gums on the cheek side were swollen. After the temporary filling fell out, I did not install a new one. What to do? Is it related to the root or the nerves?” Answer : “Most likely, the periosteum became inflamed because the canals were not treated in time. It was necessary to treat them and put a permanent filling. In your case, the tooth needs to be removed, but if you consult a doctor urgently, there is a small chance of saving it.”
- Question : “Can a tooth hurt after filling? It’s been 2 hours since the filling was placed, but I feel a little pain.” Answer : “Mild pain in a filled tooth is a natural physiological reaction to surgical intervention in the dental cavity. Periodic painful sensations may be felt for 2 months until complete healing. They will pass unless the pain becomes more severe and increasing.”
- Question : “Yesterday we got a filling, but the tooth still hurts. A small rash and itching appeared near him. I can’t stand it any longer, what should I do?” Answer : “You need to see a doctor to replace the filling. You have developed an allergic reaction to it. This is quite a rare occurrence."
- Question : “A week ago I was treated for caries and a filling was placed at the 6th unit below. But the tooth did not stop hurting. It especially bothers me at night; I can’t sleep due to the throbbing pain. Should a tooth hurt after filling?” Answer : “Most likely, the dentist treated you for deep caries due to periodontitis or chronic pulpitis and made a mistake, guided only by a visual examination of the oral cavity. In any case, it was necessary to take an x-ray of the tooth affected by caries. We urgently need to remove the filling and treat the canals.”
- Question : “2 weeks ago a permanent filling was placed without removing the nerve, but it still hurts me to chew. In addition, the tooth reacts to cold and hot food and at times there is aching pain.” Answer : “Such symptoms may indicate the development of chronic pulpitis or the development of an abscess inside the tooth.”
If various pains appear in the tooth after the filling procedure, then the only recommendation is to contact a qualified specialist. After all, the reasons can be completely different.
Pulp - what is it for?
The pulp is a fibrous connective tissue penetrated by nerve endings and blood vessels.
Its shape completely follows the tooth, and is located in the center of the root part, filling the entire cavity. On top, the pulp is protected by a hard enamel layer, which prevents injury from the outside.
Main functions of the dental nerve:
- responsible for the formation, proper growth of teeth and blood supply;
- protects channels from pathogenic microbes;
- supplies the tooth with useful micro- and macroelements.
In addition, the pulp is responsible for the sensitivity of the tooth, that is, for its reaction upon contact with hot, cold, sour, sweet, and so on.
Reference! The dental pulp in adults is thinner than in children. This is due to age-related changes and a slowdown in regeneration processes. The older a person is, the thinner and weaker the nerve becomes, and the tooth begins to experience a deficiency of nutrients.
Tooth hurts after nerve removal and filling
Only a dentist after an examination will help you figure out why a tooth hurts after removing a nerve and filling its canals. Treating teeth on your own without a diagnosis is highly discouraged.
In dental practice, the procedure for treating tooth canals by removing a nerve is a rather complex manipulation. Cases of medical error are common. They are fraught with various complications, in which the filled tooth continues to hurt.
The main reason why a “dead tooth” (without a nerve) is bothersome is:
- removal of the filling material beyond the apex of the tooth - this occurs due to incorrect definition
- working tooth length;
- the doctor filled the canal incorrectly;
- a tool broke off in the canal;
- root perforation of the tooth;
- If your tooth aches, you may be allergic to the filling material.
It is worth considering that a tooth under a filling can hurt even without a nerve. After all, during the extraction procedure, only a small part of it is removed from the root canal, which branches off from the main nerve trunk. In addition, when removing and filling canals, dental tissues are damaged. When an anesthetic is applied to a tooth, pain is not felt; it begins to be felt after the anesthesia wears off. Such painful sensations are called post-filling.
After removal of a nerve, neighboring teeth can often be bothered, but it seems as if it is the treated tooth that is hurting. An experienced doctor will examine the dentition to identify and eliminate this problem. However, it is worth sounding the alarm when the nerve has been removed for a long time, and the tooth continues to hurt - this symptom may signal the development of chronic pulpitis or periodontitis.
Conservative treatment
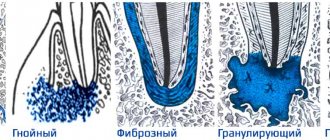
The conservative method of treating inflammation is otherwise called biological and involves the preservation of nerve endings. Unfortunately, this option is only suitable for restoring a tooth at an early stage of pathology; in case of extensive tissue damage, more drastic methods will have to be used.
Conservative treatment is indicated for acute pulpitis, in cases where the chamber was opened due to negligence, as well as for the chronic course of a fibrotic disease.
This method also has a number of contraindications. The main ones are considered to be old age and the presence of serious inflammatory processes of the periodontium.
Also, this method of treatment will have to be abandoned if caries is detected in the neck or roots of the tooth, if prosthetics are needed in the future, if you are allergic to the materials used, as well as if existing diseases worsen at the time of treatment.
Tooth hurts after root canal filling
Dental clinic patients are often concerned about the question of why their tooth hurts after inserting filling material into the tooth canal after removal of the nerve. Since any intervention in the body has its consequences, toothache is an “echo” of the filling procedure.
The most common reasons for a tooth to ache after root canal filling are:
- burns and overdrying of dentin;
- allergic reaction to filling material;
- depressurization of the seal;
- change in bite;
- exposure to polymerization lamps;
- shrinkage of the filling.
After the procedure, the dentist usually advises you on how long the tooth under the filling hurts. However, if you feel increasing pain in a filled tooth for more than 2 weeks, you should urgently consult a doctor. Such pain can occur when an instrument breaks off in the canal, root perforation, or improper treatment of pulpitis.
When is channel cleaning necessary?
There may be several reasons for this:
- For caries and pulpitis, the inflamed pulp is removed and the canals are sealed;
- Before installing a crown - sometimes you will also have to remove the pulp for this (but only when installing certain types of dentures);
- In case of periodontitis - if the pulp has already been removed, but inflammation of the tissue continues, it means that the procedure was not carried out well enough (you will have to repeat everything all over again).
If you are worried about toothache and have been putting off visiting the dentist, don’t do it any more. Make an appointment with a dentist at the NAVA clinic, and the specialists of our medical institution will help you cope with any of your problems. Our experienced specialists will make the treatment painless, because the procedure uses modern equipment.
This article was checked and approved by Kokaya’s doctor, Madlena Dzhenerovna.
Restoring tooth shape
If the crown restoration is not sealed, infection from the oral cavity easily penetrates into the root canals and provokes repeated inflammation, the treatment of which requires retreatment with the removal of the filling material. It is possible that improper restoration will lead to tooth loss.
Our Center uses 2 methods depending on the degree of tooth decay:
- Artistic restoration A nanocomposite is applied layer by layer, taking into account the fissures, anatomical shape and natural shade of the enamel. Indicated when the crown is destroyed up to 50%.
- Orthopedic design Installation of an artificial crown, inlay or veneer. It is recommended if most of the tooth is destroyed, there is extensive caries, and enamel abrasion.
How to diagnose the disease
The decision on depulpation is made by the endodontist and he performs the procedure only after assessing the examination results.
A number of diagnostic measures are carried out, complementing each other:
- Sight image Allows you to determine in which tooth the nerve needs to be removed, because pain can radiate to neighboring ones, and a person cannot always accurately determine which tooth hurts. It makes it possible to assess the degree of development of the inflammatory process and see the structural features of the tooth.
- Computed tomography 3D image gives an idea of the condition of the tooth itself and the tissues surrounding it. Allows you to accurately determine the number and location of root canals. Identify possible root fractures, foci of inflammation at its apex, determine their location and size.
- Examination under a microscope Multiple magnification of the working field allows the endodontist to visually detect any changes in the tooth tissues - root caries, microcracks. Examine the anatomy of the tooth in all its detail and the smallest detail, identify the narrowest and hidden canals.
When is depulpation performed before prosthetics?
Until recently, nerve removal was a routine process before the installation of permanent structures. Recently, the views of dentists have changed. The fact is that a tooth without pulp is considered “dead”. There is no tissue exchange, secondary dentin is not produced. He becomes fragile. In addition, when there is no pulp, the inflammatory process can completely destroy the tooth, because there will be no pain for a long time.
On the other hand, if the pulp becomes inflamed under the crown, then an expensive and complex restoration will have to be removed in order to carry out treatment.
There is no consensus among dentists whether it is necessary to remove the nerve during prosthetics. Each point of view has its defenders and opponents. The golden rule of dentistry is to carry out manipulations strictly according to indications.
Temporary filling
In some cases, medicine is introduced into the canals for a certain period of time. Manipulation is carried out for:
- elimination of pathological microflora;
- stopping the inflammatory process;
- isolation of the canal, when it is impossible to carry out treatment in one visit.
Indications for temporary installation of a filling are injuries, perforation of walls, periodontitis in acute or chronic form.
The main active components of medicinal non-hardening pastes are antibiotics.
Why is it important to preserve the nerve?
If a nerve is removed from a tooth, it is called dead, since it ceases to receive nutrition and all the necessary microelements. Such units may cause a lot of discomfort in the future. For example, dead teeth are believed to be very fragile and break quickly. Also, the enamel of units without pulp quickly darkens and is visually different from the dentition.
If you had to deal with surgical intervention to remove a nerve in a tooth, you shouldn’t worry. Modern restoration methods will help eliminate aesthetic defects
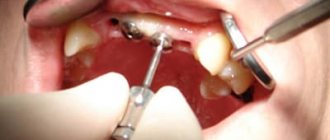
How does tooth depulpation occur before prosthetics?
The decision about whether to perform depulpation or not is made by the doctor. The main diagnostic method is x-ray. It shows the presence of inflammation, the condition of the roots, and the thickness of the dentin. Another method is a visual examination, which evaluates the condition of the oral cavity and the physical location of the teeth. Based on clinical data, a treatment plan is drawn up. If a decision is made to remove the nerve before prosthetics, the procedure follows the following algorithm:
- Anesthesia
. Most often it is an injection into the gum. In some cases, sedation may be performed. - Removal of affected tissue
. If there is no caries, then this stage is skipped. - Opening access to the pulp and canals
. To do this, the dentist has to remove part of the hard tissues - enamel and dentin. - Removing pulp
from the pulp chamber. This is a simpler stage. - Extraction of loose pulp
from canals. This is a difficult stage. The manipulation is carried out blindly; how thoroughly he cleans the canals depends on the skill of the doctor. - Treatment of canals
with an antiseptic solution - Drying the surface
- Canal filling
. They do this to prevent pathogens from entering the canal. - Applying a gasket
to isolate the channels. For this purpose, different types of dental cements are used. - Temporary filling
. Only necessary when using medication. A temporary filling is placed for a period of up to 14 days. It can be easily removed if complications arise and additional treatment is needed. If no problems arise, move on to the next step. - Replacing a temporary filling
with a permanent one. Filling is carried out with durable composite materials. - Grinding away excess filling
. - The finishing touch is polishing the filling
.
This is vital removal. No preliminary manipulations are performed with the neurovascular bundle; the amputation is performed live.
The devital method involves mummification of the pulp followed by its removal. After access to the pulp is opened, a paste containing paraformaldehyde is placed into the hole. Or, as people say, arsenic. Then the paste is carefully isolated, covered with a temporary filling and waited until the neurovascular bundle mummifies. After 3-7 days, the cavity is opened again and the pulp is removed. The canals are processed and sealed. This method is rarely used due to the risk of toxins getting into other tissues.
During the work, control images are taken to monitor the quality of canal blockage.