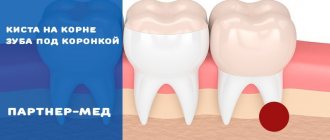
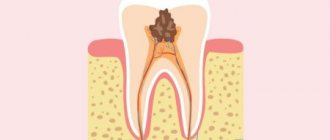
Methods of modern dentistry are aimed at preserving the dental unit. Removal is resorted to as a last resort if gentle treatment techniques are ineffective. Resection of the apex of the tooth root (apicoectomy) is a microsurgical intervention for excision of tissue affected by infection with part of the injured tooth root. The operation is performed if the inflammation has taken the form of a cyst or granuloma. The main condition for the success of such a surgical intervention is the timeliness of the patient’s visit to the dentist. If the pathological process spreads to most of the root, the tooth will have to be removed.
Indications for surgery
- Poor endodontic treatment leading to inflammation of the root apex;
- the presence of a cyst, granuloma or other neoplasm, no more than 1 cm in diameter;
- perforation of the root walls during filling;
- pin or stump inlay in the dental canal;
- obstruction of the dental canal due to a congenital developmental defect;
- a crown or bridge placed on a tooth.
If a wisdom tooth is removed
In addition to restoring the dentition in the event of a missing tooth in the frontal or lateral group of teeth, the question often arises of restoring the dentition in the event of removal of a wisdom tooth. A very important criterion in such a situation is the functionality of the extracted tooth, whether it was in the bite, whether it was involved in chewing, and how it was located. If the removed wisdom tooth was involved in the act of chewing, then the issue of its restoration becomes relevant. The complexity of this clinical situation is that it is impossible to restore the tooth using treatment options such as bridges or removable dentures. Installing an implant in this area is the only right solution!
Currently, the installation of implants is the most modern treatment method, the result of which satisfies all the necessary requirements, causes minimal trauma to the patient and is the most convenient design to use and care.
When surgery is not performed
Like any other surgical intervention, apicoectomy has limitations and contraindications. These include:
- Mobility of teeth II-IV degrees;
- destruction of the crown part of the tooth (more than 50%);
- the presence of cracks in the affected root;
- severe curvature of the root canal (impossible to fill);
- crowding of teeth, which does not allow identifying the affected root;
- acute infectious, viral disease;
- severe bleeding disorders;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- severe immunodeficiency;
- oncology in the active stage.
Some of the limitations to root resection are the indication for removal of the affected unit. The second part refers to general contraindications to any surgical intervention. The risk of surgery for the patient is assessed individually.
The specialists at the Ilatan Clinic make every effort to save the dental unit, if possible. But if there are direct indications for removal, for example, extensive damage to dental tissue, the doctor will not suggest apicoectomy.
When do you need a doctor's help?
Does your tooth ache for a long time after root resection? If discomfort persists for more than a week, you should consult a specialist. Discomfort may indicate the development of complications and concomitant diseases. Reasons to visit a dentist are also:
- increased body temperature,
- severe swelling of soft tissues,
- neoplasms on the gums,
- white plaque on the oral mucosa,
- putrid odor from the mouth,
- loosening of the dental unit,
- sensation of a foreign body in the mouth,
- numbness of the cheek or lip.
There is no need to wait for the problems listed to disappear. These symptoms are typical for many diseases, so you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. It is easier to eliminate any problem at an early stage.
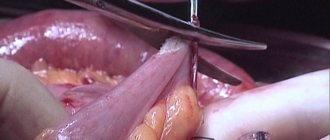
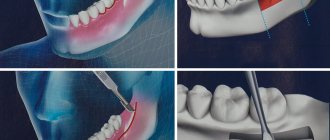
Resection stages
- Formation of access
- the dentist cuts through the gum, exposing the jaw bone. Forms a small hole in the bone tissue (in the projection of the root apex), gaining access to the pathological focus. Often, the bone tissue has dissolved in the projection of the cyst; there is no need to cut out a hole. - Excision of tissues and correction of the apex
- the doctor removes the source of inflammation along with the dead apex of the root, cutting it off perpendicular to the upper dental axis (to the level filled with the filling mass). The empty space is filled with osteoplastic material (bone volume is restored faster). - Suturing
- suturing the wound area is sometimes performed with the installation of drainage for the outflow of ichor. Drainage is installed between the seams and is removed after 1-2 days.
Root resection takes 40-60 minutes, depending on the location of the tooth. It is easier to intervene on canines and incisors than on multi-rooted units.
So what should we do with it?
There are always several options for developing a situation.
- Nothing to do
- Conservative treatment
- Radical surgical
- Tooth-preserving operations
An option for the curious is not to treat and see how it ends. It won't be boring, I promise. Whatever one may say, periodontitis is a chronic inflammation that will manifest itself sooner or later. As long as the immune system is in order, there will be a chronic phase, which may practically not manifest itself at all, showing itself only as weak sensations of heaviness, fullness, discomfort and unpleasant sensations when biting on a sore tooth. The chewing habit reflexively changes to avoid impact on the problem area, which can lead to damage to the jaw joints from improperly distributed load.
As soon as the immune system stops considering this place the most important and turns its attention to something else, for example, with a common cold, periodontitis of the tooth will go into the acute phase of inflammation - pain, swelling, and temperature immediately appear. The immune cells of the granulation shaft around the root no longer keep the microbes in check, the microbes joyfully rush beyond their habitat, eating bone tissue and actively multiplying - pus accumulates in the jaw bone under the tooth, which needs to go somewhere - either under the gum (flux or periostitis with colossal swelling of the cheek, which requires serious surgical intervention - and this is still a favorable outcome) or in adjacent anatomical areas, which leads to immediate hospitalization and long treatment, there are even fatal cases. There have been many cases of deaths from untreated teeth. And this is in the 21st century!
It consists of eliminating infection from the tooth canals, read in more detail in the article “I will not remove the treatment - where to put a comma?”
Ruthless removal of a tooth from which an infection occurs, scraping out the altered tissue. No tooth - no problem. Only then do you need to decide how to restore the lost combat unit.
A conservative surgical treatment option that allows you to remove inflammation while preserving the tooth. These include resection of the root apex, hemisection of the tooth, and root amputation.
Recovery period
The entire operation lasts about an hour, the recovery period takes up to six months or more, depending on how quickly the bone tissue regenerates. In the first 1-2 days after the surgical procedure, the patient is bothered by moderate pain, swelling, and redness of the gums. After 3-4 days, the unpleasant symptoms decrease and the condition improves. To ensure that the postoperative period passes quickly and without problems, the doctor will give the necessary recommendations for care, prescribe painkillers, as well as a short course of antibiotic therapy.
Wound healing time
The oral mucosa takes approximately 2 weeks to heal. After this period, all symptoms of surgical intervention disappear, and chewing loads do not cause pain. Complete healing of bone tissue requires more time - from 6 to 12 months. During this period, the hole in the bone heals. To monitor this process, radiography should be performed regularly. This diagnostic procedure is prescribed a few days after resection and 6-7 months later.
Care after tooth resection
- Do not chew on the operated side.
- Until the wound heals, avoid irritating, solid foods (food should be warm and soft).
- Do not use a hard toothbrush, aggressive pastes, or mouthwash.
- Take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor to prevent infection.
- Rinse your mouth after eating with an antiseptic solution.
- For the first week after surgery, limit physical activity to moderate, and exclude extreme, contact sports.
- Do not visit the bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna until the wound is completely healed.
- Avoid eating too hard foods until the bone is completely restored (at least 3 months).
- Visit your surgeon regularly to evaluate the results of the operation.
Recommendations for recovery
After resection, for successful recovery it is necessary to follow the following recommended measures:
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor. These can be antibiotics, anesthetics, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and other drugs.
- Eat soft pureed foods. You can start taking solid foods only after the wound has completely healed.
- Avoid foods that irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- Avoid physical activity.
- Try not to be nervous.
- Do not overheat the body: avoid hot baths, steam baths, saunas, solariums and other thermal treatments, do not sunbathe, and do not drink too hot drinks.
- Perform regular oral hygiene with a soft toothbrush using antiseptic paste and mouthwash.
- The first meal can be taken 2-3 hours after surgery.
Possible complications
Root resection is a micro-operation, the purpose of which is to preserve the full functionality of the affected tooth. Usually, the risk of complications is minimal, but they cannot be completely excluded. Sometimes the following complications are possible:
- Bleeding due to injury to nearby vessels;
- infection of a postoperative wound;
- recurrence of cysts, granulomas (if all affected tissues were not removed);
- perforation of the maxillary sinus, nasal passage;
- damage to the nerve passing along the alveolar ridge;
Sometimes complications are caused by structural features of the jaw, for example, the proximity of the roots to the maxillary sinus. Complications caused by non-compliance with medical recommendations include swelling and tissue inflammation. Ignoring advice on limiting physical activity is fraught with the development of bleeding, and failure to maintain hygiene can lead to wound infection.
Contraindications to the procedure
Surgery is not performed in the following cases:
- Inflammation of periodontal tissues.
- An advanced stage of periodontal disease, when the neck of the tooth is exposed and the unit itself has become mobile.
- Tight adherence of the roots of adjacent healthy teeth to the source of infection.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Excessive tooth mobility.
- Weakened immunity.
- Cancerous formations in the tooth area.
- Active form of the inflammatory process.
- Pregnancy period.
Cost of tooth root resection
The price of root resection is determined depending on the volume of surgical intervention, the cost of consumables, and anesthesia. The result of the procedure fully justifies the money spent. After all, it is cheaper than removal with further implantation and prosthetics. The doctor will tell you exactly how much tooth resection costs after examination and diagnosis.
Recommendations after surgery, what you definitely shouldn’t do
After surgery, you should not additionally load the area of the dental system that has undergone surgery with food. It is important to follow all the dentist’s recommendations and not self-medicate. It would not hurt to take several control radiographs (for example, after 3, 6 and 12 months). You can disinfect the oral cavity with antiseptics or soda solution to prevent the development of purulent processes in the gums.
It is necessary to follow a gentle diet - do not eat solid foods: nuts, dried fruits, sweets, etc. Avoid sour and sticky foods.