Salivary gland cysts
Symptoms of a salivary gland cyst
Depending on which gland it forms in, the symptoms of a salivary gland cyst can be distinguishable.
Small gland cyst
If a small gland has undergone a neoplasm, then the cyst is noticeable on the surface of the mucosa from the lower lip, and less often - on the mucosa of other parts. The small gland cyst does not exceed 1 cm in diameter and grows slowly. In appearance, it is a round elastic movable sphere protruding above the mucous membrane. It is practically imperceptible to the patient. If accidentally bitten or damaged by hard food, the cyst opens and secretes a viscous fluid, after which it closes again and mucus accumulates inside it again.
Sublingual gland cyst
Its location is under the base of the tongue. Such a cyst has a spherical or oval shape and a bluish light tint. When the cyst is located near the mylohyoid muscle, it takes on an hourglass shape.
A cyst of the sublingual gland can cause inconvenience because, as it increases in size, it provokes displacement of the frenulum of the tongue. Its incorrect position causes difficulties while eating and talking. Periodically, the cyst may spontaneously empty and be filled again with transparent or translucent secretion due to the fact that the gland continues its work.
Submandibular gland cyst
This cyst manifests itself as a fluctuating, round-shaped formation with a soft, smooth surface, located in the lower jaw, closer to the jaw joint. It can also spread to the sublingual area of the oral cavity and manifest itself as swelling of its bottom. In advanced cases, a submandibular gland cyst causes facial deformation. Like other types of similar neoplasms, this cyst can empty and fill again with liquid contents.
Parotid cyst
The parotid type of cyst, like others, has the shape of a ball with an elastic structure. A cyst forms on the mucous membrane inside the mouth near the auricle. Typically, a parotid cyst affects only one side of the mouth, which can cause facial deformity due to swelling of one cheek. The skin over the site of the cyst does not change color or structure. On palpation, the gland affected by the cyst does not show signs of fluctuation and does not cause pain.
In the absence of treatment and subsequent infection, the cyst can be complicated by abscess processes, accompanied by hyperemia of the skin and pain in the ear area. In this case, opening the mouth becomes very difficult, fluctuation and a slight increase in temperature in the tissues of the cheek are observed.
Causes of retention cysts
A retention cyst can form in both adults and children.
The cause of cyst formation is often a blockage of the excretory duct of a small salivary gland, which occurs due to an accidentally bitten lip. And since each gland has an excretory duct, due to a bite or injury it heals with the formation of a scar. If this scar gets on the excretory duct of the salivary gland, it becomes blocked. The secretion of the gland has nowhere to go, it accumulates in the gland and it begins to grow in size. Therefore, this cyst (retention) is nothing more than an enlarged salivary gland.
Removal of the parotid, submandibular gland, removal of cervical lymph nodes
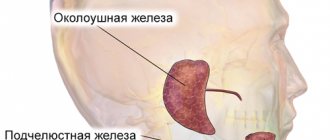
The salivary glands are divided into minor and major salivary glands. There are 3 pairs of large salivary glands: the parotid salivary glands, located below and in front of the auricle directly under the skin, the submandibular salivary glands and the sublingual glands, located under the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth. The minor salivary glands are located in the mucous membrane of the mouth, palate, cheeks and lips. Various tumors, stones, and recurrent infections are the most common reasons for operations on the salivary glands.
Treatment methods for retention cysts
If this type of cyst appears, under no circumstances should you bite it, as its shell will collapse and removal of this cyst will be impossible.
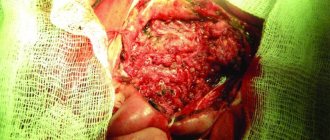
The main treatment method for retention cysts of the sublingual salivary gland is surgical - cystotomy and cystectomy (rarely). The procedure takes a few minutes (10-15), and is performed under anesthesia and is absolutely painless.
During surgery on a retention cyst, the part located under the mylohyoid muscle is removed and the isthmus is ligated. After this, a cystectomy of the part of the cyst located in the oral cavity is performed.
Complications after surgery
During surgery to remove the parotid gland, the facial nerve can be impacted, sometimes causing facial nerve palsy, usually the inferior branch, which can cause the corner of the mouth to droop. Typically, facial nerve paresis recovers within a few weeks with facial exercises, and only in rare cases does the facial nerve fail to recover.
Sometimes the cancer affects the facial nerve and then the facial nerve is completely removed, in which case the paralysis is permanent. However, the condition can usually be improved through various surgical interventions.
After removal of the parotid salivary gland, the pinna of the ear is usually partially numb, but over time some sensitivity returns. Due to the risk of frostbite, the auricle must be properly protected from the cold.
During surgery to remove the submandibular gland, the facial nerve may be injured (stretched), causing temporary dysfunction of the corner of the mouth, but permanent damage caused by this branch of the facial nerve is very rare. Damage to the sensory and motor nerves passing under this gland is extremely rare.
After parotid surgery, saliva may leak from the wound, especially when eating. Salivary secretion is harmless and usually ends spontaneously. Surgery to remove one salivary gland does not cause noticeable dry mouth.
Removal of the cyst with resection of the hyoid bone
A midline neck cyst is a congenital pathology that occurs as a result of a violation of the intrauterine development of the baby. It is formed from the thyroid-lingual duct, which should disappear (overgrow) even before the baby is born, in the second month of the mother’s pregnancy, but in some cases this does not happen, and then the duct forms a closed cavity, which fills with fluid over time. Such a cyst often remains invisible, and can be detected not only in childhood or adolescence, but also in adulthood - either when it begins to grow and cause discomfort, or accidentally, during any medical examination of the neck for another reason. The growth of a cyst in adolescence or adulthood can be triggered by injury, infectious disease, or pathologies of the lymphatic or circulatory systems. Initially, cervical cysts are benign, but over time they can transform into malignant formations. In addition, suppuration can develop inside the cyst, and if the pus breaks out, a fistula is formed, but if the pus breaks inside the neck, then, in addition to the fistula, serious intoxication occurs in the body. If the cyst is not removed, then suppuration can be repeated many times, weakening the human body and increasingly threatening not only his health, but also his life. A cyst without inflammation can also cause discomfort - interfere with swallowing, change your voice, cause a sore throat and other unpleasant phenomena. There is no conservative treatment for cervical cysts, so the only option for eliminating them is surgery. If there is a need to carry out such an operation, it is extremely important to find a competent and experienced professional who will remove the cyst on the neck as carefully and safely as possible and completely, since if any fragments of the cyst remain unremoved, there will be a possibility of relapse.
As a rule, such an operation is planned, and before it, the doctor, as before any other operation, prescribes a detailed examination of the patient. As part of such an examination, a specialist may prescribe an ultrasound or tomography - computer or magnetic resonance imaging (CT or MRI, respectively). Urine and blood tests, puncture of the contents of the cyst, as well as other studies may be prescribed to exclude an oncological process and to obtain the maximum amount of information about both the formation and the general condition of the patient. If the patient comes with a suppurating cyst, before performing the operation, the doctor removes the pus from the cyst using a puncture method, prescribes treatment to eliminate inflammation, and only then proceeds to prepare for removal of the cyst. The operation is performed using general anesthesia in a sterile operating room. After the anesthesia is administered and begins to take effect, the doctor treats the surgical area with an aseptic agent and makes a skin incision in the projection of the cyst and up to the hyoid bone. Next, the specialist removes the tissue covering the cyst and reaches the formation itself. Since the thyroglossal duct passes through the middle part of the hyoid bone and fuses with it, when removing the cyst, it is necessary to remove a fragment of this bone to avoid the development of relapses. The doctor cuts the bone on either side of the cord of cyst formed from the duct, so as to avoid damage to the nerves leading to the tongue and located under the bone. Next, the doctor separates the bone fragment to be removed, as well as the remains of the thyroglossal duct from the remaining tissues, muscles and organs and removes the separated fragments along with the cyst as a single whole. The doctor brings the ends of the remaining fragments of the hyoid bone as close to each other as possible during suturing of the muscles. After this, the doctor stops the bleeding and sutures the wound, layer by layer connecting the tissues that were affected during the operation. A sterile bandage is applied to the wound.
After the operation, the patient remains under the supervision of specialists until his condition stabilizes, after which he can go home and only visit the doctor for observation and removal of stitches. During the rehabilitation period and until full recovery, the patient must carefully follow all medical instructions and restrictions, and then he will not be afraid of complications and will soon forget about the illness and completely return to a full, healthy life.
The multidisciplinary clinic “Medistar” brings together a galaxy of highly qualified specialists, true professionals in their field, conducting both diagnostic and advisory practice, and successfully treating ailments of any complexity. Our own laboratory, modern equipment for diagnostics and therapeutic manipulations allow us to go through all stages of the fight against the disease - from diagnosis to complete recovery, without leaving the medical center in search of the desired method of diagnosis or therapy.
Causes of parotid gland tumor
The causes of tumor growths of the salivary glands are not fully understood; it is believed that they can be caused by:
- past infections (influenza, scarlet fever, measles and others);
- various chronic diseases, especially diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (the salivary glands are part of a single digestive process);
- eating disorders;
- insufficient oral care;
- genetic factors and unfavorable environmental influences.
Removal of cervical lymph nodes (cervical dissection)
When removing a malignant tumor of the salivary gland, the cervical lymph nodes are usually removed, a so-called cervical dissection is performed. The lymph node is usually small, surrounded by a bean-shaped capsule, and lymph fluid flows through it. There are a large number of lymph nodes in the neck.
The first metastases of salivary gland cancer are usually found in the cervical lymph nodes and therefore it is believed that their removal is necessary in the case of cancer. Typically, surgery to remove the salivary gland, which also involves a cervical dissection, takes 1 to 2 hours longer.
Hypertrophy of the masticatory muscles
Along with a tumor of the salivary glands, there is hypertrophy of the masticatory muscles, which also leads to disproportions of facial features, but is sometimes caused by dental and neurological problems. To understand the true causes of the deficiency, it is necessary to conduct a detailed examination and determine whether the glands are directly enlarged or just the muscles.
When it comes to muscle hypertrophy, botulinum toxin injections come to the rescue, blocking excessive muscle activity and over time they decrease in size.