Theory and practical experience in ultrasound diagnosis of salivary gland pathology
Ultrasound scanner HS60
Professional diagnostic tools.
Assessment of tissue elasticity, advanced 3D/4D/5D scanning capabilities, BI-RADS classifier, options for expert cardiological studies.
In domestic and foreign literature there are many works devoted to sialogy (from the Greek Sialon - saliva and logos - study) - the science of diseases and injuries of the salivary glands, methods of their diagnosis and treatment. According to various authors, diseases of the salivary glands account for up to 24% of all dental pathologies. Currently, in clinical practice, the most common are dystrophic, inflammatory diseases of the salivary glands (sialoadenoses, sialadenitis), as well as tumors and congenital malformations of the salivary glands. In addition, pathological changes in the salivary glands often accompany other diseases (diabetes mellitus, bronchiectasis, sarcoidosis, liver cirrhosis, hypertriglyceridemia, lymphogranulomatosis, etc.).
Various instrumental methods are used to diagnose diseases of the salivary glands [1]:
- radiography (if the formation of stones in the ducts of the salivary glands is suspected, but in 20% of the stones of the submandibular salivary glands and 80% of the parotid salivary glands are non-radiographically opaque);
- sialography (examination of the ducts of the salivary glands with a radiopaque substance, is rarely useful in differentiating tumors from inflammatory processes, but it can help differentiate the mass formation of the salivary glands from formations in neighboring tissues. In patients with suspected autoimmune disease of the salivary glands, a characteristic pattern of saccular expansion may be detected ductal system. In case of acute infection of the salivary glands, sialography should not be performed [2]);
- computed tomography together with sialography;
- ultrasound method (is the most accessible, safe and informative in the process of differential diagnosis of the pathological condition of the salivary glands).
Anatomy of the salivary glands [3]
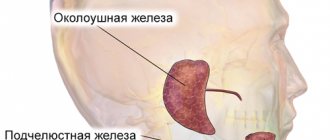
There are three pairs of major salivary glands (SG) and many small ones. The large ones include paired parotid, submandibular and sublingual SGs. The parotid salivary gland (PSG) is located on the outer surface of the branch of the lower jaw at the anterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, as well as in the retromandibular fossa. Dimensions vary widely: length 48-86 mm, width 42-74 mm, thickness 22-45 mm. The OSJ is covered by the parotid fascia, which is its capsule and is tightly fused with it. Sometimes, at the anterior edge of the parotid duct, there is an additional lobule measuring 10-20 mm, which has its own duct flowing into the parotid. The parotid duct emerges from the gland at the border of its upper and middle thirds, then it passes along the outer surface of the masticatory muscle parallel to the zygomatic arch and turns 90° inward, penetrating the fatty tissue and buccal muscle. The projection of the parotid duct onto the skin of the cheek is determined on the line connecting the tragus of the auricle and the corner of the mouth. The parotid duct opens in the vestibule of the oral cavity at the level of 1-2 large molars. The diameter of the duct is on average 1.5-3.0 mm, its length is 15-40 mm. The thickness of the gland contains the branches of the external carotid artery, the facial nerve and its branches, and the auriculotemporal nerve. There are many lymph nodes around the OUSG and in its parenchyma (Fig. 1), which can serve as a primary or secondary collector for draining lymph from teeth and oral tissues.
Rice. 1.
Lymph nodes in the thickness of the parotid salivary gland.
The submandibular salivary gland (MSG) is located in the submandibular triangle between the body of the mandible and the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle. The dimensions of the gland are: anteroposterior 20-40 mm, lateral 8-23 mm, superior-inferior 13-37 mm. Posteriorly, the PNJ is separated from the OSJ by a process of the fascia propria of the neck. The medial surface of the gland in the anterior section lies on the mylohyoid muscle. The submandibular duct, bending over the posterior edge of this muscle, is located on the lateral surface of the hyoglossus muscle. Then it goes between the medial surface of the hyoid gland and the genioglossus muscle to the point of its exit in the area of the hyoid papilla. The facial artery and its branches, the lingual artery and the veins of the same name pass through the gland.
The sublingual salivary gland (SSG) is located on the floor of the mouth in the sublingual region parallel to the body of the lower jaw. The dimensions of the gland are: longitudinal 15-30 mm, transverse 4-10 mm and vertical 8-12 mm. The duct of the parathyroid gland passes along its inner surface and opens in the region of the anterior section of the sublingual ridge independently or together with the submandibular duct. Sometimes the PJS duct flows into the middle section of the PJS duct.
The minor salivary glands - labial, buccal, lingual, palatine, incisive - are located in the corresponding areas of the mucous membrane. They can be a source of development of adenocarcinomas of the oral cavity.
Pathology of the salivary glands
SG malformations are rare. The most common are anomalies in the size of the glands (agenesis and aplasia, congenital hyperplasia (Fig. 2) and hypoplasia), their location (heterotopia, accessory glands), and anomalies of the excretory ducts (atresia, stenosis, ectasia, cystic transformation, ductal dystopia).
Rice. 2.
Hyperplasia of the left sublingual salivary gland.
Sialadenitis is a large group of polyetiological inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (Fig. 3). Primary sialadenitis - sialadenitis considered as an independent disease (for example, mumps). Secondary sialadenitis is sialadenitis that is a complication or manifestation of other diseases (for example, sialadenitis with influenza). The echographic picture for different etiologies is not very specific. Etiology has clinical significance in determining treatment tactics.
Rice. 3.
Sialadenitis of the right submandibular salivary gland.
According to the etiological factor, sialadenitis is classified [4] into:
- sialadenitis developing under the influence of physical factors (traumatic sialadenitis, radiation sialadenitis (Fig. 4) occurs during radiation therapy of malignant tumors of the head and neck);
- sialadenitis developing under the influence of chemical factors (toxic sialadenitis);
- infectious sialadenitis (routes of infection penetration into the fluid: stomatogenic (through ducts), contact, hematogenous and lymphogenous);
- allergic and autoimmune sialadenitis (recurrent allergic, Sjogren's disease and syndrome, etc.);
- myoepithelial sialadenitis caused by a pathological process, previously designated as a benign lymphoepithelial lesion. The term benign lymphoepithelial lesion was first used by JT Godwin in 1952, replacing the concept of Mikulicz disease;
- obstructive sialadenitis, which develops when there is difficulty in the outflow of saliva due to obstruction of the excretory duct with a stone (Fig. 5-7) or thickened secretion, as well as due to cicatricial stenosis of the duct. According to the prevalence of the process, they distinguish between focal, diffuse sialadenitis and sialodochitis - inflammation of the excretory duct. The course of the process can be acute or chronic;
- pneumosialadenitis, which develops when there is air in the gastric tissue in the absence of a bacterial gas-forming infection. Air enters the gland from the oral cavity when the pressure there increases through the duct. Pneumosialadenitis is typical for a number of professions, primarily for glassblowers and musicians playing wind instruments.
Rice. 4.
Post-radiation sialadenitis.
Rice. 5.
Stone of the duct of the submandibular salivary gland.
Rice. 6.
Stone in the parenchyma of the submandibular salivary gland.
Rice. 7.
Stone in the duct of the submandibular salivary gland.
Tumors of the salivary glands
Tumors of the salivary glands are divided into two groups: epithelial and non-epithelial. Epithelial tumors predominate in adults (95%). In children with SG, epithelial and non-epithelial tumors are equally common. In addition to true tumors, processes resembling tumors (tumor-like lesions) develop in the GS.
Among epithelial tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, benign neoplasms are distinguished, as well as malignant ones - carcinomas.
Benign epithelial neoplasms of the stomach include ductal papillomas, adenomas and benign sialoblastoma. SG adenomas are divided into two groups: polymorphic (the most common SG adenoma) and monomorphic (all other) adenomas. Tumors of different structure, origin and prognosis were artificially included in the group of monomorphic adenomas.
Pleomorphic (polymorphic) adenoma (mixed tumor of the gland) is a adenoma of the gland, built from two types of cells: ductal epithelium and myoepithelial cells. Macromorphological picture. The tumor is usually an elastic or firm nodule of lobulated grayish-white tissue, usually partially encapsulated. Typical of a pleomorphic adenoma is the so-called chondroid stroma, resembling hyaline cartilage. Variants of the echographic image of pleomorphic adenomas are presented in Figure 8.
Rice. 8.
Pleomorphic adenoma of the gastrointestinal tract.
Warthin's tumor is an adenolymphoma in which multiple cystic cavities are formed, covered with double-layered epithelium. The papillae protrude into the lumen of the cysts. A pronounced proliferation of lymphoid tissue occurs in the tumor stroma. This tumor almost exclusively develops in the parotid gland.
Other types of benign tumors are less common. These are benign oncocytoma (oxyphilic adenoma), basal cell adenoma, tubular adenoma, benign cystadenoma sialoblastoma.
Among benign primary non-epithelial tumors, the most common are hemangioma, lymphangioma, neurofibroma and lipoma.
Among malignant non-epithelial tumors, malignant lymphomas are more often found (they arise, as a rule, against the background of myoepithelial sialadenitis, Sjögren's disease and syndrome).
Tumor-like lesions of the salivary glands
Rice. 9.
Salivary gland cysts.
- Salivary gland cysts (mucoceles). There are two types of mucocele of the gland: the retention type (retention cyst of the small gland, formed when saliva is retained in the excretory duct) and the type of interstitial secretion, when, when the wall of the duct is injured, saliva enters directly into the fibrous tissue surrounding the gland. Mucoceles in the floor of the mouth are also called ranulae.
- Cysts of the excretory ducts of large SGs are pronounced dilatation of the excretory duct due to retention of secretions in it. Blockage of salivary outflow can be caused by various reasons: tumor, stone, thickened mucus, post-inflammatory stenosis, even cicatricial obliteration of the lumen.
- Sialoadenosis (sialosis) is a non-tumor and non-inflammatory symmetrical increase in SF due to hyperplasia and hypertrophy of secretory cells. The outcome of sialosis is often SG lipomatosis. The process has a chronic relapsing course. Sialosis occurs in a number of diseases and conditions: diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, malnutrition, alcoholism, liver cirrhosis, hormonal disorders (hypoestrogenemia), reactions to medications (most often antihypertensive), neurological disorders.
Adenomatoid hyperplasia of small SGs leads to their increase to 0.5-3.0 cm in diameter. The causes of adenomatoid hyperplasia are trauma and prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation.
Oncocytosis is age-related changes in secretory cells and epithelium of the ducts of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the SF may slightly increase, but usually their value does not change.
To summarize, I would like to note that ultrasound using Doppler sonography in many of our observations helped to accurately determine the nature of the pathological process in the gastrointestinal tract. However, this diagnostic method does not allow one to unambiguously confirm or refute the malignant nature of the formation of the salivary glands.
Literature
- Benign and malignant tumors of soft tissues and bones of the face. A.G. Shargorodsky, N.F. Rutsky. M.: GOU VUNMTs, 1999.
- Topographic anatomy and operative surgery. I.I. Kagan, S.V. Chemezov. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2011.
- Salivary glands. Diseases and injuries. V.V. Afanasiev. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2012.
- Inflammatory diseases of the tissues of the maxillofacial area and neck. A.G. Shargorodsky. M.: GOU VUNMTs, 2001.
Ultrasound scanner HS60
Professional diagnostic tools.
Assessment of tissue elasticity, advanced 3D/4D/5D scanning capabilities, BI-RADS classifier, options for expert cardiological studies.
Preparation
Typically, an ultrasound of the salivary glands is preceded by a consultation with a general practitioner. At the initial appointment of a patient with pain symptoms in the glandular area, the doctor examines visually, collects a detailed history and diagnoses using palpation. Next, the patient will be asked to undergo laboratory tests or undergo an ultrasound scan. There is no need to specially prepare for an ultrasound of the salivary glands. It is completely painless and does not cause radiation exposure to the patient’s body. Ultrasound diagnostics are easily tolerated by people of any age. There are only a few recommendations for obtaining a more informative ultrasound examination. Before going to see a specialist, it is recommended to stop eating food 3-4 hours in advance, and to thoroughly clean the oral cavity before performing the diagnosis.
Previous NextPhysical properties and composition of saliva
Biological fluid in a healthy person has a number of physical and chemical properties. They are presented in the table.
Table 1. Normal characteristics of saliva.
| Index | Characteristic |
| Transparency | Transparent, minor inclusions of air, pieces of food. |
| Density | Slightly higher than the density of water, depending on the composition - from 1 to 1.12 g/ml. |
| Color | Normally – absent. |
| Viscosity | Insignificant and unstable, depends on the current state of the body. |
| Taste | Absent. |
| pH | Alkaline – 7.4–8.0. |
The main component of oral fluid is water – up to 98%. The remaining components can be roughly divided into acids, minerals, trace elements, enzymes, metal compounds, and organics.