Diode laser
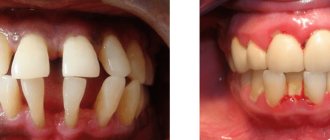
Modern technologies are increasingly used in medicine. Today, laser treatment of periodontitis is commonplace. The healing properties of a narrowly targeted flow of energy are manifested in dentistry, creating the possibility of quick and painless dental treatment. The wide range of services provided with its help, coupled with relative affordability, contributes to the growing popularity of this method.
Laser in dentistry
There are several types of dental laser: diode, argon, neodymium, erbium, carbon dioxide. The difference between the devices is in power, wavelength, point or constant flow of pulses. Each type of laser beam is used for specific procedures. It is used with equal success for therapeutic treatment and surgical intervention.
PROTECTION OF PERSONAL INFORMATION
5.1. In accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents, the Organization has created a personal data protection system (PDS), consisting of subsystems of legal, organizational and technical protection.
5.2. The legal protection subsystem is a complex of legal, organizational, administrative and regulatory documents that ensure the creation, operation and improvement of the legal protection system.
5.3. The organizational protection subsystem includes the organization of the management structure of the CPPD, the permitting system, the protection of information when working with
employees, partners and third parties, protection of information in the open press, publishing and advertising activities, analytical work.
5.4. The technical protection subsystem includes a set of technical, software, software and hardware tools that ensure personal data protection.
5.5. The main PD protection measures used by the Organization are:
5.5.1. Appointment of a person responsible for the processing of personal data, who organizes the processing of personal data, training and instruction, internal control over compliance by the institution and its employees with the requirements for the protection of personal data;
5.5.2. Identification of current threats to the security of personal data when processing them in ISPD, and development of measures and measures to protect personal data;
5.5.3. Development of a policy regarding the processing of personal data;
5.5.4. Establishing rules for access to personal data processed in the ISPD, as well as ensuring registration and accounting of all actions performed with personal data in the ISPD;
5.5.5. Establishing individual passwords for employees to access the information system in accordance with their production responsibilities;
5.5.6. Application of information security means that have passed the compliance assessment procedure in accordance with the established procedure, accounting for computer storage media of personal data, ensuring their safety;
5.5.7. Certified anti-virus software with regularly updated databases;
5.5.8. Certified software for protecting information from unauthorized access;
5.5.9. Certified firewall and intrusion detection tool;
5.5.10. Compliance with conditions ensuring the safety of personal data and excluding unauthorized access to them, assessment of the effectiveness of measures taken and implemented to ensure the security of personal data
5.5.11. Establishing rules for access to processed personal data, ensuring registration and accounting of actions performed with personal data, as well as detecting facts of unauthorized access to personal data and taking measures;
5.5.12. Restoration of personal data modified or destroyed due to unauthorized access to them;
5.5.13. Training of the Organization's employees directly involved in the processing of personal data, the provisions of the legislation of the Russian Federation on personal data, including requirements for the protection of personal data, documents defining the Organization's policy regarding the processing of personal data, local acts on the processing of personal data;
5.5.14. Implementation of internal control and audit.
Therapeutic laser dental treatment
In therapeutic dentistry, laser therapy is used in the following cases:
- Relieving inflammation.
When treating gingivitis, stomatitis or herpes, electromagnetic waves are directed to the source of infection and destroy pathogenic bacteria. - Sterilization.
Periodontal pockets and tooth canals are treated with a diode laser before installing a filling. - Treatment of caries.
Affected tissues are effectively removed using an erbium apparatus. - Filling.
Curing of light polymer fillings occurs under the influence of an argon laser. - Teeth whitening.
The laser beam activates the hydrogen peroxide-based whitening gel without heating the tooth tissue, that is, without the risk of overheating or burning the pulp. Thanks to the local pulse effect, the patient does not experience discomfort during the procedure.
All the best for children
Laser therapy is successfully used in the fight against caries even in baby teeth, although only at the initial stage of the lesion. It is advisable for the child to be at least seven years old, but diligent and calm children can take advantage of the latest technology at a younger age.
For the treatment of small patients, the following rules apply:
- it is necessary to use only equipment with the ability to adjust the radiation power;
- During the procedures, a slight tingling sensation may occur, which the child should be warned about.
All other advantages of laser dentistry are common to children and adult patients.
Application of laser in dental surgery
During surgery, a laser device is used for painless and bloodless tissue dissection—during the procedure, the beam instantly seals the vessels. The incision is smaller and thinner than with a scalpel, so no stitches are required during the operation, and after the wounds heal there are no scars or scars. In dental surgery, laser is used to solve the following problems:
- Removal of tumors.
The liquid inside the papilloma, cyst or fibroma is evaporated under the influence of electromagnetic waves. - Carrying out dental implantation.
Thanks to the laser, implant installation is delicate. Thanks to laser implantation, the soft tissue contour is better preserved. - Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the lips and tongue.
The fold is excised lengthwise or crosswise depending on the clinical case. - Gum correction.
Excess tissue is trimmed before prosthetics, filling or orthopedic treatment. The laser is also used for gum surgery after implantation or if there are other indications.
Indications and contraindications
With the help of electromagnetic waves, it is possible to achieve positive therapeutic results even in the most difficult situations, and the absence of the need for anesthesia allows the device to be used for people with allergies to painkillers. The use of laser in dentistry is one of the safest and most effective methods of treatment, which is indicated for almost everyone. However, there is still a small list of contraindications.
- Nervous system disorders
- Late stage diabetes mellitus
- Kidney failure
- Oncological diseases
- Pregnancy (1 - 6 months)
- Open tuberculosis
- Elevated thyroid hormone levels
- Allergy to sun rays
Attention!
Insufficient qualifications of a specialist and failure to comply with safety rules significantly increase the risk to the patient’s health during laser treatment. Contact only trusted clinics, where your eyes are protected from radiation with special glasses, and the room is brightly lit during the procedure.
PROCESSING OF PERSONAL DATA
4.1. Receiving PD
4.1.1. All PD should be obtained from the subject himself. If the subject's personal data can only be obtained from a third party, then the subject must be notified about this or consent must be obtained from him.
4.1.2. The operator must inform the subject about the purposes, intended sources and methods of obtaining PD, the nature of the PD to be received, the list of actions with PD, the period during which the consent is valid and the procedure for its revocation, as well as the consequences of the subject’s refusal to give written consent to receive them.
4.1.3. Documents containing personal data are created by:
a) copying original documents (passport, education document, TIN certificate, pension certificate, etc.);
b) entering information into accounting forms;
c) obtaining originals of the necessary documents (work book, medical report, characteristics, etc.).
The procedure for access of a PD subject to his PD processed by the Organization is determined in accordance with the law and is determined by the internal regulatory documents of the Organization.
4.2. PD processing
4.2.1. Processing of personal data is carried out:
- with the consent of the subject of personal data to the processing of his personal data;
- in cases where the processing of personal data is necessary for the implementation and fulfillment of the functions, powers and responsibilities assigned by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- in cases where the processing of personal data is carried out, access to an unlimited number of persons is provided by the subject of personal data or at his request (hereinafter referred to as personal data made publicly available by the subject of personal data).
Employees' access to processed PD is carried out in accordance with their job responsibilities and the requirements of the Organization's internal regulatory documents.
Employees admitted to PD processing, upon signature, familiarize themselves with the organization’s documents establishing the procedure for PD processing, including documents establishing the rights and obligations of specific Employees.
The organization eliminates identified violations of the legislation on the processing and protection of personal data.
4.2.2 Purposes of PD processing:
- ensuring the Organization of providing medical care to the population, as well as the most complete fulfillment of obligations and competencies in accordance with Federal Laws of November 21, 2011 No. 323-FZ “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens of the Russian Federation”, dated April 12, 2010 No. 61-FZ “On circulation of medicines" and dated November 29, 2010 No. 326-FZ "On compulsory medical insurance of citizens in the Russian Federation", Rules for the provision of paid medical services by the Limited Liability Company "Celladent" (LLC "Celladent"), approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 4, 2012 No. 1006;
- implementation of labor relations;
- implementation of civil law relations.
4.2.3. Categories of personal data subjects
The Organization processes personal data of the following subjects:
- individuals who are in labor relations with the institution;
- individuals who are close relatives of employees of the institution;
- individuals who have left the institution;
- individuals who are job candidates;
- individuals who are in civil legal relations with the institution;
- individuals who applied to the establishment of Selladent LLC for medical assistance.
4.2.4. PD processed by the Organization:
- data obtained during the implementation of labor relations;
- data obtained for the selection of candidates for work in the organization;
- data obtained during the implementation of civil law relations;
- data obtained during the provision of medical care to Celladent LLC.
The full list of personal data is presented in the List of personal data approved by the General Director of the Organization.
4.2.5. Personal data is processed:
- using automation tools.
- without the use of automation tools.
4.3. PD storage
4.3.1. Subjects' personal data can be received, undergo further processing and transferred for storage both on paper and in electronic form.
4.3.2. PD recorded on paper is stored in locked cabinets or in locked rooms with limited access rights (registry).
4.3.3. Personal data of subjects processed using automation tools for different purposes are stored in different folders (tabs).
4.3.4. It is not allowed to store and place documents containing personal data in open electronic catalogs (file sharing services) in ISPD.
4.3.5. PD is stored in a form that makes it possible to identify the PD subject for no longer than required by the purposes of their processing, and they are subject to destruction upon achievement of the purposes of processing or in the event of the loss of the need to achieve them.
4.4. Destruction of PD
4.4.1. The destruction of documents (media) containing personal data is carried out by burning, crushing (grinding), chemical decomposition, transformation into a shapeless mass or powder. A shredder can be used to destroy paper documents.
4.4.2. PD on electronic media is destroyed by erasing or formatting the media.
4.4.3. Destruction is carried out by a commission. The fact of destruction of personal data is documented by an act of destruction of media, signed by members of the commission.
4.5. Transfer of personal data
4.5.1. The organization transfers PD to third parties in the following cases:
- the subject has expressed his consent to such actions;
- the transfer is provided for by Russian or other applicable legislation within the framework of the procedure established by law.
4.5.2. List of persons to whom PD is transferred
Third parties to whom PD is transferred:
- Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for accounting (legally);
- Tax authorities of the Russian Federation (legally);
- Social Insurance Fund (legally);
- Territorial Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (legally);
- medical insurance organizations for compulsory and voluntary medical insurance (legally);
- banks for payroll (based on agreement);
- judicial and law enforcement agencies in cases established by law;
- credit history bureau (with the consent of the subject);
- law firms operating within the framework of the legislation of the Russian Federation, in case of failure to fulfill obligations under a loan agreement (with the consent of the subject).
Advantages of the method
Today, laser dental treatment in Moscow is widespread in dentistry. Despite the high cost, it is deservedly popular among patients who appreciate the advantages of laser treatment.
- Delicacy.
The absence of unpleasant noise and vibrations makes the operation easier. - Short duration of procedures.
Depending on the nature of the manipulations, the process takes from two to twenty minutes. - No need for anesthesia.
The device does not touch the tissues of the teeth and gums, but acts at a distance, so there is no pain from mechanical action. - Accuracy.
The rays are directed only at the affected tissues, healthy areas are not damaged. - Reduced injury rates.
The laser seals the vessels and edges of the wound, so even complex operations do not require stitches and bandages to stop bleeding. - Fast rehabilitation.
After treatment, the incision heals in a matter of hours and is not accompanied by swelling or pain.
How laser therapy affects tissue: biopsy results
Research on the effectiveness of laser therapy is carried out not only by measuring the effectiveness in patients, but also in laboratories, at the cellular level. One of these experiments made it possible to track changes in the cellular structure of the periodontium over 5 sessions of laser exposure and, based on its results, determine the effectiveness of therapy.
Histological and cytological studies of tissues before the start of treatment showed that the mucous membrane was affected by the inflammatory process, wound healing was sluggish, and there were practically no full-fledged cells.
After two laser sessions, the healing process intensified. After 4 sessions, the studied samples already showed signs of bright coagulations, a gradual restoration of erythrocytes and leukocyte cells.
After the 5th session of laser therapy, a biopsy showed the presence of full-fledged cells - red blood cells, leukocytes, and fibroblasts. The results indicate the patient's complete recovery.
Treatment of cysts and granulomas with laser
Granuloma usually occurs as a result of poor treatment of caries and pulpitis. The disease is asymptomatic at the first stage, and is later accompanied by swelling of the gums, pain and darkening of the enamel. When treating dental granuloma with a laser, the affected area is drilled and an electromagnetic beam is sent into the hole, destroying the contents of the cyst and sealing the vessels. The doctor then installs a filling.
Without timely treatment, the granuloma develops into a cyst, which can provoke even more serious complications. Gentle treatment of dental cysts with a laser is considered a good method, as it allows you to save the tooth. The procedure takes place without pain, stress and stitches. In addition, treatment of a dental cyst with a laser without removal eliminates the risk of re-development of inflammation. The patient’s comfort and the absence of complications justify the additional costs, because the price when treating a dental cyst with a laser is higher than when using other methods.
How much does laser dental treatment cost?
As a rule, prices for laser dental treatment in Moscow depend on the type of dental disease and the severity of the pathology. You must be prepared for the fact that in any case it will be significantly higher than when using classical methods. Treatment of caries at the initial stage of the disease will cost from 800 rubles. The price for treating a dental cyst with a laser without removal will be approximately 1,500 to 2,000 rubles. For laser whitening you will have to pay from 8,000 to 11,000 rubles.
Obviously, the high cost of therapy is the only drawback of this technology. However, numerous rave reviews about laser dental treatment confirm the fact that patients are willing to pay for comfort, efficiency and peace of mind, the absence of irritating drill sounds and the frightening prospect of using anesthetics.
Flaws
- The inability of the operator to qualitatively consider all the small details in the area of manipulation. This is due to the need to wear special safety glasses;
- There is a high probability of gum damage during laser operation. A dentist working with laser equipment must be very careful and careful;
- The need to combine a drill with a laser when filling a tooth. The laser is not able to adjust the installed filling to the bite and perform its final polishing;
- High cost of the procedure compared to traditional treatment methods.