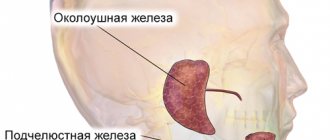
Salivary gland cancer is a very dangerous cancer. According to statistics, this type of malignant tumors is very rare. The salivary glands are capable of secreting a special secretion - saliva, which plays a huge role in the human digestive system. The oral cavity contains a large number of salivary glands. Cancer usually affects the large parotid glands. Today, medicine has made enormous progress in the treatment of this type of malignant tumor. Treatment of salivary gland cancer in Israel is considered very successful.
If you need highly professional medical care, our company, the medical service “Tlv.Hospital,” is ready to help you organize treatment for salivary gland cancer in Israel, having experience in the field of medical tourism for more than 10 years.
If you are interested in the information, you can learn more about the features of medicine in Israel and the possibilities of clinics for foreign tourists.
Causes of salivary gland cancer
The causes of cancer in the salivary glands are not yet known to science. But it was possible to establish a number of factors that increase the likelihood of a dangerous disease:
- Smoking (it increases salivation, the gland becomes overloaded);
- Radioactive exposure;
- Hereditary factor.
Symptoms of salivary gland cancer
There are certain symptoms that may indicate the development of cancer in the salivary glands:
- Swelling in various areas of the face: near the ears, on the cheeks, in the jaw area;
- Numbness of part of the face;
- Possible facial paralysis.
The presence of alarming symptoms is a good reason to undergo an examination. Since early diagnosis significantly increases the likelihood of a full recovery.
Causes of the disease
A number of factors can provoke the manifestation of the disease, which include various influences from the outside world. Any patient can encounter this, even with good oral hygiene.
Main causes of the disease:
- pathogenic microorganisms that have entered the patient’s oral cavity;
- some viral diseases;
- toxic substances contained in food.
Another reason for the formation of salivary gland adenoma is considered to be an addiction to smoking tobacco. Smoke that enters the body contains many carcinogens that damage the glandular epithelium of the salivary glands. As a result, protective mechanisms are activated, which provokes increased cell division, resulting in the formation of an adenoma.
Types of salivary gland adenoma
Adenoma is characterized by slow growth, so the patient may not even be aware of the existence of this disease in his body for decades. Many people discover the presence of the disease only when undergoing examinations for other problems, or during a routine examination. Rapid tumor growth indicates its malignant degeneration.
Classification:
- Polymorphic or pleomorphic . It is a dense encapsulated node containing light fluid, lymphoid cells and fibroblasts.
- Basal cell . It is a small, clearly demarcated node, the structure is dense, uniform, grayish-whitish or brownish in color. May be multiple.
- Canalicular . It is distinguished by the content of prismatic epithelial cells, which are collected in thin bundles.
- Greasy. This is a clearly demarcated tumor formed from different shapes and sizes of sebaceous cells, with cystic changes. The surface has a grayish-whitish or yellow color. There is no danger of relapse.
- Adenolymphoma . The tumor is mobile, contains lymph, is benign, and consists of glandular epithelial structures.
- Monoform. It consists of large cells with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and a small dark nucleus, and is light in color.
- Adenocarcinoma . A malignant epithelial tumor develops in the large and small salivary glands, has proliferation of the epithelium in ductal formations in the form of papillary, cribriform, tubular structures. The prognosis is unfavorable.
The most common type of salivary gland adenoma by location is the parotid. Adenomas of the submandibular glands, small glands and sublingual glands are also isolated. Regardless of the location of the tumor, the only way to treat the disease is to remove the adenoma.
Treatment of salivary gland cancer in Israel
Israeli medical institutions use advanced treatment methods and modern ultra-precise equipment. An integrated approach to the treatment of salivary gland cancer is very effective. Therefore, treatment in Israel in most cases gives a positive result, returning thousands of people to normal life every year.
Treatment of this type of cancer depends on many factors - the size of the tumor, the location of the cancer, the patient's health status, etc. Particular importance is attached to the stage of the disease. It is customary to distinguish four stages of salivary gland cancer:
Stage 1 – the tumor reaches a maximum size of 2 cm and does not extend beyond the boundaries of the gland;
Stage 2 – the size of the neoplasm is from 2 to 4 cm, does not extend beyond the organ;
Stage 3 – tumor dimensions are about 4 cm, begins to grow into adjacent tissues and lymph nodes;
Stage 4 – the tumor grows into the skin, nerves, bones, and metastases begin.
In practice, the following treatment methods for salivary gland cancer are used in Israel.
Surgical treatment of salivary gland cancer
Surgery is the main treatment method for salivary gland cancer in Israel. The choice of surgery is determined by the location of the tumor and the stage (how far the disease has spread in the body).
Surgery for salivary gland cancer is carried out by a team of specialized doctors with experience in performing this type of surgical intervention:
- Maxillofacial surgeon.
- ENT surgeon.
- Consultant in restorative dentistry.
- Plastic surgeon.
- Anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
- Nurse.
In Israeli clinics, specialized surgical interventions are performed: on the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands.
Israeli clinics use the latest technologies in treatment, including intensity-modulated radiation therapy or stereotactic radiosurgery, which provide a powerful flow of radiation to malignant cells, limiting the negative impact on surrounding healthy tissue - the eyes, optic nerves, brain and spinal cord.
Surgery on the parotid glands
The parotid glands are divided into two lobes - superficial and deep. Between them passes the facial nerve, which is important for actions such as closing the eyes, wrinkling the nose and moving the lips.
If the tumor is located only in the superficial lobe, the neoplasm has a low degree of malignancy, it is possible to remove only it. This operation for salivary gland cancer is called superficial parotidectomy. If the tumor involves the deep lobe or both, complete resection of the parotid gland will be necessary. A total parotidectomy is performed.
The surgeon makes an incision from the front of the ear, down a line to the cheek, and along the jaw line. A scar will remain, shaped like the English letter S.
This is a complex operation because the facial nerve passes through the middle of the gland. Wherever possible, the surgeon will try to remove only the gland and preserve the facial nerve. Most people experience good recovery and full range of facial movement after surgery for salivary gland cancer. If the doctor is forced to remove part or all of the facial nerve, he transplants a nearby nerve or a nerve from the calf muscle.
Along with the parotid gland, the surgeon removes some of the surrounding tissue. This is necessary to resect all cancer cells and reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Rarely is it necessary to remove part of the jaw. Resection of nearby lymph nodes may also be necessary.
Surgery on the submandibular glands
If the tumor occurs in one of the submandibular glands, the surgeon will remove the entire organ, as well as some surrounding tissue, to reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
If the presence of malignant cells in the lymph nodes is suspected, they will also be resected. Rarely does it become necessary to remove some jaw bones.
There are 3 nerves near the submandibular gland that control the lips and part of the tongue. The surgeon will try to remove the gland without damaging these nerves. Sometimes this happens, in most cases the problems are temporary, as a rule, mobility is completely restored within a few weeks. Sometimes it takes several months.
Before surgery for salivary gland cancer, the surgeon will explain what exactly will be removed and also give information about possible side effects. After surgery, the scar will be located below the jaw line.
Surgery of the sublingual salivary glands
Under the tongue there are two sublingual glands. The surgeon makes an incision inside the mouth, removes the gland and some surrounding tissue, and sometimes part of the jaw bone. This reduces the risk of the disease returning.
A nerve runs along the sublingual gland that controls sensation and taste on the sides of the tongue. In some cases, its removal is required. Or it may be damaged during the operation. After this, insemination may be observed on that side of the tongue. This is usually a temporary phenomenon that lasts from a few weeks to a couple of months.
There is a risk of cancer cells in nearby lymph nodes, which will require resection. This may mean an additional incision on the side of the neck.
Removal of lymph nodes in the treatment of salivary gland cancer in Israel
Lymph nodes in the neck are resected in the following situations:
- If the tumor has a high degree of malignancy.
- The lymph nodes are swollen and there is edema.
- Diagnostic tests show the presence of cancer cells in them.
Selective neck dissection involves removing some lymph nodes. When cancer has affected more than one node, all lymph nodes on the affected side of the neck are resected. This operation is called modified radical cervical dissection. If the tumor process affects other nearby structures, the surgeon removes these structures as well - performs a complete cervical dissection. It includes the sternocleidomastoid muscle, accessory nerve, and internal jugular vein. This surgery helps stop the cancer from spreading or returning.
Israeli doctors prefer minimally invasive methods. The operation to remove the salivary gland is quite complex, since several important nerves are located nearby. Israeli surgeons have extensive experience in performing minimally invasive operations that provide better cosmetic results and fewer unwanted consequences.
Reconstructive surgery in the treatment of salivary gland cancer
Basically, in most people with this disease, only the salivary glands are removed. In rare cases, the pathological process affects the bones or deeper surrounding tissues. If this occurs, surgery is required to remove the tumor and reconstruct the mouth and jaw. The purpose of surgery is to restore appearance, as well as function - food intake, fluid intake, speech.
The choice of type of operation is determined by the position of the tumor and its spread. It may only be necessary to take skin or tissue from other parts of the body for reconstruction. Some people need dental implants to replace part of their jaw and teeth.
If reconstructive surgery is truly required, the doctor will fully brief the patient and talk about the possible side effects of the operation. It is important to ask a specialist all your questions.
A number of tests will be required before surgery, which may include:
- Blood tests.
- Chest X-ray or CT scan.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG), stress ECG.
- Breathing tests.
Radiation therapy for salivary gland cancer in Israel
In the fight against malignant tumors, radiotherapy uses ionizing radiation. It can be prescribed as the main method, as well as in combination with surgery.
After surgery, radiation is recommended if the tumor is highly malignant or has spread to the lymph nodes. Radiotherapy reduces the risk of the disease returning.
As the main treatment method for salivary gland cancer, radiation therapy is used in the following cases:
- If the tumor is in a place where it is difficult to remove.
- When the tumor is too large to be resected.
- There are other health problems.
- To manage symptoms of metastatic cancer.
When treating salivary gland cancer in Israel, external radiation is used, directed using a linear accelerator to the affected area. If radiation therapy is prescribed after surgery, the procedures are carried out daily, on weekdays, for 1-1.5 months.
When radiotherapy is recommended as the primary method, the number of treatments depends on the individual characteristics of the disease. For metastatic tumors, therapy generally lasts four weeks.
Before treatment for salivary gland cancer begins, the radiotherapy team carefully plans the radiation treatment, calculating the total radiation dose and the area to be treated. A CT, MRI or PET scan is performed.
A custom mask is made to keep the head still, ensuring that the radiation reaches the affected area accurately.
When choosing a treatment program for salivary gland cancer in Israel, a personalized approach has been used. The treatment plan is determined based on highly accurate genetic tests that detect certain types of tumor mutations.
Possible side effects
Side effects usually develop gradually. Most people experience some undesirable effects, which mostly get worse towards the end of the course. 2-3 weeks after the end of therapy, the condition gradually normalizes. This may take up to 6 weeks.
Typically, radiation therapy causes fatigue, redness, and inflammation in the treatment area. It is important to know that you should not use any lotions, powders or creams in the treatment area without the advice of doctors.
Dry mouth
The salivary glands produce saliva, which moistens the mouth and throat; helps maintain dental health; helps swallowing, digesting food, improving taste. Radiation therapy stops saliva production. The doctor communicates with the patient before the start of irradiation.
Usually only the glands that are exposed to radiation are affected. On the other side, they continue to function normally. It is extremely rare for people to experience persistent dry mouth after treatment for salivary gland cancer.
For problems with dryness, special medications are prescribed that help maintain moisture and reduce the risk of infections and caries. Regular dental check-ups will be necessary.
Most people resume salivary production within 4 to 8 weeks after completing radiotherapy.
Inflammation of the throat and mouth
Painful sores may develop in the mouth and throat area. If they cause severe pain, painkillers, such as morphine, are prescribed. Your doctor may recommend Gelclair, which forms a protective barrier in the mouth to reduce soreness. This will make it easier to take food and liquids.
Changes in taste sensations
Radiation therapy to the head and neck often affects taste. Taste may be lost and strange taste sensations may arise. People often notice a metallic taste after radiation therapy and some types of chemotherapy. Loss of taste reduces appetite.
Hearing loss
Radiation therapy to the parotid gland can cause damage to the inner ear and hearing loss.
Dental problems
Irradiation of the oral cavity can cause tooth decay. There will be a need for more frequent visits to the dentist. Fluoridation helps protect teeth by rinsing with a special liquid twice a day. Any dental work can only be carried out after interaction with a restorative dentistry consultant. If it becomes necessary to remove some teeth after radiation, this should be done under the guidance of an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Chemotherapy in the treatment of salivary gland cancer in Israel
The basic treatment for this disease is surgery. In the initial stages, chemotherapy is not used. There is currently insufficient evidence that treatment with cytotoxic drugs reduces the risk of cancer. However, chemotherapy is used for metastatic processes, as well as for contraindications to surgery or radiation therapy.
The following drugs are used in the treatment of salivary gland cancer:
- Cisplatin
- Carboplatin
- cyclophosphamide
- Doxorubicin
- Methotrexate
- Paclitaxel
Most cytostatic drugs cause certain side effects, most often noted:
- nausea;
- decrease in the number of blood cells;
- fatigue;
- changes in kidney function;
- impaired lung function.
When prescribing chemotherapy, it is important to inform your doctor about the dietary supplements you are taking. There is not enough information about their interaction with cytostatic agents. Some of them may reduce the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Treatment
Removal of a salivary gland adenoma is a simple surgical operation; the prognosis for treatment in most cases is favorable. The only difficulty that can be encountered during treatment is damage to the facial nerve. However, a solution has been found for this problem.
To gain access to the tumor, the surgeon dissects the facial nerve by carefully lifting it upward. Only after this the tumor is removed. Removal of the node is carried out within a few minutes in the maxillofacial departments of dental clinics. If the results of histological analysis of the tissues of the removed tumor confirm its benign nature, no additional treatment will be required.
Publications in the media
BENIGN TUMORS . Approximately 80% of parotid tumors are benign. More often they are painless. Many of them are multicentric and often cause local relapses. Very careful identification and surgical treatment are required, consisting of removal of the tumor along with healthy adjacent gland tissue. If it spreads to the deep lobe, a total parotidectomy is performed. During surgery for a benign tumor of the parotid gland, the facial nerve should be preserved.
Mixed tumors consist of both stromal and epithelial cells • Of all neoplasms of the parotid gland they make up 60% • Although they grow slowly, at the time of the initial visit to the doctor they reach a significant size • With enucleation, which during surgery seems easy and radical, leaving is inevitable tumor nests, leading to relapse and the need for repeated intervention • Mixed lesions such as hemangiomas and lymphangiomas are detected in the parotid gland.
Papillary lymphomatous adenocystoma (Warthin's tumor) is found 6 times more often in men aged 40–60 years • Consists of epithelial and lymphoid elements • Tumors (cysts) are soft on palpation • When dissected, a mucus-like substance resembling pus is found inside the tumor. However, despite this appearance, tumors are not inflammatory in origin, but typically neoplastic • Malignant degeneration occurs rarely, mainly in patients who have undergone radiation.
Benign lymphoepithelial tumor (Godwin's tumor) • More often occurs in women of middle age and older • Characterized by slowly progressive lymphoid infiltration of the gland • Malignant lymphoma must be excluded • Rarely, Godwin's tumor does not have a capsule. In such cases, it imitates the inflammatory process • In case of relapses, a good effect can be obtained by irradiation with small doses.
Oxyphilic adenomas consist of acidophilic cells (oncocytes) • They are more often detected in elderly patients • Characterized by slow growth, so the size usually does not exceed 5 cm.
MALIGNANT TUMORS account for 20% of all tumors of the parotid salivary gland. Histological classification: mucoepidermal, mixed tumors, rarely - squamous cell carcinoma, cylindroma, adenocarcinoma.
• Clinic: characteristic symptoms - growth of a tumor-like formation. Characterized by pain and paralysis of the facial nerve, which extremely rarely occurs with benign tumors. The primary diagnosis is established on the basis of clinical examination, palpation, and neurological examination of the cranial nerves. MRI is the method of choice due to the high contrast of soft tissue examination, the ability to determine the growth of the base of the skull, deep tissues of the neck, and base of the tongue. • TNM classification •• T1 - tumor up to 2 cm in greatest dimension without extraparenchymal spread •• T2 - tumor more than 2, but less than 4 cm in greatest dimension without extraparenchymal spread •• T3 - tumor with the following signs: tumor more than 4 , but less than 6 cm in greatest dimension, extraparenchymal spread, but without involvement of the facial nerve •• T4 - tumor more than 6 cm in greatest dimension or extends to the base of the skull, facial nerve • N1 - metastases in one lymph node no more than 3 cm in greatest dimension measurement on the affected side • N2 - metastases in one lymph node on the affected side more than 3 and less than 6 cm in the greatest dimension, or metastases in several lymph nodes on the affected side less than 6 cm in the greatest dimension, or metastases in the lymph nodes of the neck on both sides , or on the opposite side up to 6 cm in greatest dimension.
• Grouping by stage • Stage I: T1–2N0M0 • Stage II: T3N0M0 • Stage III: T1–2N1M0 • Stage IV •• T3N1M0 •• T4N0–1M0 •• T1–4N2–3M0 •• T1–4N0–3M1. • Treatment. The standard of treatment in most institutions is a combination of radiation therapy and surgery.
Low-grade mucoepidermal tumors are usually found in children. In most cases, they are encapsulated and soft on palpation. Treatment is removal of the tumor while preserving the branches of the facial nerve that are not involved in the process. With adequate treatment of low-grade tumors, the 5-year survival rate is 95%.
ICD-10 • C07 Malignant neoplasm of the parotid salivary gland • D11.0 Benign neoplasm of the parotid salivary gland
Complications
Despite the fact that treatment of salivary gland adenoma does not pose a serious problem, it is important to remember that untimely removal of the tumor can lead to a number of complications. The most serious of them is the transformation of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one. Unlike malignant tumors, salivary gland adenoma can exist asymptomatically, only in some cases causing facial asymmetry. Therefore, if you detect the slightest swelling, you must immediately consult a doctor. Timely removal of the tumor will prevent many very unpleasant problems.
The most common postoperative complications:
- the risk of developing Frey's syndrome (occurs when autonomic nerve fibers are damaged, accompanied by redness and sweating of the operated area of the face);
- a feeling of dry mouth when the gland is completely removed.
Observation and regular consultations with a doctor can reduce all postoperative complications to a minimum.