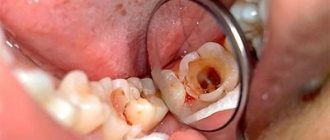
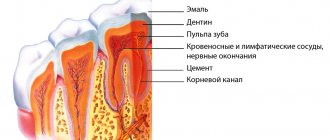
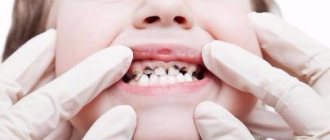
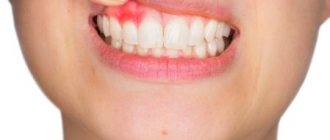
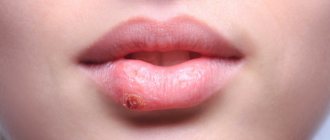
Pulpitis is the inflammation of the pulp, the tissue located inside the tooth. This disease poses a fairly serious threat to the child’s body as a whole. Therefore, it should be taken as seriously as possible.
For those who doubt whether pulpitis of baby teeth occurs in general, we will answer unequivocally: it happens. And besides, it usually progresses much faster than in adults. In children, the hard dental tissues are thinner, and the dentinal tubules, on the contrary, are wider, which leads to the rapid development of infection inside the teeth. Therefore, in childhood, this disease much more often acquires a chronic form with all the ensuing consequences.
Why does pulpitis of a baby tooth occur? How to detect it? And what should parents do if this misfortune befalls their dear child?
Causes of pulpitis of primary teeth in children
Most often, according to dentists, this very unpleasant disease in childhood is caused by:
- If caries treatment is not carried out on time - in this case, microbes developing in the carious cavity and tooth tissue disintegrating under their influence provoke the active release of toxins. Under their influence, the inflammatory process of the pulp most often begins, which, if left untreated, can lead to very serious consequences.
- An acute infectious disease suffered by a child - during the course of an infection, tooth pulpitis in a child, as a rule, occurs against the background of decreased immunity and the appearance of a large number of bacteria.
- Injury to a baby tooth - this can be either an accidental damage to the tooth during play or rest, or too rough treatment of the oral cavity in the presence of caries, or even a careless action of the dentist;
- Medical errors in the treatment of caries - inflammation of the pulp can develop under the influence of incorrectly selected filling material or as a result of treating the oral cavity with too strong antiseptics, for example, alcohol, as well as due to overheating of dental tissues during the preparation of a carious cavity.
Incidence of pulpitis
Many parents do not take their children to the dentist, believing that pulpitis cannot develop in a child at 2 years old. Mothers think that if they don’t give their baby sweets, then caries won’t affect the enamel. Unfortunately, they are wrong. Tooth pulpitis can strike a child at 2, 3, or 5 years of age.
- At 2 years of age, pulpitis affects the baby's front teeth;
- From 3-4 years of age, children more often suffer from pulpitis in the back teeth. Often a 4-5 year old child comes to the dentist crying from pain in his molars. Surprisingly, such inflammations occur several times more often than pulpitis in the front teeth of children.
Possible consequences
If pulpitis is advanced and nerve removal is already required, then after 3-4 months the pathological process will make itself felt by darkening of the teeth. In addition, they will become brittle and dull. If the enamel has acquired a bluish tint, the dentist may have made a mistake when filling. This happens if there were traces of blood in the canal at that moment.
It is worth remembering that it is impossible in principle to cure pulpitis using traditional methods. Moreover, there is no single medicine that a doctor can prescribe to a patient for this diagnosis. Each case is individual, so treatment methods are selected taking into account the characteristics of the clinical picture: the degree of tooth damage, the presence of caries, purulent contents, diseases of the oral cavity, etc. Therefore, if signs of this disease occur, be sure to consult a doctor.
What symptoms indicate pulpitis of primary teeth?
The following will help you tell if your child has pulpitis:
Complaints about toothache
As a rule, it worsens in the evening and at night, as well as during the process of chewing food. There is almost always a reaction to cold or hot drinks. Painful sensations may occur when tapping the tooth. With an exacerbation of the inflammatory process, the pain becomes aching and constant.
However, it should be borne in mind that the rapid transition of the disease into a chronic form, characteristic of childhood, often leads to the disappearance of pain. Which does not mean there is no problem. And you should visit a doctor even if the tooth stops hurting.
Cheek swelling (swelling)
This symptom can often be found in photographs of pulpitis in baby teeth. However, it is not always observed. And, in addition, it can signal diseases such as periodontitis or periostitis. But pulpitis should not be ruled out. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. And you may have to take an x-ray.
Increased body temperature and deterioration of general condition
If the child has a strong immune system, then a high temperature may also indicate the development of the disease. In this case, the body reacts to the inflammatory process that began in the pulp. And if there are no suspicions of other diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature, be sure to show the child to the dentist.
If your baby has a toothache, or you observe any of the above symptoms, you should immediately visit a doctor. Perhaps it's time to start treating baby tooth pulpitis. In any case, there is definitely a reason to visit the dentist’s office.
Diagnosis of the disease
Treatment of hypertrophic pulpitis is prescribed after correct diagnosis. The disease must be differentiated from soft tissue pathologies such as gum overgrowth and granulation tissue. This can only be done by a qualified dentist based on a visual examination and diagnostic test data.
When examined, excessive soft deposits are found on the side of the diseased tooth due to insufficient oral hygiene and eating on the healthy side. In addition, you can see a deep carious cavity filled with granulation formations, which, when lightly pressed, begin to bleed. During pressing, the patient experiences virtually no pain, but further insertion of the probe is characterized by pronounced pain symptoms.
If the disease is at an early stage of development, the color of the granules will be bright red, while at a late stage it will be light pink. In the case where a polyp has formed, its density and absence of pain when pressed are noted. However, further, deeper probing is characterized by intense pain symptoms.
As a rule, in addition to a visual examination, the dentist prescribes the following diagnostic tests:
- radiography - allows you to identify the absence of a partition between the tooth cavity and the cavity affected by caries;
- thermal test - detects the lack of reaction of the affected tooth to thermal stimuli;
- electroodontodiagnostics - aimed at determining the sensitivity of the nerve when an electric current of varying strength is passed through it.
How to treat pulpitis of baby teeth
If you suspect that your son or daughter is suffering from this particular illness, then the best thing to do is to seek professional help as soon as possible. Because the disease is quite serious, and it requires correct diagnosis and qualified medical intervention.
There is no need to remove the tooth at all. Moreover, early removal can lead to the formation of an incorrect bite. The course of treatment of pulpitis in children largely depends on the stage of tooth development at which it is detected.
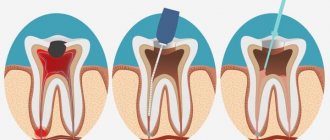
The fact is that the pulp can be completely removed only in the formed roots (and this takes several years from the moment the tooth erupts). Therefore, in most cases, the doctor removes the pulp only partially. As a rule, carious lesions are removed simultaneously with its part located in the crown of the tooth. This procedure is carried out after an anesthetic injection. After that, a medicine is placed at the bottom of the cavity and at the mouths of the canals, designed to disinfect the remaining tissues. Or, the pulp is first mummified, also through the application of drugs, and then removed.
Over time, such a “gasket” of medications is replaced or left under a permanent filling.
In case of pulpitis of milk teeth, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process and prevent complications in the form of periodontal damage, which can cause improper formation of permanent teeth. There are 3 main methods in total.
Vital amputation
This procedure involves preserving the pulp in the dental canals, but at the same time it is removed from the crown area. Vital amputation is done in cases where a multi-rooted tooth is affected. It is not used on single-rooted plants due to the lack of a boundary between the root and the coronal pulp zone.
Treatment proceeds as follows:
- Anesthesia (local) is performed.
- The doctor drills out carious lesions.
- The pulp is removed.
- Tissues are treated with drugs.
- The dentist makes an insulating pad.
- A temporary filling is placed.
Subsequently, the specialist may recommend physical therapy and medication.
Biological method of treating pulpitis in children
Several years ago, dentists began to practice conservative methods of treating pulpitis in children. This conservative therapy does not require surgical intervention, is easier for the baby to tolerate and causes minimal complications.
Conservative treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth is carried out in stages:
- The doctor opens the inflamed cavity.
- Covers the bottom of the gum and pulp with a special mixture consisting of Shostakovsky balm, calcemin and artificial dentin.
- After the mixture dries, the dentist seals the tooth using fluorine cement or phosphate cement spacers.
Doctors are ambivalent about such a procedure. Some consider biological treatment of pulpitis in children to be an excellent way to relieve the child of pain and create the most favorable conditions for the development of the apices of the roots of permanent teeth.
Many dentists believe that it is the conservative method of treating pulpitis of baby teeth that can provoke various periodontal inflammations.
In any case, treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth requires repeated visits to the doctor and a serious approach. Therefore, be persistent and patient, and also try to set up your child correctly so that every trip to the clinic does not become stressful.
Please note that there is no general approach here. The inflammatory process occurs differently each time. And only a doctor can decide how to treat pulpitis of a baby tooth in each specific case.
Second visit:
- The doctor removes the temporary filling.
- The canal is washed with antiseptics and then dried.
- The canal is sealed. To do this, the dentist uses a gutta-percha point and paste. The pin is used to compact the filling compound.
- Finally, you need to take an x-ray to make sure that all actions were performed correctly and that the filling is tight to the top of the canal.
- A temporary filling is placed again. After this, painful sensations may persist for some time. To eliminate them, it is allowed to take ibuprofen, ketanov, nimesil and other drugs that the dentist should recommend.
Possible mistakes when treating pulpitis
Unfortunately, it is not at first glance that tooth pulpitis in a child is a simple ailment. Incorrect treatment can provoke nightmares such as periodontitis, periostitis and even acute polio.
The most common mistakes when treating pulpitis in children are:
- Incorrect assessment of the condition of the pulp and, consequently, partial removal of inflammation. In this case, the baby will very soon suffer from a new exacerbation.
- Loose bandage when removing pulp. In rare cases, doctors do not apply a temporary bandage with arsenic tightly enough, which can lead to burns and necrosis of the tissues of the cheek, tongue and mucous membranes.
- An overdose of arsenic can cause acute periodontitis, which requires longer treatment than pulpitis in a child.
- Trauma to the periodontium with a root needle. Incomplete cleaning of root canals during the treatment of acute or chronic pulpitis in children can also provoke periodontitis.
First visit:
- The doctor performs anesthesia. Thanks to painkillers, all manipulations performed by the dentist will be comfortable for the patient. Mandibular anesthesia is sometimes required for mandibular molars.
- Carious and partially healthy dental tissues are drilled out. The latter are used to open the mouth of the root canal and provide access to them for working with instruments.
- A rubber dam is placed to protect the canals from saliva, which may contain pathological microflora.
- A pulp extractor (a very thin barbed needle) is used to remove the nerve.
- A special devitalizing paste without arsenic is applied to the treatment site (it is not used in modern products due to toxicity).
- The doctor determines the length of the root canal using radiography with an apex locator. In cases where there are several canals, a K-file is inserted into them one by one, which, when penetrating deeper, indicates that the instrument has reached the apex of the tooth root. This is done with each channel separately, since their depth is not the same.
- The canals are widened for subsequent filling. At the same time, washing with antiseptic agents is carried out constantly.
- Placement of turundas into the canals and installation of a temporary filling.
Treatment of pulpitis: how to adjust a child
Pulpitis of baby teeth causes a lot of trouble for the baby. There is no need to aggravate the already difficult days of the child; parents should definitely prepare him for a visit to the dentist.
Talk to the baby. Explain that the doctor will treat tooth pulpitis carefully and the patient will not feel pain. It is important that the child does not associate going to the dentist with torture chambers. Choose a positive doctor whom you trust, and dental treatment will become an exciting attraction.
The main task of parents is not to let the disease take its course. Since chronic pulpitis of the baby tooth, which is most often seen in the photo, can lead to further spread of the inflammatory process and damage to the rudiments of permanent teeth.
And don’t forget that preventing trouble is always easier. Therefore, do not allow pulpitis. Ensure that your child brushes their teeth correctly and regularly using high-quality oral hygiene products. And be sure to visit your dentist regularly.
ASEPTA BABY toothpaste for babies from 0 to 3 years old will help you quickly teach your baby to brush their teeth. The soft gel carefully cares for your teeth, reliably protecting them from caries. And the sweet taste of tutti-frutti makes the procedure pleasant and tasty.
Pulpitis of permanent teeth in children
Pulpitis of permanent teeth in children is a common ailment among adolescents. Surprisingly, newly erupted molars are especially sensitive to external influences, because during the first few years they are not yet saturated with mineral components.
Pulpitis of permanent teeth in children most often develops against the background of deep or medium caries. And if in children with formed tooth roots, pulpitis develops in the same way as in adults, then in adolescents with just developing roots, this ailment is significantly different from what is usual for parents.
Symptoms of pulpitis of permanent teeth in children
Acute pulpitis
Features of pulpitis in permanent teeth with incomplete growth include:
- Spontaneous pain. Children complain of unexpected, mild pain in the mouth. Unpleasant sensations arise suddenly, for no apparent reason. The pain can torment a teenager for hours, or it can go away on its own in 15-20 minutes. Often, various irritants, such as cold or hot food, cause discomfort.
- With acute diffuse pulpitis of permanent teeth in children, discomfort intensifies in the evening and at night. Soon the pain becomes constant, radiating to the temple, back of the head, ear or infraorbital area. Very soon, painkillers become ineffective.
- Softened dentin of the carious cavity, weakly pigmented, also indicates tooth pulpitis.
- Acute throbbing pain radiating to the trigeminal nerve is also a symptom of acute purulent pulpitis with incomplete root formation. It is noteworthy that the pain intensifies when consuming hot food or drinks and is relieved by cold food.
Chronic pulpitis
Chronic pulpitis of permanent teeth with unfinished growth, as in baby teeth, can occur as a primary process without an acute stage. The following symptoms are characteristic of chronic inflammation:
- Aching spontaneous pain;
- Unpleasant sensations when eating or pressing on a tooth;
- Prolonged pain from cold or hot food;
- Pulp bleeding.
Chronic gangrenous or fibrous pulpitis of permanent teeth in children can occur in both open and exposed pulp chambers. Fibrous inflammation is characterized by a dark red chamber that bleeds unpleasantly when touched. Gangrenous pulpitis is usually accompanied by gray-green discharge with a putrid odor.
Chronic pulpitis in children goes away sluggishly, the pain returns every now and then. A teenager complains of attacks of pain spreading along the trigeminal nerve.
Treatment of pulpitis of permanent teeth in children
Doctors distinguish two methods of treating pulpitis in permanent teeth. At the discretion of the doctor, therapy is carried out with partial or complete preservation or removal of the pulp. Let's look at each method in more detail.
Conservative treatment
“A living tooth has a better chance of survival than a dead one” - you’ve probably heard this common and, of course, fair phrase. Recently, dentists have mastered the biological method of treating pulpitis of permanent teeth in children, which is recommended for diseases such as:
- Pulp hyperemia;
- Traumatic pulpitis;
- Acute serous pulpitis;
- Chronic fibrous pulpitis without destruction of periodontal tissue;
- Acute pulpitis, lasting no more than a day;
Unfortunately, science has not yet moved that far forward, and biological treatment of pulpitis is effective when the child is in good condition and has a shallow carious cavity.
For adolescents with incomplete root formation, dentists treat pulpitis using the method of partial nerve preservation. This method helps complete the formation of the root system.