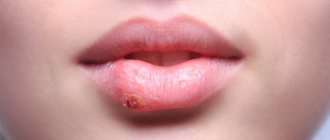
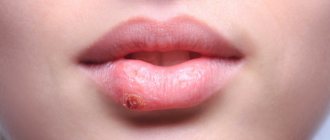
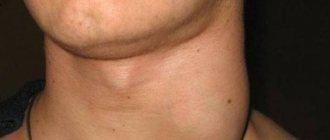
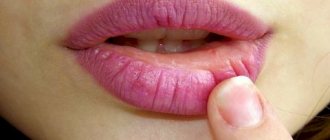
A lump appeared on the gum: what could be the reason?
A lump on the gum, by and large, is a compaction that is caused by damage to periodontal tissue in a certain area. The cause of the lesion is another point on which the treatment plan and possible complications in the absence of timely medical care depend. First of all, the doctor determines the nature of the appearance of the lump on the gum, which comes in two types.
- Infectious nature.
Infection caused by pathogenic bacteria is the most common cause of lumps and lumps in the gum area. - Non-infectious nature.
This includes injuries, mechanical, chemical damage, as well as other factors not related to the activity of microorganisms.
A lump on the gum above a tooth or under a tooth (in the case of the lower jaw) appears much more often as a result of infections, however, the treatment regimen is individual for each case, depends on the specific symptoms and is drawn up after collecting an anamnesis. Next, it makes sense to describe in more detail the diseases and pathologies that provoke the appearance of seals on the gums.
Causes
The most common causes of bumps on the gums are:
- illiterate and irregular dental care;
- n injuries in the oral cavity;
- n consequences of wearing dentures.
Lack of regular dental care causes plaque to appear on them, which becomes a suitable habitat for pathogenic bacteria. As a result of their reproduction, a lump with pus often appears on the gum.
Often the tumor appears after injury or unprofessional installation of dentures. This occurs after the use of low quality materials and insufficient antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity.
Lumps on the gums in most cases indicate the presence of dental diseases. Most of them can cause significant discomfort, which necessitates immediate contact with a specialist.
Infectious diseases that can cause a lump on the gum
- Periostitis (flux).
Periostitis, or flux, usually occurs against the background of complications of caries, pulpitis and periodontitis, when infection and pus extend beyond the periodontal tissues and penetrate into the soft tissue area. You can notice with the naked eye that there is a swollen lump on the gum. - Complications of periodontitis (granuloma, cyst).
When infections occur at the root apex, a periodontal abscess occurs. Gradually, pus penetrates into the periosteum area, and then directly under the mucous membrane. Thanks to its elasticity, the patient often does not feel any unpleasant symptoms from the lump that appears, so he is in no hurry to see a doctor. Quite dangerous are cases when the pathology takes the form of a fistula, which looks like a small white lump near the tooth. The fistulous tract allows pus to come out, but this does not mean that the inflammatory process will disappear on its own; - Gingivitis and periodontitis.
With periodontal inflammation, swelling and hardening of the gums are almost always observed. Gingivitis is considered the initial stage of the disease, therefore it is characterized by the so-called red ball (gum tumor), while with periodontitis, purulent discharge is observed, and the tumor acquires a beige or grayish tint. In some particularly advanced cases, against the background of periodontal problems, gumboil may appear, which visually looks much more noticeable.
Non-infectious diseases that can cause a lump on the gum
- Epulis.
A small growth that has some kind of stalk, which occurs mainly due to injuries, malocclusions, improper prosthetics, during teething (in children), and also due to hormonal disorders (less often). In appearance, epulis may resemble a tumor due to gingivitis, so diagnosing the disease may require x-rays and histological examination. - Ecostosis.
This pathology is a bone growth that is formed due to a jaw anomaly. The main cause of ecostosis is considered to be a genetic predisposition, but pathology can develop after injuries and traumatic tooth extraction. In this case, the bone extends beyond its usual boundaries, resulting in the formation of a noticeable lump. The disease is not accompanied by an inflammatory process, but it can occur due to mechanical damage to the growth. - Hematoma.
It is formed as a result of a strong blow and may well go away on its own or with the use of special means. If the tissue structure is disrupted as a result of injury, the help of a surgeon is needed.
It hurts/doesn’t hurt: in what cases does pain occur?
Periostitis is considered the most painful. With this complication, the main inflammatory process is localized in the area of the bone and periosteum, which causes severe pain. Seals caused by the inflammatory process in the periodontium (gingivitis, periodontitis) are disturbing when pressed, thermal and mechanical influences are applied. Epulis and ecostosis, as a rule, are not accompanied by pain, but when damaged and inflamed, they also disturb the patient.
A lump near a tooth with periodontitis may not cause noticeable pain, especially if it has a fistulous tract. It is important to understand that the absence of pain does not mean that treatment can not be carried out. In most situations, the tooth can be saved, but some patients are very negligent about their health and consult a doctor in extreme cases. A lump above (or under) a tooth is quite an alarming signal, which often indicates the development of quite serious diseases.
Diseases leading to the appearance of lumps
Gum bumps can form in parallel with dental diseases occurring in the oral cavity. They are not painful if they are formed as a result of:
- hematomas after removal of tooth roots;
- fistula;
- epulis;
- periodontitis.
A hematoma in the form of a watery tumor occurs as a consequence of an incorrectly extracted tooth. Such a neoplasm is not dangerous and is prone to spontaneous resorption.
The fistula (in the form of a white lump on the gum) is often chronic. It is a neoplasm with a hole for draining pus, located on the gum above or below the tooth and appears as a result of advanced pulpitis.
Epulis
- a formation that has a natural color or red color. This type of cone is distinguished by the presence of a stalk, and mainly affects the lower jaw. The reasons for its appearance are everyday mechanical stress, poor quality dentures, malocclusion and hormonal imbalance in women.
Periodontitis appears as a hard lump on the surface of the gums. An abscess forms at the base of the tooth root, transforming over time into a cystic formation.
Painful bumps occur as a result of periostitis (flux) or gingivitis. Flux is known as inflammation of bone tissue, accompanied by severe pain, increased body temperature, swelling of the mucous membranes, and enlarged lymph nodes. With gingivitis, small red spherical formations appear, and bleeding from the soft gum tissue often develops.
Bumps on a child’s gums form for the same reasons as in adults. To the factors already listed is added the period of teething, during which tumor-like formations appear in the oral cavity.
Most types of bumps on the gums require mandatory treatment. In the absence of proper therapy, the patient may develop dangerous irreversible complications.
Lump after crown installation
Improper denture fitting is a very common cause of lumps on the gums. Most often, errors occur at the tooth preparation stage, when the depulpation procedure is carried out. Poor canal filling provokes the development of infection, which, in turn, leads to periodontitis. Another common reason is a poorly made prosthesis or defects during its installation. In this case, the prosthesis injures the mucous membrane and causes swelling, abscesses and growths. Treatment almost always involves removal of the prosthesis and subsequent replacement of the prosthesis (if possible). The sooner a complication is detected, the higher the chance that it can be successfully treated. A well-installed prosthesis should not cause pain, discomfort or injure the mucous membrane. The tooth under the crown should also not hurt, since the dental nerve is killed before permanent prosthetics.
Preventive measures
Preventing gum bumps is quite simple. The main methods will be daily thorough oral hygiene and timely visits to the dentist.
To prevent the appearance of cones, rinse with aloe juice diluted with water in a ratio of 1:4. For the same purpose, use an infusion of fresh sorrel leaves: to complete the procedure, 2 tbsp. of crushed raw materials, brew 200 ml of boiling water and leave for at least 1 hour.
For patients who have a lump on their gum, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are of great importance. Only a qualified specialist will help you safely get rid of gum formation, minimizing the risk of developing unwanted complications.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
Treatment of lumps on the gum
The treatment plan depends entirely on the results of the diagnosis, which is designed to determine the root cause of the lump or ball on the gum, which is why the patient should not self-medicate, but go to the doctor as soon as possible. If the cause of the lump is an infection, then you need to eliminate the cause of its appearance. For complications of pulpitis and periodontitis, treatment can take a long time. The lump is opened, a drainage is installed to pump out the pus, after which the doctor prescribes conservative or surgical treatment to the patient, depending on the severity of the disease. In case of periodontal inflammation, professional cleaning and sanitation of the oral cavity are carried out, special ointments and antiseptics are prescribed. In more complex cases, curettage, physiotherapy, and so on are used. With epulis and ecostosis, pain and inflammation are often absent, so the decision about intervention is made together with the patient. Most often, the pathology will be removed after surgery: even a small bump on the gum (especially in the smile area) spoils the aesthetics, so it is understandable that a person wants to get rid of it.
A lump on the gum: what is it and what diseases can it indicate?
When taking care of your own health, you should remember that not only problems with teeth pose a potential threat: problems with gums can also signal the presence of serious problems in the body. We will devote this article to a fairly pressing issue - what to do if a lump (ball) appears on the gum? We will try to thoroughly study the issue, as well as understand what diseases this symptom may signal.
What is a lump on the gum?
In this case, we are talking about compaction of the soft gum tissue: visually this manifests itself in the form of the formation of a ball or lump - the problem is diagnosed through a visual examination, not to mention the fact that the affected area may hurt and cause discomfort.
Any change in the color of the gum tissue is always a reason to consult a dentist. If there is a lump (ball), you should go to the doctor immediately.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of such a lump - treatment tactics depend on the correct diagnosis, which the specialists of Dr. Efremov’s Dentistry can do. But generally speaking, there are two natures of the disease - infectious and non-infectious. Let's consider both factors separately.
Infectious causes of the formation of lumps on the gums in Kirov
Infection is always associated with the activity of pathogenic bacteria, which can infect absolutely any tissue of the human body. Gums are no exception: in this case, compaction is associated with infectious inflammation, which can occur for several reasons:
- Flux or periostitis. This phenomenon can be considered a complication of diseases such as caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. The infection may well affect not only the teeth, but also the adjacent tissues, that is, the gums. The result is the formation of a lump (or ball), which is noticeable even to the naked eye;
- Acid or granuloma, which can be classified as complications of periodontitis. The apex of the root is precisely the area where, due to various complications, an abscess often occurs - pus can penetrate into the periosteum area, and then under the mucous membrane. The insidiousness of this phenomenon lies in the fact that the tissues of this area are quite elastic, so at first a person may not notice negative symptoms and not experience discomfort. Only then, when the problem becomes serious, does a ball appear - this is a real fistula, which requires immediate contact with an experienced dentist;
Periodontitis and gingivitis. When inflammatory processes form in the periodontium, in almost 100% of cases the formation of various seals is observed. In the case of gingivitis, the ball acquires a red tint, and periodontitis is accompanied by the presence of a gray lump. If you do not seek high-quality or effective treatment, the disease transforms into a flux, which becomes even more noticeable and potentially dangerous to the general condition of the body.
This is exactly what the most common cases of infectious nature of the formation of a lump on the gum look like in Kirov. Next, we will look at the non-infectious cause of this problem.
Non-infectious causes of lump formation on the gums
There are also three most common options - we will again consider them individually:
- Epulis is a small growth. Visually, epulis resembles a tumor diagnosed with gingivitis, however, x-rays and/or histological examination will help to understand the true cause of the disease. This could be malocclusion, consequences of injuries, hormonal disorders, and even the result of unprofessional dental prosthetics;
- Ecostosis is a bone growth that occurs due to jaw abnormalities. Most often, this is observed due to genetic predisposition, however, the factor of injury should also not be excluded. The fact is that bone tissue can go beyond its usual limits, resulting in a noticeable lump. As a rule, inflammatory processes are not observed in this case, however, they may well appear during mechanical damage to the growths;
- A hematoma is a blood clot in the gum area, which is a direct consequence of the injury. Although, from time to time there are cases when a hematoma forms without external influence - this is also a reason to consult a dentist to solve the problem and prevent the development of complications.
So, we looked at the three most common causes of non-infectious origin of a lump on the gum in Kirov. Next, we will find out in what cases painful sensations occur in the presence of such a ball, as well as what methods of solving the problem exist today.
If the lump hurts?
If you suddenly find a lump on your gum, however, there are no pain symptoms, this does not mean that you should refuse professional diagnosis and treatment. Yes, it is likely that everything will go away on its own, however, in most cases this is not the case - there is a risk of tooth loss!
If the lump begins to hurt, you should immediately visit the dentist; however, even in this case, it is not always possible to save the tooth.
As for the most acute pain in the presence of a ball (bump) on a tooth in Kirov, this may signal periostitis. If the seal only bothers you when you apply pressure or eat warm or cold food, you can most likely diagnose gingivitis or periodontitis. In turn, epulis and ecostosis may go completely unnoticed, however, there may still be a slight feeling of discomfort.
Incorrect crown installation
Separately, I would like to pay attention to such a reason for the formation of a lump as incorrect installation of the crown (we have already mentioned this factor above). There are two possible factors to highlight here:
- Incorrect or poor-quality treatment of tooth canals before prosthetics, which can lead to periodontitis (we have repeatedly spoken about the complexity of the tooth depulpation procedure);
- Incorrect measurements or poor-quality prosthesis/crown. This is also very common, since an artificial element can injure the mucous membrane of the gums, causing irritation and the appearance of seals.
Treatment depends on the cause: in the first case, it is re-treatment of the tooth canals in Kirov, in the second - re-prosthetics (if, of course, it is possible).
Treatment of lumps on the gum in Kirov
And finally, a few words about how the ball is removed and the lump on the gum is treated. The order depends entirely on the nature of the disease. For example, infectious pathologies are treated by identifying and eliminating the root cause - this is done both through mechanical manipulation and with the help of medications. If periodontal inflammation occurs, measures such as sanitation and cleaning of the oral cavity, curettage, physiotherapy, etc. may well help. As for non-infectious manifestations, here the issue is resolved on an individual basis: sometimes the disease is simply observed without any active action, and in some cases surgical intervention is required.
We invite you to Doctor Efremov’s Dentistry: sign up for a consultation and get answers to all your questions! Information by phone: 8 (8332) 255-717 . Be healthy and take care of the beauty of your smile!