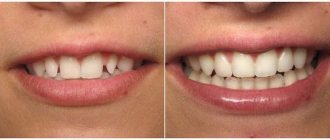
The problem of food getting between teeth is one of the most common in dentistry. Most people, immediately after eating, need to thoroughly clean the interdental spaces with floss or a toothpick, since food debris getting between the teeth causes very unpleasant and even painful sensations.
Unfortunately, many take this situation for granted and continue to try to eliminate the discomfort without trying to identify and eliminate its cause. But it’s worth thinking about why pieces of food get stuck between the teeth and what the consequences might be; moreover, it’s necessary to take measures to solve the problem. This situation can be corrected quite easily; all you need to do is contact a qualified dentist.
What should you do if food gets stuck between your teeth regularly? The problem can be solved in two ways: by visiting the dentist to identify and eliminate the causes of this phenomenon, and by daily cleaning of the interdental space to prevent the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Causes of food getting stuck between teeth
The main reason for food getting between the teeth is a violation of the density of their contact with each other (in dentistry this concept is referred to as a “contact point”), which can be caused by:
- low-quality fillings (prostheses). An incorrectly placed filling may not exactly follow the topography of the tooth and may have an overhanging edge. A sign of poor quality fillings can be either stuck food or breaks in the dental floss during its use;
- natural structure of the dentition. This may be curvature of the teeth, diastema (gaps between the lower or upper central teeth), trema (gaps between the lateral teeth);
- deformation of the dentition due to injury, tooth extraction, and various diseases of the oral cavity.
- Unprofessional prosthetics. There may be a gap between the crown and the tooth; the denture design does not correspond to the anatomical shape.
- There is no papilla between the tooth and gum. It fills the interdental space, and in the absence of such a papilla, the problem of food getting stuck appears.
- Crevices. May appear as a result of injuries or diastema. As a result, pieces of hard food constantly get stuck in the cracks, which have to be removed with thread or a toothpick.
- Loss of teeth. As a result, the integrity of the dentition is compromised, which provokes the occurrence of the problem in question;
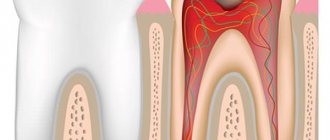
- Caries. As a result of carious lesions, the enamel is destroyed and a cavity is formed. Residues of food accumulate here, which can only be removed purposefully: ordinary rinsing and salivation will not cope with this task.
Recommendations
First of all, take good care of your mouth. When the first signs of food stuck appear, we recommend contacting your dentist for specialist advice. Don't forget to go to the prof 2 times a year. inspections. During a consultation with our specialists, you can find out which teeth should be treated and which fillings need to be replaced with new ones. You also need to come for professional teeth cleaning twice a year.
Secondly, we recommend contacting only trusted clinics with many years of history and experienced doctors. We would like to warn you against the temptation to use free dentistry under compulsory medical insurance; remember, good treatment and prosthetics cannot be free. Don't skimp on your health!
We hope that our article helped you and you found answers to your questions. If you have any further questions or would like to make an appointment, there is an appointment form below.
Consequences of regularly getting food stuck between teeth
Some people don’t even think about how to get stuck food out of their teeth. They are guided by the principle, it doesn’t hurt and it’s okay, making a big mistake. Meanwhile, such neglect can lead to dire consequences. For example:
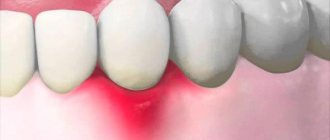
- Gum diseases - food debris is an irritant that damages the mucous membranes, which provokes the development of dental diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.;
- Unpleasant odor - the food remaining between the teeth begins to decompose, which, in addition to the amber, creates a favorable environment for the life of pathogenic bacteria;
- Root injury – irritation of the gums can cause exposure of the neck of the tooth, which increases sensitivity and causes pain;
- Caries - stuck pieces of food is one of the main causes of carious lesions of the enamel; this disease can only be eliminated through dental intervention;
- Tissue destruction – if you do not clean the interdental space, the teeth begin to gradually deteriorate, which can lead to complete loss.
How do dentures change the microflora of the oral cavity?
The presence of dentures in the oral cavity, as we have already said, inevitably leads to changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the microflora. Here are some examples of the effect of dentures on the microflora of the oral cavity.
- Chromium-nickel metals provoke a decrease in the total number of beneficial bacteria within 14 days after installation of structures.
- Almost any removable denture leads to a doubling of the amount of microflora in the mouth after 6 months.
- With complete removable prosthetics, there is a significant change in the composition of the usual microflora. Fungi of the genus candida, E. coli, sarcina, and actinomycetes appear in large quantities in the mouth. Klebsiella is diagnosed in the mouth, atypical bacteria that provoke the development of many unpleasant diseases. In addition, removable dentures help reduce the amount of lactobacilli in the mouth, and, therefore, reduce the body's resistance to infections.
- When studying denture plaques using microscopes, scientists discovered that this foreign part of the oral cavity consists mainly of bacteria, similar to dental plaques in gingivitis. As a rule, Candida fungi are always sown on dentures in the form of single scattered cells among rod-shaped and filamentous bacteria.
How to remove food if it's stuck between teeth
If food gets stuck between your teeth and your breath smells, you need to use hygiene products to care for your teeth.
The most common cleaning methods:
- The toothpick should be positioned at an angle of 30-40 degrees relative to the gum, pressed against the gingival papilla and the plane of the tooth. Remains of food are removed by moving the toothpick upward.
- Dental floss. The floss is pinched with your fingers and inserted into the interdental space. Cleaning with dental floss is carried out in a reciprocating motion.
It is important to understand here that both of these methods are quite traumatic, and any careless movement can damage the gums. Then how to remove food stuck between teeth? To do this, you can use an irrigator.
Irrigators are absolutely safe to use: pieces of stuck food are removed with a stream of water. This allows you to efficiently clean even hard-to-reach places without damaging the gums and interdental spaces. In addition, irrigators are ideal for the care of denture structures.
How to determine that a denture has a bad effect on the microflora of the oral cavity?
It has been proven that the prosthesis and prosthetic material negatively affect the oral mucosa, as well as numerous elements of its homeostasis.
Dentists consider the subjective complaints of patients to be the main criterion for the influence of a design. Often, denture owners complain of symptoms such as:
- dry mouth;
- continuous burning;
- changes in the usual tastes of foods.
When choosing dentures, the dentist is based on the characteristics of the defects in the dentition and the condition of the remaining teeth. But, unfortunately, doctors very rarely take into account the condition of the mucous membrane itself and its microflora, although they know that the degree of sedimentation of microorganisms on prosthetic materials can vary significantly.
The work of the salivary glands also changes under the influence of dentures:
- the intensity of salivation changes (its sharp decrease is observed);
- the concentration in saliva of total protein, sodium, potassium, as well as biogenic amines decreases;
- lipid peroxidation is activated;
- The protective capabilities of saliva are significantly reduced.
Removable dentures often cause significant dysbiosis in the oral cavity, creating favorable conditions for many pathogenic microorganisms. For example, several years ago scientists discovered such microorganisms under plate structures as:
- enterococcus;
- non-hemolytic streptococcus;
- diplococcus;
- pathogenic staphylococcus;
- gram-positive rods;
- mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- lactobacilli.
As we have already said, most often pathological reproduction of Candida fungi occurs due to a decrease in the body’s immune defense and further colonization of the entire mucous membrane by fungi. While salivation decreases, the number of fungi increases, the microbial balance of the oral cavity changes, which often leads to the development of various types of inflammation of the tissues of the prosthetic bed.
Microorganisms release waste products, and lipid peroxidation processes are activated. Toxic elements increase inflammation and pain reactions and can ultimately cause tissue atrophy.
What to do if there is a smell from under the crown
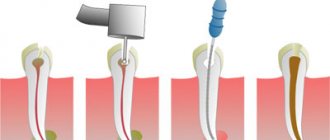
If the smell has already appeared, you should go to the doctor immediately. It is impossible to reverse the destruction process that has begun, but it can be stopped. To achieve this, treatment should be started as early as possible.
An unpleasant odor indicates that a putrefactive process is developing. When the pus does not find a way out, it begins to spread to the surrounding tissues. First, nearby soft tissues become infected, then the process begins to spread to the bone. Such processes can have very serious and health-threatening complications.
The doctor will remove the prosthesis. This allows you to solve two problems:
- Allow the dentist access to the diseased tooth for examination and treatment.
- Clean the prosthesis.
If the tooth can still be saved, you will be prescribed treatment. After this, the cleaned prosthesis will be installed in place.
When a patient seeks help late, it is often impossible to save the tooth. In this case, it is removed and anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out. After removal of the supporting unit, the dentition can be restored in different ways:
- Make an implantation. Usually the operation is performed simultaneously with removal. An implant is implanted into the hole and a temporary crown is installed.
- Do re-prosthetics. This method is suitable if implantation is impossible for some reason.
The doctor will tell you about possible treatment options for your clinical case. Together with your doctor, you can choose the best option.
The latest technology for prosthetics and microprosthetics
Advantages
First : with the help of metal-ceramics, it is possible to achieve complete identity of artificial teeth with natural ones in appearance and function.
Second : with metal-ceramic artificial teeth you can chew food perfectly (provided they are made correctly), just like with your own teeth, and in some cases even better.
Third : microbial plaque settles several times less on metal-ceramics than on your teeth or metal. Consequently, metal-ceramic teeth are more “hygienic”. This is especially important for patients with periodontitis.
Damage to dentures due to gum disease
- gum recession, in which they become smaller and sag under the denture by several millimeters;
- gingivitis;
- stomatitis;
- periodontal disease;
- destruction of the intergingival papilla due to the listed diseases or incorrect implantation;
- accumulation of tartar, which prevents the clasp bridge from being firmly secured.
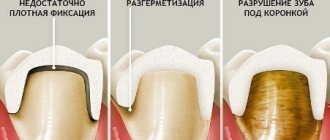
Most often, problems arise after the installation of crowns. If a specialist missed the initial stage of caries or did not polish the stump well, it continues to rot. Inflammatory fluid accumulates in the roots, causing swelling and swelling. The mucous membrane seems to squeeze out the prosthesis and make it unstable.
If food gets under your dentures, you should contact your dentist. The reason often lies in the discrepancy between the size of the acrylic jaw and the human gums. Therefore, it is important not to skip fittings with the orthodontist. The deficiency can be eliminated by rebalancing the structure. Sometimes the patient simply cannot secure the locks or latches correctly, so a simpler and more comfortable prosthetic option is selected for him.
Selecting a crown system
| Type | Material | Purpose |
| Solid metal | The design is based on a cobalt-chromium alloy or gold | A popular type of prosthetics, but less and less used |
| Ceramic | Ceramics | Individual unit prosthetics and bridges |
| Metal-ceramic | Metal frame covered with ceramics | Dental crowns per unit, production of fixed bridges and removable dentures |
| Zirconium | The surface is covered with ceramics, and the base is zirconium dioxide. | dental crowns per unit, production of fixed bridges and removable dentures |