Flux is a common, non-medical name for a whole group of diseases that require immediate, and in some cases, emergency care. One of the main manifestations of flux is a violation of the shape of the face associated with a complication in an inflamed tooth.
The main groups of diseases that are commonly called flux: periodontitis, periostitis, osteomyelitis, abscess and phlegmon, lymphadenitis, odontogenic sinusitis.
Periodontitis
- inflammation of the tissues of the apical part of the tooth.
Periostitis
– inflammation of the periosteum in the area of the teeth.
Osteomyelitis
– inflammation of the jaw bone, which necessarily ends with necrosis (death) of the affected area of the bone.
Abscess
- This is a limited purulent inflammation of fatty tissue.
Phlegmon
- This is a diffuse purulent inflammation of fatty tissue.
Under the skin, under the mucous membrane, under and between the muscles there is fatty tissue. With an exacerbation of odontogenic infection, pus spreads under the periosteum, axillary and intermuscular spaces, causing inflammatory and edematous-infiltrative changes in the soft tissues of the face and neck.
Inflammatory diseases of the maxillofacial area (flux, abscess, phlegmon) and neck are divided into two main groups according to localization. The first is abscesses and phlegmons located near the upper jaw. The second is abscesses and phlegmons located near the lower jaw.
Lymphadenitis
– inflammation of the lymph node (group of lymph nodes) adjacent to the odontogenic (dental) focus of infection. Odontogenic sinusitis is often an inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) sinus (sinusitis), caused by the anatomical features of the position of the roots of the maxillary teeth involved in the pathological process, in which the roots of the teeth either stand in the lumen of the maxillary sinus, or are located close to the bottom of the maxillary sinus. In this case, infection of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus occurs with the subsequent development of sinusitis.
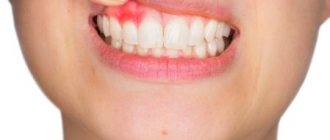
What is tooth flux?
Flux, or, in dentist's language, periostitis, is a very unpleasant pathology, which is characterized by inflammation of the periosteum and soft tissues. The causes of flux on the gums can be different: trauma, gum disease, poor-quality dental treatment - all this can lead to a complication in the form of periostitis. The localization of the disease does not depend on the area of the jaw: flux of the upper and lower teeth occurs equally often.
Flux under a tooth (or above a tooth, if we are talking about the upper jaw) visually resembles an inflamed sac. However, this is far from the only possible manifestation of periostitis. There is also a serous form, when the periosteum becomes inflamed as a result of trauma and damage, as well as one of the most unpleasant types - diffuse, when the infection is localized in different parts of the jaw, which requires extensive surgical intervention with the participation of a maxillofacial surgeon.
Stages of surgical treatment of flux:
- anesthesia (usually local);
- opening the focus of suppuration (gum incision);
- removal of pus;
- drainage (installation of drainage to ensure the outflow of inflammatory fluid);
- X-ray (to determine the cause of periostitis);
- removal of a diseased tooth or drug treatment.
In addition, for acute purulent periostitis, antibiotics, physiotherapy and painkillers are usually prescribed. Treating periostitis with antibiotics at home without consulting a doctor can cause side effects and resistance of pathogenic bacteria to the drug.
Symptoms of gumboil
Flux on the gums in adults occurs much more often than in children (approximately 80-90 percent of all cases). A characteristic feature of the pathology is that it does not go unnoticed. This is one of the most unpleasant diseases, causing severe discomfort. The most striking symptoms are the classic purulent flux.
Symptoms
- Severe throbbing pain.
- Inflammation and swelling of soft tissues. At the advanced stage, the side of the face on which the flux is diagnosed swells.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Discomfort and pain when eating and talking.
- Flux of the lower tooth (in the molar area) can lead to numbness of the lip and part of the chin.
- Weakness, headache, fever.
Causes and symptoms of periostitis
Symptoms of periostitis include swelling of the gums and face, suppuration, fever, and severe pain. The severity of dental flux manifestations depends on the form and severity of the disease. Swelling and asymmetry of facial contours depend on the location of the inflammation. With periostitis of the upper jaw, swelling of the upper lip, cheek and infraorbital area occurs. With periostitis of the lower jaw, swelling can be observed in the lower part of the face.
The causes of flux can be:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- diseased or untreated teeth;
- consequences of complex tooth extraction;
- jaw injuries;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the body;
- weakened immunity.
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.
How to treat flux in a child?
Quite often, parents ignore the fact that they have baby teeth affected by caries, reassuring themselves that permanent teeth will soon grow in their place. However, an infected gum can cause gumboil to develop. The child’s body does not always react to periostitis with an elevated temperature, and the only symptom may be minor pain, which is not given any importance. The immunity of children is weaker than that of adults, so the disease progresses quickly.
In order to prevent complications, it is necessary to begin treatment at the first sign - clean the canal, close the hole in the tooth with a filling.
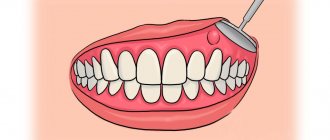
Treatment methods
The attending physician should tell you after the examination how to treat gumboil and what measures need to be taken to achieve a successful result. The mechanism is approximately the same, but each clinical case has its own nuances. Today, several techniques are used aimed at eliminating the disease and its manifestations. As a rule, they come together.
Antibiotics for gumboils
Antibiotic treatment is an important stage of rehabilitation. The most effective antibiotics for fighting inflammation and infection are Metronidazole, Lincomycin, Amoxiclav and their analogues. Any tablets and antibiotics for tooth flux should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
Physiotherapy
Used as an additional measure to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. Recommended procedures include electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound therapy.
Therapeutic treatment
It is carried out if it is decided to save the tooth. This includes endodontic treatment and filling of root canals, as well as resection of the root apex if necessary. If the cause of the flux is periodontitis, then a series of manipulations are carried out to eliminate the accumulation of bacteria in the periodontal pockets.
Surgical procedures
This includes tooth extraction and periostotomy - the main procedure for treating flux. The doctor makes an incision into the purulent sac, and then installs a drain through which the purulent exudate comes out.
Local therapy and rinsing for tooth flux
For better release of pus, pain relief and reduction of swelling, gels and ointments are used topically: Metrogyl Denta, Levomekol, Cholisal. Many people are interested in how to rinse gumboil on the gums. Miramistin and soda solution are usually used for rinsing. As an alternative, you can use folk remedies: decoctions and tinctures of propolis, chamomile, sage or calendula. A tooth after gumboil is still very vulnerable: to minimize the risk of re-infection, these treatment and preventive procedures are very important.
Compresses and lotions
Compresses and lotions have an analgesic effect, limit the spread of the inflammatory process, and have a detrimental effect on pathogenic microorganisms.
Compresses with dimexide
Dimexide, when applied topically, perfectly penetrates into the inflammatory focus, inhibits the vital activity of microbes and increases their sensitivity to antibiotics. It is also able to eliminate pain. For a compress with flux, dimexide is diluted with warm water to a solution concentration of 20-30% (80 ml of liquid per 20 ml of the drug), after which a sterile napkin made of several layers of gauze is moistened with it. The compress is applied to the cheek in the affected area. The duration of the procedure is 1-2 hours. Repeat twice a day until pain and signs of inflammation are eliminated.
Before using Dimexide for the first time, it is necessary to test for an allergic reaction on the back of the elbow.
Lotions with soda
To treat gumboil, wrap a teaspoon of baking soda in several layers of gauze and place it between the cheek and gum for several hours. This will reduce swelling and relieve toothache. The lotion must be repeated 2-3 times a day.
Compress with salt
Salt has an anti-inflammatory effect, quickly relieves pain and reduces inflammation. To prepare a compress, dissolve 2-3 teaspoons of salt in 100 ml of warm water. A gauze or cotton swab is moistened with the solution and placed between the sore gum and cheek. Every 2 hours, change the compress to a new one until the acute symptoms subside.
It is better to use sea salt, which, due to the presence of iodine components, helps to relieve inflammation even better.
It is impossible to cure gumboil yourself without the participation of a dentist. Self-medication can be not only ineffective, but also dangerous. At home, you can only carry out those therapeutic procedures that have been recommended by a specialist.
Is a tooth removed during gumboil?
A tooth can be removed due to flux, but in modern dentistry the emphasis is on tooth-preserving manipulations. This also applies to flux. A tooth must be removed when its crown is seriously damaged and cannot be restored with a pin or inlays. If an infection occurs under the crown, then re-prosthetics are often difficult. In some cases, a tooth has to be removed because it is impossible to unfill the canals after a previous unsuccessful treatment, but this happens extremely rarely. In any case, the doctor makes the decision to remove a tooth based on the clinical picture.
Treatment of periostitis with physical factors
The complex approach to the treatment of periostitis is complemented by the use of therapeutic physical factors:
- ultra-high-frequency therapy (an electromagnetic field, or UHF, acts as a therapeutic factor in inflammatory processes);
- magnetic applicators (magnetotherapeutic treatment of inflammatory processes);
- medicinal electrophoresis (using an electric current of low voltage and low strength, a medicinal substance is introduced into the body as an additional therapeutic factor);
- helium-neon laser rays (have anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, regenerative effects).
Why is tooth flux dangerous?
An inflammatory process of this type tends to develop and, as it spreads, affects deeper layers of tissue. If left untreated, flux often develops into phlegmon - a serious purulent inflammation that has no definite boundaries. The most severe forms of flux provoke the development of sepsis, which can lead to infection of the entire body and even death. It is important not only to know how to cure gumboil and visit the dentist on time, but also to follow a number of preventive measures so that the likelihood of complications developing is minimal.
- Regular and high-quality hygiene.
- Treatment of caries at the initial stage. Flux, dental cysts and other complications often arise due to untreated pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Preventative visits to the clinic to assess the condition of the oral cavity and carry out professional cleaning.
Ointments and gels
Local use of ointments for periostitis contributes to the rapid extinction of inflammatory processes, faster healing of damaged tissues, and effective elimination of pain.
Vishnevsky ointment
With flux, Vishnevsky ointment can stop the development of the purulent process, quickly eliminate tissue swelling and relieve toothache. The xeroform included in the drug has an antibacterial effect, birch tar increases blood flow at the site of injury, and castor oil promotes deeper penetration of medicinal components.
Vishnevsky ointment is used in the initial stages of the disease or after opening the abscess. The drug is applied to a sterile small gauze pad and applied to the skin of the cheek in the area of inflammation for several hours.
You cannot use Vishnevsky ointment if you suspect the presence of a purulent focus at the site of periostitis. This can cause worsening of the condition and the development of complications.
Metrogyl denta
The drug is available in the form of a gel, which contains antibacterial components: metronidazole and chlorhexidine. Therapeutic substances penetrate perfectly into the source of inflammation, quickly relieve pain, eliminate tissue swelling and prevent the development of purulent complications. The gel is generously applied directly to the gum mucosa above the site of periostitis. After using it, you should refrain from drinking or eating for at least 30 minutes. The procedure is repeated three times a day until the inflammatory reactions subside.
Levomekol
The ointment contains ingredients that have a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity and promote rapid tissue regeneration. Levomekol does not lose its properties in the presence of pus, therefore it is preferable in cases where it was not possible to avoid the process of suppuration. The ointment is used three times a day. It is applied to a sterile gauze or cotton swab and applied to the flux for 2-3 hours. If a purulent focus has been opened, the drug can be injected directly into the resulting cavity. It is necessary to treat dental flux with Levomekol until complete recovery.
Propolis tincture
Propolis tincture has a strong anti-inflammatory effect and wound healing effect. Tannins relieve pain well. And essential oils and flavonoids are powerful natural antibiotics. To treat gumboil, 15 ml of propolis tincture is diluted in half a glass of warm boiled water. The solution is used for rinsing. You can moisten a cotton pad with undiluted tincture and apply it to the inflamed area overnight.
Treating flux with propolis in its natural form is also effective. It must be chewed throughout the day until the toothache disappears.
Propolis tincture can be purchased at a pharmacy or prepared at home yourself. To do this, 20 g of propolis is finely crushed and filled with 100 ml of 70% medical ethyl alcohol. Infused in a dark glass bottle for 14 days.
Sage
Sage essential oils have pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. At the first signs of periostitis, you need to brew 60 g of sage leaves and 2 tablespoons of oak bark with boiling water, let it brew for 20-30 minutes in a warm place or in a water bath. Rinse your mouth with the prepared solution at least 8-10 times a day.
No less effective is an infusion of sage and iris roots, for the preparation of which you need to mix 50 g of each component. Pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture with boiling water and leave for half an hour to infuse. Rinse your mouth with the resulting product every hour until the pain decreases.
Baked onion
Thanks to the abundance of essential oils, phytoncides and flavonoids, onions have a pronounced antimicrobial effect, actively eliminate inflammation, and relieve pain. In flux therapy, a good effect is achieved by applying a compress moistened with fresh onion juice to the inflammatory lesion. Every 2-3 hours the application is replaced with a new one.
You can quickly soothe a toothache with baked onions. The whole onion is cut in half and divided into separate plates, which are baked in the oven until translucent. Apply to the gum above the flux area, changing every 20 minutes.
Folk recipes
Herbs and plant extracts have a beneficial effect on oral tissues. They can be used to relieve inflammation. When dealing with flux, you should arm yourself with:
- Oak bark. An infusion is prepared from it: pour two spoons into 200 ml of boiling water and wait for one hour. After filtering, the composition is ready for use. All products based on oak bark stain teeth. This is their significant drawback.
- Sage. You should mix a teaspoon of aromatic dry raw materials with a glass of hot boiling water. After half an hour, filter. During the procedure, the medicine should be slightly warm.
- Chamomile. Very popular for various dental diagnoses. Excellently suppresses inflammatory processes. Antiseptic. It can be combined with string and yarrow. The preparation recipe is standard: a tablespoon of vegetable mixture per glass of boiling water.
- Propolis. Suitable for making tinctures with alcohol. It must be infused strictly at room temperature. Dilute a teaspoon in a cup of water and rinse the flux in the morning, afternoon and evening.
Clinical picture
The main symptom for all types of flux is severe toothache at the site of infection, sometimes diffuse (with extensive bone damage). Swelling gradually begins to increase: first it is localized above the site of inflammation, and then along the surrounding tissues, sometimes affecting the neck, temple and eye.
Important! Sometimes flux occurs painlessly or with a mild pain effect, which, as a rule, indicates the development of a chronic form with sluggish inflammation and periodic relapses.
Inflammation is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pulsation at the site of the lesion;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile and febrile levels;
- headache;
- enlarged lymph nodes on the affected side;
- weakness, lethargy, lack of appetite;
- pain when swallowing, talking, opening the mouth;
- pain when pressing on the gum;
- redness of the oral mucosa at the site of the lesion.
Swelling on the inside of the cheek
Anesthesia makes tooth extraction easier. But, if after treatment of a tooth your cheek is swollen, you should find out the origin of the pathology. You may need treatment for your gums. Discomfort appears in many patients after depulpation. Pain and swelling on the inside of the cheek can be observed from 2 hours to 7 days. If discomfort intensifies or occurs 2 days after surgery, you should immediately consult a dentist.
If, after removing the nerve, in addition to painful sensations, the gums become inflamed, purulent discharge appears, and the temperature rises, you should visit a dentist. He will find out why the cheek is swollen and how to remove the gumboil.
Attention! You cannot take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs before consulting a doctor; this will complicate the diagnosis, which will not allow you to prescribe adequate treatment.
Contraindications to the use of furatsilin for periostitis
You should not use this medication if you have:
- Bleeding in the mouth from the gums
- Allergic reactions to the active substance and nitrofural derivatives
- Increased individual sensitivity to the medication.
If, while using the drug, deterioration occurs in the form of irritation, increased pain, then it is better to stop taking this medication and switch to more gentle means as prescribed by the treating dentist.
Pharmacy products for flux processing
The pharmacy offers a wide range of solutions that can be used for diseases of the oral cavity. So, suitable for rinsing:
- Chlorhexidine. Aqueous composition that does not require additional dilution. It is allowed to use it five to six times a day. But under no circumstances should you swallow!
- Miramistin. Chlorhexidine substitute. Shows pronounced antiseptic properties. Accelerates the regeneration of affected tissues. It is often combined with oral antibiotics.
- Furacilin. Antimicrobial agent, nitrofuran derivative. Active against a number of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. You need to take one crushed tablet per glass of water.
- Betadine. Antiseptic containing iodine. If a person has a thyroid disease or is allergic to iodine products, this medicine will not suit him. Dissolve a tablespoon of Betadine in a glass of water. The only thing you need to remember is that the medicine can stain the enamel yellowish.
- Rotokan. Alcohol composition based on chamomile, calendula, yarrow. You need to take one tablespoon per liter of water. Dentists recommend using the solution at intervals of three hours.
- Malavit. A preparation containing silver and copper ions. A very powerful, yet safe antiseptic. Destroys pathogenic microflora. If you use it to remove flux, the swelling will quickly go away. You only need to add ten drops of Malavit to a glass of water. There is no need to swallow it.
It is optimal if the dentist selects the medicine for rinsing. With periostitis, any amateur activity is unacceptable.
Types of disease
Flux is classified according to its development into the following types:
- Odontogenic. Pathology occurs against the background of advanced diseases of teeth and gums,
- Hematogenous. The disease develops when infection penetrates through the circulatory system.
- Lymphogenic. The cause of the disease is pathogenic microorganisms in the lymphatic system.
- Traumatic. Flux occurs at the site of injury to the periosteum, often after unsuccessful dental procedures during dental treatment.
According to the degree of spread, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- An ordinary flux that does not affect the periosteum.
- Fibrous flux, characterized by the onset of inflammation in the tissues of the periosteum.
- Orthodogenic flux, which develops as a complication - osteomyelitis, which requires tooth extraction.
- Albuminous flux, characterized by a chronic course, subfertile temperature and the occurrence of suppuration.