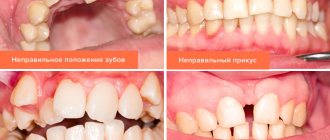
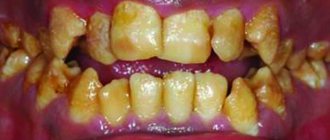
The lateral and chewing teeth take the most active part in the process of biting and chewing food, and therefore crowns on chewing teeth should be installed from the most durable materials. Metal-ceramics are suitable as a prosthesis for the restoration of chewing teeth; the best metal crowns for chewing teeth are also widely used, allowing them to withstand the heaviest loads. A chewing tooth implant is usually made of titanium. For many patients, the aesthetic side of treatment is of paramount importance, especially when it comes to restoring the front teeth, while function fades into the background. This position cannot guarantee a long-term result, since if the functional component is violated, sooner or later the aesthetics begin to suffer. That is why modern restorative dentistry is aimed not only at creating ideal aesthetics, but also at completely restoring lost function.
Bridge prosthetics
The principle of installing a bridge is simple and known to many - adjacent teeth are ground down, a structure is made of three crowns - two “empty” and one solid in the middle. Empty crowns are used to cover ground teeth, and the structure is attached to dental cement. A full-bodied crown replaces a missing tooth in a row.
Advantages of the method: fast, inexpensive.
Disadvantages: traumatization of healthy teeth, since in most cases they need not only to be ground for a prosthesis, but also to be depulped. Injured teeth can soon cause new problems, and you will have to worry about restoring your dentition again.
Dental clinic No. 2
The use of composite materials to restore the shape and function of chewing teeth that have been subjected to various types of diseases, injuries and abrasion is becoming increasingly popular.
Recent studies have proven that the longevity of restorations depends not only on how the tooth is restored, but also on many other factors, such as: the patient's exposure to dental caries, the location of the tooth in the dentition, the patient's habits, the number of affected tooth surfaces, the quality of adhesion and the ability of the material to form a continuous connection at the restoration/tooth interface.
This means that successful restoration of distal teeth depends on the skill and experience of the doctor.
This article will review a clinical case of this procedure with the goal of creating a daily treatment protocol. This will allow the clinician to pay attention to many details when working with composite materials, avoid various technological errors and achieve high quality restorations.
This treatment protocol has 6 points:
Diagnostics and control of initial occlusal contacts Isolation and separation of adjacent teeth with wedges Modeling of the cavity and its finishing Restoration of contact points and occlusal surface Staining of fissures (optional) and imparting secondary and tertiary anatomy Grinding, polishing and alignment of occlusal relationships
Initial data: carious lesions located on both premolars and molars, the presence of old, unaesthetic and non-functional restorations to be replaced on teeth 1.6, 1.7
The existing occlusal contacts were checked using 40 micron thick articulating paper. This allows the doctor to determine how the teeth meet their antagonists in order to properly prepare and restore the tooth.
A rubber dam is used to isolate the working field. In cases of distal restorations, I prefer to apply it to the entire quadrant. This technique provides the doctor and his assistant with better visual and manual control during the treatment process. The teeth were cleaned with brushes, paste and airflow to remove plaque and dyes. This procedure is mandatory because it prevents contamination during subsequent stages of treatment.
Wedging the teeth even before starting preparation is a very important point because:
Provides protection for the proximal parts of the rubber dam from damage during preparation. The wedges move the rubber dam and gum more apically. Provides separation of teeth, which facilitates the preparation of their proximal surfaces.
The cavity modeling process includes three stages:
Providing access. Necroectomy. Creating a fold.
Most often, to create access to the cavity, I use a bur, the working part of which has the shape of a rounded cylinder with a diameter of 0.9 mm.
For necroectomy I use carbide burs in combination with a mechanical handpiece
I finish the cavity preparation by creating a rebate. This will ensure the future restoration has reliable integration with the dental tissues. For these purposes, it is important to use only low abrasive burs. At this stage, I prefer to use an Arkansas stone and a micromotor at low speeds. The main rule of cavity modeling is that the process should start at high speeds using water-air cooling and end at low speeds without water
Type of modeled cavities. Wedges were very useful in proximal preparations
The proximal wall was reconstructed using a metal matrix and ring. First I install the matrix, then the wedge, after which I use two small pieces of Teflon tape to better fit the matrix to the tooth, and then I secure it all with a V-ring
The matrix is in place. Also at this stage it is important to correctly select the height of the matrix in order to subsequently obtain the proximal ridge we need
Once we have restored the contact point, we can remove the matrix and begin creating the occlusal surface, guided by the original tooth anatomy
In the case of the second premolar, we used only a matrix, a wedge and a Teflon film. As mentioned above, the Teflon film provides a better fit of the matrix to the proximal surface of the tooth, and also helps the doctor fill the mesial cavity of the adjacent molar
Both premolars have been restored. At this point you can finish the restorations before working on the molars.
Matrix for molar. For the aesthetics of the future restoration, it is important that the height of the molar matrix corresponds in height to the proximal ridge of the premolar
View of the proximal ridges immediately after removal of the matrix and ring
For finishing I also prefer to use Arkansas stone, carbide burs and rubber discs. If desired, after this procedure you can apply paints to the occlusal surface. Here I used brown
Occlusal relationships were checked using 40 micron thick articulation paper. Both static and dynamic samples must be taken into account during this procedure
Final view of the restoration. Polishing was done using a cotton wheel, aluminum oxide paste and water. Using this protocol you can achieve excellent surface polishing
Author of the article: Dan Lazar
Removable dentures
Removable orthopedic structures can be made from various materials - nylon, acrylic, plastic with a metal base, etc. They can be used in cases where there is nothing to attach the bridge to, that is, to solve the problem of an end defect.
Advantages of the method: affordable price, no trauma to hard tissues or mucous membranes, the ability to correct the end defect.
Disadvantages: lack of comfort, long habituation, hygiene requires daily removal of the prosthesis and its cleaning outside the oral cavity, relatively short service life.
Methods
In dentistry, there are two methods of artistic restoration:
- direct way,
- indirect method.
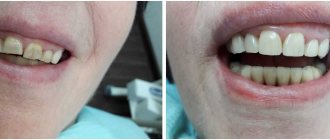
Direct restoration is provided immediately at the time of the visit to the doctor; the time frame fits into one visit. For restoration, high-quality composite filling materials are used that match the natural shade of the enamel. Modern composite materials harden under the influence of light, have X-ray contrast, and are optimally suited for restoring the aesthetics and functionality of both anterior and posterior teeth.
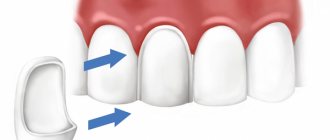
The indirect method involves the use of lumineers, veneers or half-crowns. Before installation, the tooth is slightly ground down, then an impression is taken from it, which is then used to make the onlay.
The doctor determines the appropriate method depending on the problems to be solved and the clinical picture.
Classic implantation
If one tooth or several scattered defects are missing, you can use classic dental implantation. Its essence lies in the fact that an implant is surgically installed in place of the extracted tooth and takes root without any load. After complete engraftment, which is after 2-4 months for the lower jaw, and after 3-5 months for the upper jaw, the patient is given permanent prosthetics. It is important to choose strong and durable materials for prosthetics. So, for example, ceramics are not suitable for the chewing zone - they are aesthetic and very naturalistic in appearance; they will not withstand chewing loads for a long time. In this case, metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide are well suited as prostheses. Zirconium can be used on absolutely everyone, and metal ceramics can only be used on patients who do not have allergic reactions to metals.
Advantages of the method: reliability, durability, no trauma to other teeth in the row, absolute comfort in using dentures on implants.
Disadvantages: the need for surgical intervention, high cost compared to conventional prosthetics.
Restoration of chewing teeth
Chewing teeth perform a vital function in the digestive process: chewing food. That is why they are in a state of constant stress and more often than other teeth are subject to destruction. A restoration procedure will help stop the destruction process and restore the appearance and functionality of chewing teeth.
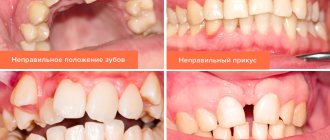
Restoring lateral teeth has its own difficulties. When building up, restoration is very important, taking into account all the cusps of the occlusal surface, the shape of the entire tooth and compliance with the bite.
Aesthetic restoration is divided into 2 methods: direct and indirect. Direct restoration is most convenient for patients because it is cheaper and faster. Extensions with composites and compomers are performed in one visit to the clinic. Compomers strengthen tooth enamel due to the fluoride released, and composites are fixed to the teeth using a special glue.
Indirect restoration of posterior teeth will be more expensive and take more time. But such restoration is much more durable.
Single-stage implantation
Separately, it is worth mentioning about one-stage dental implantation in the chewing zone. If at a dentist's appointment you hear a disappointing verdict that a tooth needs to be removed, do not rush to the surgeon's office. Find out from your dentist if there are any indications for immediate implantation in your case.
This is a protocol that is minimally invasive. The problematic tooth is removed and an implant is immediately inserted into the fresh socket. There is no need to cut the mucosa and apply stitches. In addition, one-stage implantation saves time, since the patient does not need to wait for the wound to heal after removal so that classical implantation can be done.
Advantages of the method: minimal trauma among all implantation protocols, reliability, longevity of the result.
Disadvantages: not suitable for all patients. If the bone tissue under the diseased teeth is destroyed or thinned out, it will not be possible to place an implant at once.
ALTERNATIVE METHODS
In the absence of lateral chewing teeth, only removable prosthetics can be considered as an alternative technique. It is often not possible to install a bridge. To fasten it, two teeth are needed - and the end defect of the row is characterized by the presence of support on only one side. That is why the only solution is a removable denture fixed to the gums and partially preserved teeth.
A removable denture is a fairly inexpensive design that is accessible to a large number of patients from a financial point of view. But if we consider its effectiveness, we can highlight quite a few negative aspects of wearing it:
- discomfort - the prosthesis has a fairly massive acrylic gum, so it can rub and put pressure on the gums, especially during the period of adaptation,
- quite poor fixation - often patients need to use additional means (glue, ointment, gel),
- no load on the bone - it sags and atrophies because it does not receive pressure, so over time the prosthesis will be attached unevenly, and frequent relining will be necessary.
If you choose between a removable denture and a denture fixed on implants to restore chewing teeth, the second option is more preferable. In terms of comfort, durability, functionality and normalization of the entire jaw system.
1 According to the World Health Organization (WHO). 2 According to wikipedia.org.
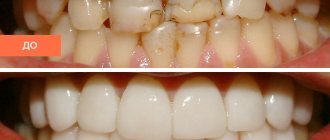
Filling as part of caries treatment
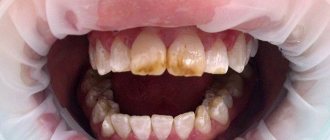
The cause of molar destruction is most often caries, which usually develops due to abundant accumulations of plaque and hard deposits - the result of insufficient cleaning and hygiene. As a result, the tooth gradually deteriorates, and before the infection reaches the nerve, it is important to begin treatment as soon as possible. At the appointment, the dentist will remove all necrotic and damaged tissue, perform an antiseptic treatment and begin restoring the integrity of the crown.
Source: dentalperfection.in
Today, modern photopolymer materials are used for this purpose - such composites harden under the influence of a special polymerizing lamp. This property allows you to apply the material in layers to return the crown to its original appearance - it helps to recreate the anatomical relief as accurately as possible to restore the aesthetics and functionality of the tooth. In addition, photopolymers are durable and wear-resistant - their service life can reach 20 years, of course, with proper and regular care.
Prosthetics with crowns - on a pin or stump tab
If caries is not treated in time, sooner or later the pathological process will reach the pulp - the neurovascular bundle. The main characteristic symptom in this case will be acute pain. In such a situation, most often it is necessary to completely remove the nerve , clean and fill the canals, although sometimes in the early stages it is possible to relieve inflammation with medication.
If by the time you go to the doctor the tooth is already too badly damaged, then the restoration tab will not hold well. In such a situation, you can choose prosthetics with an artificial crown, and for the restoration of the distal parts, metal prostheses, metal-ceramics, zirconium or ceramic composite are usually chosen. It is important that the material is as durable as possible, even at the expense of aesthetics.
If the walls of the visible part of the tooth are preserved and the root is in satisfactory condition, the prosthetic procedure will be carried out in one of the following ways:
Source: dentalsolutions.ru
- with pin installation : to securely fix a single prosthesis, a pin is first inserted into the root canal. Today, strong, but at the same time quite elastic, fiberglass structures are more often used for this purpose, although a metal anchor pin can also be chosen for molars. The fiberglass product usually does not exceed 2 mm in diameter. In appearance, it is a thin matte rod, which becomes the connecting link between the root and the artificial crown,
- on a stump tab : unlike a restoration tab, this tab partially replaces the root system. This is a stronger and more reliable design, which is used when the coronal part is completely destroyed, but subject to the preservation of the root. The lower end of the product is inserted into the root canal, and the tip remains above the gum and serves as a support for the prosthesis.
Source: anzub.ru
What problems are encountered during mandibular implantation?
When restoring teeth in the lower jaw, it is necessary to clarify the location of the vessels and the mandibular nerve on it. Before the procedure, a computed tomography scan is required to determine the topography of the nerve and plan the location of the implants so as not to damage it in any way.
The loss of bone tissue in the lower jaw is smaller. For implantation, bone splitting or special thinner implants are often used. Their engraftment is faster than on the top one. And this is the key difference when implanting both jaws.
Frequently asked questions about composite restorations
- What determines the success of dental restoration?
From the quality of the chosen material for restoration, the qualifications of the doctor. Before choosing a specialist in the field of restoration, familiarize yourself in detail with his work and reviews. - Are there any contraindications for dental restoration?
In general, there are almost no disadvantages to the restoration. With the exception of complex diseases of organs and blood. - Is it possible to resort to artistic composite dental restoration if patients want the “Hollywood smile” effect, but are not ready to spend money on ceramic veneers?
Yes, you can. At a free preliminary consultation, the dentist will determine the number of teeth that need restoration.
How does bone grafting proceed in the lateral parts of the jaw?
The sinus lift procedure on the upper jaw, according to our observations, is required in 80-90% of cases. In most cases, we use a protocol in which sinus lift is performed simultaneously with implantation. This allows you to reduce treatment time.
Sinus lift surgery can be closed or open. The closed type is more gentle and is easier to tolerate by the body.
When creating a bed for an implant, the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus is lifted with a special tool and a limited amount of biomass is placed into the resulting cavity. Then implantation is performed. The implant takes root as the bone matures. The process takes 5-6 months.
Open sinus lift takes longer. A “window” is cut into the maxillary sinus from the side of the jaw, and then an osteoplastic mass is placed into the cavity, the hole is closed with a bioresorbable membrane and sutured with a gum flap. The engraftment period is 6-7 months.
In the lower jaw, bone grafting is performed using other methods. This is due to the predominant decrease not in the height of the bone, but in the width. To get rid of this deficiency, most often the bone is split and a non-load-bearing implant is implanted. The implantologist will be able to tell you after diagnosis which method of bone grafting is suitable in your case, and whether this procedure can be avoided and teeth implanted in one visit. Come for a consultation!