How teeth are cut: the order in which they appear
Every adult can understand how a baby feels when his first teeth are cut - just remember how the so-called “wisdom teeth” appeared.
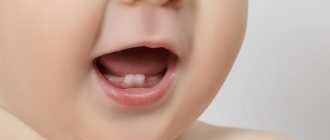
Swelling of the gums, itching and pain - you must admit, this is not pleasant. Therefore, infants often become capricious during the teething process. They may lose appetite and sleep, and even have a slight rise in temperature. The earliest time for baby teeth to erupt is at the incisors (front teeth). There are four of them on each jaw. As a rule, the lower two incisors erupt first (at 6-8 months), then the upper central incisors. The teeth appear in pairs opposite to each other, this is important for the formation of a correct primary bite. At 8-12 months, the baby develops lateral incisors (first on the lower jaw, then on the upper). At one year old, a child should have eight teeth. After this there is a short break in their appearance.
Next in the sequence are fangs. There are two of them on each jaw. The location and structure of these teeth makes their eruption especially difficult and difficult for the child. At the age of 16-20 months, fangs will appear on the lower jaw, and then on the upper jaw. Then comes the turn of the painters (large molars). They begin to erupt at 20-30 months, each child at its own time. There are a total of 20 teeth in the primary occlusion, 10 on each jaw: 4 incisors, 2 canines and 4 painters. All of them should appear by 2.5-3 years.
Stool color in children - the norm and its variations
When breastfeeding, your stool should be yellow or apricot in color.
The stool of children and adults is colored by the bile pigment bilirubin, a derivative of erythrocytes, red blood cells. The liver filters out this pigment, then removes it through the bladder and intestines. It is considered normal for children's stool to be brown in various shades.
If this is the stool of a newborn or a baby under one year of breastfeeding, then it is predominantly yellow or apricot in color. For bottle-fed or mixed-fed babies, a cream, brown or gray tint is added to the traditional color, depending on the type of complementary foods or formula.
In children older than one year, the color of the stool can be affected by the foods the baby eats. Thus, beets give the contents of the pot a red color, carrots give them a bright orange color, and drugs taken for anemia turn them dark brown or black. The predominance of meat products in baby food also turns the stool dark brown.
Signs of teething
How can parents understand that their child is teething? The easiest way to find out about this is by the child’s changed behavior. He sleeps worse and is capricious. He loses his appetite (may completely refuse to eat). But similar symptoms can be caused by other reasons. Therefore, the most obvious sign can be considered swelling of the gums (a small red bump appears on it, which parents can feel rather than see).
The child's changed behavior is associated with the movement of the tooth in the jaw. It seems to tear the gums from the inside, which explains the unpleasant sensations: itching, burning and pain. To remove them, the child can scratch his gums, pull various objects into his mouth, and bite. You cannot stop this behavior; you just need to replace inappropriate objects (for example, toys) with special teethers, the purpose of which is to help relieve the unpleasant consequences of teething.
It is because of the unpleasant sensations that the child may begin to refuse food, especially hot food (increases the pain). A light massage of the gums may help, which should be performed before feeding. It will relieve some of the itching and pain.
During teething, the baby's temperature can rise to 38º, but not higher. Until the teeth appear, parents should pay as much attention to the child as possible, distracting him from unpleasant sensations. This will help the baby get through a difficult time for him.
Refusal of complementary feeding
Many parents anxiously await the period of introducing complementary foods, as they associate it with the next stage in the baby’s development, his maturation and the emergence of new skills. Most usually already have a clear action plan: when to introduce complementary foods, where to start, how much to give. And this is absolutely correct, because the timely introduction of complementary foods with the inclusion of all necessary products in the child’s diet is the key to his further successful development.
But the wishes of the parents do not always coincide with the needs or capabilities of the child. Unfortunately, sometimes it is during this period that parents have many problems and disappointments, among which the most common is the child’s refusal to accept medication.
With what it can be connected?
Let's try together to understand some of the reasons for this condition.
There are 2 groups of reasons: organizational and medical.
Organizational reasons
- Complementary feeding started early
There is no exact figure for when complementary feeding should be introduced, since this process is very individual and depends on the general maturity of the child and his readiness to assimilate new and dense foods. It is known for sure that complementary feeding should not be introduced before 4 months. It is important that by the time complementary foods are introduced, the child’s spoon-pushing reflex has died down, and food interest and the ability to swallow thick foods have been developed. Early introduction of complementary foods can cause choking, frighten the child and delay his further interest in new foods.
What to do?
You can temporarily postpone the introduction of complementary foods to a later time.
- Complementary feeding started late
The introduction of complementary foods after 6-7 months is considered late. Many children are conservatives, and the later complementary feeding is introduced, the more cautious they are about new food, reluctant to accept it, preferring their mother’s usual breast or bottle with formula.
What to do?
Try to regularly offer your child new foods, developing his interest in food, take him with you to the table during family meals, allow him to take food from your plate with his hands, etc.
- The desire to feed the child at any cost
The biggest mistake parents make is trying to feed their child at any cost. When parents know the norm for consumption of certain foods (which is correct), it often plays a cruel joke on them: they try to forcefully give the child exactly this amount of food, without taking into account the individual needs of the baby. Violence during meals is unacceptable, since it can subsequently lead to persistent eating disorders, up to the child’s complete refusal to eat or to very strong selectivity in food.
What to do?
Completely eliminate any violence while eating. For example, violence includes: feeding with blindfolds, feeding with a syringe, feeding with cartoons/toys/gadgets.
It is very important to feed the baby in a calm environment, without any distraction from food. If the baby refuses to eat, then he should be quietly removed from the table until the next meal (in 3-3.5 hours), without offering any snacks during this interval.
- Having snacks between meals.
This is one of the main reasons for refusing complementary foods.
If the child’s appetite is reduced or he refuses to eat during the main meals, parents try to feed him “at least something” during the breaks. But the notorious “let him eat at least something” leads to a new problem: the baby eats and demands only sweets or only a very limited amount of food (cookies, curds, fruit spiders, dried fruit, etc.).
What to do?
A child who refuses complementary feeding should not be given any snacks between meals, even if he has eaten very little or has refused to eat at all.
The child can and should be allowed not to finish his allotted portion.
If the child does not express a desire to eat, then you can even skip feeding (and more than one!),
It is important not to be afraid of leaving your child hungry : it is much worse to strengthen in him the habit of sweet snacks, selectivity and refusal of “normal” food. This can subsequently lead to eating disorders and become a huge problem for parents.
- Lack of variety in food, incl. in its consistency and appearance.
Sometimes parents are afraid to expand their child’s diet and give their child the same porridge or vegetables for weeks. Often the baby receives food directly from a jar of baby food. Such monotony in food, lack of variety in tastes and textures certainly does not increase the child’s appetite and reduces the baby’s food interest.
What to do?
It is important to regularly introduce your child to new tastes and introduce a new product into his diet every 5-7 days.
Also, you should not give food directly from a jar, but rather put the food in a beautiful plate.
It is important to periodically offer the child different consistencies of the dish: make it either thinner or thicker, in order to develop the baby’s preferences.
The temperature of the dish also matters: it should not be too hot or very cold.
It is important to remember that the child has his own individual preferences for the taste, consistency and temperature of the dish.
Medical reasons
A child may refuse complementary feeding if he has any health problems, for example:
- The child is sick or becomes ill
At the onset of any infectious disease, the baby's appetite may decrease.
What to do?
There is no need to insist on complementary feeding. During this period, it is important to give the baby plain water, offer the breast more often, or give only formula milk at the baby’s request.
- Baby is cutting teeth
Severe pain during teething can be very disturbing for the child and can also lead to a complete refusal of dense foods.
What to do?
Do not insist on complementary feeding. During this period, give the child, at his request, only liquid food (breast milk, formula, liquid porridge).
- The child was vaccinated the day before
For several days after vaccination, the child may have a slight malaise and fever, which can lead to a decrease in appetite and refusal to feed complementary foods.
What to do?
Do not insist on complementary feeding, but give only liquid food at the child’s request
- The child has digestive problems that cause general discomfort during or after eating (constipation, abdominal pain, increased flatulence, regurgitation, enzyme deficiency, including lactase deficiency)
What to do?
It is important to consult with a specialist, find out the cause of existing complaints, carry out diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- The child has neurological problems and has difficulty swallowing thick foods.
What to do?
Consult with a specialist.
Dear parents, it is important to remember that food is not just about calories, but also about our respect for the child, his needs and desires. Food should not be a cult and a super task, but should bring joy and pleasure to develop healthy eating behavior in a child.
Lukoyanova Olga Leonidovna
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Leading Researcher of the Laboratory of Nutrition of Healthy and Sick Children of the Federal State Institution "National Medical Research Center for Children's Health" of the Ministry of Health of Russia
Replacing baby teeth with permanent teeth
Eruption of molars begins at the age of 6-7 years. First, the large molars are shown (usually on the lower jaw). Then the pattern of baby teeth eruption is repeated. The incisors on the lower jaw are the first to change, and at the age of 7-8 years, the incisors on the upper jaw are also replaced. At the same time, the lower lateral incisors can also change.
At 8-9 years old, the upper incisors will change. It's the fangs' turn. At the same time (9-10 years), teeth that were not in the primary occlusion - premolars - begin to grow. There are four premolars on each jaw - two on the left and two on the right. At the age of 12, the fangs on the upper jaw will change. At this stage, the formation of the height of the bite begins, which has both aesthetic and functional significance.
The last teeth (wisdom teeth or third molars) appear between the ages of 17 and 25. Only after this can we say that the formation of the dental arches is completely completed.
When replacing baby teeth with permanent molars, it is important to pay attention to the bite. It is easy to correct at a young age, while adults will have to correct it throughout their lives. By regularly visiting a pediatric dentist, you can intervene in the process of bite formation in a timely manner. In addition, a specialist can monitor the eruption of baby and molar teeth (so that it is not too early or late), give recommendations to alleviate the child’s condition, and recommend special baby suppositories or gels for teething.
Changing your diet as a cause of light stools
The appearance of light-colored stools is usually very alarming for parents, but often the reason for this may simply be changes in the children's menu. Most often this is the consumption the day before of a large amount of dairy food with a high percentage of fat content - undiluted homemade milk, cream, cottage cheese, sour cream, fermented milk drinks. They can give the stool a light yellow or light cream tint.
The same color of stool may appear when a child eats a large amount of sweets. If the child feels well, does not show anxiety, there is no fever or abdominal pain, it is worth observing the stool for 1-2 days. Usually, after adjusting the diet, this symptom disappears.
Rotavirus infection and the contents of a child's potty
Fever and vomiting may be symptoms of rotavirus infection.
If, in addition to a change in the color of the stool, a child experiences an increase in temperature, as well as signs of intoxication such as diarrhea or vomiting (usually both of these signs), then it is quite possible that he has a rotavirus infection.
The stool changes color from light yellow on the first day to gray-white in the next two to three days. In addition to these symptoms, respiratory manifestations may appear: redness of the throat, runny nose, cough, as well as headache and abdominal pain.
Symptoms of teething in a baby:
- ♦The gums are red/white and swollen;
- ♦Salivation has clearly increased;
- ♦Redness/rash appeared around the mouth (due to a large amount of saliva);
- ♦The baby pulls into his mouth and bites all kinds of objects (rattles, pens, daddy’s glasses);
- ♦A runny nose may appear;
- ♦Slight dilution of stool (again due to increased salivation);
- ♦Appetite may worsen (due to pain in the mouth);
- ♦And also the baby has become noticeably more capricious, his sleep is more restless, his mother’s warmth and care are more needed (“hangs in his arms”).
It is important to remember that this period is temporary and will end. Be patient, gather your willpower and try to help your child survive this process. The mother’s actions to permanently return the former dream to the family are the same as during the child’s illness.
And now the important information. Key, I would say! Attention!
Dysbacteriosis and light stools
Dysbacteriosis in children can occur after taking antibiotics.
One of the side effects of taking antibiotics can be dysbiosis - a change in the balance of microflora in the intestines and stomach towards the predominance of pathogenic bacteria. This condition is manifested by a violation of the usual stool consistency, alternating diarrhea and constipation, and the appearance of light-colored stools with pieces of undigested food and mucus.
Loss of appetite, restless sleep, weight loss due to dysbiosis are also common. You should not attempt to correct this condition on your own; you should consult a gastroenterologist.
Most likely, he will advise taking prebiotics (Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin, Acipol), after which the stool should take on a normal color and consistency.
Light-colored stools are a reason to get tested for hepatitis
Hepatitis can cause changes in a child's stool.
It is this reason that the child’s parents try to exclude when they see white stool, which is one of the signs of infection with the hepatitis virus. In addition, the following symptoms may be present:
- darkening of urine (dark beer color)
- pain in the right upper abdomen and severe bloating
- yellowing of the skin
- yellowing of the sclera of the eyes
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- heat.
To clarify the diagnosis, you need to contact a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist. Most likely, they will order laboratory tests to clarify the diagnosis. Hepatitis can also have a smoothed course, when there are no other symptoms except increased fatigue and pain in the right hypochondrium.
How to distinguish teething from bad sleep in principle?
Let's be honest with ourselves and check the following points:
- ♦You monitor your child’s routine: avoid over-excitement, overstimulation before bed, and maintain sleep hygiene. But the dream suddenly deteriorated for no apparent reason;
- ♦The baby feels unwell throughout the day, and not just when trying to put him to sleep and at night;
- ♦Time passes, but the situation does not change. We remember! Teething lasts 2-5 days. (An exception may be molars). I repeat: 2-5 days. Not a month, not six months!
Therefore, if your pediatrician reassures you that your whole family has not been sleeping for two months now because of a tooth, it makes sense to think about replacing it. And a reason to contact our Children's Sleep Center for help from a sleep consultant
Vera Borisovets Senior supervisor
Medicines that change stool color
This symptom may be a side effect when using certain categories of medications. Stool becomes discolored due to the liver's reaction to certain medications. They may be:
- Paracetamol
- Acetylsalicylic acid derivatives: Aspirin, Laspal
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesulide
- Antifungal: Griseofulvin
- Antiepileptic drugs: Acediprol, Valproic acid, Convulex, Leptilan
If such a reaction to the use of drugs occurs, you should consult with the specialist who prescribed the treatment in order to avoid complications for the liver and gastrointestinal tract.