Fast passage
Colds Influenza Infectious mononucleosis Labial herpes (herpes on the lips, cold sores on the lips) Herpes aphthous stomatitis Enteroviral stomatitis
Conditions that we used to call “colds” are most often affected by young children who do not yet have antibodies to respiratory viruses due to their early age. Over time, such antibodies developed in children who have recovered from the disease become their natural defense. The only acute respiratory viral infection that can be protected against through vaccination is influenza.
According to statistics, a child from birth to school can get ARVI more than 50 times (from 6-8 times a year). To date, more than 200 types of viruses that cause colds have been identified.
Most often, colds are observed in young children who have just started attending kindergarten (and in younger schoolchildren who have not attended kindergarten, have not been exposed to certain viruses and do not have immune protection). At this time, the usual complaints of parents at a pediatrician’s appointment are complaints about the caretakers’ oversight: “hypercooled,” “blown,” etc. In fact, the role of hypothermia and drafts in the development of colds is no longer seriously considered by science.
“Cold” (eng. - cold) is most often associated with a large-scale exchange of viruses between children in large children's groups.
Kindergartens, development centers, sports sections and even outdoor playgrounds are an excellent “collective reservoir” of infectious pathogens, and young children who are not yet accustomed to personal hygiene are super-spreaders (in many cases asymptomatic) of various respiratory viruses.
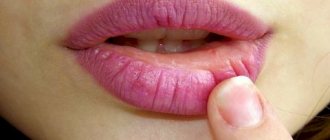
Symptoms and treatment of lip jams in adults and children
The popular name for angulite is zaeda.
The disease is characterized by the presence of cracks in the corners of the mouth, erosion and irritation. In some cases, slight bleeding may occur. Common causes of sticking at the corners of the mouth include infection, irritation, and damage to the skin at the corners of the lips. Angulitis is rare in children. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in adults. Predisposing factors:
- decreased general immunity;
- deficiency of B vitamins;
- the presence of a bacterial infection;
- habit of licking lips, malocclusion;
- hypothermia;
- long-term use of corticosteroid drugs;
- eating unwashed vegetables and fruits;
- presence of caries;
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, anemia, HIV, liver disease).
Your pediatrician will tell you at your appointment what causes seizures in babies.
Cold
The first symptoms of a cold most often manifest themselves in the form of a sore and sore throat, nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, and cough. They usually occur 2–3 days after exposure to a virus (usually rhinovirus). The child may look lethargic, complain of increased fatigue, headaches and muscle pain, eat poorly or refuse to eat at all, and have a fever.
There is no specific treatment for colds (there are no proven effective drugs). To relieve headaches, muscle pain, and reduce high fever, the child can be given paracetamol or ibuprofen (children over 3 months).
Attention: aspirin should not be given to children! The dosage of such medications should be recommended by a doctor. Always follow the instructions for the drug if a quick consultation with a pediatrician is not possible.
There is no evidence that over-the-counter antihistamines and decongestants (decongestants) provide relief in children under 6 years of age. Moreover, medications containing decongestants can cause unwanted side effects in young children, ranging from increased excitability and hallucinations to abnormal heart rates, especially in infants.
It is very important that during illness the child drinks a lot (the best option is clean drinking water, but you can offer what he likes best - juices, compotes). Ventilate the room regularly, use a humidifier, and rinse the child's nose with saline solution. Children over 1 year of age can be given honey (no more than half a teaspoon); rubbing the chest with menthol ointments to relieve cough is not recommended for children under 2 years of age. Cough lozenges or tablets are recommended for children over 4 years of age; a small child may choke on them. Do not use multi-ingredient over-the-counter cold and cough medicines if your child is under 6 years of age. They are ineffective and can cause serious side effects. The use of such drugs is questionable in principle, but it is also important to understand that they may contain paracetamol and lead to an overdose if you have already given it to a child.
For colds in children, the use of alternative treatments (echinacea, etc.), increased doses of zinc or vitamin C has been proven ineffective. They do not relieve or reduce symptoms and can cause severe side effects in young children.
If your child's condition does not improve after 3 days from the onset of symptoms, make an appointment with your pediatrician. An examination is necessary to exclude other diseases (streptococcal infection, sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia) and prescribe adequate treatment.
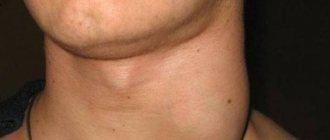
See your doctor immediately if you have the following symptoms: cough with a lot of mucus, difficulty breathing, severe weakness, vomiting, dehydration, severe sore throat, fever of 39 °C or more, fever for 24 hours or longer, abdominal pain, pain in the ears, enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
Types of angulite
Considering the etiology, seizures can be primary and secondary. In turn, the primary ones are divided into: streptococcal, viral and candidiasis.
Viral seizures. They are caused by a viral infection (herpes virus). In this case, a doctor will help you choose an ointment for sticking in the corners of an adult’s lips.
Streptococcal seizures are caused by streptococcal infection. A characteristic manifestation is the formation of a yellowish-red crust.
Candidiasis angulitis. The cause is a fungal infection. This type is characterized by a chronic course and the absence of a crust.
About the disease
Herpetic infection is a collective concept that is used to refer to diseases that are provoked by different types of the virus of the same name.
Traditionally, in pediatric practice, pathology caused by type 1 is encountered. This is the so-called labial herpes (rash on the lips). Its peculiarity is its chronic course. It is impossible to completely get rid of the pathogen. With adequate treatment of a child with symptoms of labial herpes, stable remission can be achieved. However, at this time the virus “hides” in the nerve ganglia (ganglia), where it can remain inactive for as long as desired. When favorable conditions arise (primarily decreased appetite), it is activated again. Another common form of herpes infection that can occur in children is varicella (chickenpox). The disease is provoked by the herpes virus type 3. It is important to remember that after successful recovery, the pathogen also goes into a latent form and persists in the nerve ganglia. The risk for the patient may be a reoccurrence of the infection. The type 3 virus, when reactivated, can cause herpes zoster, which is characterized by a more pronounced clinical picture with a deterioration in the child’s well-being and the appearance of rashes along the intercostal nerves.
The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic have extensive experience in early diagnosis and treatment of all pathologies caused by herpes viruses. Doctors provide the necessary monitoring and quality treatment for children with any form of herpetic infection.
Angulitis during pregnancy: how to get rid of it
Pregnant women are very vulnerable to various infections. Risk factors in this case are vitamin deficiency and increased stress on the body.
Causes of angulitis during pregnancy:
- licking lips in the cold;
- allergic reactions;
- caries;
- dry lips;
- general decrease in immunity.
On our website Dobrobut.com you will find more information on this issue. Here you can make an appointment with a doctor, who will tell you how to get rid of the jam and which ointment is best to use in your case.
Causes of herpes
All variants of herpes infection occur against the background of the activity of the virus of the same name of different types. Since upon initial penetration into the human body the pathogen no longer leaves it, it is important to know the factors that can provoke the activation of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- seasonal colds;
- any conditions that provoke a decrease in immune defense (poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis and others);
- exacerbation of chronic somatic diseases;
- contact with an infected patient.
The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, so it is extremely difficult to completely prevent a child from encountering pathogenic particles.
Angulitis: clinical manifestations
The symptoms of angulitis are very similar to the manifestations of herpes, so it is extremely important to promptly contact a specialist who will make the correct diagnosis and tell you how to quickly cure angulitis.
Symptoms of seizure:
- redness in the corners of the mouth;
- cracks;
- multiple blisters with purulent contents;
- slight bleeding (not always);
- purulent crusts.
Treatment of lip jams in adults depends on the etiology and form (acute or chronic). It is very important to start treatment on time, because without it, the affected area can increase, causing significant discomfort to the patient.
Herpes symptoms
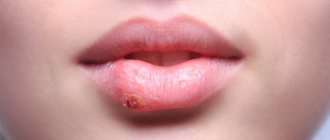
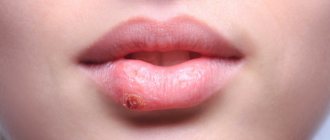
Labial herpes is the simplest and most harmless form of the disease, which occurs most often in children. Apart from discomfort for the baby and parents, in most cases the disease is not accompanied by serious consequences. Typical clinical picture:
- the formation of painful blisters filled with serous fluid in the lip area;
- itching and burning in places where skin elements appear;
- loss of appetite. Breasts may refuse to breastfeed due to pain during feeding;
- general weakness, lethargy, emotional lability;
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.5 ° C (rare).
With adequate treatment, signs of the disease can disappear after 3-4 days.
Chicken pox is a typical representative of “childhood infections”. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of rashes with serous contents throughout the body of a small patient. A characteristic feature that allows you to quickly differentiate chickenpox from other infectious pathologies is the obligatory presence of pustules on the scalp and the formation of crusts after removal of the blisters. The disease is also accompanied by a rise in body temperature to 38-39.5 ° C. The severity of the pathology depends on the individual characteristics of the child’s immune system and the aggressiveness of the pathogen.
Herpes zoster is accompanied by:
- the occurrence of rashes along the intercostal nerves;
- severe pain in the area where the pustules spread;
- high fever;
- pronounced general intoxication syndrome.
If you detect at least one of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. SM-Doctor specialists point out that chicken pox and herpes zoster are diseases that require isolation of a small patient in a hospital to monitor his condition and prevent the spread of the pathogen to other family members and the environment.
Diagnosis of the disease
Unfortunately, patients with angulitis very rarely turn to a specialist for help, but in vain. After all, the acute form of the disease is easier to cure, thereby preventing the disease from becoming chronic.
Required research:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood sugar test;
- biochemical analysis and liver tests;
- ELISA blood test for herpes viruses;
- blood test for syphilis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Consultation with highly specialized specialists may also be required.
Flu
An annual flu vaccination is the most reliable way to prevent severe disease and complications (otitis media, pneumonia) of the disease.
Vaccination of children against influenza is permitted from the age of six months.
Influenza is an acute respiratory viral disease caused by influenza viruses (usually types A or B; type C rarely causes serious symptoms). It is very easily transmitted from person to person, as confirmed by annual epidemics of the disease. People with the flu are most contagious in the 24 hours before symptoms appear and until symptoms subside (about a week).
The flu can be confused with a cold, but most often it is more severe. Symptoms - fever, chills, headache and muscle pain, runny nose, sore throat, cough, ear pain, loss of appetite, weakness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea - appear approximately 2 days after exposure to the virus.
Most children with the flu recover at home, but if the disease is severe or has complications, they will need hospital treatment.
There are no effective cures for the flu; it is necessary to ensure that the child drinks plenty of fluids and is not dehydrated, gets plenty of rest and sleep; in general, the same tactics are followed here as with any ARVI. To relieve flu symptoms (reduce fever and reduce pain), you can use paracetamol or ibuprofen, rinse your nose with saline solution (for infants, saline solution is dripped into the nose, an aspirator is used to remove nasal discharge), and monitor the level of humidity in the room.
Important: antibiotics are not used to treat influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections.
Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms worsen, severe cough, difficulty breathing, fever in children under 3 months of age that lasts longer than 3 days, headache that does not go away with paracetamol or ibuprofen, stiff neck ( meningeal symptom).
More details
Flu
Treatment of lip jams in adults
After examining the patient and studying the test results, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, usually consisting of medications (local or general action) and vitamin-mineral complexes. It is extremely important to give up bad habits and avoid irritating factors during treatment.
If there is an infection, the patient will be prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy (taking into account the type of pathogen). For a viral infection, antiviral drugs are recommended, and for candidiasis angulitis, antimycotic drugs, such as nystatin and lamicon. Trimistin and tetracycline are prescribed for mixed forms of the disease. All this applies to the treatment of the disease in adults. Your pediatrician will tell you how to treat jams in the corners of the mouth in children. After examining the baby, the pediatrician will prescribe drug therapy and suggest the most effective traditional medicine.
Treatment of herpes
SM-Doctor doctors select treatment for herpetic infection for each child individually.
Our specialists prescribe medications depending on the severity of the clinical picture of the pathology and the presence of concomitant diseases. The following means are traditionally used to combat the virus:
- acyclovir is a specific drug to destroy the pathogen;
- antipyretic medications (paracetamol, ibuprofen) for fever above 38°C;
- auxiliary medications (painkillers, antiallergic and others).
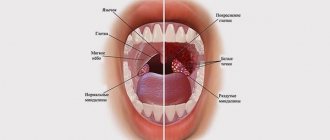
Herpes aphthous stomatitis
In children under 5 years of age, herpes simplex can affect the mouth, gums, and tongue (herpes aphthous stomatitis). In this condition, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity turns red, swells, the child begins to drool, small superficial ulcerations (aphthae) appear once within 1–2 days - single or grouped, the child becomes irritable, his gums swell, he complains of pain, loses appetite. The temperature usually rises (can reach 40°C) 1-2 days before the above symptoms.
After 3–14 days from the onset of symptoms, the child’s condition returns to normal, the temperature decreases, aphthae heal, inflammation and pain decrease, and appetite appears. With a more severe course, a repeated increase in temperature, aphthae may appear again, and the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged. Recovery in this case may take up to 10 days. A complication of herpes aphthous stomatitis can be the transition of the disease to a recurrent form. The addition of a bacterial infection can cause otitis media, bronchitis or pneumonia.
Treatment of herpes aphthous stomatitis is aimed at eliminating symptoms (lowering temperature, pain relief with paracetamol or ibuprofen, drinking plenty of fluids, rest). Rinsing with aseptic solutions, the use of local anesthetics, antiviral ointments for treating aphthae (acyclovir), steroids in the form of gels and pastes are prescribed. Local treatment with lidocaine-based anesthetic ointments should not be administered to young children.
Pediatric stomatitis
Treatment of mild herpetic stomatitis
Thanks to timely consultation with a doctor, the inflammatory phenomena subside within a week.
Antiseptic rinses (spray irrigation)
Antiseptic solutions destroy pathogenic microflora of the oral cavity, protecting against the addition of a secondary infection. Your doctor may prescribe rinsing 3-4 times a day for 15 minutes. Convenient to use spray irrigation when the child refuses rinsing. After using the antiseptic solution, you should refrain from eating for about an hour.
Pain relieving anti-inflammatory gel
Anesthetic gels contain an anesthetic solution. They are used to treat painful erosions before eating. The gel is applied for 5 minutes to the surface of the erosion in a thin layer.
Keratoplasty (drugs to stimulate mucosal healing)
After the inflammatory phenomena subside, oil solutions of vitamins are used for external use. They improve metabolic processes in the epithelium, which accelerates the healing of erosions. Sterile gauze wipes soaked in an oil solution are applied to the erosions for 7-10 minutes. After this, you should also refrain from eating so as not to remove the formed film from the erosion.
Treatment for the presence of lesions on the skin around the mouth and the red border of the lips
After the bubbles open, crusts form. Their mechanical removal provokes the formation of other bubbles. Crusts on the lips make it difficult to speak and eat. Violation of their integrity opens the bleeding mucosa.
Therefore, crusts must be treated with solutions of proteolytic enzymes to soften and remove them. Oil solutions of vitamins are also used to heal the skin and mucous membrane underneath. Lips are treated with moisturizing balms to prevent them from drying out.
Special food and feeding
Food should not further irritate the inflamed mucous membrane, therefore it is recommended:
- make food liquid, at room temperature;
- exclude sour, salty foods;
- Before eating, treat erosions with anesthetic gel.
Oral hygiene for stomatitis
Maintaining hygiene is one way to combat re-infection of the mucous membrane. Also, all treatment solutions must be applied to a clean surface. After each meal, it is necessary to rinse the mouth with plain water to prevent the development of pathogenic microflora.
The herpes simplex virus is contagious and can enter a child’s body through environmental objects (shared dishes, toys). Therefore, it is necessary to treat them and protect a child with herpetic stomatitis from contact with other children.