There are many reasons that worsen the condition of the oral cavity and teeth in children: poor hygiene, unlimited consumption of sweets, insufficient intake of vitamins. Against the background of these reasons, immunity decreases and the risk of oral diseases increases.
Main dental diseases in children
The first year of a child’s life can also present surprises to parents in the form of oral diseases. Most often, these are injuries to the oral mucosa, which still has a very delicate structure that can be easily damaged even by a soft pacifier. There is also a danger of developing fungal diseases or the appearance of herpetic stomatitis, sometimes even recurrent.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
Those manipulations that an adult is able to calmly endure will become the strongest test for a child, both physically and psychologically. Pain management in pediatric dentistry is given a special place, because the psychological trauma from pain received in childhood at a dentist’s appointment will accompany a person throughout his life, and the fear of the dental office will turn into a real phobia. The use of anesthesia by pediatric dentists will remove pain and, accordingly, fear of procedures.
The use of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry has a number of features:
- for the youngest there are restrictions on the use of most products that can be used from 4 years old;
- the doctor must have experience and high qualifications to accurately calculate the active drug;
- children are afraid of treatment of baby teeth , and in general of all dental instruments, especially syringes and injections;
- Quite often, children experience allergic reactions to anesthetic drugs.
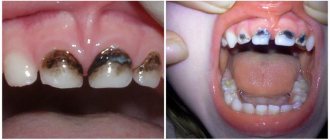
Caries
With the appearance of the first teeth, the most common disease is caries, which develops much faster at an early age than in adults. If you do not pay attention to it, untreated caries can provoke complications such as: pulpitis, periostitis and periodontitis, and they are serious diseases that require serious treatment. However, caries in children can be treated quickly and almost painlessly, and as we know, any disease is easier to prevent.
To maintain dental health in children, it is important for parents to pay attention to the following points:
- teach your child to maintain oral hygiene;
- monitor your diet, make it balanced, reduce the amount of sweets;
- Monitor the condition of the child’s teeth, contact a specialist at the first symptoms of caries.
At what age should a child be taken to the dentist for the first time?
According to the WHO schedule, you should go to the dentist for the first time when the child is 9 months old. Some doctors indicate an age of 11-12 months. During a dental examination, several parameters are assessed.
1. How many teeth are there?
Based on the number of teeth present, the child’s development is assessed and pathologies are diagnosed. It is normal for children to erupt 5-8 milk teeth by the age of 9-12 months.
2. What condition are the teeth in?
From the first days of teeth appearing there is a danger of caries. Also, teeth should be examined for non-carious lesions - hypoplasia, in order to exclude the appearance and development of caries.
3. What is the condition of the mucous membranes?
Small children put everything in their mouths, so they are at risk for infectious diseases - stomatitis and intestinal infections. The more common fungal form of stomatitis, which must be treated promptly to avoid complications.
At the age of 9-12 months, a dental examination is more necessary for preventive purposes. The doctor will tell you what toothpaste to use, what toothbrush to choose, and how to teach your child hygiene. Until the child reaches two or three years of age, visits to the dentist should be regular - every 3-5 months.
Thrush
With thrush, white spots first appear on the palate, tongue, cheeks, and lips on the inside, then they merge, forming a solid white coating. The disease is caused by yeast-like fungi, which, under the influence of unfavorable factors, exhibit their pathogenic effects. It is necessary to consult a doctor to eliminate the cause of the disease.
Dental clinic "Sanident" offers a wide range of dental services to preserve and maintain healthy baby teeth. If necessary, our highly qualified specialists provide consultations and carry out preventive measures to care for the child’s oral cavity. In our practice, we use only high-quality filling materials and find an individual approach to each little patient.
Dental clinic "Sanident" is located at the following addresses:
- Shchelkovo, st. Tsentralnaya, 80 (railway station Voronok);
- Ivanteevka, st. Novoselki, 4 (Ivanteevka railway station).
Do baby teeth need to be treated? What are the consequences of ignoring problematic baby teeth in the future?
The doctor’s answer to this question is clear, says FAN’s .
"Of course yes. Baby teeth need to be treated! If you leave everything to chance, the child will inevitably suffer from pain and discomfort. Moreover, it is advisable not to delay this process so that the little patient does not have a negative experience in dental treatment,” explains Victoria Arutyunova.
Of course, it is better to limit ourselves to preventive measures, but if, after all, time has already been lost, then therapeutic manipulations are absolutely necessary, since the infection gets into the tooth, and then through the nerves and canals it enters the bone and ultimately can infect and damage the germ of a new tooth . If this happens, then there are several scenarios for how the situation could develop further. The rudiment may die altogether and stop developing, or the tooth may erupt with a slight visual defect. Typically, this phenomenon is called enamel hypoplasia. In addition, possible complications include swelling, periostitis, inflammation of the gums with subsequent release of infection and pus and, accordingly, painful removal and an incision to drain the exudate.
Naturally, this procedure, which is unpleasant for the child, causes persistent negativity and provokes difficulties in further interaction with the pediatric dentist.
“In addition, during such removals, anesthesia may not work well, since the infectious exudate does not allow the anesthetic to penetrate deep enough. The child will remember such a visit for a long time, so it is better to treat without leading to such complications,” says our expert.
What are the consequences of a frivolous attitude towards children's health? If you still have to remove a baby tooth, the place will be empty, and nature, as we know, does not tolerate emptiness. As a result, neighboring teeth will begin to tilt towards the missing one. As a result, the further appearance of permanent teeth will be difficult; they will erupt in the wrong position and at the wrong time, which will cause orthodontic problems. With a high degree of probability, in the near future, parents will have to seek the services of an orthodontist to correct the situation with the help of plates or braces.
pixabay.com/
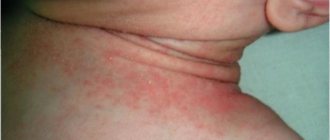
How to prevent gum disease
For the reasons listed above, we recommend that you:
- Closely monitor how thoroughly and correctly your child brushes his teeth;
- Use a special fingertip to massage the baby’s gums during teething;
- Explain to your child how important it is to actively chew food on both sides;
- Contribute to timely correction of bite and solution of other problems;
- Monitor the temperature of your baby's food and drink and ensure that he does not have the opportunity to injure the delicate gum tissue.
Modern pediatric dentistry believes that minimizing the unpleasant consequences of developing a serious disease by strengthening preventive measures is the easiest way to protect your child from diseases of the gums and other periodontal tissues.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry, types
1. Application of local anesthesia
Most often used. It is carried out in 2 stages - “freezing” with a gel or spray, after which the drug is injected. Typically, children of any age tolerate this type of anesthesia well. Sensitivity is not completely lost; minimum contraindications.
2. Use of sedation
A sedative is inhaled. The child relaxes, but remains conscious. This is not anesthesia in its “pure form”; there is no strong analgesic effect. It is often used with an injection of an anesthetic drug.
3. Use of general anesthesia
It is used in extreme cases, because the risk of complications after dental treatment under general anesthesia exceeds that with local anesthesia. The pediatric dentist must have good reasons for using general anesthesia, because this causes profound depression of the nervous system, which can be followed by complications. The primary thing is to correctly calculate the dosage and take into account the individual characteristics of the small patient.
The anesthetic drug is given by inhalation: by inhaling the vapor of the drug, the child falls asleep. The doctor gets the opportunity to quickly and calmly treat the tooth, and the child will not feel pain or get stressed.
Stages of tooth decay
Any damage to a child’s teeth does not develop immediately, but gradually. The first stage is characterized by the accumulation of a large number of pathogens on the enamel, which over time form a dense dark film - spots. Also, the beginning of the destruction process may be indicated by the appearance of bad breath.
At the same time, tissue sensitivity increases, and the baby may experience discomfort when eating cold or, conversely, hot food. Also at this stage, small black spots and cavities can be found on the teeth. At this time, the deeper tissues of the tooth begin to deteriorate. As a result, the child may complain of severe pain with any mechanical impact and even without it.
Further, the process affects the nerve endings, so the pain may decrease or disappear completely. This suggests that very soon the decay will reach the root of the tooth, as a result of which the unit will most likely have to be removed surgically. The sooner parents seek help from a professional dentist, the greater the chance of saving the tooth.
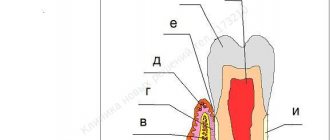
Vulnerability zone
Let's look at gum disease in children. Your child's healthy gums are delicate and very vulnerable tissue of a pale pink color. Unlike adult gums, they can be easily injured, but they are capable of rapid regeneration. Another peculiarity of children's gums is that they often reflect the general condition of the body, being a litmus test for systemic diseases.
The most common diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues: gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that occurs as a result of the adverse effects of local and general factors, occurring in 80% of children; gum atrophy, which develops in more than half of the child population; various types of childhood stomatitis, which most often occurs in infants and preschoolers; Periodontitis is a disease in which all periodontal tissues become inflamed and affects up to 5% of young patients. Periodontal disease (dystrophic changes in periodontal tissue) and other pathologies practically do not occur in childhood.
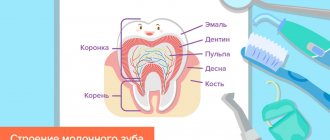
What does dental health depend on?
The enamel on baby teeth is not yet strong and strong enough, so it is susceptible to any mechanical stress. Unfortunately, many adults believe that it is not necessary to treat baby teeth, because they will very soon be replaced by permanent ones. However, such a judgment is fundamentally wrong! The health of molars is directly related to the condition of their predecessors.
The fragility of the enamel may be due to a hereditary factor: perhaps one of your relatives has very fragile teeth that are prone to destruction. Also, factors such as unfavorable environmental conditions in the region of residence, poor-quality tap water, mental health problems and much more can lead to the depletion of a child’s tooth enamel.
An important factor can be a woman’s careless attitude towards her health during pregnancy. In particular, this applies to drinking alcohol and smoking. This negatively affects not only the development of the baby’s bones and teeth, but also his overall health. Also, the cause of tooth decay can be liver pathologies, problems with the thyroid gland, gastrointestinal diseases, etc.