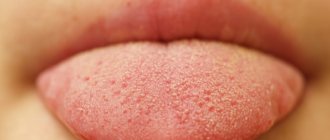
At home, you can conduct a quick health diagnosis yourself. All that is necessary for this is to examine the tongue with a mirror. A change in its color and shape will tell you a lot about the functioning of internal organs. This simple method should not be neglected. With its help, you can prevent the development of dangerous pathologies in time. Some of them are indicated by a rough tongue.
Tongue is an indicator of health
It is recommended to examine the tongue in the morning, on an empty stomach. In a healthy person, its color is pale pink, and the taste buds are easily distinguishable. Normally, it has a faint whitish coating that can be easily removed with a toothbrush or a special scraper. The complete absence of such cover should be no less alarming than its excessive amount.
Any changes that occur in the oral cavity should attract a person’s attention. They may indicate the formation of pathological processes in the body. A decrease in the amount or complete cessation of saliva production leads to the development of severe dry mouth. A rough tongue will immediately signal this to a person, since due to a lack of moisture on its surface, difficulties will arise when swallowing and chewing food.
Dry tongue can occur with severe nervous excitement or stress. From a physiological point of view, this is a normal situation. As soon as the person calms down, saliva production returns to normal. If there have been no emotional upheavals, and dryness has been observed for a long time, you should look for other causes of a rough tongue. An experienced doctor will help in this situation.
The causes of dry tongue may be the following:
- dehydration and intoxication;
- heart pathologies;
- tongue burn;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- glossitis;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- liver pathologies;
- stagnation of food;
- blood diseases;
- HIV;
- kidney problems;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- inflammation of the salivary glands, as well as their malignant and benign tumors;
- diabetes;
- infectious lesions.
Despite the impressive list of pathologies that cause roughness and dryness of the tongue, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, pulmonary system, and infections are most often diagnosed. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis after a thorough diagnosis. He will prescribe treatment that will help defeat the underlying disease. After this, the rough tongue will definitely return to normal.
Treatment methods
Treatment of leukoplakia may require a collegial approach: the participation of the oncologist in developing an action plan. The basis of therapy is the elimination of provoking factors: quitting smoking, changing jobs due to occupational hazards, following a soft diet with no spices, etc. According to indications, correction of dentures, replacement of fillings, treatment of caries, removal of teeth that cannot be restored and other measures are carried out .
As part of complex treatment, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Preparations for restoring the normal structure of the oral epithelium. It is usually used in the form of applications to the affected areas.
- Antiseptics. Used for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory complications of the disease.
- Painkillers and symptomatic therapy. Systemic medications or applications of local anesthetics used in dentistry may be used.
Self-medication for leukoplakia in the mouth is strictly not recommended. Many drugs, including some anti-inflammatory drugs, are irritating and increase the risk of developing malignant tumors.
If the disease is severe, hospitalization may be required. The presence of ulcers and erosions is an indication for the use of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, proteolytic enzymes, etc. Surgery is indicated when conservative treatment is ineffective. Cryodestruction and excision with a scalpel are usually used.
Pathologies of the digestive tract
Reflexes that can influence the motor and secretory functions of the stomach and intestines are produced by tongue receptors. The opposite effect also occurs. That is, internal organs influence the appearance of pathological reflexes on the surface of the tongue. For example, its rough root and white coating will tell the doctor that the patient suffers from gastritis with low acidity. Pain and burning sensations in the esophagus, heartburn can complement the clinical picture.
A rough tongue covered with a gray coating may indicate the development of an intestinal ulcer. An additional factor indicating this pathology is heartburn and a burning sensation in the mouth.
Colitis, in addition to roughness, is characterized by an increase in the size of the tongue; teeth marks may even remain along its edges. With duodenitis and biliary dyskinesia, the thickness of the plaque increases significantly. A slight roughness of the tongue rarely causes discomfort. But a dense coating can negatively affect the sense of taste, reducing the sensitivity of the papillae.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Gastroenterologists know that white plaque can be a symptom of problems with the gastrointestinal tract. The surface of the mucous membrane is smooth and dry. This often happens with the development of gastritis with low acidity. This is a clear sign that inflammation has begun in the gastric mucosa. But a rough surface may indicate that the acidity of gastric juice has increased significantly.
Gastritis is easy to diagnose by symptoms such as heartburn, burning and pain in the esophagus and stomach. If the disease is chronic, the symptoms will not be as severe as in the acute form. Such patients often break into a sweat and feel general weakness.
The ulcer may cause plaque and red spots in the middle of the tongue. A duodenal ulcer causes a burning sensation, a feeling of heartburn.
White plaque may be a symptom of gastrointestinal problems.
Colitis and enterocolitis provoke the appearance of plaque at the base of the tongue. It swells quite a lot. Because of this, teeth marks can be seen along its edges. In such patients, bowel movements are disrupted, they complain of nausea and pain.
Diseases of the pulmonary system
A white, rough tongue occurs in patients at an early stage of the development of diseases of this organ. Inflammation in the bronchi is indicated by a thick and dry plaque located at its tip. If it begins to thicken and acquire a yellow tint, this will tell the doctor that the pathology is progressing. Additionally, the patient will experience other symptoms. For example, weakness, unpleasant odor and dry mouth.
Characteristic changes in the condition of the tongue are observed in pathologies such as scarlet fever. First, an extensive yellow or gray-white coating forms. It thickens every day. The fungiform papillae are clearly visible under the plaque. They are distinguished by a rich red color and are surrounded by a white border. After a week, the plaque disappears, and the tongue changes color to crimson.
Symptoms and manifestations
At the initial stage of development, there may be no characteristic symptoms of leukoplakia. Gradually, small white or gray lesions appear in the mouth - up to several millimeters. The surface of the altered areas is rough and hard. The mucous membranes around the lesion may appear unchanged and healthy.
The disease can spread to almost any part of the oral cavity. When lesions appear on the gums, discomfort and slight pain when chewing and brushing teeth may be added to the external symptom.
Typically, a visit to a doctor occurs when the lesion develops up to 2-4 cm and other manifestations of the disease occur: impaired taste perception, difficulty chewing, pain, repeated inflammation of areas of the mucous membrane.
Infectious and other diseases
There are many pathogenic fungi and bacteria in the oral cavity. Their growth is inhibited by the body's immune system. As soon as its operation fails, the infection begins its attack.
In humans, a rough tongue and a white coating on the tonsils may indicate the development of follicular or catarrhal tonsillitis. The disease is accompanied by a sore throat and fever. The causative agents of the disease are streptococci and staphylococci.
The culprit of oral thrush is the fungus Candida. A very dense white coating appears on the surface of the tongue. If you try to remove it, the mucous membrane underneath will begin to bleed. The development of this chronic pathology is observed in patients with HIV infection.
Dry tongue is accompanied by disruption of the thyroid gland. Symptoms such as sweating, loss of appetite, diarrhea, irritability and anxiety are observed.
Diabetes mellitus is characterized by the development of thirst, the patient’s tongue becomes rough and dry.
If dense white plaque is concentrated on its sides and tip, this may indicate the development of hidden renal failure. This is a very serious problem that can cause death. Therefore, if you notice such formations on your tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Other reasons
If a white coating appears on the tip of the tongue, this indicates inflammation of the bronchial tubes. But the location at the base and on the sides can warn of renal failure. This is a very serious diagnosis that needs to be given the highest attention.
Other symptoms of this most dangerous disease are an unpleasant odor and dry mouth, constant fatigue, and weakness. Such patients cannot withstand even slight physical exertion. If these symptoms occur, you should consult a nephrologist.
A rough tongue can also occur in diabetes. It is knitted, and a dense gray coating is visible on it. It is located in the center. These symptoms are explained by the fact that diabetes may impair the function of the glands located under the jaw. They produce less saliva and the following symptoms appear.
If a white coating appears on the tip of the tongue, this indicates inflammation of the bronchial tubes.
With glossitis, the white plaque is accompanied by a burning sensation, pain and loss of taste.
With anemia, red spots form on the tongue, around which a white coating is visible. This is due to the process of atrophy.
Note! A dense white coating can warn that a malignant neoplasm has appeared in the gastrointestinal tract.
As you can see, the reasons can be very serious. If the plaque is not removed after cleaning and other symptoms are added to it, the tongue has become rough, it is better to consult a doctor about this problem.
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia affects the mucous membranes. Often this is the reason why the tongue becomes rough. This pathology can be easily confused with thrush. A white coating also appears on the tongue, but it has clearly defined edges. Its surface is rough and dry. It is impossible to remove plaque with a spatula.
The reasons for the development of this pathology have not been fully identified. It is believed that the main role is played by provoking factors: thermal, physical and chemical irritation. Particularly dangerous is the influence of several agents at once. For example, irritation by galvanic current, which is formed as a result of the use of dissimilar metal prostheses. As well as mechanical damage to the mucous membrane from dental instruments. In smokers, leukoplakia can occur as a result of exposure to smoke and high temperatures.
Internal factors play an important role in the development of the disease. These are hormonal abnormalities, gastroenterological diseases, and lack of vitamin A. The danger of the disease is that it can gradually transform into cancer.
Types of leukoplakia
The type of disease determines treatment tactics, as well as specific symptoms. There are several forms of the disease.
Flat
Flat leukoplakia is the most common variant. In most cases, the disease is discovered accidentally, as part of a routine dental examination or during treatment for other oral diseases. For a long time, this form of the disease does not make itself felt. Only a few weeks or months after the onset of the disease, a slight burning sensation, a feeling of pressure and retraction of the affected area appear. If the tongue is affected, the disease is detected earlier. This is due to loss of taste sensitivity.
In a flat form, the focus of changes is a dry, rough surface of any shape and size. When the inner surface of the cheeks is affected, the pathology often forms around the excretory ducts of the salivary glands. When it appears on the palate, tongue or under it, the lesion often looks like white stripes with alternating dark areas. In half of patients with leukoplakia, the formation rises above the surface of healthy mucous membranes by 1-3 mm. The color of the plaques can be milky, white or grayish. As a rule, the disease is not accompanied by inflammatory complications.
Verrucous
Verrucous leukoplakia can be a consequence of flat leukoplakia if the provoking factor has not been eliminated. Hyperkeratosis becomes more pronounced, the lesion rises above the surface of the mucous membranes by 3-5 mm. When palpated, it has a hard surface and can be mobile. Usually this form is not accompanied by pain.
The color of the affected area gradually changes to yellowish. Other characteristic symptoms include severe burning during eating and when exposed to water, a feeling of tightness, and discomfort in the oral cavity. This form has a high risk of malignancy.
Erosive
This type of leukoplakia develops from verrucous in 1/3 of all cases. Multiple small ulcers and cracks form in the pathological area of the mucosa. This leads to severe pain. The size of the damage increases, and eating and even talking become difficult.
Violations of tissue integrity become entry points for infection. Therefore, the erosive form is often accompanied by inflammatory complications depending on the location of the pathological focus - gingivitis, glossitis, stomatitis, etc.
Tappeiner's leukoplakia
This form of the disease is characteristic of smokers. Smoking 10 cigarettes a day increases the likelihood of developing the disease by 50 times. Usually areas of the soft and hard palate are affected, and less often - the gums. If you give up a bad habit, the disease may go away on its own.
The mucous membranes of the palate become bluish or gray and acquire a folded structure. The narrowing of the ducts of the salivary glands leads to the accumulation of secretions in the tissues, stagnation and the development of inflammation. The disease has the appearance of multiple red nodules, accompanied by inflammatory processes.
Soft
This type is a benign formation. The lesion is characterized by severe peeling until large areas of keratinized epithelium fall off. Ulcerations and cracks appear on the formation, bleeding is observed. The size of the tumor can reach five centimeters in diameter and rise above healthy tissue by more than a centimeter. Such oral leukoplakia can develop as a result of sudden hormonal changes, depression, and stress.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor can prescribe treatment only after he determines exactly why the tongue is rough. Sometimes the cause can be identified immediately and there is no need for numerous diagnostic procedures. But in some cases it may be necessary:
- complete blood count;
- bacteriological study of oral microflora;
- gastroscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- bronchoscopy;
- acid reflux test.
Once the underlying disease is identified, the doctor will be able to prescribe treatment for the patient. The tongue will return to normal as soon as the patient’s condition begins to improve. To eliminate dry mouth and reduce pain, the doctor additionally prescribes rinses with various antiseptics.
Diagnostic features
Diagnosis of the disease begins with a visual examination by a dentist. The doctor will ask questions about the general state of health, clarify how long ago the complaints appeared, and identify risk factors for the development of the disease. A specialist can confirm this assumption using several methods:
- Biopsy. One of the most accurate diagnostic methods, in which a section of altered tissue is taken and further studied in the laboratory.
- Smear for oncocytology. It is a scraping of the surface cells of the mucosa.
- Schiller's test. An iodine solution is applied to the mucous membrane; the changed areas are not stained.
- Laboratory tests - general blood test, tumor marker testing, etc.
Other diagnostic methods may be required depending on the clinical picture.
Treatment with traditional methods
There are several effective traditional medicine recipes that help alleviate the patient’s condition. It is recommended to rinse a rough tongue with infusions of the following medicinal plants:
- sage;
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- Oak bark;
- mint;
- sea buckthorn.
To prepare the infusion, pour a teaspoon of the selected ingredient into a glass of boiling water and leave for several minutes. After the liquid has cooled, it is filtered and used for rinsing. You can add a drop of iodine, aloe juice or honey to the finished infusion.
In addition, you can put a cotton pad soaked in rosehip oil, propolis tincture or a mixture of carrot and potato juices on your tongue for a few minutes. This procedure will relieve pain, moisturize, soothe and disinfect the mucous membrane. After 3-5 minutes, the cotton pad should be removed and your mouth should be rinsed with warm water.
Reviews about the treatment
Patients often leave reviews about how they managed to cure a rough tongue. In some cases, therapy does not take much time. Improvement occurs quickly after using regular rinses with medicinal herbs. Lubricating the surface of the tongue with sea buckthorn oil gives good results.
In the event that dryness, plaque and roughness of the tongue are associated with the development of serious pathologies, it is not possible to manage only with antiseptic rinses. Patients often write that they have come a long way before they were given the correct diagnosis. Only after complete recovery were they able to forget about the problem of dry and rough tongue.
Treatment
If the tongue is uneven, you need to fight the underlying disease. The doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes comprehensive treatment. To alleviate the condition, rinsing with antiseptic solutions may be prescribed locally. Creams and ointments are also prescribed. They relieve pain, inflammation, and accelerate healing. At home, treatment boils down to cleaning, rinsing, and applying ointments.
A rough tongue and plaque on it are symptoms of a number of diseases. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause in a particular case. Even he will need to diagnose and prescribe a series of tests for the patient. But self-medication can lead the disease to an advanced form. Then it will be much more difficult to overcome it.