A child’s first tooth erupts is a joyful event for parents. But what if there are no teeth at 6 or 8 months or even later? Is this really a problem or can it wait?
Milk teeth: by the age of 2–2.5 years, exactly 20 of them should grow
Sometimes the replacement of teeth with permanent ones is delayed, so sometimes an examination may be required to determine whether everything is in order.
Why may teeth not grow on time?
Individual characteristics
The average time for the appearance of the first baby tooth is 6 months, but teeth can begin to erupt at three months or a year, and both options are normal. If the child’s teeth do not appear, but there are no other complaints and the pediatrician does not notice any problems, then there is no need to worry until the child is a year or more old.
The same applies to the late beginning of the change of milk teeth to permanent ones. For some children, permanent incisors begin to appear already in the senior group of kindergarten, while others experience this moment at school. The normal period for the formation of a permanent bite is from 7 to 13 years.
Later than the average period, teeth may erupt in weakened, often ill children.
What to do?
Monitor other complaints, contact doctors if necessary, and if there are no complaints, then nothing. You cannot influence the rate at which teeth appear.
When do the first teeth appear?
At the time of birth, the baby's teeth are in a state of formation inside the jaw bones. The bone contains a complete set of primary teeth at different stages of growth. The front incisors are the earliest to form and begin to emerge through the gums at six months of age. With the correct development of the child, dental units continue to erupt in pairs, i.e. one on each side. A full set of twenty primary teeth should appear in the first three years of a child's life.
Partial edentia
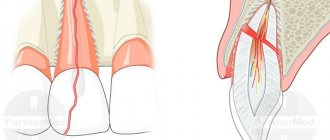
Adentia is the congenital absence of tooth buds. Most often, the top two “twos” are missing. Moreover, there may be a lack of both milk and permanent teeth, or both.
Adentia is a congenital condition; it occurs due to a malfunction in the embryonic period during the formation of the main organs and systems.
It is very difficult to notice partial edentia of baby teeth: the teeth are small, they are all of a similar shape, and others take the place of the missing ones. Such adentia does not harm the chewing process in any way.
If permanent teeth are missing, this is already noticeable visually. In this case, malocclusion may develop, since the “threes” are pulled up to replace the missing “twos”, and the following teeth are also displaced.
Partial edentia - absence of upper incisors
Partial edentia - there are no upper incisors, but “threes” have taken their place
The exception is wisdom teeth, also known as “eights.” Their functions are not so important; in most people they remain impacted, and if they are lost, they are not replaced with prosthetics. Their absence does not affect the health and aesthetics of the smile.
What to do?
If there is a partial lack of permanent teeth, it is most often necessary to correct the bite and prepare a place for prosthetics. If you do not make dentures, but cover the empty space with neighboring teeth, then this will not be a complete solution to the problem - the dentition will be narrower than it should have been.
Reasons for delay in teething
There can be many reasons for delays in teething.
- Hereditary factor. If parents cut teeth later than other children, then this symptom may also be observed in their children.
- Prematurity or low birth weight of the baby.
- Diseases of the expectant mother during pregnancy, injuries during childbirth, as well as illnesses of the child in the first few months after birth.
The factors listed above most influence the timing of eruption, as well as the quality of formation of dental units.
Other reasons include:
- violations in the child’s diet;
- lack of certain vitamins and minerals;
- hypothyroidism;
- rickets and its consequences.
It should also be taken into account that girls are ahead of boys in development, and, therefore, their teeth appear earlier.
Completely edentulous
This is a rare phenomenon - the complete absence of tooth buds (deciduous or permanent). In this case, teeth cannot erupt because they are simply not in the jaw bone.
Complete edentia in the picture
In medicine, cases have been described when a patient had milk teeth, but permanent teeth were completely absent. The loss of baby teeth was timely, but permanent teeth did not appear in return. At this moment, the child’s parents paid attention to the problem, and the dentist made a diagnosis.
In addition to congenital, adentia can be acquired if the child has undergone severe treatment (chemotherapy) at an early age. Due to the toxic effects of drugs, tooth buds may be damaged.
What to do?
Edentia is clearly visible on a CT image. If such a diagnosis is made, the only option is complete prosthetics. Since the case is rare, the question of when to get dentures and in what way should be decided individually.
If you do not replace missing teeth with prosthetics, the chewing process cannot be complete. Even the lack of 2-3 teeth affects digestion. Bone tissue, if the jaws do not receive enough load when chewing, undergoes resorption (resorption), and this leads to weakening and loosening of the remaining teeth, increasing the risk of periodontal disease.
Therefore, if you have any complaints about your child’s teething being too slow, you should consult a doctor. In most cases, it turns out that there is no pathology, all teeth are fine and will grow a little later. But in rare cases, prosthetics may be required, which is better to know in advance. Then you can schedule treatment on time.
Other articles:
If a child does not want to be treated by an orthodontist...
When should your child see an orthodontist?
How to help your child not be afraid of dentists
How to help your baby?
Initially, the dentist will take an X-ray of the baby's jaw to make sure that the baby has the rudiments of teeth inside. If there is, then eruption will happen soon. At first, the gums will swell a little and salivation will become very abundant: these are the main symptoms of the rapid appearance of teeth. You can help them a little:
- Teether toys are an excellent device for training gums; they help relieve severe itching and reduce pain.
- Mothers should learn how to gently massage their baby’s gums. It is better to massage with a clean finger lubricated with a special gel for children's gums.
- It is important to add healthy purees and healthy foods to your baby’s diet that will help the child’s body receive the necessary microelements and vitamins.
If the baby generally develops within normal limits, eats well, sleeps, is active and cheerful, then the absence of teeth at 1 year is definitely not a reason to panic. Each child develops at his own pace. In general, boys tend to lag slightly behind girls in some physiological parameters.
From this article it follows that you should not worry unnecessarily! If in any doubt, seek advice from a pediatric dentist at our Babydent
Show more tips
Feeding rules
Frequent regurgitation can be prevented by following a few feeding rules.
- After feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby upright. Even if your baby is tired or wants to sleep, you shouldn’t put him to bed right away. It is very comfortable to hold infants on your shoulder. After waiting for the air to burp, the child can be given any position.
- The same should be done before feeding. The thing is that in an upright position the child can release excess air from the stomach. If this is not done before eating, belching is guaranteed.
- There is a certain position recommended for breastfeeding. One of the main goals of correct positioning of a nursing mother and baby is to prevent regurgitation. The semi-vertical position of the baby with the head raised above the level of the body must be maintained during each feeding.
- Feedings should be frequent, but in small portions. Overfeeding is fraught not only with regurgitation, but also with other digestive problems.
- It is important not to feed your baby when he is crying or laughing, otherwise he will swallow excess air.
- If feeding is carried out using a bottle with a nipple, it is necessary to ensure that the hole in the nipple is not too large, and the position of the bottle is such that the nipple is always filled with mixture and not with air.
- You should refrain from active games in the first half hour after feeding.
Following these simple rules will help reduce the frequency of regurgitation.
Treatment
Treatment is required if respiratory complications occur or if irritation of the esophageal mucosa is suspected. In this case, the specialist will prescribe medications that reduce the acidity of gastric contents. This will not help with regurgitation, but will prevent further trauma to the esophagus. Specific medications are selected individually at an appointment with a pediatrician.
If the cause of regurgitation is an anatomical defect, surgical treatment may be required. Indications for surgery and its scope are specified by the surgeon.
For advice on infant feeding, please contact the specialists at the CELT clinic. Extensive experience, highly qualified clinic doctors and modern equipment are the key to the health and successful development of your children.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Tips for parents
Let's figure out how to avoid possible dangers associated with regurgitation. The main thing that responsible parents need to know is that most often children burp while lying down. This position is dangerous due to aspiration (inhalation) of gastric contents.
Preventing aspiration is simple - just bring the baby upright or turn him on his side or stomach immediately after he burps. Then the baby will be able to push food out of his mouth.
It is worth remembering that it is unacceptable to leave a child with regurgitation syndrome without adult supervision, especially when lying on his back.
The period of active growth and weight gain continues
At nine months, your baby will still look like a baby—with a big head, chubby legs and arms, and an adorable belly. As he begins to move more and test his strength in standing and walking, the outline of the child's figure will begin to change.
According to Russian pediatricians, on average at nine months your baby will have:
- weight gain per month of 500 g, weight up to 8600-9000 g;
- height increase per month of 1.5 cm, height approximately 74 cm;
- head circumference - 44.5-45.5 cm;
- chest circumference - 46.5-47.5 cm.
Teething symptoms
There is an opinion that the appearance of the first teeth is accompanied by the development of a whole complex of pathological processes (fever, the appearance of a rash, abnormal stool, vomiting, convulsions, etc.). In fact, the formation of a temporary bite is a natural process that is not characterized by the symptoms described above. Pathologies detected during the teething period are most often manifestations of infectious diseases or a consequence of changes in diet.
In particular, factors that can lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms include:
- introduction of artificial complementary foods;
- hypovitaminosis;
- acute viral infections;
- stomatitis;
- tonsillitis;
- runny nose;
- otitis;
- vaccination, etc.
The true symptoms of teething are:
- hyperemia and gradual swelling of the gums;
- the appearance of a small bluish hematoma on the gum tissue;
- slight bleeding from the gums;
- wet cough;
- mild itching caused by mechanical irritation of sensitive nerve fibers in the gum tissue;
- increased salivation;
- various somnological disorders;
- sharp deterioration in appetite;
- tearfulness, capriciousness.
What about the deadlines?
Some parents use a special formula to determine how many teeth a baby should have at nine months. It looks like this:
K=M – 4,
where K will be equal to the number of teeth, and M will be the number of months of the toddler’s life.
But even if teething begins only at one year, parents should not panic. This is also the norm.
Children's teeth may appear one at a time or in pairs. Moreover, in this way not only the first ones erupt, but also those following them. There are cases when a baby has as many as four teeth coming out at the same time. By the way, massive teething will affect the timing.
It is human nature to doubt. Especially for parents of little ones. It often happens that a child is 9 months old and has no teeth. Why? If at this age or even a year the baby does not have a single tooth, you should consult a doctor to make sure that the little one does not have rickets or hypothyroidism.
Typically, the first twenty teeth should appear before two and a half to three years of age. Each baby’s jaw should have four incisors, two canines (also called canines) and four molars. In an adult, it is considered normal to have twenty-eight or thirty-two teeth - on each jaw there are 4 incisors, two canines, four premolars and from four to six molars.
When baby teeth begin to emerge, there are initially no gaps between them. This is normal. A little later, when the child’s jaw grows, by the age of four the teeth begin to diverge and gaps form between them. This process is necessary to accommodate the molars because they are much larger than baby teeth. If such gaps do not appear, then subsequently the molars will not be able to fit in and will grow crookedly.
Main signs and symptoms
Many parents are in a hurry to find out how their children are teething, especially those who are faced with this phenomenon for the first time. Rarely does such a process go unnoticed; most often it manifests itself with characteristic symptoms.
Experts call the following main symptoms that a child is teething:
- worsening sleep;
- increased moodiness and tearfulness of the baby;
- Bad mood;
- swollen and sore gums;
- loss of appetite, sometimes even leading to refusal of food;
- increased salivation;
- the child puts everything into his mouth, so he tries to relieve the pain;
- the formation of various redness and rashes around the mouth caused by skin contact with saliva.
In addition to the main signs indicating the appearance of teeth in children, accompanying symptoms can also be traced. Due to the increased function of the salivary glands, the following may be observed:
- runny nose;
- hoarseness of voice;
- cough without sputum production;
- indigestion in the form of diarrhea.
Often, as a child teethes, the body temperature rises. Usually it stays at around 37.5 ̊C, but it can rise to 39 ̊C.
The most severe pain is accompanied by the eruption of fangs. They have very sharp edges that cut through the gums and cause severe pain. The appearance of the upper “eye teeth” is especially painful, as they are closely connected to the facial nerve.
The approximate timing of eruption of milk jugs is presented in the table below.
| Tooth name | Baby's age |
| Central incisors | Below - at 6-9 months, above - 7-10 |
| Lateral incisors | On the upper gum – 9-11 months, on the lower gum – 11-14 |
| First molars | In the bottom row - in a year and a half, in the upper – 13-20 months |
| Fangs | In the lower dentition - 16-22 months, in the upper dentition - 17-23 |
| Second molars | Below - at 20-26, above - at 26-33 |
Please remember that this is just a rough guide to teething timing. Later dates are also acceptable, but not later than 6 months.
What to do to ensure that your child’s teeth develop normally
Before and during pregnancy:
- Maintain dental health.
- Eat well and varied.
- Eat more foods high in calcium.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Walk in the fresh air more often to maintain a healthy level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Treat in strict accordance with medical recommendations.
After childbirth:
- provide the child with a rich and balanced diet;
- monitor the baby’s hygiene;
- walk in the fresh air to harden the child’s body;
- prevent infection and diseases of internal organs;
- Consult a doctor in a timely manner in case of painful syndromes.
What are the complications, and when to see a doctor?
| Symptom | Teeth are being cut, there is no need to go to the pediatrician | The disease develops, contact your pediatrician |
| Cough | A coughing attack begins due to excess salivation. The cough is wet and infrequent. | The cough gets worse, does not go away, does not allow the baby to sleep, and prevents him from eating. Doesn't stop for more than 2 days. Breathe heavily. |
| Nasal discharge | Nasal discharge is transparent and watery and disappears by the 4th day. | The runny nose does not go away for the 4th day. Lots of yellow or green discharge. |
| Heat | The temperature does not exceed 38 °C and lasts no more than 2-3 days. Rapidly decreases under the influence of antipyretics. | Fever above 38.5 °C for more than 2 days. Signs of a cold appear (severe cough and runny nose). |
| Loose stools | Lasts less than 72 hours. | Lasts more than 72 hours. |
| Changes in the oral cavity | The gums become swollen and red. | The oral mucosa is covered with white plaque or ulcers. |
Recommendations for avoiding delay
- After tooth loss, you should not eat or drink hot drinks for several hours.
- The plug that forms in the hole cannot be removed to avoid infection. It will disappear on its own.
- It is not advisable to eat solid food for the first time after the loss.
- If you experience pain, redness, swelling or other signs of exacerbation, you should immediately contact your dentist. Remember, our specialists are always ready to help and answer your questions by phone.
Reasons why there may be more teeth than normal at 8 months
There is another problem - parents think there are too many teeth. That is, a child at 8 months has grown more than 8 teeth. Is this really a pathology, and should parents worry?
There is no need to panic. When the first teeth appear after 3 months, this is an indicator of the norm. This happens if the expectant mother constantly takes prenatal vitamins or drinks them while breastfeeding. This is also possible in bottle-fed children. This means that the child’s body has enough microelements and essential substances.
This is interesting: Bad breath in a child: causes, symptoms and remedies
It’s another matter when the first incisors appeared before 3 months of age. In this case, there is reason to suspect diseases of the endocrine system. You need to show your baby to a doctor and undergo an examination.
What determines the timing?
The timing of the formation of both temporary and permanent dental units in children can be compared with certain phenomena.
- Floor. In girls, all teeth, except the first upper chewing one, erupt earlier than in boys.
- Jaws. Teeth appear faster on the lower jaw than on the upper jaw.
- Position of teeth. Molars and premolars most often erupt with a delay.
- Bite. In primary dentition, delay occurs much less frequently than in permanent dentition.
- Population. Scientists have found that people living in different countries have different timing for the appearance of teeth. For example, among Europeans, delayed eruption is a fairly common occurrence.
- Climatic conditions. In warm climates, teeth erupt faster than in cold climates.
- Level of urbanization. City residents develop teeth faster than those in rural areas.
- Evolution. Recent generations are more likely to encounter anomalies in the eruption of wisdom teeth and canines in the upper jaw. Scientists explain this phenomenon with the evolution of humans as a species, and with the lack of space due to a decrease in the overall size of the jaw.