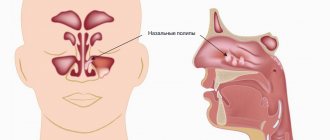
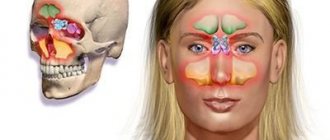
A sinus cyst is a fluid-filled formation with elastic walls; the location of the cyst affects the symptoms of the disease. Most often, cysts form in the maxillary sinuses. The reasons for the development of cysts in the nasal sinuses are varied; there are a number of reasons for the appearance of a neoplasm:
- Blockage of the ducts of the mucus-secreting glands.
- Dental diseases, tooth roots protruding into the paranasal sinuses.
- Allergic diseases of the nose.
- Frequent inflammatory processes.
- Anatomical features of the structure of the nose.
- Mechanical injuries of the nose.
In the oncology department of the Yusupov Hospital, you can undergo examination using MRI, CT, ultrasound, diagnosis of diseases of the paranasal sinuses if a nasal tumor is suspected. The patient will be able to undergo a full examination at the diagnostic center, take tests in the hospital laboratory, and receive advice from an otolaryngologist, oncologist and other specialists.
Cyst in the sinus: symptoms and consequences
Sinus cyst, symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the cyst, there are false and retention. The cyst can increase in size and eventually block the sinus cavity. A false cyst in the sinuses can develop due to an inflammatory, allergic process, while a true cyst develops due to blockage of the ducts of the mucus-secreting gland. A cyst of the paranasal sinuses may not manifest itself as pronounced symptoms for a long time, then nasal congestion, headache, and soreness in the face, on the side of the affected sinus cyst, begin to bother you. The pain can intensify when diving, and inflammatory processes in the nose often develop.
As the cyst of the maxillary sinuses develops, it manifests itself in the following disorders:
- Constant nasal congestion.
- Respiratory dysfunction.
- Pain in the area of the sinus affected by the cyst.
- Unpleasant sensations and false symptoms of increased intraocular pressure.
- Severe headaches.
- Purulent discharge (concomitant development of sinusitis).
- Partial or complete loss of smell.
The consequences of cyst development are negative:
- A growing cyst provokes an inflammatory process and can lead to the development of sinusitis.
- Reduces the patient’s quality of life and causes constant severe headaches.
- A large sinus cyst can lead to destruction of nasal tissue, reach the nasopharynx, impair respiratory function, and deform the face.
- Some sinus cysts can develop into a malignant tumor.
Possible risks
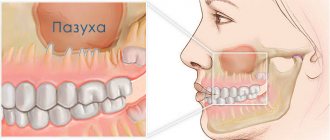
A cyst in the maxillary sinus and sinus lifting can be complicated in different ways and seriously interfere with any dental interventions by the doctor. When a cystic formation is removed, the risk of perforation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus only increases, as do subsequent associated problems. It is also possible for the cyst to accidentally open and spill its contents into the sinus. This threatens further infection and the development of acute or chronic sinusitis.
When performing a sinus lift for a maxillary sinus cyst, the doctor must remember that the formation promotes the resorption of bone tissue. The thinner the alveolar bone, the less load it can bear. Therefore, any careless movement can lead to a fracture of the bone crest.
During the sinus lifting process, a barrier membrane is necessarily installed that will protect the operated area from unfavorable external factors and the additional impact of osteoclasts (cells that destroy bone).
In addition, only the safest and highest quality grafts are used in the bone grafting process with minimal risk of rejection. This precaution is due to the fact that a significant deficiency of bone tissue will not suffer additional problems in the form of poor engraftment. The doctor will not be able to perform a second operation, and he will have to look for alternative solutions.
Main sinus cyst: symptoms, treatment
A cyst of the main (sphenoid) sinus develops more often in young people and rarely in older people. The cavity of the main sinus of the nose is covered with mucous membrane. The sheath glands secrete mucus; disruptions in functioning lead to blockage of the gland ducts and the formation of a cyst of the sphenoid sinus. Inflammatory processes, injuries, and allergic reactions have a negative effect on the mucous membrane. A growing cyst of the sphenoid sinus is accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the nose, nausea and dizziness may occur, a headache that radiates to the back of the head, and visual disturbances rarely develop.
If a sinus cyst is detected, treatment is carried out after a complete examination. The doctor prescribes diagnostic tests for the patient using:
- X-rays to determine the location of the cyst, changes in the condition of the facial bones and nasal septum.
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which determines the condition of the skull bones, tissues, and blood vessels. A more informative study than radiography. Computed tomography has the same capabilities. Research is carried out as prescribed by a doctor.
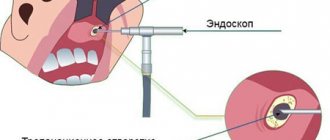
- Research using an endoscope allows you to examine the nasal cavity and perform a biopsy of nasal tissue.
After the studies, conservative or surgical treatment may be prescribed. Conservative treatment is aimed at pain relief, relieving an allergic reaction, and treating the inflammatory process. If conservative treatment is ineffective or the cyst is large, the patient is referred for removal of the formation.
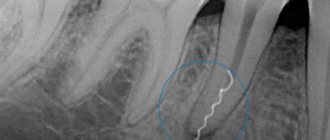
A small cyst can only be detected by x-ray
When the neoplasm is small, less than 10–15 mm, it is almost impossible to find out about its existence, since no alarming signs are observed. At this stage, the only option to identify pathology is to do a computed tomography scan. A dentist may also suspect its presence during a routine examination or other doctors if a person needs to visit them.
At the initial stage, the problem can only be detected on an x-ray
Removal of sinus cyst without surgery
If a sinus cyst is detected, treatment without surgery is carried out using decongestant sprays, antibiotics, painkillers, mucolytics, steroids and antihistamines. They treat concomitant diseases - allergies, sinusitis, inflammatory processes of the gums, teeth, nasal mucosa. In combination with these drugs, various means for rinsing the nasal cavity, regenerating and restorative sprays are used. Treatment is prescribed by the doctor based on the results of the patient’s examination.
Types of cystic formations
There are several types of cystic formations of the upper jaw - true (retention), false, odontogenic.
| Variety | Description |
| True (retention) | They are formed from the glands of the mucous membrane, the exit ducts of which are clogged. Their wall is lined with ciliated epithelium. |
| False (cyst-like) | The main difference between cyst-like formations is the absence of an epithelial lining. The reasons for their development are not fully understood; the main etiological factor is considered to be exposure to an allergen. |
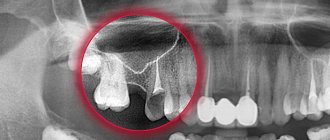
| Odontogenic | Odontogenic cysts are associated with dental diseases. They are always localized at the bottom of the VChP, while other varieties can arise in any area. |
Separately, there are 3 forms of cystic formation depending on the nature of the contents:
- mucocele (mucus);
- pyocele (pus);
- hydrocele (serous contents).
Cyst in the sinus: surgery, reviews
Patient reviews give preference to the endoscopic method of cyst removal. When performing the classical method and laser vaporization, an incision is required under the upper lip to gain access to the cyst. Classic removal of a sinus cyst involves dissection of the soft tissue under the upper lip from the frenulum to the first molar (Caldwell-Luc method) or using the Denker method, which is also carried out through the facial part. Classic operations are more traumatic, with long postoperative recovery, but these techniques allow you to gain access to a cyst located in a hard-to-reach place. Endoscopic removal is carried out using an endoscope, the cyst is removed through a small burr hole, the operation is performed under local anesthesia.
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients will be able to undergo a full examination using modern diagnostic equipment. The hospital hosts doctors from various fields, there is a clinical laboratory, and a rehabilitation center. In the hospital you can recover from surgery or illness, and patients have a 24-hour inpatient facility.
Rehabilitation period
Figure 4. A cyst removed from the maxillary sinus with a tooth in it.
Source: Indian journal of ophthalmology / Open-i (Attribution 2.0 Generic) After surgery to remove a sinus cyst, no special recovery or treatment is usually required. Full recovery takes only a few days. With a small amount of intervention, patients feel well within a few hours after the intervention.
For the first time after surgery, it is advisable to avoid physical activity. You cannot visit the pool and sauna, you must not allow injuries. To avoid inflammation and other complications, you need to ensure high-quality oral hygiene and follow your doctor’s prescriptions.
Why you should entrust treatment to the ENT department of dentistry
ENT dentistry combines two areas of medicine - dentistry and otolaryngology. This is a comprehensive approach to the treatment of combined inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses of odontogenic origin.
The main difficulty in diagnosing and treating ENT-combined situations is that 100% of patients, when symptoms appear or cysts are accidentally discovered, turn only to an otolaryngologist or dentist. Narrow specialization does not allow us to determine the cause-and-effect relationship and create a thoughtful, comprehensive treatment plan.
- The ENT doctor prescribes a standardized conservative treatment, which does not bring results without eliminating the cause, namely the dental cyst.
- The dentist, by persuasion of the patient, tries to save the tooth, but in case of extensive neoplasms, therapeutic treatment of cysts is ineffective.
A person travels from one doctor to another in search of an adequate specialist and a solution to the problem; money and time are wasted on unsuccessful treatment, and the situation does not change.
70% of patients turned to our Center after unsuccessful treatment of cysts , many painful “punctures” of the sinus by an otolaryngologist, or attempts to persuade dentists not to remove, but to cure a tooth cyst without removal.
It is better to entrust the situation to a maxillofacial surgeon with ENT training together with an otolaryngologist. A multidisciplinary approach to patient problems in our Center, extensive experience and practice in two related areas, the necessary diagnostic and operating equipment greatly expand our overall chances of success and increase the overall quality and comfort of treatment.
KolchinSergey Alexandrovich
Maxillofacial surgeon, 7 years of experience
Surgeon with ENT training. He specializes in ENT dentistry, including performing endoscopic operations and carefully removing tumors in the sinuses.
More about the doctor
Diagnostics
Typically, such a pathology is discovered by chance when a person is tested for the presence of another disease.
To do this, they go to a dentist (if the disease concerns the jaws and teeth) or an otolaryngologist, who then issues a referral for an x-ray or another type of examination. ENT specialists can be involved in the diagnosis.
Laboratory tests will not accurately evaluate a cyst.
The doctor may do the following:
- Examine your nose.
- Refer him for endoscopic examination.
- Prescribe an x-ray or computed tomography scan of the patient’s sinuses and skull.
X-ray
X-rays reveal blockage of the sinuses.
Large tumors will appear in black on the image. An odontogenic cyst is identified by adjusting the x-ray to a specific projection. The x-ray will show the size of the cyst:
- Light areas indicate the sinus.
- Dark ones signal a cyst.
Tomography
Currently it is the most effective diagnostic method.
Thanks to it, it is possible to determine with high accuracy where the cyst is located and what the thickness of its walls is, what substance accumulates inside it. Based on the tomography results, the doctor obtains a layer-by-layer section of the patient’s skull. This helps to assess the structure of the formation, which is especially important when selecting a further treatment method.
Puncture
The method involves puncturing the cyst.
The color of the fluid that flows from the wound determines the appropriate diagnosis. This method is only suitable for identifying large tumors. For this, local anesthesia is used. The procedure is not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic. After pumping out the fluid, the person’s breathing returns to normal. The cyst shrinks and the patient's condition improves for a while.
Sinuscopy
An accurate way to study clogged areas and determine their location. The doctor inserts an endoscope into the excretory anastomosis.
With its help, it is possible to examine the tumor in detail and study it for other pathologies.
Preventive measures
During the postoperative period, it is better to eat non-solid food at room temperature, so as not to irritate the nervous system and not fully restored tissues.
After and before the course of treatment, it is allowed to use traditional medicine.
Here are a few of them:
- The leaf of any plant must be washed and placed in the refrigerator, keeping it there for at least 3 days. Then the juice is squeezed out of it, mixing the resulting substance with water and instilling 3-5 drops of the resulting mixture into the nostrils several times a day.
- 2 gr. mumiyo and 5 ml. glycerol dissolves in warm water. Place this solution in the nostrils 3-5 times a day.
- Make an infusion of eucalyptus, tea and honey (in equal parts). The nasal passages are instilled in the morning, afternoon and evening.
Their individual use will not give great results, but together with other methods they provide a significant effect, reducing the size of the tumor and clearing the ducts. Plus, they must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Classification
Cysts are classified according to several criteria:
| Criterion | Varieties |
| Due to the occurrence | In medicine, there are three types:
|
| By content | Neoplasms may contain a number of substances inside:
|
| By location | It is formed in one or more places:
|