The enamel of baby teeth is thin and delicate. Therefore, the first teeth are susceptible to caries. Often, tooth decay occurs before the child begins to eat sweets: literally some time after teething. If in the first years it was possible to avoid caries, then at the age of 3–5 years the risk increases: children at this age already try chocolate and other desserts, and do not always brush their teeth thoroughly. However, it is not recommended to remove baby teeth ahead of time. How and why to treat them and how to decide which treatment is appropriate?
Baby teeth last for several years, but it is important to preserve them
Differences from adult pulpitis
Pulpitis
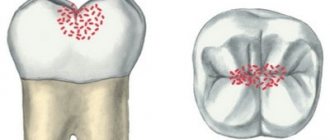
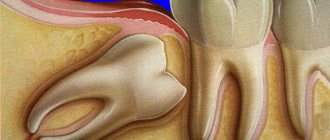
The structure of baby teeth is different from permanent teeth. They have practically no roots, very thin enamel and large pulp. Because of this, caries flows into pulpitis much more easily and quickly - it needs to overcome a very small barrier to the dental nerve.
At the same time, the baby teeth themselves are smaller in size than the molars, and this complicates treatment - there is a high risk of damaging the pulp chamber, and cleaning the canals is very problematic.
At the same time, childhood pulpitis is characterized by a very rapid transition to a chronic form. That is, severe pain does not last long and then goes away, but the tooth remains painful and can get sick again, provoke inflammation of neighboring teeth, or even cause destruction of the permanent tooth germ.
All these features interfere with diagnosis and treatment, so it is important that this is done by a pediatric dentist who is familiar with the specifics of pulpitis of primary teeth. An adult doctor usually does not have enough experience and skills to treat.
Diagnostic methods
Typically, parents or a dentist detect fistulas at a very early stage. They are localized on the outer or inner side of the gums and reveal themselves by noticeable swelling and the appearance of a whitish lump.
It is very important not to self-treat when a problem is discovered. If your baby has baby teeth, improper treatment can pose a risk to the formation of the dentition. When the teeth are molars, there will also be a lot of problems, and there is a risk of needing extraction.
At the dentist's appointment, the doctor will carefully examine the child and take an x-ray. The location of the inflammation, its nature, and estimated depth are taken into account. Already at the first visit, the doctor begins to develop treatment methods to try to solve the problem without surgical intervention.
Causes of pulpitis in children
Pulpitis in children
The causes of pulpitis in children are basically the same as in adults.
Untreated caries in time. Under the influence of caries, the tooth is gradually destroyed, and bacteria sooner or later penetrate into the pulp, causing its inflammation. Since the enamel and dentin of baby teeth are very thin, caries can sometimes develop into pulpitis in a few months or even weeks, that is, very quickly. In addition, the situation is complicated by the fact that parents often do not pay attention to childhood caries, since “the teeth will soon fall out anyway.”
Injury to a baby tooth. This often happens during play - the child hits his face and the teeth seem to be intact, but in fact the root or pulp is damaged. As a result, due to trauma, pulpitis can develop even in a tooth that outwardly appears completely healthy.
Medical error in the treatment of caries. Since a child's pulp is very close to the surface of the tooth, during normal caries it is easy to accidentally damage the tissue and open the pulp chamber. And even if there is no injury, the pulp can become inflamed simply due to exposure to the filling material, too strong an antiseptic, and even overheating during treatment. Most often, this happens when a child is treated by an inexperienced dentist or an “adult” doctor who is not accustomed to working with baby teeth.
Acute infection. Sometimes bacteria penetrate the pulp not from the outside, but from the inside, through the blood. This happens if a child suddenly gets sick with something, for example, a sore throat. Such “internal” pulpitis is rare, but you need to be aware of its possibility in order to connect a recent illness and toothache in time.
Ways to correct a gap between a child's teeth
Eliminating diastema is not so difficult. The many ways to correct gaps between a child's teeth give parents and dentists a wide range of choices. Depending on the width of the gap, individual characteristics and financial capabilities, correcting the anomaly will take some time (from 1 procedure to several years). Among the treatment options for diastema, you will see the most common dental procedures. So, below we present a list of methods for returning teeth to their natural healthy position.
Braces are considered the most common and widely available way to correct a malocclusion. Gradual straightening of the teeth allows the gap to be eliminated. It is best to install braces in childhood, since bone tissue is at the stage of formation and is easier to change. If you install braces in adulthood, you need to be prepared for the fact that after completing the course of wearing braces, you will need to wear a retainer for a long time to consolidate the effect and rebuild muscle memory.
Braces to eliminate gaps between the front incisors are a safe and gentle way to achieve a beautiful, straight smile.
Another way to correct the position of teeth is plates . They belong to the category of removable structures and are designed mainly to be worn by children under 12 years of age. The removable nature of the plates simplifies the process of orthodontic treatment compared to braces, however, if the gap between the incisors is large, the plates will not bring the desired effect.
mouthguards are the dream of many patients, because they are made of transparent material individually in each case and are designed to be worn for several hours a day. Clear aligners have the same effect as braces and plates, but are not suitable for severe overbites.
Another method is to install veneers and crowns on the front teeth. This solution to the problem of diastema does not require a long process of correcting the bite. In this case, the dentist selects a shade of veneers that completely matches the natural shade of the patient’s tooth enamel, which makes the teeth straight and well-groomed, closing the unaesthetic gap. Before installing veneers, you will have to carry out some preparatory work - grinding the teeth.
If the diastema is mild, the dentist may suggest improving the quality of your smile with a cosmetic filling that reduces the gap between the teeth. There is a more aesthetic and modern way to eliminate the gap - artistic restoration. It consists of building up teeth using a composite filling material. After such procedures, care must be taken when chewing hard food and actively using the front teeth while eating.
If the cause of the diastema is an anomaly in the frenulum of the upper lip, an operation to plasticize it is necessary, and then correct the position of the teeth or mask the gap in any way.
Symptoms of pulpitis of baby teeth
The following symptoms are characteristic of childhood pulpitis.
Strong pain. Most often it occurs in the evening and at night, or during chewing and pressure. In addition, the child may refuse to eat hot or cold food or complain of pain outside in the cold.
There is one problem with this symptom - due to the rapid transition of pulpitis into chronic pain, the pain can go away in just a couple of days, so sometimes the child simply does not have time to complain, and the parents do not have time to react.
In addition, if pain bothers a very young child, he often cannot clearly explain what is wrong, so you need to focus on external signs - crying, moodiness, refusal to eat.
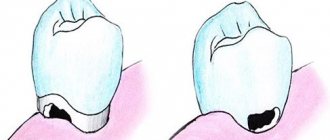
A noticeable carious cavity on a tooth . This is not a mandatory sign - sometimes the tooth is externally intact, but the pulp in it is inflamed. However, if a child complains of pain or feels unwell, and one or more teeth are damaged, this is a sign of pulpitis.
Loosening of the tooth. Due to injury or destruction of the pulp, the tooth may begin to become loose, although it is too early for it to fall out.
Increase in temperature and deterioration in general health . It is especially common in young children, as they react particularly acutely to inflammation.
Swelling or swelling of the cheek. It doesn't happen very often, but it is a clear sign that something is wrong with your teeth. This can be a symptom of both pulpitis and periodontitis or periostitis - a doctor will make an accurate diagnosis.
All these symptoms are weak and unexpressed, sometimes even the child himself ignores them. Only a doctor can accurately diagnose pulpitis, and various methods are used for this, from a simple examination to an x-ray. Therefore, it is important, even in childhood, to regularly take your child to the dentist in order to recognize the disease in time.
Why does the disease occur?
Deep caries can appear in children from three, or even from two years old, if the previous stages of the disease were left unattended.
There may be several reasons.
- An unhealthy lifestyle for the expectant mother is smoking and drinking alcohol in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- The consequence of infections and severe toxicosis.
- Prematurity.
- Infectious diseases suffered by a child in the first months of life.
- Malocclusion.
- Dental caries in the baby's parents.
- Frequent feeding of the child with pureed foods, lack of solid foods in the diet, which leads to insufficient saliva production.
- Excessive amounts of sweets, which promotes the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, carbohydrate fermentation processes and the formation of lactic acid.
- Lack of foods with phosphorus, fluorine and calcium in the diet, which leads to demineralization of teeth and their gradual destruction.
- Insufficient hygiene. Neglecting simple rules - brushing your teeth twice a day and rinsing your mouth after eating - also negatively affects dental health.
At what age does pulpitis occur in children?
Development of pulpitis
Some parents believe that a small child cannot develop caries, not to mention pulpitis. They think that a newly erupted tooth is protected from disease, so they do not examine the child’s mouth or take him to the dentist.
However, children's teeth are actually very susceptible to disease. The risk of developing pulpitis is especially high in cases where the child is often given sweets, but even if you do not overfeed the baby with sugar, his teeth can still get sick.
Even at two years old, pulpitis can affect the front milk teeth. But at 3–4 years of age, caries and pulpitis most often affect the posterior chewing teeth, while the anterior teeth remain virtually unaffected by inflammation.
What is a fistula
A fistula (gingival fistula) is a small seal on the gum. It is characterized by the presence of an open canal, as well as the constant discharge of pus. In many cases, the presence of such a fistula can be recognized visually when a tubercle appears on the child’s gum, the diameter of which usually does not exceed 2 cm. It has a reddish tint, gradually becomes inflamed, and a small funnel appears. As inflammation progresses, more signs of a problem appear.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that a child has such a pathology as early as possible. If this problem is not detected, the fistula can cause serious complications that will have a significant negative impact on the child’s health.
This phenomenon is especially dangerous for the reason that it often occurs in children when they do not yet know how to speak and cannot complain to their parents or describe the essence of the problem.
Next, we will talk about why a child has fistulas on the gums, what to do to prevent them and properly treat them.
Why do you need to treat pulpitis of baby teeth?
Often parents believe that baby teeth do not need to be treated at all. If they do not bother you, it is better to simply not touch them, and if they do bother you, remove them, since the tooth will soon fall out anyway. But there are several reasons why treating childhood pulpitis is very important:
- Acute inflammation can spread to the germ of a permanent tooth, and it will immediately erupt into the patient.
- Extracting a tooth too early will lead to malocclusion - baby teeth will move into empty space, and permanent teeth will erupt incorrectly because of this.
- Pain in an untreated tooth can periodically return and greatly ruin a child’s life and interfere with chewing food normally.
- Losing a tooth at an early stage of speech formation can cause serious speech therapy problems - the child will not be able to pronounce individual sounds normally.
For all these reasons, even baby teeth need treatment.
Gap between teeth - diastema
Diastema is a fairly common phenomenon. In adults, you can often notice a gap, expressed to a greater or lesser extent. Statistics show that literally every second baby is at risk of developing a gap between the front teeth.
If the gap between the upper or lower front teeth is more than 1 mm and varies in width up to 10 mm (most often the limit is 2–6 mm), we can confidently speak of a diastema. The spaces between other teeth have another name - trema.
Due to the formation of a gap, all sorts of inconveniences arise in the implementation of everyday and vital functions. Diastema complicates the normal process of eating and affects diction, so if there is a sufficiently pronounced gap, the child speaks poorly. In addition, the gap is an additional stimulus for the occurrence of caries and periodontitis.
There is a classification of diastemas, including false ones: this involves the presence of a gap between the baby teeth, which naturally disappears during the change of teeth to molars.
If a gap occurs after the appearance of permanent teeth, measures should be taken to eliminate it as soon as possible. And although dentists eliminate diastema even in adulthood, it is most comfortable to carry out treatment in childhood.
What kind of gap could there be? The main division assumes the existence of symmetrical and asymmetrical diastemas. In the first case, the upper or lower incisors are at an equal distance from each other. In the second, only one tooth has an incorrect position, while the second remains in its rightful place.
Also, the spaces between the teeth can be conditionally divided according to the direction of growth of the incisors. The gap can be caused by the divergence of the incisors in different directions with parallel roots (lateral deviation of the crowns) or by a divergence starting from the roots (corpus lateral displacement).
In addition, a so-called medial tilt is possible, when teeth grow with rotation around their axis or have a clear direction to the side.
Treatment of pulpitis in children
There are several ways to cure pulpitis of a baby tooth.
Classic non-vital amputation
This method is now considered outdated, but it is still used in some clinics, especially in free public dentistry. The essence of this method is as follows:
- The doctor drills out the carious tissue, opens the pulp and applies a special paste to it that kills the nerve. Previously, pastes with arsenic were used - they killed the nerve in two days, but were not very beneficial for health. Now they use safer means, but they take a week to kill the nerve.
- When the nerve is killed, a special mixture is pumped into the tooth to mummify the pulp. Sometimes the pulp is partially removed.
- At the last visit, the doctor installs a permanent filling.
In adults, this method is now practically not used, since the tooth turns gray after it, and the pulp can become inflamed. However, when treating baby teeth, the method has the right to be used, since the baby tooth will still quickly fall out, and pulpitis will not have time to reoccur.
The main advantage of this technique is its simplicity and low cost. The treatment can be carried out by almost any dentist, so in rare cases the use of this method is justified. But in order not to expose the child’s body to stress, it is better to use other treatment methods.
Vital pulp extraction
This method exists today thanks to the advent of modern powerful anesthetics. It is most often used to treat pulpitis in adults, and is often used on children.
The essence of the technique is that, under powerful anesthesia, the living pulp is completely removed from all root canals of the tooth. After this, the canals are carefully processed and then filled with a special paste.
In adults, gutta-percha is used for filling, but it does not dissolve over time—in a child’s tooth, this would prevent it from falling out. Therefore, for children, the canals are filled with zinc-eugenol paste, which will gradually dissolve along with the roots.
This method is good, but requires special skill of the doctor, as well as the use of expensive materials and instruments. Therefore, treatment of pulpitis using this method is rarely offered in public clinics, and in paid clinics it can cost several thousand per tooth.
Vital amputation
This is a very rare method, since it is applicable only at the very beginning of the onset of pulpitis. That is, you need to run to the doctor as soon as the child complains of tooth pain - only then will this method be effective.
Its essence lies in the fact that under anesthesia, only the inflamed area of the nerve is removed from the tooth. An antiseptic and anti-inflammatory medicine is applied to the rest of the nerve, and then everything is carefully sealed. This technique allows you to partially preserve the pulp and extend the life of the tooth, but when using it there is a high risk of recurrent pulpitis.
Treatment methods for caries of anterior teeth
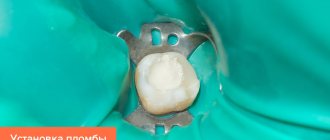
The treatment method is selected individually with the dentist and depends on the severity of the tooth damage, the location of the caries, and the patient’s age. If the lesion has not reached the stage of pulpitis, then the dentist uses local anesthesia to reduce sensitivity and prevent pain. In some cases, at the Karmen-Med dental clinic, specialists, after agreement with the patient, administer sedatives. Then the dentist drills with a drill and removes the caries. After drilling, a noticeable depression remains. To return the tooth to its original shape, a filling is placed.
If the tooth is severely damaged, veneers or crowns can be installed. If a large percentage of the tooth surface is damaged, the doctor may resort to removing it altogether.
Photos before and after caries treatment:
Prevention of childhood pulpitis
Treating pulpitis in baby teeth is difficult and expensive, so it is best to avoid it. The following preventive measures will help with this:
- Start oral hygiene from the eruption of the very first tooth, and gradually accustom the child to it.
- Brush children's teeth with special toothpastes containing age-appropriate fluoride.
- Avoid giving your child too many sweets, especially sugary drinks. The most dangerous thing is to give a child sweets from a bottle - because of this, the front teeth are often affected by caries, and then pulpitis.
- Make sure your child's diet includes plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits. Solid foods are especially beneficial - they strengthen teeth and help remove plaque.
- Every six months, take your child to the dentist for preventive examinations so that the doctor can notice and treat caries in time.
- At the first signs of even mild dental damage, do not let the process take its course, but take the child to the dentist.
These measures will help you prevent pulpitis and keep your child's baby and permanent teeth healthy.
Why is caries of the front teeth dangerous?
Caries seems harmless until a person begins to feel discomfort. But destructive processes begin already in the first stages. First, the top layer becomes thinner, then depressions form on the surface of the tooth. Then the patient begins to feel pain.
Deep caries will lead to tooth destruction, endless sharp pain, an unpleasant odor will constantly emanate from the oral cavity (brushing, chewing gum and other fresheners will not help), and you will also notice a strong cosmetic defect. The longer you delay with the problem, the less chance you have of saving the tooth.
How to treat caries in a child
The method of treating caries in children is determined by the stage of the disease. If it is detected at the very beginning, silvering, remineralization or ozone therapy is prescribed.
Silvering is a minimally invasive and painless method of treating caries, which consists of applying a silver solution with a cotton swab to the surface of a tooth affected by caries. The silver composition has an antibacterial effect and is good at destroying cariogenic microbes. This method has a significant drawback. After silvering, tooth enamel darkens without the ability to restore its natural shade. You'll have to wait for the molars to grow in.
Remineralization is a procedure for saturating enamel with minerals. The method is effective at the stage of a white spot, onto which compositions with calcium, magnesium and phosphorus are applied. Several sessions are required to completely restore the surface of the tooth. In order to quickly introduce microelements into the enamel, ultrasound, electrophoresis or vacuum are used.
Ozone therapy is one of the most modern methods of caries treatment, in which ozone is applied to the tooth through a small silicone cup. It sterilizes the carious cavity. This procedure, which lasts only a few minutes, ends with remineralization.