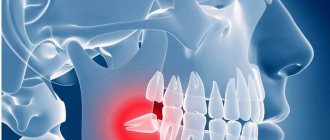
Exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the tooth sometimes leads to swelling of the cheek. The symptom of swelling occurs due to inflammation of the periosteum, which in dental terms is called periostitis.
It must be said that swelling indicates that the stage of inflammation is seriously advanced. If the cheek is swollen from a tooth, then most likely the patient ignored the long period when the tooth was destroyed by caries. Then the infection penetrated into the pulp chamber, where the nerve of the tooth is located, and pulpitis began. But even at this stage the patient did not visit the dentist, but endured acute tooth pain with the help of painkillers. Then the pathogenic bacteria penetrated deeper into the periodontal tissues, which connect the root of the diseased tooth with the alveolar processes of the jaw, and from there they reached the periosteum, causing periostitis.
Causes of the pathological condition
There are many reasons that lead to a swelling of the cheek from a tooth. Among them are:
- Toothache. A tooth hurts due to caries or pulpitis. Swelling may also occur after the element is removed. With proper treatment, the symptom goes away on its own within 2-3 days.
- Inflammation of the salivary glands and ducts. The cheek swells due to improper oral care or infection with viral and infectious pathogens.
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses. Swelling spreads to other areas of the face - eyes and cheeks.
- Damage to the lymphatic system. This factor is the most common cause of cheek swelling without tooth pain.
- Neuritis of the facial nerves. Pathology develops due to hypothermia of the body. Additionally, the problem is accompanied by impaired facial expressions and pain when talking and eating.
- Mumps is a viral disease that leads to damage to the salivary glands. One of the symptoms of mumps is swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes and cheeks. Swelling can manifest itself both unilaterally and bilaterally.
- Infectious mononucleosis. In terms of symptoms, the disease is similar to a sore throat and occurs in an acute form.
- Diphtheria. Occurs due to damage to the body by the Loeffler bacterium. Diphtheria is accompanied by the appearance of white plaque on the tonsils and fever. Antibiotic therapy does not give a positive result in treatment.
- Traumatic injuries to the soft tissues of the cheek. The healing period after injuries takes 2 to 3 weeks.
- Allergic reactions. There are situations when the cheek is swollen due to individual intolerance to food or oral hygiene products. You can get rid of the problem only by eliminating the provoking factor.
Swelling on the inside of the cheek
Sometimes the swelling is located on the inside of the cheek. This can be caused by most of the reasons already mentioned - dental problems (decay and infection), ulcers, swollen salivary glands, mouth and cheek ulcers, trauma, infections (bacterial or viral), tooth abscess, lymph node problems (especially preauricular, submandibular nodes and tonsillar lymph nodes), mumps.
Additionally, various procedures such as fillings, oral surgery, tooth extractions, cheek piercings can also lead to swollen cheeks inside the mouth.
This problem occurs in both adults and children and can be accompanied by numbness in the cheek. Treatment for a swollen inner cheek will depend on the underlying cause of the condition.
Tumor due to improper treatment
Why else can pathology be observed? Separately, it should be noted the swelling of the cheek, which arose as a result of illiterate therapy. If the cheek is swollen after a complex tooth extraction, then this is a variant of the norm. The symptom disappears on its own after a few days. Typically, such swelling is small in size and does not cause pain to the patient. The situation does not require repeated surgery.
The opposite situation arises if we are talking about an infectious process that has begun after medical care has been provided. Complications are more often observed after the removal of wisdom teeth or a retained element. Such operations cannot be performed without significant damage to soft tissue. Complications arise due to doctor errors or when the patient fails to comply with the dentist’s recommendations during the recovery period.
The impacted tooth is located in the deep tissues of the gums due to incomplete eruption or incorrect location
The gums also swell due to improper sanitation of the diseased tooth. In this case, repeated assistance from a specialist is required, followed by taking medications and local treatment of the affected area. After complex removal of an element, swelling can be observed for up to 2 weeks.
Swelling also often develops due to allergic reactions to painkillers used by the dentist during treatment. In this case, additional symptoms are observed (heavy breathing with whistling, shortness of breath), but the tooth does not hurt. A person requires urgent hospitalization to cleanse the body of the allergen.
What to do when your cheek is swollen, but your teeth don’t hurt
Every person wants to have an attractive appearance. Therefore, special attention is paid to facial care. But what to do if the aesthetic appearance of your face is spoiled by a swollen cheek? This problem cannot be hidden with the help of cosmetics such as powder and foundation.
There are many reasons why cheek swelling occurs. In a matter of hours it can become quite noticeable. Why does this happen and how to resist the disease? In this article you will find answers to your question.
Symptoms that require urgent help
You should not postpone a visit to the doctor if your cheek is swollen from a tooth. The condition can be fatal.
The list of dangerous signs includes:
Headache after tooth extraction
- Unbearable toothaches that appear constantly. The condition indicates that an infection has attached to the surgical field. Severe pain is acceptable only after operations involving cutting out part of the bone tissue. Pain sensations decrease after 1-2 days, otherwise urgently contact the dentist.
- Temperature rises to 38 degrees and weakness.
- Pain when opening the mouth, swallowing and eating food.
- A compaction revealed by palpation of the problem area.
- Absence of a blood clot in the socket. A clot does not form due to intensive mouth rinsing on the first day after surgery or other illiterate actions of the patient that provoked a violation of soft tissue regeneration. The condition threatens the occurrence of acute symptoms and infection of the maxillofacial tissue.
Also, immediate consultation with a doctor is required in cases where the tumor is rapidly growing in size.
Due to the lack of blood clot formation, infectious complications develop after a tooth has been removed (pulled out).
When to see a doctor
As soon as discomfort and other suspicious sensations appear, it is better to immediately go to the doctor for a consultation. Pain does not arise out of nowhere, especially if it is accompanied by swelling of the soft tissues, bad breath and discharge of pus. All these are clear signs of a pathological process that can lead to serious complications, including tooth loss. Therefore, the sooner you seek dental help, the easier and faster it will be possible to eliminate the pathology, avoiding irreversible consequences.
First aid measures
What can you do at home to reduce the intensity of the symptoms? If the gums are swollen, but the condition is not accompanied by a general deterioration in the condition: a rise in temperature and signs of intoxication, then first aid measures can be carried out.
How to remove a tumor? First aid includes the use of various herbal remedies to rinse the mouth. For this purpose, chamomile, St. John's wort, and oak root are used. Herbs will relieve inflammation and stop the proliferation of pathogenic flora in the mouth. The procedure is performed every 2 hours for 1-2 minutes.
Instead of herbal decoctions, antiseptic drugs are used - Stomatodin, Chlorophyllipt. The drugs are diluted with warm water and rinsed with them every 3-4 hours.
Chlorophyllipt is used in dentistry for exacerbation of infectious diseases
What should not be done if the gum area is swollen? If a tumor occurs, they refuse to heat the problem area. This leads to a worsening of the situation and further spread of the pathological process.
If your tooth hurts badly and your cheek is swollen, take anti-inflammatory drugs - Nise, Nurofen, etc. Analgesics – Solpadeine and Ketanol – can help relieve swelling well. The latter remedy has many side effects, but can cope with any type of pain. If a child’s cheek is swollen, then preference is given to anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of syrup.
What medications will help relieve pain and reduce swelling?
Before visiting a specialist, you should try to relieve the pain and stop the spread of the inflammatory process. This can be done by rinsing with antiseptics, for example, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin or Miramistin.
Antiseptic rinses will help relieve pain
Applications using local drugs, including Levomekol, Cholisal or Metrogyl Denta, will help reduce swelling. Like cooling anti-inflammatory gels (Troxevasin, Fastum Gel), these drugs are best used after consultation with a doctor.
All of the above recommendations are only part of symptomatic therapy. It is impossible to eliminate the source of inflammation and restore the affected tissue without the participation of a dentist. Do not self-medicate to avoid serious complications later.
1Barer G.M. Therapeutic dentistry, 2008.
Treatment of pathology
What to do if there is a problem? After providing emergency assistance, the patient should consult a doctor. The specialist performs the necessary manipulations and then gives the patient recommendations regarding caring for the damaged area at home. These include mouth rinsing, physiotherapeutic procedures and local treatment of the soft tissues of the mouth. Providing emergency assistance for a cheek tumor is prohibited for children; women during pregnancy; adults who suffer from immunodeficiency; persons prone to allergic reactions.
General antibacterial drugs
Ideally, a suitable medication is prescribed after taking a swab from the mouth and identifying the causative agent of the problem. But if the situation is urgent, then to quickly eliminate the flux, the patient is prescribed new generation antibiotics. The action of the tablets is aimed at destroying and slowing down the spread of bacteria. For pathology use: Biseptol, Ampiox, Amoxiclav, Lincomycin.
Ointments
In addition to antibiotic therapy, topical medications are used. The use of products is permissible only with the permission of the dentist, since self-prescription of ointments rarely leads to recovery.
To reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process, Levomekol containing metaluracil and chloramphenicol is prescribed. Levomekol is rubbed into damaged membranes of the oral cavity 3-4 times a day. After treatment, you should not eat or drink water for 1 hour.
List of ointments that are used if a child’s cheek is swollen
To quickly get rid of the symptoms of swelling, you can use antimicrobial ointments in combination, for example, Streptomycin and Ichthyol. The drugs are mixed in equal proportions and applied to the damaged gum. Another popular drug of combined action is Metrogyl Denta.
Means for rinsing procedures
How to rinse the problem area? To quickly get rid of the remaining pus after surgery, and to prevent the development of swelling of the cheeks, use folk and household rinses. Several recipes are suitable for this purpose:
- Soda solution: 1 tsp. the main ingredient is dissolved in 100 warm water. Mouth baths are done at least 4 times a day.
- Miramistin. The drug is sold ready-made and does not require prior dilution. To treat foci of infection, take 20 ml of liquid into the mouth and rinse the mouth for 1 minute. After this, the liquid is spat out.
- Propolis solution. The drug is purchased at the pharmacy and diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:10. The product is used after meals.
- A mixture of St. John's wort, oak bark and sage: take 1 tsp. each ingredient and pour 500 ml of boiling water. The product is infused in a tightly closed container for 6 minutes. After filtering, the solution is used 3 times a day to relieve gum inflammation.
- A blend of green tea and sage. The dry collection is brewed with 500 ml of boiling water with the addition of 1 tsp. salt. The solution is recommended to be used warm. Before each procedure, it is advisable to prepare a fresh product.
- A mixture of chamomile, birch buds and calendula: the components are mixed in equal proportions and diluted with 1 liter of water. The mixture is boiled for 10 minutes, and then left to cool completely.
It is important to refuse the procedure in the first 24 hours after the intervention so as not to wash out the clot.
Prevention
The main procedure for preventing cheek swelling is timely treatment of caries and other dental problems.
Simple recommendations will also help maintain oral health:
- Regular dental care. Dentists advise using more than just a brush and paste. To effectively clean your mouth from plaque, you can use dental floss, floss and irrigators. You should also not forget about cleaning your tongue, since most of the bacterial flora is concentrated there.
- Pay attention to the condition of your gums. If these structures are loose and bleeding, they turn to a specialist - a periodontist.
- Visit your dentist at least once every 6 months for a diagnostic examination and professional teeth cleaning.
- Change your eating habits. Carbonated drinks, sweets and alcohol have a detrimental effect on the condition of teeth and enamel. To maintain dental health, it is better to consume fermented milk products, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Swelling of the cheek should not be ignored; in addition to aesthetic problems, the condition can threaten human health. More often, the problem develops against the background of developing caries and improperly performed dental work. If the inflammation is not accompanied by bleeding, fever and other dangerous signs, then emergency measures are taken at home, and then see a dentist. Preventive methods regarding cheek swelling are simple and accessible to every person. Their implementation will minimize the frequency of visits to the dentist.
Swelling of the cheeks and gums
Swelling of the cheeks and gums can be caused by any of the reasons mentioned.
In addition, gum problems may be associated with gingivitis, teething syndrome, herpetic stomatitis, parulis, periodontal disease, malnutrition, ill-fitting dentures, and viral or fungal infections. It is also known that pericorinitis (inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums) leads to swelling of the gums and cheeks.
With this type of swelling, the affected area may be numb and painful when chewing. To reduce swelling, you can try applying a cold compress, rinsing with a saline solution, and using antifungal medications.
Read also: Abscess on a child’s gum