In the lateral sections, teeth (molars, premolars) are subject to regular high loads, while their anatomical structure and location in the dentition makes care more difficult. Therefore, chewing units are destroyed faster due to various injuries and dental diseases. Prosthetics of molars and premolars involves the use of structures made of durable, reliable materials that are resistant to severe chewing loads. Dental crowns are orthopedic structures for single restorations, indicated when the upper part of the tooth is destroyed by more than 60%, when the installation of a filling is ineffective.
Types of dental crowns for chewing teeth
Molars and premolars are a kind of millstones that grind food before it enters the esophagus. They experience a high load, which can exceed 75 kg per 1 cm2. Therefore, chewing units are characterized by a massive size, a surface with many protruding tubercles. To restore molars and premolars, strong, reliable materials are used that can withstand increased loads. Orthopedic dentistry offers the following types of crowns for chewing teeth:
- Metal
– durable, corrosion-resistant, service life up to 10-12 years. The list of materials from which these structures are created includes: nickel-chromium alloy, cobalt-chromium alloy, titanium, alloys of noble metals (platinum, silver, gold, palladium). Solid metal alloy prostheses can be coated or not. These are the most inexpensive crowns, but the aesthetics leave much to be desired. Structures containing gold are characterized by high ductility and fit precisely to the tooth stump. The disadvantages of such dentures include excessive abrasion of the antagonist tooth (molar, premolar on the opposite jaw) with constant contact, poor aesthetics, and the development of allergies to the components of the metal alloy (beryllium, chromium, nickel). - Metal-ceramic
- reliable, durable dentures with a metal frame coated with a layer of ceramic mass. Metal-ceramic crowns are quite aesthetic, with an optimal ratio of reasonable price and good quality. Over time, the metal base begins to appear through the gums (gray stripe effect), which negatively affects the aesthetics. Therefore, it is not recommended to place such dentures on teeth along the smile line. - Crowns made of zirconium dioxide
are strong, durable structures that retain their original appearance throughout their service life (more than 15 years). The aesthetics are not inferior to ceramics and provide the tooth with a natural appearance. The biocompatible material is suitable for patients with metal allergies and is used for restoration of the frontal and chewing areas. The structures are manufactured using CAD/CAM technology, on a robotic machine, by milling. This eliminates any errors or inaccuracies, ensures precise fit of the structure to the tooth stump and gum, taking into account the type of jaw closure and the characteristics of the bite. - Metal-plastic
- inexpensive structures, which are a frame made of a metal alloy lined with plastic mass. Due to the porosity of the material, the surface of the prosthesis quickly darkens and absorbs dyes and odors from foods, drinks, and cigarettes. The metal alloy can provoke inflammation and allergies. Service life up to 3 years. Typically, such products are used for temporary prosthetics; they are unreliable as a permanent prosthetic structure.
Ceramic crowns are not suitable for the restoration of molars and premolars. Fragile ceramics are not able to withstand high chewing loads and quickly chip and crack. Ceramic crowns are placed on the front teeth, where the main criterion is high aesthetics. The incisors and canines are not subject to high loads, but participate in the formation of a smile and are visible during conversation. Ceramic restorations are identical to natural enamel in color and transparency and do not stand out from the dentition.
Names of teeth
It is worth familiarizing yourself with them before starting to study numbering algorithms.
Each row of teeth is symmetrical, and it consists of left and right parts. There are several groups of teeth that differ in structure, function, and location.
For adults they are:
- Incisors. These are the front (central, medial) teeth, designed for biting food. They are flat and have sharp edges. There are 8 of them in total - 4 each in the bottom and top rows. In numbering they are often called ones and twos;
- Fangs. They follow the incisors. If you count from the first central incisor, then the canine will be the third from it - both to the right and to the left. For those who are not familiar with dentistry, the name of this type of teeth may seem funny. They wear it not in vain. These are strong teeth with a wide crown and sharp edges, having a conical shape. They are designed for biting off high-density food (for example, meat). Fangs have the longest roots. In total, a person has 4 fangs - 2 above and 2 below, and dentists call them triplets;
- Premolars. They follow immediately after the fangs and have a prismatic shape. On each side of the jaw - both upper and lower - there are 2 premolars, i.e. there are 8 in total. They are the 4th and 5th, and they are intended for chewing food;
- Molars. Their numbers are 6, 7, 8, if you count from the central incisor. Thus, the total number of them is 12 - 6 on each jaw (3 on each side). These are large chewing teeth with a wide surface. They are designed to literally grind food, being strong and powerful.
A child's dentition differs from an adult's in the number of its components. Babies have 5 of them on each side, i.e. 10 each on the upper and lower jaws. The last ones in each row are fives. But when their dentition begins to change, permanent molars are one of the first to appear.
The name of teeth used by dentists is one of the “beacons” by which they determine their location. But this is not enough for the most accurate description, and therefore an error-free diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, different numbering systems are used.
Haderup system
It is used in dental practice quite often, but doctors are divided on its convenience and the degree of risk of erroneous decoding. This algorithm involves designating teeth by a serial number with an index indicating their specific location.
Their numbers are formed as follows:
- Numbers 1-8 are used to indicate the number. The number 1 represents the central (front) incisor, and the number 8 represents the third molar. Accordingly, 2 – second front incisor, 3 – canine, 4 and 5 – premolars, 6-8 – molars;
- To indicate the location, the indices “+” and “-” are used, where the first is the upper jaw, and the second is the lower jaw;
- Considering that the report goes from the front to the molars, it is necessary to indicate the side - right or left. This is done through proper index placement. If the side is right, it is placed after the number, and if it is left, before it.
For example:
- 5+ is the upper second premolar on the right;
- -2 is the second lower front incisor on the left.
According to this system, children’s tooth numbers are indicated in a similar way, but a 0 is placed before the number and numbers from 1 to 5 are used.
For example:
- 02+ is the primary front incisor on the upper right;
- -01 is the primary front incisor on the lower left.
Square-digital system
Its other name is the Zsigmondy-Palmer system. It also provides for numbering using numbers 1-8, as in the Haderup system, but the location is indicated using the corner icon, in which the desired number is indicated. According to this algorithm, each jaw is divided into two segments, and the countdown, as in the previous case, begins with the central incisors. Those. 1 is the front incisor, and 8 is the third molar.
How to decipher the symbols?
- The angle directed downwards and to the left is the lower right jaw;
- The angle looking down and to the right is the lower left jaw;
- The angle depicted up and to the left is the upper right jaw;
- The angle directed upward and to the right is the upper left jaw.
For example:
- The number "5", located in the corner looking down and to the right, indicates the second premolar in the bottom row on the left;
- The number “2”, depicted in the corner directed to the left and upward, indicates the anterior second incisor on the right jaw from above.
In the case of designating baby teeth in children, the same algorithm is used, but they are designated by Roman numerals IV.
Two-digit system
Today it is increasingly used in dentistry, being one of the most convenient and modern. It involves dividing the jaws into four segments. In this regard, the algorithm is similar to the previous ones, but it differs in the designation of the segment - each of them has its own number:
- Upper right – 1;
- Upper left – 2;
- Bottom left – 3;
- Bottom right – 4.
The teeth themselves are numbered using numbers from 1 to 8. As in previous cases, 1 is the front incisor, 8 is the third molar.
The number consists of two digits:
1 – segment;
2 is its serial number.
For example:
- 36 – first molar on the left in the bottom row;
- 15 – second premolar on the right in the upper row;
- 43 – canine on the lower jaw on the right.
To designate baby teeth in children, the segments are designated by numbers 5-8:
- Upper right – 5;
- Upper left – 6;
- Bottom left – 7;
- Bottom right – 8.
The number of the teeth themselves is indicated by numbers 1-5.
For example:
- 62 – second front incisor on the left in the top row;
- 84 – first premolar on the right in the bottom row.
Alphanumeric system
It differs from others primarily in that it involves the use of letter designations. They correspond to the name of the teeth, and it is indicated in Latin letters. For clarification, a digital index is added to them in all designations except fangs.
In the case of adult dentition, capital letters are used:
- I1 – central first incisor (unit);
- I2 – central second incisor (two);
- C – fang (three);
- P1 – first premolar (quad);
- P2 – second premolar (five);
- M1 – first molar (six);
- M2 – second molar (seven);
- M3 – third molar (figure eight).
To designate children's milk teeth according to this system, Latin lowercase letters are used:
- i – incisors;
- c – fang;
- m – molars (4ths and 5ths).
Modern specialists today very rarely use the alphanumeric system, since it does not allow specifying the exact location - upper or lower jaw, side. Since dentists’ tooth numbers are designed to perform this function, such an algorithm is not informative for diagnosis and treatment.
Universal system
It is comfortable and light. This numbering method does not involve division into segments, the use of letters, or the use of several symbols. The principle is simple - each tooth has its own serial number, which is determined by its location:
- The count starts from the 3rd upper right molar. He, according to this system, has the number 1;
- Next, the markings proceed in order to the upper left 3rd molar, which is numbered 16;
- Number 17 is the lower left 3rd molar, and the numbering continues from there towards the 3rd lower right 3rd molar, which is numbered 32.
Capital Latin letters are used to designate baby teeth in children:
- AE – right upper dentition (from 5 to 1);
- FJ – left upper dentition (from 1 to 5);
- KO – bottom left row (from 5 to 1);
- PT – bottom right row (from 1 to 5).
Features of numbering of baby teeth
Unlike the molars that adults have, children have only 20 teeth, whereas in the first case there are 32. But at the age of 5-6 years they begin to be replaced by molars, which happens gradually, and this process is completed by about 13-14 years . Thus, during this period, a child, as a rule, has both one and the other at the same time. This may make them somewhat difficult to describe.
In this regard, not all numbering systems are convenient to use. Most often, dentists in this case use a two-digit algorithm, which implies the following designations:
- 51-55 – right segment of the upper jaw;
- 61-65 – left square of the top row;
- 71-75 – right segment of the lower jaw;
- 81-85 – left square of the bottom row.
Numbering of teeth is a necessary condition for an accurate description of diagnostic and therapeutic dental procedures, since without a description of their location, errors may be made.
Kostyuk Hanna Volodymyrivna
Orthopedic dentist of the first category
Did you like the article?
Rate: ( 4.50 out of 5)
Loading…
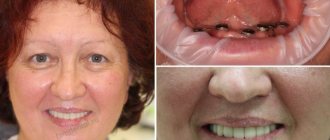
Stages of installing a crown on a chewing tooth
- Diagnostics
– a comprehensive examination (orthopantomogram, 3D tomography), the dentist determines the general condition of the oral cavity, identifies dental problems, the presence of contraindications, draws up a treatment plan, and selects the optimal orthopedic design. - Preparation
- sanitization of the mouth (removal of plaque, tartar), treatment of teeth and gums (according to indications). The tooth is prepared for covering with a crown - the enamel is prepared, giving the stump the desired shape, the nerve is removed, the canals are filled, and, if necessary, the root is strengthened with a pin or inlay. To install zirconium structures, minimal tissue grinding is required; at the ILATAN clinic, a dental microscope is used for preparation, which allows you to remove enamel within a fraction of a millimeter. - Casts
- the doctor takes impressions of the patient’s jaws, from which a prosthesis is made in the laboratory. To protect the tissue, a temporary plastic crown is fixed to the prepared tooth. - Installation
- the finished crown is tried on, adjusted if necessary and fixed to the support with dental cement.
Filling as part of caries treatment
The cause of molar destruction is most often caries, which usually develops due to abundant accumulations of plaque and hard deposits - the result of insufficient cleaning and hygiene. As a result, the tooth gradually deteriorates, and before the infection reaches the nerve, it is important to begin treatment as soon as possible. At the appointment, the dentist will remove all necrotic and damaged tissue, perform an antiseptic treatment and begin restoring the integrity of the crown.
Source: dentalperfection.in
Today, modern photopolymer materials are used for this purpose - such composites harden under the influence of a special polymerizing lamp. This property allows you to apply the material in layers to return the crown to its original appearance - it helps to recreate the anatomical relief as accurately as possible to restore the aesthetics and functionality of the tooth. In addition, photopolymers are durable and wear-resistant - their service life can reach 20 years, of course, with proper and regular care.
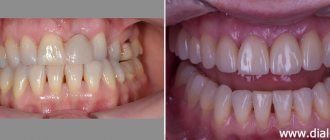
The best crowns for chewing teeth
Since the main requirements for prosthetics of molars and premolars are the strength and durability of orthopedic systems, the best crowns for chewing teeth are made of zirconium or metal-ceramics. Zirconium is the most durable, lightweight material; installation of such structures requires minimal preparation of the abutment tooth, which is a big advantage over metal-ceramic products. The doctor will decide which restoration to use in a particular case after a detailed assessment of the clinical picture, the characteristics of the patient’s body, his wishes and financial capabilities.
How much do crowns cost in Moscow?
The cost of treatment depends on the complexity of the case, the volume of intervention, restoration material, and manufacturing technology. Installation of metal crowns in Moscow costs on average from 10,000 rubles. per unit, metal ceramics will cost from 15,000 rubles, and a zirconium dioxide crown – from 30,000 rubles.
The ILATAN clinic operates a case payment system, which protects the patient from unexpected expenses and hidden fees. The turnkey price includes all necessary measures for tooth restoration - from consultation to manufacturing and installation of a crown. Treatment of teeth, gums, production and installation of a core inlay, dismantling of old restorations are paid separately. The doctor will announce the exact amount of treatment during the consultation, after examination and diagnosis.
Teething order
At the time of birth, the baby has no teeth, but there are exceptions to this rule. Often, the order of growth of baby teeth is as follows:
- Teething begins at the age of 6-8 months. The first to appear are the central incisors of the lower and then the upper jaws. This is the very moment when you should worry about choosing the first toothbrush for your offspring.
- Between 8 and 12 months, the lateral incisors are added.
- At 10-16 the fangs take their place.
- At one and a half years, the back teeth (or molars) usually erupt completely.
The primary dentition completes its formation by the age of three, when the second back teeth begin to grow.
Carefully monitor the teething process until it is completed, since during this period the first pathologies may appear, such as childhood bruxism (teeth grinding). At the slightest suspicion, consult an orthodontist.
Answers to common patient questions
What is the name of a wisdom tooth? The dental unit, which is the third extreme molar, can often be heard called “eight”. It usually has 3 to 5 roots. At the moment, in medicine they are recognized as a vestigial organ. Their growth is observed at the age of about 20 years. Where does the name wisdom tooth come from? They began to be called that because they begin to form later than the main elements of the dental system, that is, when a person becomes an adult.
What are sharp teeth called? These are long, deep-set dental units, otherwise called canines. Their peculiarity is that they have single roots. Teeth have the same name on both the lower and upper jaws of a person.
In addition to the names of the upper and lower teeth, you should know their anatomy. Each dental unit consists of enamel, dentin, pulp, and root canal. The upper part makes up the crown, the inner root. The crown part usually protrudes above the gum, the root part is located inside, fixed in the hole of connective tissue.
We tried to cover as fully as possible how human teeth are correctly called. Specialists at the AlfaDent dental clinic are always ready to advise on the designation of an element of the dentition and the appropriate dental treatment.
Dental formula
To understand how to count teeth, you can use a dental formula. It indicates the arrangement of elements in order, which is written using specialized notations. This is how the formula with the numbering of teeth is determined. The doctor examines the jaw and draws it up. The radical units are designated by Arabic values, and the temporal ones by Roman ones. The symbol looks like this:
I2/2C1/1P2/2M3/3=32.
In the expression, incisors are designated – I, premolars – P, molars – M.
In addition, dentists use tooth numbering. It is counted from the middle of the segment in the direction from left to right. Sometimes a number is added to the ordinal value to indicate the location zone. For example, the right canine on the top row is numbered thirteen.
Types of tooth number designations
There are four systems:
- The first was founded by Sigmund-Palmer. It is based on the use of Arabic numeric symbols from one to eight. Milk formations are designated by Roman values.
- Digital is used all over the world. The elements are designated in order from one to eight, to which a quadrant is added. As a result, there will be a two-digit value. This method allows you to avoid a long description, eliminates the occurrence of errors, and accurately indicates the location.
- The universal one uses Arabic numeric values from one to thirty-two. Elements begin to be counted from the right side of the top row. Temporary ones are marked with letters of the Latin alphabet.
The teeth diagram is included in the formula. For each segment there is a capital letter, in words denoting milk teeth. To accurately indicate the location, numbers are added to the designation.
If you are interested in how to count teeth in dentistry by numbers, then a two-digit numbering system is used. It is convenient for dentists and computers from all over the world. Each tooth has its own separate meaning, which depends on the location and type. To determine which teeth are located at numbers 5 and 6, let’s look at the designation scheme in more detail.
Incisors are designated by values one-two, canines - three, premolars - four-five, molars - six, seven and eight. In addition, the jaw is divided into sections: right and left. For the top row, use numbers one and two, and for the bottom row, three and four. In children, the milk series is indicated by numerical values from five to eight.
The elements must be counted from the left, the first number means the segment, and the second – the dental unit. Therefore, each number in the numbering will correspond to a specific element. Knowing how teeth are counted, it will be easy for the client to have a conversation with a specialist. He will feel confident, understand each stage of treatment, and will be able to read the diagnosis in the medical record.
Which prosthetic option is optimal?
There is no type of prosthetics that is universal and ideal in all respects. Each technique has both advantages and disadvantages. Among the advantages of removable orthopedic devices are the following:
- the most simple, non-invasive installation, during which the patient does not experience any discomfort;
- financial accessibility – the cost of removable dentures can be called low;
- minimal number of contraindications - removable structures are suitable even for pregnant and lactating women.
However, there are also many shortcomings. The main one is the insufficient reliability of fixation of the structure. The denture must be removed from the mouth every day and cared for carefully. In this case, wear will be quite rapid.
Some removable structures have another problem - not the most aesthetic appearance. For example, if clasps are used for fastening, they will be noticeable to others.
Crowns and bridges are an affordable solution, which has two main advantages - high aesthetics and a relatively affordable cost. However, their installation requires turning, which significantly complicates the procedure and increases the list of contraindications.
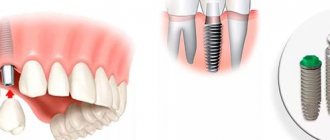
Today, the most reliable option is implantation. Implants are the most functional solution. Teeth restored using implantation look aesthetically pleasing and last a long time. However, their installation is an invasive procedure in which the gums are prepared. However, this process goes smoothly and practically does not cause pain or discomfort in the patient. This is followed by a period of rehabilitation, when the patient needs to take medications and undergo regular dental examinations.
In our dental complex, the problem of missing chewing teeth will be solved individually. PRESIDENT specialists will select the method that best suits you!