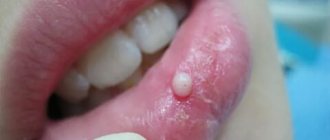
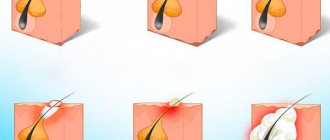
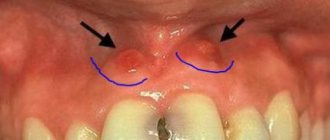
A common reason for visiting a dentist is a lump on a child’s gum. Upon examination, the doctor discovers a round formation of varying degrees of density, painless or with a mild pain symptom.
In most cases, in the area where the pathological element occurs there is a dilapidated or filled tooth. But sometimes the tooth turns out to be intact (undamaged), and the surrounding gum has a normal color. The reasons for the appearance of a lump can be varied. To determine them, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess
Young children do not properly care for their oral cavity. Poor brushing of teeth promotes the accumulation and proliferation of bacteria. Penetrating into the tissue, they provoke the development of inflammatory processes, including a purulent lump.
Other factors also influence the formation of an abscess:
- New teeth.
In some babies, the eruption of baby teeth is preceded by the appearance of small tumors filled with white fluid. If such a lump on the child’s gum does not hurt, then there is no reason to urgently consult a doctor.
- Gum injury.
Damage occurs due to the active lifestyle of babies, solid foods or accidental biting. The injured area becomes red and inflamed. Usually everything goes away on its own, but sometimes, when an infection occurs, ulcers and lumps appear.
- Oral diseases:
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- periostitis;
- cyst;
- fistula;
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis.
Inflammatory processes on the gums are often accompanied by abscesses. Purulent complications can be avoided by promptly consulting a doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment of oral lesions in newborns
Infants often develop lesions in the oral cavity, which cause discomfort for themselves and cause anxiety for their parents. The most common disorders and diseases include congenital and neonatal teeth, various oral mucous cysts in newborns, ankyloglossia and congenital epulis of the newborn. In this article we will look at the features of diagnosis and treatment of this type of disorder and try to give readers an idea of the correct methods of treating and counseling young patients and their parents.
During their practice, doctors encounter various cases of oral lesions in newborns: from physiological characteristics associated with the development of the child to cancerous tumors. Awareness of such disorders plays an important role in correct diagnosis, counseling and treatment planning. The purpose of this article is to inform healthcare professionals about the diagnosis and treatment of the most common oral disorders in newborns.
Congenital and neonatal teeth
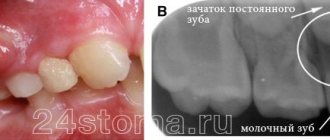
The eruption of the first baby tooth occurs approximately six months after the baby is born. But some babies reach this age already having congenital (the baby is born with them) or neonatal (erupted during the first month of life) teeth in their mouths.
Almost all congenital teeth (about 90%) erupt in the incisor area of the lower jaw. As a rule, they have the correct shape, but may be characterized by discoloration and an uneven surface. Their typical distinguishing feature already during the development period is increased mobility due to the absence or short length of roots. Most of the congenital teeth are subsequently included in the row of twenty primary teeth, but about 10% of them turn out to be supernumerary. Congenital teeth are rare: one case in two to three thousand births of healthy children, and, as a rule, this deviation is random. But in some cases, the appearance of congenital teeth can be a symptom of certain syndromes, malformations and gingival tumors.
If the congenital tooth turns out to be supernumerary and is not included in the row of baby teeth (this can be determined using an x-ray) or interferes with breastfeeding, it is recommended to remove it. Excessively mobile teeth should also be removed to prevent possible aspiration. In addition, congenital teeth can cause traumatic ulceration of the ventral surface of the tongue (Rigi-Fede syndrome), but this disorder is not an indication for tooth extraction and is cured by smoothing the rough cutting edge of the congenital tooth.
Newborn cysts
To refer to oral mucous cysts in newborns, many terms are used that replace each other, causing some confusion. But, based on the different histogenesis of the lesions, all of them can be divided into two categories: palatal and gingival.
Palatal cyst of a newborn
The palatal plates are bilateral rudimentary processes that join along the midline of the oral cavity in the eighth week of fetal development to form the hard palate. They also fuse with the nasal septum, resulting in complete separation of the oral and nasal cavities. In this case, the connective epithelial lining between the plates is destroyed under the action of enzymes, providing the possibility of fusion of the connective tissue. Neonatal palatal cysts, or Epstein's pearls, form from epithelial inclusions along the fusion line of the palatine plates. This disorder is characterized by high prevalence and is observed in 65%-85% of newborns. Cysts are small (1-3 mm) yellow-white bumps along the palatal suture, especially often located at the junction of the hard and soft palate. Histological examination reveals that these cysts are filled with keratin. No special treatment is required, since the cysts atrophy and disappear soon after their contents are removed.
Gingival cysts of newborns
Gingival cysts develop from the dental lamina (ectodermal ligament), which serves as the basis for the formation of primary and permanent teeth. Its remains can proliferate to form small cysts and subsequently cause the development of various odontogenic tumors and cysts. Depending on the location of formation, cysts that appear on the gums of newborns are called Bohn's nodes (present on the buccal and lingual surfaces of the alveolar ridges) or gingival cysts (formed on the process of the alveolar ridge).
Neonatal gingival cysts have a high prevalence: for example, Taiwanese infants screened within three days of birth had a 79 percent prevalence of the disorder.
Typically cysts look like small whitish lesions of constant size. Those that form on the anterior ridge of the lower jaw can be mistaken for congenital teeth. No separate treatment is required as cysts often rupture due to secondary trauma or friction.
Ankyloglossia
The term “ankyloglossia” (tongue-tied) describes the clinical situations of fusion of the tongue with the floor of the oral cavity or insufficient length of the frenulum of the tongue, limiting its mobility. Ankyloglossia can occur in representatives of various age groups, but is most often observed in newborns. According to research, the frequency of this disorder in newborns ranges from 1.7% to 10.7%, in adults – from 0.1% to 2.1%. Based on this, it can be assumed that some milder forms of ankyloglossia resolve with age.
Ankyloglossia of an infant can cause difficulty in breastfeeding and even cause pain in the nipple area for its mother or wet nurse. The preferred treatment for this disorder in newborns is simple frenectomy, where the frenulum is cut off at its thinnest point with small scissors. The procedure can be performed under superficial anesthesia, which ensures minimal discomfort and reduces the likelihood of bleeding. But bleeding is not necessary. Thus, according to the results of a study involving 215 newborns who underwent frenectomy without anesthesia, 38% of children had no bleeding, and 52% had only a few drops of blood. In 80% of cases, nutrition improved within 24 hours after the start of the procedure.
Congenital epulis of the newborn
This disease is a rare tumor of unknown histogenesis. As a rule, the lesion forms on the alveolar ridge of newborns. The course of the disease is as follows: the tumor does not increase in size from the moment of birth, sometimes it can decrease over time, which indicates a reactive rather than a neoplastic etiology. Most often, this tumor is found in the frontal part of the alveolar ridge of the upper jaw and has the appearance of a round attached formation, usually less than 2 cm in diameter (but sometimes larger ones are found), with a smooth lobulated surface. These types of tumors are more common in girls, which may indicate the influence of hormones, although estrogen and progesterone receptors have not been identified. In 10% of cases, multiple lesions may occur, confirming the need for a thorough oral examination.
As a result of histological studies of congenital epulis, large granular cells with small nuclei were identified. Unlike granular cell tumors, staining with the S100 protein antigen in congenital epulis gives a negative result. Other markers of neurogenic origin also showed negative results, confirming a nonspecific mesenchymal origin of the tumor. Surgical removal is recommended for the treatment of congenital epulis, especially if there is difficulty breathing or feeding problems, or if there is a need for histological confirmation of the diagnosis. For smaller tumors, a wait-and-see approach is acceptable, since cases of spontaneous regression of the tumor are known. There were no cases of relapse, even with incomplete removal of the tumor, or malignant degeneration.
Authors:
Van Heerden, Van Zyl
Symptoms of an abscess
The initial stage of the formation of a white bump on the gum may be asymptomatic. The abscess gradually increases, leading to the following symptoms:
- formation of a painful protrusion;
- smell from the mouth;
- bleeding from gums;
- pain when eating.
If you do not help the child at this stage, further development of inflammation will lead to intoxication. The baby's temperature will rise and signs of weakness and malaise will appear.
Why do my gums hurt when teething?
To appear on the surface, the tooth needs to pass through the jaw bone and gum tissue. Although this is a natural process, it can be painful, because the tooth “grows” through the gum and violates its integrity. The gums become sensitive during tooth eruption, and pain may occur when pressing on them. These unpleasant sensations go away as soon as the tooth moves apart the gum and looks out.
Treatment of inflammation
Removal of a lump with pus on a child’s gum should be started immediately. Only a dentist can help the baby.
IMPORTANT! Self-medication, as well as piercing and squeezing are strictly prohibited! Such an intervention will lead to serious complications.
When an abscess forms over a baby's baby tooth, the doctor most often removes it. Such measures are necessary to exclude the possibility of destruction of the rudiments of the root. If a child has a lump on his gum next to a permanent tooth, treatment begins with a thorough examination. Sometimes the dentist will send you for an x-ray to assess the extent of the damage. Removal of a permanent tooth is carried out in extreme cases.
Manifestation of hyperplasia
- The color of the enamel changes. Yellow spots appear on it. Discoloration of the enamel may be accompanied by pain, but the tooth still retains its integrity.
- Underdevelopment of enamel, which manifests itself in the form of wavy enamel and furrowed depressions.
- Complete absence of enamel.
The most severe disease is the complete absence of the top layer of enamel, which can manifest itself as: tooth deformation, pain due to temperature changes, pain due to mechanical impact on the teeth.
Risk factors for the development of hyperplasia on permanent teeth:
- Disease of rickets or various infectious diseases.
- Excess of vitamins A, C, D in the body.
- Syphilis disease.
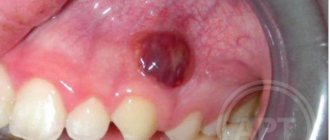
The main risks of gum fistula and the risk of complications
Without proper timely treatment, fistulas often cause complications. They can affect not only the oral cavity, but also the internal organs of the baby.
There are several common risks:
- Severe intoxication of the body. Occurs because pus is constantly secreted from the wound. The pathogenic microflora that develops poses a great danger.
- Tooth loss. Sometimes it is necessary to remove only the one whose root has been affected. But cases with gradual spread of inflammation are also common, when several teeth need to be removed.
- Damage to the periosteum. It has far-reaching consequences associated with inflammation of tissues and bones, and the need for surgical intervention.
- Sinusitis. The infection quickly spreads to the human maxillary sinuses and begins to rapidly progress, covering ever larger areas.
Other dangerous potential complications include the need for perforation of the cheek, flux, removal of tonsils, and gastrointestinal disorders.
As with any other type of inflammation, the hours begin to count. Therefore, if a problem occurs, you need to seek dental help as quickly as possible.
Prevention methods
Fistula can appear in any child, so it is very important to correctly approach the methods of its prevention. Among them are:
- Strict adherence to oral hygiene practices.
- Moderate consumption of sweets, avoidance of candies and anything that can hurt your gums.
- Regularly inspect your gums for damage.
- Treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
- Periodic examinations at the dentist.
The sooner the problem is identified, the easier it will be to get rid of it and the less harm it will cause to the baby’s body.
How to treat a fistula at home
We emphasize that home treatment is only one of the auxiliary methods prescribed by a doctor.
At home, you will need to treat the oral cavity using special decoctions with a pronounced calming and antiseptic effect. You can use decoctions of calendula and chamomile, solutions of salt and soda.
Also allowed are lotions made from aloe and Kalanchoe, and the application of special ointments prepared at home. They are made using crushed chamomile herbs mixed with sea buckthorn oil.
This home treatment can significantly speed up the recovery period and reduce your child’s discomfort.