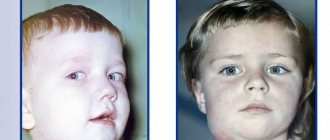
Diagnosing and solving problems that lie on the border of two or three medical specialties requires the most time and effort. One of these pathologies is odontogenic sinusitis, which is treated by an otolaryngologist and dentist.
Odontogenic (from the Greek odus, genus odontos - tooth, genesis - origin, development) maxillary sinusitis or sinusitis is a chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus, provoked by pathology of the teeth of the upper jaw, namely periodontitis, tooth extraction with the formation of communication between the oral cavity and sinus, or the entry of plastic material into the sinus when filling the canals of the teeth. The share of this disease in the structure of all maxillary sinusitis ranges from 10 to 40%, and up to 75% of all unilateral sinusitis.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The formation of an acute purulent process in the subcutaneous fat layer near the lymph nodes can be triggered by a significant decrease in immunity. If there is inflammation of the lymph node itself, then a delay in lymph outflow and increased vascular permeability are observed.
Adenophlegmons develop due to ongoing inflammatory processes of any localization. Often this pathology is diagnosed against the background of malignant tumors, some types of dermatitis, chronic dental pathologies, and inflammation of the tonsils.
Diagnostics is aimed not only at identifying adenophlegmon, but also at establishing the cause of its occurrence - medical tactics for this pathology depend on this.
User Questions (6)
- Evgeny 2018-03-01 21:49:07
When I fell on the glass, I cut my jaw. At the hospital the cut was stitched up. But after 2 days it became bad, they sent me to surgery, they opened the wound, and it was discovered that the salivary gland was affected. They diagnosed phlegmon. U... read the answer >> - Olga 2018-02-03 13:54:20
Hello! After the removal of the lower wisdom tooth, facial phlegmon formed, I was operated on. The incision healed normally, but a month later a small rash appeared in the place where the phlegmon was, in some places... read the answer >> - Irina 2017-02-17 17:40:18
Hello, after the removal of the seventh tooth on the lower right, a phlegmon formed, I spent a week in surgery, today I was discharged home, but there was a lump under my chin, they didn’t open it, they dropped methadone... read the answer >> - Alexey 2016-11-20 11:32:14
Hello. There was phlegmon of the lower jaw under the lingual. They had an operation. As of today, the stitches have been removed, a week has already passed. But in one place it does not linger and the Treasure stands out abundantly. Which... read the answer >> - Tatyana 2016-05-20 17:08:16
We had an autopsy of the phlegmon, but the tumor remained - the wound had not yet completely healed. tell me whether the ointment will draw out the liquid or be sure to consult a doctor (the person cannot walk, but they take him to the hospital... read the answer >> - Tamara 2015-12-03 02:16:33
Hello! I constantly have a clicking sound in my ear and it hurts to chew. They prescribed painkillers, UHF, etc., nothing helps, there is no dislocation on the X-ray, the dentist suspects “Arthrosis”... read the answer >>
Medical institutions you can contact:
Dental Office, network of dental clinics all addresses Orto Plus, dental office DiaGroup, medical center all addresses Biomed, dentistry Aristocrat, dental clinic SENDO, medical center Apollonia, dental office Zubok, dental clinic Doctor Gis, dental clinic Nor-Stom, dental office Dentline, dental clinic all addresses Delta, dentistry Denta-Lux, dental clinic DOCTOR, medical center Generation, medical center all addresses Diamant, dental clinic Favorite dentist, dental center Nika Spring, network of medical centers all addresses Dentist and I, dental office (Yunist ) SMILE, dental center
Symptoms of adenophlegmon of different types
Symptoms depend on where adenophlegmon developed:
- With submandibular adenophlegmon, body temperature rises, swallowing may be difficult, problems with speech arise, swelling forms in the affected area, redness of the skin and pain when palpated are observed.
- With adenophlegmon of the neck, symptoms appear only when there is a critical accumulation of coccal microflora in the tissues of the anterior or lateral part of the neck. There is an increase in body temperature, pain when feeling the neck, redness of the skin, but swelling may be absent.
- With inguinal adenophlegmon, the clinic develops against the background of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. This type of adenophlegmon is characterized by rapid progression, while the patient experiences severe pain, due to which he cannot move freely. There are also signs of general intoxication of the body.
- With adenophlegmon of the axillary region, symptoms more often occur with open wounds of the upper extremities. Signs are pronounced: enlargement of regional lymph nodes, deterioration of general condition (including increased body temperature).
The symptoms for different types of pathology in question are similar, the differences lie only in the location of the lesion. If adenophlegmon occurs in children, then loss of appetite, increased drowsiness, lethargy, and lack of interest in games and others will be noted.
How to deal with the disease
After the diagnosis has been confirmed, the patient is sent to the hospital. Treatment of APO includes several successive stages:
- Surgical intervention. It is performed under local (adults) or general (children) anesthesia. In a situation where a tooth has become the source of infection, it is subject to extraction or depulpation (the dental canal is cleaned and a filling is placed). If necessary, an incision is made on the skin and the pus is released from the capsule - often such manipulations are not required, the contents come out on their own under internal pressure. As such, additional cleaning of the affected area is not carried out; the postoperative area is covered with a protective bandage (it is changed daily).
- Drug therapy involves taking anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and restorative drugs.
- The wound is treated with local antiseptic solutions.
Treatment of APO is exclusively surgical - removal of pus from the capsule followed by the use of local antiseptics and systemic anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. At home, in addition to traditional treatment, you can use several proven effective recipes. First of all, the action of the following compositions is aimed at strengthening the body's defenses and improving the general well-being of the patient.
Take 100 g of dry St. John's wort and 50 g of propolis, pour in 300 ml of vodka (medicinal alcohol). The mixture is poured into a glass container and sealed tightly. The medicine is infused for 7 days in a cool, dark place, filtered. When ready, the tincture is used for rinsing the mouth (the procedure is carried out at least 6 times a month, proportions - 20 g / 100 ml of warm water) and therapeutic compresses.
Compilation of anamnesis, analysis of complaints, visual examination of the patient and assessment of the results of clinical studies are components of the diagnosis of adenophlegmon
A few tablespoons of crushed dry eucalyptus leaves are poured into a thermos and steamed with boiling water and left for several hours. It is recommended to take a third of a glass of this infusion at least 4 times a day before meals. Burdock leaves are washed under running water, finely chopped, mixed with sour cream (2:1). The finished mass is applied to the affected area and left for half an hour. Manipulations are carried out daily.
Treatment of anderophlegmon
The solution to the problem is to carry out complex treatment:
- The purulent focus is opened under local anesthesia or general anesthesia;
- it is being sanitized;
- install drainage without suturing the wound;
- apply a sterile bandage with a mandatory change once a day.
When treating adenophlegmon, antibiotics are used - not only in the form of tablets or injections, but also topically, to wash the abscess cavity. If you seek qualified medical help in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. But we must not forget that there is a high risk of developing sepsis.
Information about in what cases adenophlegmon of the floor of the mouth develops and what features of treatment of the disease you need to know is contained on our website https://www.dobrobut.com/.
Features of children's APO
Children aged 3 to 7 years are at risk. The trigger for the development of pathology can be untreated acute osteomyelitis of the jaw. At an older age (10–14 years), adolescents are faced with adenophlegmon resulting from soft tissue injuries, followed by infection of the wound canals.
The list of main causative agents of the inflammatory process includes:
Treatment of tooth abscess
- staphylococci (white, golden);
- streptococci;
- diplococci, etc.
Important! If the baby suddenly begins to be capricious, begins to refuse to eat, complains of pain under the jaw, there is severe hyperthermia (sometimes the body temperature jumps sharply to 40 degrees) - this is a reason to immediately seek medical help from a pediatrician.
Diagnosis of phlegmon
- symptoms, complaints, when they started and how long they last,
- physical examination of the patient,
- the patient's previous medical history, medications taken,
- palpation on physical examination.
Cutaneous cellulitis is always visible, while internal cellulitis is more difficult to diagnose.
Anaerobic phlegmon of the back
Examinations may include:
- blood analysis
- Analysis of urine
- Ultrasound
- x-ray
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- CT (computed tomography)
Rehabilitation therapy and rehabilitation
After surgical opening of the phlegmon, ointments, antibiotics and therapeutic techniques are prescribed that help remove residual pus from the wound and quickly cleanse the skin. Among products with herbal ingredients, preference is given to sea buckthorn oil, rosehip extract and Troxevasin ointment. If the wound does not heal for a long time and the skin does not tighten, the patient is prescribed dermoplasty.
Dermoplasty is a skin graft that is performed in case of severe damage to the dermis during trauma and extensive surgery. When removing phlegmon, this operation is prescribed in the case of removal of extensive inflammatory foci in which soft tissue necrosis has begun. In addition to the use of local remedies that promote rapid recovery and healing of the wound, the patient is prescribed conservative treatment methods aimed at restoring the immune system, relieving intoxication and preventing re-inflammation.
Bed rest is mandatory throughout the entire rehabilitation period. The area of the body where surgery was performed should be in a slightly elevated position. If there is pain, painkillers are prescribed and injected into the muscle.
All patients who have undergone surgery to remove cellulitis must take a course of antibiotics. The medications are prescribed by the attending physician depending on the individual characteristics of the patient and the type of virus that provoked the inflammation. If anaerobic cellulitis has been removed, intramuscular injections of anti-gangrenous serum are prescribed. To restore and normalize the acid-base balance, a solution of methenamine is prescribed. To restore tone to the walls of blood vessels, calcium chloride in solution is used.
To relieve the effects of intoxication and restore the functioning of the heart muscle and circulatory system, adonylene and caffeine are prescribed. Patients need to adhere to proper nutrition, it is imperative to exclude fatty and fried foods, and it is not recommended to consume large amounts of flour. Be sure to drink plenty of plain water; fruit compotes and fruit drinks are allowed to restore the immune system. Antibiotics are used until the inflammatory process is completely removed.
Complications of cellulitis
Purulent-necrotic phlegmon of the leg in the process of cleansing the wound surface and forming granulations.
The main ones are:
- gangrene,
- sepsis,
- thrombosis of arteries and veins of the lower extremities, mesenteric vessels,
- abscesses of the liver, kidneys, spleen, respiratory organs, lungs, brain,
- thromboembolism of small and large branches of the pulmonary artery,
- multiple organ failure.
Purulent-necrotic phlegmon of the back
With a progressive disease, pus accumulates in the deeper layers of the skin, causing the development of inflammation of the surrounding tissues, affecting the blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves.
Cellulitis of the posterior thigh