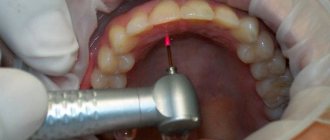
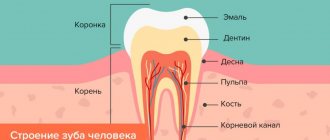
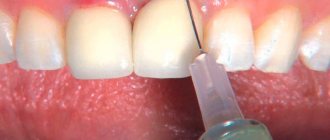
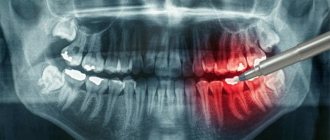
Gum coagulation is a surgical procedure that involves cutting off the soft tissue of the gums using a heated instrument.
In other words, gum coagulation is plastic surgery using electric current. Moreover, the procedure is completely bloodless and as safe as possible (compared to a scalpel). The coagulation method is widely used for the resection of malignant and benign tumors, as well as a number of other diseases.
What is gum coagulation in dentistry?
The procedure is otherwise called cauterization. In dental practice, it is used mainly for excision of excess gums. It is similar to gingivectomy, but less traumatic. Using instruments that apply electric current or laser radiation, excess gum tissue is removed through coagulation - the sticking together of particles.
When exposed to high temperatures, protein and blood clot. Excess mucous membrane is cut off, the rest shrinks and becomes smaller. After the operation, the edges of the gums surrounding the tooth are aligned and become aesthetically pleasing.
The procedure is absolutely painless as it is performed under local anesthesia. There is no blood or risk of infection. The rehabilitation period is easy and short, as wounds heal quickly.
Unlike gingivoplasty, which can be used to close gum recession, it does not replace the missing tissue volume. Plastic surgery is primarily done to correct gingival contours and lift gums during atrophy.
Preparatory activities
No special preparation of the patient is required before the gum removal procedure.
It is recommended to eat before visiting the dentist, since immediately after the procedure you will not be able to eat for several hours. On the day of surgery, you should not drink alcohol, as it significantly impairs blood clotting.
Before carrying out the procedure, it is advisable for the dentist to show his medical record or extracts from specialized specialists - if the patient has any chronic diseases or characteristics of the body.
You should also inform the doctor whether the patient is allergic to local anesthetic drugs, since the operation is performed under local anesthesia.
If a dentist has questions about the nature of the neoplasm , he can refer the patient to various specialized specialists - oncologist, periodontist, infectious disease specialist or other specialist.
Immediately before coagulation, the oral cavity is sanitized, hygienic cleaning and (if necessary) removal of hard dental plaque.
If the condition of the patient’s oral cavity is unsatisfactory, there are inflammatory elements or signs of infection, then a course of treatment is carried out first.
Types of coagulation
The operation is performed using two devices: an electrocoagulator or a laser. Using a heated metal tool is an outdated but possible method. Laser therapy is more gentle compared to its predecessors.
Cauterization of gums in dental clinics is carried out using two methods:
- Monopolar. It is performed using an electrical device - a monopolar coagulator. Alternating current with high-frequency oscillations is supplied to the electrode, and through it into the tissue. It then passes through the body and returns to the end plate. In this case, coagulation occurs in a certain area. The procedure is safe and does not have a negative effect on the body.
- Bipolar. The tip of the electrocoagulator is bifurcated and does not have a closing plate. The current only affects the tissue sandwiched between the two ends that supply the electricity.
The bipolar technique is simpler and safer, but can only be used to remove small formations. Monopolar is suitable for all cases, but carries some risks. A burn may occur due to equipment malfunction or medical error. However, modern clinics are equipped with good equipment and experienced doctors, so you should not be afraid of the procedure.
Methods
The advantage of the coagulation effect over the traditional mechanical effect (excision of the gums with a scalpel) is that under the influence of ultra-high temperatures, tissue cells are compressed, and bleeding does not occur in the area of exposure, which significantly reduces the healing time.
Coagulation of gums is carried out using various instruments:
- Electrocoagulator. Now there is a wide range of these devices on the market, and they are stationary, portable, having different modes, voltage and current.
The basic principle of operation of such devices is to expose tissue to high-frequency alternating current. - Laser. It affects the gums in a targeted and most gentle manner. The most effective and gentle method.
- Heated sharp instrument. Today it is practically not used, as it is a traumatic procedure and requires long recovery.
With the help of these devices, the pathologically changed area of tissue is cut off, and the cells at the site of damage are compressed, preventing the development of bleeding and eliminating infection. This way the tissue heals quickly.
Monopolar technology
A special return plate is placed on the patient’s body, which is responsible for closing the electrical circuit. A weak electrical impulse is passed through the patient's entire body and through the surgical instrument. With this procedure, you can get rid of even large neoplasms and tumors located in the deep layers of tissue. Due to its effectiveness, this method is used more often than others.
Bipolar technology
An electrical discharge is passed locally, only through the part of the body in which the tumor or inflammation is located. Therefore, the end plate is not used. This method is effective for the treatment of mild dental diseases.
The gum cauterization method is widely used in dental practice and shows good results in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Before performing the operation, the doctor examines the patient’s oral cavity for injuries to the mucous tissues, since their presence can cause complications.
Bipolar gum coagulation technology
Upon completion of the operation, the patient is given a list of recommendations and a prescription for medications. For each patient, recommendations are made individually, depending on the disease and its severity.
Indications and contraindications
The operation is especially in demand for hypertrophic gingivitis. This is an inflammatory gum disease. If left untreated, soft tissue grows, covering the crown of the tooth. The gingival papilla, which is located between adjacent dental units, is most susceptible to hypertrophy.
Coagulation is carried out in the presence of:
- tissue hyperplasia in gingivitis and other diseases;
- neoplasms: hemangiomas, fibromas, warts;
- abnormalities of gingival tissue;
- periodontitis (root canal coagulation);
- inflammation in periodontal pockets during periodontitis;
- caries on the neck, tooth root.
The list of restrictions includes individual intolerance to electric current, acute infections, exacerbation of chronic diseases, terminal stages of diabetes mellitus or other endocrine disorders, severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
Therapy for hypertrophic gingivitis
The disease is one of the most common in dentistry - it occurs with equal frequency in both adults and children. It is characterized by the proliferation of soft interdental tissues, which, if left untreated, can overlap the crowns of the teeth. The appearance of pathology is provoked not only by poor oral hygiene and hormonal imbalance in the body, but also by chewing hard pieces of food that injure the interdental spaces, and improper use of personal hygiene items (threads to remove plaque, brushes, etc.).
In complex therapy (taking anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy, gingivectomy) to treat the disease, dentists recommend using a method such as coagulation.
Preparing for surgery
Before the procedure, professional oral hygiene is carried out: removing plaque, removing tartar. If there are concomitant diseases, the patient is referred for examination to specialized doctors. After eliminating contraindications, a treatment date is set.
Before visiting the doctor, you need to eat a hearty meal, since after dental procedures you cannot eat for several hours. It is recommended to quit smoking and alcoholic beverages the day before the procedure. Alcohol and nicotine have a bad effect on blood clotting.
How to perform gum cauterization
The operation is performed by a dental surgeon. The patient is anesthetized with local anesthetics. It is important to relax, as sudden movements will disturb the doctor.
Using an electrocoagulator or laser device, excess gingival tissue is excised and tumors are removed. The procedure time depends on the amount of work, but usually does not exceed a quarter of an hour.
To treat pulpitis or periodontitis, coagulation is carried out through the root canal. If the caries is located below the gum level, the tissue is coagulated to gain access to the affected area. In case of periodontal disease, coagulation of the contents of periodontal pockets is carried out.
Manipulation techniques
For diathermocoagulation, special devices and devices are used. The manipulation itself can be carried out in the following ways.
Processing with a heated tool
This method is quite old and is practically not used in modern dentistry. A spatula, plugger or dental trowel was used as a cauterization tool.
This made it possible to cut off small damaged tissues localized on the gums. In addition, a heated instrument could stop bleeding from blood vessels or cauterize minor mechanical damage to the oral mucosa.
This is interesting: Gingivitis in adults: complete information about the disease
Cauterization using an electrocoagulator
These are special devices for carrying out these manipulations. Today they are widespread in all dental clinics. They are produced stationary, portable, which operate in various modes.
The operating principle of these devices is based on the use of alternating electric current, which provides heating to a special electrode. The doctor thus performs a gingivectomy or gingivotomy.
Using a laser
This technology is the most advanced and most gentle. The laser provides virtually painless removal of any tumors.
The big advantage of using this technique is that after treatment the wound does not bleed and becomes completely sterile. Thus, the laser beam provides significant prevention of the possibility of infection. You can learn how lasers are used in dentistry by watching the video in this article.
Application of laser in dentistry
After treatment with the coagulation method, the wound surface is quickly regenerated. To completely turn off sensitivity, local anesthesia is required. It can be carried out using injections or aerosol irrigation, as required by the instructions.
Basic methods of influence
Diathermocoagulation is indispensable in the treatment of cervical caries or when it affects the basal areas. Although the procedure is simple, the doctor must have certain professional skills to provide effective treatment.
Additional anesthesia allows the operation to be performed efficiently and without psychological trauma for patients. The price of diathermocoagulation is another indicator of the popularity of the technique. The cost is insignificant and additional costs are required for preparation and the postoperative period.
In addition, dentists actively use coagulation to remove tumors on the soft tissues of the oral cavity. After manipulation, as a rule, there are no complications or relapses that occur during surgical interventions by other methods.
Doctors mainly use 2 coagulation techniques:
- Monopolar technology . The peculiarity is that the electric current passes through the entire patient like a cutting instrument. This method is used most often, as it provides treatment even for deep-lying tumors or removal of large ones. To successfully carry out the procedure, a return plate is placed on the patient’s body, which allows the electrical circuit to be established.
- Bipolar technology. In this case, the electric current does not pass through the entire body, but only a certain area of the body. It closes over a short distance, providing treatment for only minor dental problems. An endplate is not required for the manipulation.
Gum cauterization is performed for various periodontal diseases. During surgery, a very important point is the absence of injury to adjacent tissues. This helps to avoid additional possible complications. After coagulation, the patient must follow the doctor's recommendations. They will be individual in each case.
Recovery period
You are allowed to eat after 3-4 hours. On the first day, you can eat soft, cold or lukewarm foods. You need to chew on the opposite side.
Hygiene procedures are allowed to be carried out the next day, but with caution. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with antiseptics Chlorhexidine, Miramestin, Furacilin, and treat the mucous membranes in the operated area with Metrogyl-Denta gel. After 5 - 7 days, you can supplement the care with means to accelerate regeneration, for example, sea buckthorn oil.
Cost of gum coagulation
The price consists of several factors: the volume of the operation, cauterization method, equipment (laser device or electrical device), additional services. If there is plaque or tartar, then professional cleaning is required, which is paid separately. The price of cauterization for 1 tooth in Moscow is from 1000 rubles to 4000 rubles and more, depending on the complexity of the case.
Our clinic uses modern equipment and employs dental surgeons with extensive clinical experience. We guarantee painless, high-quality treatment and no complications. Prices are agreed upon with the patient before the operation.