Author: Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich Deputy Chief Physician, Candidate of Medical Sciences in the specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology In dentistry, there are many ways to restore missing teeth, but sometimes an allergic reaction may occur to anesthesia and some materials. Let's figure out why allergies to anesthesia and materials for making removable dentures and crowns appear.
Allergy to dentures
The most common allergens are dentures made from base metals, zinc, copper, steel, as well as dentures made from standard acrylic plastic.
These materials are actively used in prosthetics for the production of bases for clasp and acrylic dentures, dental bridges due to their low cost. The appearance of an allergy to these materials causes one thought in people: what to do? The main signs of an allergic reaction to dentures will be the following:
- discomfort in the oral cavity - pain in any part, bitterness in the tongue, dryness and sore throat;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of the oropharynx and nasopharynx, causing problems with the respiratory tract;
- severe swelling and hyperemia near the prosthesis.
The appearance of these symptoms indicates the need for urgent diagnosis and initiation of treatment, but first of all it is necessary to urgently eliminate the irritant. The easiest way to get rid of a removable denture is made of acrylic, which can be easily removed independently; most often, in case of allergic reactions, it is replaced with an acrylic-free denture. If you have a non-removable dental structure in your mouth, you should visit a dentist as soon as possible to remove it. After eliminating the source of the allergy, the material to which it arose is identified, since several types are used in the manufacture of crowns, and other components are selected for the new prosthesis.
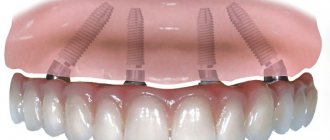
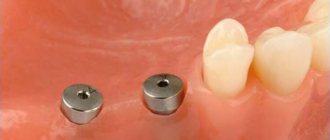
Can you be allergic to a titanium dental implant?
Allergic reactions to artificial titanium roots are extremely rare.
In only 1% of cases, hypersensitivity to this metal is observed. If removable dentures, crowns or bridges cause allergic reactions in a person, then installing implants is the best alternative. At the Partner-Med clinic, we use only proven and certified brands of dental implants:
IMPRO IMPLANT
39,000 RUR WITH METAL-CERAMIC CROWN
OSSTEM IMPLANT
49,900 RUR WITH ZIRCONIUM CROWN
ASTRA TEK
74,000 RUR WITH ZIRCONIUM
CROWN STRAUMANN IMPLANT
62,000 RUR WITH ZIRCONIUM CROWN OH
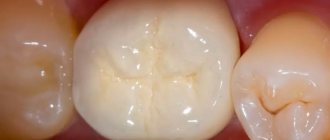
Can there be an allergy to metal-ceramic crowns?
Allergies to metal-ceramic crowns are not a common occurrence, since they consist of 2 parts - a metal frame and a ceramic lining. The frame is usually made of a metal alloy and may contain cheap allergenic species such as copper or nickel. In Russia, 50% of crowns are made of such alloys. That is why it is worth knowing how an allergy to a metal-ceramic tooth crown manifests itself. This will help you notice dangerous manifestations in a timely manner and seek help from a dentist.
The most common symptoms of an allergy to metal-ceramic crowns are:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- increased salivation;
- severe redness and swelling of the mucous membrane;
- rashes on the skin and in the mouth.
How to treat teeth if you are allergic to anesthesia
Approximately 25% of people have an allergic reaction to anesthetics, most often novocaine, less often lidocaine, used for pain relief in dentistry during dental treatment.
This injection causes a large number of side effects, nausea, headache, arrhythmia, so in most paid clinics, which include Moscow Dentistry Partner-Med, they use only proven anesthetics based on articaine and mepivacaine, and before starting treatment, a medical card is filled out and anamnesis collection. However, a negative reaction can also occur to other anesthetic drugs, which makes dental treatment and prosthetic procedures difficult, so you should only contact dental centers that have an excellent reputation.
Our clinic employs dentists who have a high professional level and are able to quickly and effectively solve the most complex problem. If a patient with a serious dental problem and an allergy to anesthetics comes to us for help, we will definitely help him. Experienced doctors working at the Partner-Med clinic know very well how to painlessly remove a tooth if the patient is allergic to anesthesia. To achieve this goal, the patient may be offered several options:
- Replace the anesthetic causing the allergic reaction
- Carry out all serious dental procedures that cause pain under general anesthesia.
- Before implantation, take an antihistamine and, while it is working, perform all painful manipulations under anesthesia.
- Carry out treatment under sedation - immersing the patient in a state of mild loss of reaction. A person in this state seems to be asleep, but at the same time hears the doctor and fulfills all his requests.
Are there allergies to zirconium crowns?
For decades, gold alloys with a high degree of biocompatibility have been considered the best solution for making crowns. However, recently it has been scientifically confirmed that the biocompatibility of zirconium dioxide is the same as that of noble metals. This confirms that zirconium crowns are not capable of provoking an allergic reaction and structures with them can be worn without fear.
Allergy to a metal pin or inlay in a tooth
No specialist can predict what the patient’s body’s reaction will be to a foreign object located in the tooth canal, so an allergic reaction is detected after the metal pin or inlay is installed in the tooth canal.
Allergies are provoked by:
- Alloy ions, actively released into the blood by the metal rod, begin to react with other substances.
- Contact of the pin with periodontal fibers (during perforation of the tooth root.
In addition, allergic manifestations can be triggered by “galvanic syndrome”. It occurs in the mouth when there are different metals there, which may be incompatible and provoke the occurrence of galvanic currents, so an allergy to a pin in a tooth may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth;
- burning of all areas of the mucous membrane;
- profuse salivation.
Just CALL US!
+7
We will answer any of your questions and will definitely help you!
What causes allergies
An allergy to a dental crown, like any allergy in principle, is a pathological reaction of our immunity, which is expressed in increased sensitivity (hypersensitivity) to some allergen substance. It is interesting here that sensitization or stage 1 occurs first - when the body first encounters an “unfriendly” substance in very small quantities. At this stage, the components of the immune system - B lymphocytes, T helper cells, mast cells, endothelial cells, dendritic cells - react weakly. That is, there are no tangible manifestations1 of an allergic reaction yet.
At stage 2, when the body encounters a large amount of allergen, the allergic reaction itself occurs, with all its manifestations and symptoms (more on them below). Moreover, from the 1st to the 2nd stage, very little time can pass - literally a few minutes or hours. Especially if the allergen is strong enough - in principle or specifically for you as an individual.
Only until 15.01 South Korean implant Osstem - from 18,500 rubles.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and lock in promotional prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Symptoms of an allergic reaction
Allergies can appear either immediately after prosthetics or over a longer period of time - after several days, weeks or months, or less often after several years. Therefore, you need to know what symptoms are signs of an allergic reaction. How an allergy to crowns manifests itself (and there can be either one symptom or several at once), we will describe further:
- problems with the gums and mucous membranes: redness, itching, pain, swelling, rash, sores, blisters with fluid inside - all this may indicate allergic stomatitis,
- unpleasant sensations on the tongue and palate: numbness, tingling, burning, goosebumps, metallic or sour taste,
- disruptions in the production of saliva: too much or too little of it is formed, dry mouth appears,
- nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing,
- pain and sore throat, dry cough, pain when swallowing,
- the appearance of rashes or red spots on the skin (on the face, neck, chest, arms),
- tearfulness, redness of the eyes,
- exacerbation of existing body diseases: asthma, gastrointestinal pathologies, etc.,
- temperature increase,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- Quincke's edema: a very dangerous condition in which some part of the body or face or neck becomes severely swollen. The danger is that due to swelling of the neck and throat, it becomes difficult to breathe (you can even suffocate). Blood vessels that supply oxygen to the brain may also be pinched.
Allergy and hypodontia
The search found three articles, and only one article dealt with the relationship between allergies and hypodontia. Third molars are the most commonly missing teeth, followed by second premolars and maxillary lateral incisors.[42] The etiology of hypodontia is considered multifactorial, with genetics and environmental factors playing important roles.[43] Yamaguchi et al[44] in 2008 studied 3683 Japanese orthodontic patients and found a positive correlation between allergies and hypodontia. They concluded that health problems, especially those related to allergies, are of great importance and may have a significant association with hypodontia.
What materials provoke allergies?
The following substances can provoke an allergic reaction in orthopedic dentistry:
- synthetic polymers: plastic, nylon, acrylic, etc.,
- metals: base metals are more likely to become allergens than noble metals,
- anesthetic drugs, filling compounds, antiseptics: if used incorrectly, they can cause local irritation,
- dental cement on which dentures are glued.
But ceramics, zirconium and aluminum dioxides, composite materials for filling, as well as titanium without impurities are considered hypoallergenic.
Don't know what type of prosthetics to choose?
We will help in the selection, advise where to read more information and compare types of prosthetics.
Consultation with an orthopedic doctor in Moscow clinics is free! Call now or request a call
Working hours: from 9:00 to 21:00 - seven days a week
However, there is still no material for prosthetics that is 100% inert, i.e. There is always a risk of allergies - to a large extent it depends on the person himself, his individual reaction. At the same time, modern high-quality materials are very well cleaned at the production stage, and the maximum amount of harmful substances is removed from them. Therefore, they can cause problems extremely rarely - in 1 case out of a million or even less often.
What are hypoallergenic crowns?
Products made from metal-free ceramics are recognized as hypoallergenic crowns. Due to the absence of a metal base, a person does not develop individual intolerance. The design is characterized by high aesthetics and reliability, but its disadvantages include high cost.
It can be made of porcelain, aluminum dioxide or zirconium dioxide. In all cases, the possibility of an allergic reaction is excluded.
Plastics and acrylic are the most allergenic materials
According to research, synthetic polymers - plastic, polyurethane, nylon, acrylic - provoke an allergic reaction in approximately 1% of cases, i.e. in 1 in 100 people. In principle, this is not little, but not very much either. As a rule, plastic crowns are often placed only on a temporary basis - so that the patient does not go without a tooth while more durable permanent ones are made. So a large concentration of potential allergens should not have time to accumulate in the tissues. But still, slight irritation of the gums or allergic stomatitis can appear in people with high sensitivity and a weakened body.
If we consider the acrylic from which artificial gums are made (it is sometimes built up around bridge crowns if the gum contour is not very smooth), then the allergen here is the acrylic monomer. But today there are materials with low monomer content or without it at all - for example, Acry-free.
Content
- Causes of allergies
- Allergy symptoms
- Allergy treatment
- Dental prosthetics for allergies
Crowns are the most common method of dental prosthetics. They are installed both on your own teeth and on implants. The goal may be not only the restoration of damaged teeth, but also the correction of dental deficiencies. The vast majority of all crowns installed today are made from hypoallergenic materials. That is, the materials are as neutral as possible and do not react with the tissues of the oral cavity. However, there are also unwanted reactions in the form of allergies.
PROMOTION
Installation of crowns, dental bridge
RUB 3,450
Ceramics and zirconium dioxide are the lowest allergenic materials
Allergies to ceramic crowns occur very rarely – almost never. The same can be said about allergies to zirconium crowns (made of zirconium dioxide) and aluminum dioxide (metal-free ceramics). Ceramics is considered one of the most low-allergenic and inert materials in dentistry. But an individual allergic reaction still sometimes occurs, for example, if dyes were used to make the prosthesis. Or, if a ceramic crown is placed on a core inlay or implant that contains allergens (aluminum, nickel, vanadium). That is, the problem here is not in the ceramics, but in what is underneath it.
Read on the topic: ceramic metal-free dental crowns - what they are and how relevant they are today.
Allergy to metal-ceramic crowns
Metal ceramics are in great demand in dentistry. Crowns based on it are characterized by high strength, aesthetics and long service life. With their help, it is possible to restore chewing molars and teeth included in the smile zone.
These crowns contain ceramic and metal. Their only drawback is the likelihood of developing an allergic reaction (due to the metal in the composition). Let's take a closer look at what metals provoke allergies and what factors increase their occurrence.
Allergic reaction to metals
An allergy to a metal crown can occur if, for example, the alloy is not of very high quality, is improperly processed, releases toxins, allergens, or is itself chemically active in the tissues in the oral cavity or in the liquid environment. Experts estimate that about 10% of the world's population is susceptible to metal allergies. Ideally, the metal for prostheses is inert, i.e. Fully compatible with the human body - does not cause inflammation, is not rejected. Let's consider which metals often provoke an allergic reaction:
- nickel: an inexpensive, highly allergenic metal, which contains 9% of stainless steel,
- copper: due to its properties, color and not very high price, it is often alloyed with gold to obtain a relatively inexpensive “noble” material. However, copper oxidizes quickly and often provokes an allergic reaction - almost as often as nickel.
- zinc: included in cements for filling, incl. root canals before prosthetics. May cause irritation, but quite rarely,
- cobalt and chromium: they provoke allergies less often than other base metals, but can release toxins,
- titanium alloys: titanium itself is almost 100% inert, i.e. should not provoke allergies. However, in dentistry, its alloys are often used, where the titanium content is 85-98.7%. Therefore, the purer the alloy, the lower the risk of an individual allergic reaction. Titanium products are coated on top with a film of titanium dioxide, which eliminates corrosion,
- aluminum and zirconium (in the form of dioxides): zirconium and aluminum dioxides are inert compounds, but in exceptional cases they can be allergenic,
- silver, platinum, palladium, gold (noble metals): also considered inert and hypoallergenic, but it all depends on the concentration of the base metal in the alloy. If it contains a lot of additives (nickel, chromium, copper), then an allergic reaction is possible.
Treatment
The main method of dental intervention is replacement of dentures. Ceramics are best suited for fixed dentures. This is a bioinert mass that does not cause allergies. Ceramic dentures make it possible to choose the material to suit your budget. Porcelain structures are cheaper than glass-ceramic ones (E-max, Empress), and they, in turn, are cheaper than zirconium ones. If it is not possible to install ceramics, then you need to select an alloy that excludes metals that cause allergies.
If you are allergic to removable dentures, the composition is also changed. Acrylic is replaced by nylon and Acry-Free polymer.
But in clasp structures you cannot do without metal. Ideally, it would be good to replace the arc and fasteners with inert metals: gold, platinum, titanium. In other cases, dentistry selects a composition that does not contain metals that were in the previous restoration. Another option may be to install a Quadrotti prosthesis. The material of construction is relatively hard thermoplastic. Clasps are also made from it. The absence of metals reduces the risk of allergies.
Anti-allergy treatment (antihistamines) is carried out against the background of dental procedures.
Metal-ceramics and metal-plastic
Can there be an allergy to a metal-ceramic crown? Here, the likelihood of an allergic reaction depends on the quality of the materials, in particular the metal used. For example, often an allergy to a metal-ceramic crown occurs if the base cap is made of a nickel alloy rather than gold or titanium. Or, for example, this option - if the metal-ceramic crown is ordinary, i.e. not on the shoulder mass, then it will provoke an allergic reaction much more often. As the gums eventually begin to come into contact with the metal along the edge of the crown, allergens will accumulate in them.
Read on the topic: metal-ceramic crowns - what they are, on the shoulder mass and ordinary ones, for whom they are suitable.
In metal-plastic materials, both metal and plastic can become an allergen. Therefore, such products should not be worn for longer than the prescribed period - several weeks or months. Or place them on artificial gums so that the edges of the crowns do not rest on the mucous membranes.
Allergies from dentures - myth or reality?
Prosthetics are an excellent chance to restore lost teeth or correct aesthetic defects. There are contraindications for installing crowns and dentures. These include allergic reactions of the patient to the dental material used.
Denture allergies are not a myth. The problem is urgent and becoming quite global; a generation is growing with a reduced or incorrect, atopic response of the human immune system.
Allergic reactions very often occur to artificial crowns that are in the mouth. They mainly react to products made of metal, metal-ceramics, or more precisely, to one of the components of the alloy.
Irritation due to galvanic syndrome
Galvanic syndrome is a condition when an electrical impulse occurs between prostheses made of dissimilar metals. Moreover, crowns can be metal, metal-ceramic, or metal-plastic (the main thing is that metal is present). Galvanism occurs not only between crowns, but also between crowns and other prostheses. For example, clasp with metal hooks or a palatal bridge, as well as implants (less often). There is a tingling sensation in the mouth, an “electric sensation,” and a sour or bitter taste.
The occurrence of galvanism depends on how dissimilar metals are able to interact with each other (how different their electrochemical activity is), and not on the quality of the metals themselves. Therefore, you should always be interested in what crowns are made of and report this important information to the dentist during subsequent prosthetics. According to statistics, 15-35% of orthopedic dentists’ patients experience galvanic syndrome. For example, galvanosis may appear due to the presence of gold and nickel-chrome prostheses.
How to identify allergies at the first suspicious signs
To reliably determine pathology, you should not rely only on your own feelings. Seeing a doctor at the first symptoms is the surest solution to the problem. Consultation with several specialists may be required; in addition to the dentist, an endocrinologist, allergist, dermatologist, immunologist and others may be involved in the diagnostic process. In a dental office, diagnosing an allergic reaction that has occurred consists of several stages:
- They begin with an examination and determination of the general condition of the body. This way the doctor will see signs of allergies, determine the course of the disease and the extent of the problem, and also evaluate the wear of fillings, crowns and dentures,
- then the prosthetic structures are removed. This is necessary to stop contact with the allergen,
- Then two informative tests are carried out: elimination and exposure of the prosthesis. The first is to remove the device from the mouth for a period until allergy symptoms disappear (usually 7 days). During the second test (exposure), the structure is returned to its place again in order to confirm the fears and finally make sure that the allergy arose for this reason.
It is no longer the dentist (usually an allergist) who conducts several additional and controlled (!) tests under the supervision of doctors directly for allergens that potentially caused a pathological reaction. Venous blood is also taken for analysis, and if antibodies to allergens are detected, a more precise diagnosis is made and a treatment method is selected.
What causes allergies?
It is clear that some materials can cause an allergic reaction on their own. Dentists and dental technicians, of course, know about this and try to process materials and make dentures in such a way as to reduce allergenicity to a minimum. But sometimes provoking factors come into play, for example, the following:
- chips, abrasions and cracks that expose the inner layers of the prosthesis: as a result, allergens enter saliva, gums,
- loose fit of the crowns to the gums and supporting teeth: therefore, when chewing, the material in contact and poorly treated areas begins to actively “give off” components, incl. allergens. They are absorbed into the gums, penetrate the blood vessels, saliva,
- poorly manufactured dentures: improper mixing of material components, too high or low processing temperature, etc.,
- changes in the composition of saliva due to certain diseases of the body (diabetes, gastrointestinal problems), climate change or even the region of residence, where the water composition is different,
- natural aging of the prosthesis, i.e. end of its service life,
- installation of a new prosthesis made of a different material (with metallic inclusions): provokes galvanosis.
%akc72%
Alternative to Nickel Titanium Braces
An alternative to nickel-titanium archwires is flexible braided stainless steel and metal fiber-reinforced composite archwires. Gold-plated archwires, TMA and pure titanium can be used without risk. There are also modified nickel-titanium archwires, which are plastic (composite-coated) nickel-titanium archwires.[36] Ionized nickel-titanium wires have a surface that is bombarded with nitrogen ions, resulting in an amorphous surface layer that makes them resistant to corrosion and displaces nickel atoms, thereby reducing the risk of an allergic reaction.
First aid at home
If you notice characteristic symptoms of an allergic reaction, you should immediately remove your dentures - if they are removable. If they are not removable, rinse your mouth and take an antihistamine. For example, “Suprastin”, “Fenistil” drops or “Tavegil”. They are considered the most powerful, but with side effects such as drowsiness and slower reactions. Next, you should immediately contact the dentist who placed the prosthesis. While you are waiting to see a doctor, eliminate any potential allergens from your environment - citrus fruits, chocolate, ketchup, dust, and have less contact with animals. Because it is possible that an exacerbation of some “old” allergy has occurred.
If there is sudden swelling of the face, neck, arms, legs, it becomes difficult to breathe, or a rash appears all over the body, then immediately call a doctor or an ambulance.