Science knows that caries develops due to bacteria that are found in plaque. Almost all types of germs can be transmitted from one person to another. In this regard, the question arises whether caries is contagious. This can be answered in the affirmative. However, everything is much more complicated than it seems.
In this article
- The problem of caries development
- Is tooth decay contagious?
- Why is tooth decay contagious in children?
- Is caries inherited?
- Does caries transfer from one tooth to another?
There are many myths surrounding caries, as one of the most common dental diseases. Most people believe that carious lesions are a consequence of poor hygiene. Some people believe that caries is transmitted through saliva, so you can get it during a kiss. Scientists claim that the main cause of this pathology is cariogenic microbes from the Streptococcus group. Moreover, each of these statements is partially or completely true. Let's try to figure out whether caries is transmitted from person to person or not. First, let's find out what causes this disease.
What is caries
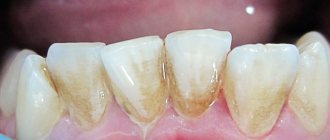
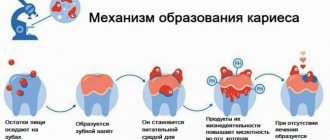
First, let's look at the essence of the problem. Carious lesion is the destruction of tooth tissue under the influence of harmful bacteria of the Streptococcus mutans group. They reproduce without access to oxygen (which is why caries often occur under fillings), feed on sucrose (which is why caries is believed to come from sweets) and secrete acid, which destroys enamel and dentin.
Interesting! Streptococcus mutans is a gram-positive anaerobic bacterium, it actively produces lactic acid and polysaccharide, which settles on the enamel and later turns into plaque or even tartar. However, bacteria can produce this polysaccharide only from sucrose. Thus, by reducing the consumption of sweets, we automatically reduce the negative impact of bacteria on teeth.
Streptococcus mutans is present in the oral cavity of every person, but this does not mean that 100% of the world's population suffers from caries (although the figure is approaching this). Timely oral hygiene, strong immunity and the absence of bad habits inhibit the rapid development of microorganisms and strengthen the enamel. Therefore, we can say with confidence that prevention in this case is a guarantee of health.
Transmission of dental caries through kissing
Caries is caused not only by pathogenic bacteria. Problems appear with excessive consumption of sweet foods, phosphorus deficiency, and poor hygiene. Today there is an opinion that caries is transmitted through saliva at the time of kissing. If there is a bacterial infection in the oral cavity in the form of oxygen-free microorganisms, the disease can be transmitted to a healthy toddler through a kiss. True, this does not threaten an adult and a child over 3 years old. After all, they already have the same bacteria in their mouths. Newborn babies can be seriously harmed.
When kissing, an abnormal bacterium enters the newborn's mouth. If the conditions of the oral cavity leave much to be desired, the microorganism will quickly multiply and damage tooth enamel. An adult can be transmitted from a sick person such unpleasant diseases as viral and fungal infections.
Factors provoking the development of caries
- childhood: children under three years of age are at risk for this disease, since they have not yet developed their own immunity and teeth are just beginning to appear,
- weakened immunity: lack of vitamins and minerals does not allow the body to build full protection,
- unbalanced diet: the predominance of sweet foods in the diet enhances the nutrient environment for Streptococcus mutans, which provokes their active growth,
- insufficient hygiene: clinically tested toothpastes, brush configurations and mouth rinses allow you to remove plaque even from hard-to-reach places, which are the habitat of Streptococcus mutans,
- bad habits: in addition to reducing immunity and destroying enamel, smoking and alcohol disrupt the microflora of the oral cavity, killing beneficial bacteria that can resist pathogenic ones,
- taking certain medications: long-term use of antibiotics, antifungal drugs and some others reduces immunity and slows down metabolic processes in the body, which is why the enamel does not receive enough calcium and fluoride to strengthen,
- hormonal disorders: a failure in the production of hormones also negatively affects metabolism, which leads to thinning of the enamel,
- wearing orthopedic or orthodontic structures: they can mechanically damage the protective shell of the tooth or fit too tightly to it, which is why the crown is not washed with saliva, dries out and cracks. And microbes penetrate into these cracks - and the development of caries begins.
Why is caries dangerous if left untreated?
In this section we will talk about the complications of untreated dental caries in a timely manner, which without exception lead to the need to remove the nerve from the tooth and fill the root canals. And in case of purulent complications, in addition, contact a surgeon to make an incision on the swollen gum.
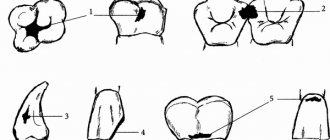
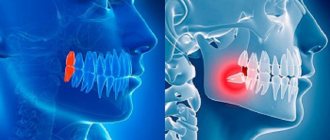
- Development of pulpitis - as the carious process spreads to the deep layers of dentin surrounding the tooth pulp, cariogenic microorganisms penetrate into the tooth pulp. The pulp is the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. As a result of infection, purulent inflammation of the pulp occurs - pulpitis. Pain due to pulpitis is usually acute and paroxysmal in nature. You can see schematically how pulpitis develops in the following pictures (Fig. 7-9) –
- Development of periodontitis – if pulpitis is also not treated in a timely manner, then pulp necrosis occurs, i.e. her death. This stage of inflammation is called periodontitis. In Fig. 11 you can see how the infection, spreading from the carious cavity through the root canals, penetrates beyond the tooth - into the periodontium and bone tissue. And as a result of this, a focus of purulent inflammation appears in the area of the apex of the tooth root (it can be designated by the term “periodontal abscess”).
On an x-ray, such an inflammatory focus looks like intense darkening around the apex of the tooth root. In addition, in Fig. 10 you can schematically see the differences between pulpitis and periodontitis. - Development of a cyst at the apex of the tooth root – as a result of infection of the near-apical tissues, their gradual destruction occurs: the bone tissue is resorbed, and in its place inflammatory granulation tissue is formed, and jaw cysts can also form. Such cysts are called radicular - from the Latin word Radix, which means “root” (24stoma.ru).
A radicular cyst is a cavity in the area of the apex of the tooth, the inner surface of which is lined with a membrane, and the cavity itself is filled with pus. Sometimes they can reach very large sizes. For example, I had to remove such cysts up to 5 cm in diameter. You can see what a radicular cyst looks like in the diagram of a section of the upper jaw (Fig. 12), as well as in the x-ray (Fig. 13), in which the cyst looks like an intense darkening at the root of the tooth.
- The development of gumboil is also a complication of pulpitis and periodontitis and includes a disease called “periostitis”, which is popularly called gumboil. Periostitis is always accompanied by severe swelling of the gums and/or cheeks. Inflammation and swelling in this case are a consequence of the spread of infection from the apex of the tooth root to the area of the periosteum, which covers the jaw from the outside. As a result, a purulent abscess occurs between the periosteum and the jaw (when the periosteum melts, pus breaks through under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity). Treatment of periostitis involves the need to make an incision in the projection of the swelling (to evacuate pus). After this, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Before starting treatment, the issue of the need to remove or preserve the causative tooth that caused the inflammation is also decided. If it is decided to save the tooth, then after the acute symptoms have subsided, the dentist will need to treat this tooth appropriately so that it does not cause purulent inflammation next time.
How can you become infected with caries?
The bacteria Streptococcus mutans enters our mouths during childhood, and the main source of infection in this case is almost always adults. Moms and dads lick the spoons with which they feed their children, older brothers and sisters give the younger ones a bite of their apple. Parents often make another mistake - they buy their kids one toothbrush between them. This happens in families with twins or triplets. Parents think that they are saving the family budget in this way, but in fact they contribute to the transmission of infection from one child to another.
There is one consolation: adults have nothing to worry about. He is not at risk of becoming infected with Streptococcus mutans because these microorganisms have been living in his mouth for a long time.
How to protect a child from carious bacteria?
First of all, you must follow one rule - do not put anything in the child's mouth that was previously in the parent's mouth. You can always moisten the pacifier with water, not saliva. The child should try food with a separate spoon or fork. If your child drops cutlery, do not lick it, as this is not the way to clean it. In the first months of a child’s life, you should also avoid kissing on the lips, especially if the parents have pronounced caries.
Be careful who and when you kiss But the problem applies not only to children, but also to people who like to kiss. Cause? The touching of tongues and the exchange of saliva that occurs during a long and passionate kiss are also an exchange of bacterial flora between partners. Bacteria literally move from mouth to mouth.
The saliva of a person who does not have cavities contains a balanced amount of "good" and "bad" bacteria, which are natural oral flora. However, at the moment of contact with the saliva of a person with caries and developed bacterial plaque, the balance may be upset. More caries bacteria appear and the risk of developing caries increases even with healthy teeth.
Moreover, the pH of the mouth may also change during a kiss, especially if one of the kissers previously ate a large portion of sweets, drank a sweet drink or wine. In this situation, the oral environment is acidified by acids produced by sugar-feeding bacteria.
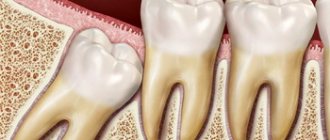
Do adjacent teeth become infected with caries?
The development of pathogenic microbes occurs in hard-to-reach places where the proper amount of saliva, which reduces acidity, or the bristles of a toothbrush, which remove plaque, do not reach. Such a place may be the closure of the walls of two crowns. If you do not use dental floss or an irrigator - special devices for cleaning the interdental space, then bacteria will actively multiply in this cramped corner - and caries will affect both crowns. Thus, the disease does not spread to neighboring units, but develops between them.
Is caries inherited?
There is an opinion that this disease is genetically determined. This is partly true, but the point is not in the defeat itself, but in indirect factors. For example, metabolic disorders can be inherited, and then weakened enamel will not be able to resist Streptococcus mutans.
Also, a malocclusion can be passed on from parents, which creates areas in the mouth that are difficult to reach with a toothbrush, where caries begins to develop.
In addition, we absorb food habits and hygiene rules from our parents. If mom and dad brush their teeth from time to time, then the child will do the same, which means a favorable environment is created for Streptococcus mutans.
What symptoms appear with average caries?
To understand when a painful reaction to sweets occurs, you need to study the structure of the tooth a little.
In addition to enamel, the human tooth consists of dentin, and all dentin is penetrated by very thin dentinal tubules, which contain processes of odontoblast cells. These cells form the surface layer of the pulp and have their own sensitivity. They are the ones who react to sweets, they ate a piece of chocolate, the tooth ached sharply, but also quickly went away.
If only this sensitivity is present, then caries can be quickly cured, since the pulp has not yet been affected.
How to find out if you have dental caries
Absolutely all people are carriers of the bacteria Streptococcus mutans, but being a carrier does not mean getting sick. If the body’s immune response is strong enough, if tooth enamel receives a sufficient amount of microelements, if a person takes proper care of his oral cavity every day, then the risk of caries is reduced several times.
For comparison! In countries where preventive medicine is properly structured, this disease occurs several times less frequently. For example, in Finland, 175-200 cases of caries are diagnosed per 1000 children aged 7-12 years, while in Russia for the same number of children there are 1000-1200 cases of caries, i.e. and sick children, and the number of affected teeth in our country is much higher.
Caries is contagious! And six more unexpected facts
June 4 is the day to fight tooth decay
Dentists suggested celebrating the Day against Caries (surprising, right?). And no wonder: this seemingly invisible disease is the most common in the world. At least in children, it occurs five or even eight times more often than bronchial asthma (asthma is the second most common in children). According to various sources, about 80 percent of teenagers at the time of graduation from school have visited the dentist at least once because of a hole in their tooth. Moreover, the peak of caries occurs precisely at the age of 15 to 17 years. And it is very difficult to meet an adult without fillings.
The beginning of June is a good time to remember some interesting facts about caries. Well, pay a visit to the dentist. Just in case.
1. Caries is contagious! Bacteria that cause tooth decay can be transmitted from person to person, American dentists warn. The thing is that the most common causative agent of caries is the bacteria Streptococcus mutans. They especially love children's teeth. Therefore, it is so important that the child has his own spoon and plate. And, moms, don't lick your baby's nipples! After all, caries, or rather the bacteria that provoke it, can be transmitted even through a kiss.
2. Lack of breastfeeding contributes to the development of tooth enamel defects in children - clouding, staining, and a low degree of mineralization. Brazilian scientists associate this with a deficiency of nutrients entering the child’s body during the period of teeth formation (the same calcium that is transmitted through breast milk).
Meanwhile, for a long time it was believed that too much breastfeeding contributes to the development of caries of baby teeth in children. Allegedly, lactose in breast milk contains too much sugar and feeding after a year can have a detrimental effect on the condition of babies’ teeth. Now researchers dispute this, blaming soft and sweet foods - complementary foods given to children - for tooth damage.
3. Older women who smoke lose teeth much more often than men, according to American scientists from the University of Buffalo: compared to non-smoking women, heavy smokers encountered dental problems twice as often. And the risk of tooth loss due to gum disease was six times higher.
4. Parents with a low level of education, with financial and psychological problems, often do not pay attention to the condition of the child’s teeth. Well, as a result, such children have more diseased and missing teeth. This was calculated by scientists from the USA (Cleveland, Ohio).
5. The further north people live, the worse their teeth are, suggests WHO. For example, according to statistics, in equatorial regions (Africa, Asia) caries is not as common as in Scandinavia and North America. However, in developing countries, the prevalence of caries is still high.
6. Even among our ancestors who lived more than six thousand years ago, traces of dental caries were found. Moreover, man is the only animal on earth suffering from this scourge. And the only one that brushes your teeth at least once a day.
7. Although we have all known this for a long time, Australian dentists once again warn: the more sugary drinks, the more caries. And not just because of the sugar.
“The risk of tooth decay should be included in all warnings about drinking sugary carbonated drinks,” says Jason Armfield from the Australian Center for Oral Health Research at the University of Adelaide School of Dentistry. — The high acidity of many sugary drinks leads to erosion of tooth enamel, and, like sugar, contributes to the development of caries.
It would be better to drink fluoridated water, scientists complain, it reduces the risk of developing caries.
BY THE WAY
Where does it come from
In general, not only Brazilian, but also all dentists in the world today associate the appearance of caries with changes in the acid-base environment in the mouth. And with microorganisms that are capable of forming organic acids during their life processes. And high-carbohydrate foods affect this. Therefore, dentists warn:
- If you like soft, carbohydrate-rich foods, then your caries will develop much faster. Love rougher foods.
— In summer, there is another danger - if there is little saliva and it is viscous, then this can contribute to the fixation of bacteria on the walls of the teeth. A larger amount of saliva helps clean the surface of the dentition from harmful microorganisms. So drink water!
— Back in 1948, Russian dentist professor I.G. Lukomsky said that the development of caries is also affected by a lack of vitamins B1 and D, calcium salts, phosphorus, fluorine, and ultraviolet rays. In his opinion, “violation of external factors leads to changes in mineral and protein metabolism in the body, ... as a result, processes develop in the hard tissues of the tooth leading to demineralization of enamel and dentin, and, ultimately, to the formation of a carious cavity.” So spend at least 15 minutes in the sun a day.
TO THE POINT
On May 27, at the 66th World Health Assembly in Geneva, WHO approved a global action plan for the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases for 2013-2020. And special attention is paid to diseases of the oral cavity. In the 2011 Political Declaration on the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs), the UN recognized that oral diseases share risk factors with the four major chronic diseases - cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases - and would therefore benefit from a comprehensive approach to addressing the problem.
HELP "KP"
Dental caries (lat. Caries dentium) “is defined as a local pathological process of external origin, occurring after teething, in which softening of the hard tissues of the teeth occurs, leading to the formation of a cavity.” (WHO definition, 1963).
“Caries is a pathological process that manifests itself after teething, during which demineralization and softening of the hard tissues of the tooth occur, followed by the formation of a cavity” (E. V. Borovsky, 2004).
How to prevent caries: preventive measures
The most effective and, importantly, cheapest way to combat carious lesions is its prevention. Since it is impossible to completely get rid of harmful bacteria, you can slow down or completely stop their reproduction and spread.
- daily oral hygiene (it is important to brush your teeth in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed, in the afternoon after lunch and afternoon snack, you need to rinse your mouth with a special solution or just water and remove food particles with dental floss),
- balanced diet (limit the consumption of sugar-containing dishes, increase the consumption of vegetables and fruits, fish and fiber),
- giving up bad habits (tobacco smoke destroys enamel and negatively affects the condition of the gums, reducing their protective function and slowing down metabolism),
- refusal of uncontrolled use of medications, especially antibiotics,
- giving up the habit of licking spoons, pacifiers, toys of small children,
- maintain overall immunity in good shape.
Thus, carious lesions can be avoided, even when infected with the bacteria that cause them.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a virus that manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes as benign neoplasms. New growths are called papillomas and condylomas. HPV is very common and is transmitted in a variety of ways. In particular, infection is possible through a deep kiss, which has been confirmed by a number of studies. There are different types of papillomavirus, but only a few of them pose the greatest threat, as they contribute to the development of malignant tumors, such as cervical cancer. The virus is also dangerous because it can lie dormant in the body for a long time and not manifest itself in any way, that is, the infected person will not even know about it.