Despite progress in medicine, a remedy has not yet been found that will be effective in the fight against the immunodeficiency virus. So the disease remains incurable. And this scares a lot of people. The only way to protect against HIV remains to prevent infection. Many people are still not familiar with the information that describes how the virus is transmitted. Their knowledge is based only on unverified rumors and their own guesses. All this only increases the fear of infection. So today the question is very relevant: “Is it possible to become infected with HIV at the dentist?” Methods of transmission of infection and standards for sanitizing instruments will be discussed in this article.
Briefly about HIV infection
Today, every person knows that the abbreviation HIV stands for “human immunodeficiency virus.” This disease is characterized by the fact that the smallest microorganisms cause disruptions in the protective functions of the body in people. The action of the virus can be described as follows. Once in the body, it affects the immune system, destroying cells responsible for protecting against infections and destroying microbes.
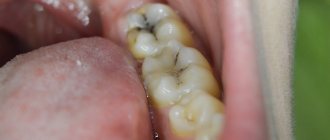
Over time, a person becomes unable to resist either external infections or bacteria or fungi. The virus multiplies only inside a person. Outside the body it dies. The duration of life outside the body is influenced by temperature and humidity. The virus dies when heated (over 56 degrees Celsius). Sterilization of dental instruments completely destroys HIV, because it is designed for more tenacious viruses and bacteria.
Is it always HIV status that can lead to implantation failure?
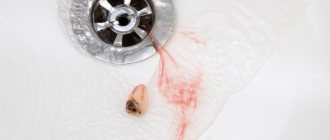
Rejection of dental implants is possible due to various reasons; the patient’s HIV status is in penultimate place . The main reasons for artificial root rejection:
- Medical error (unprofessionalism of the implantologist) - incorrect calculation of the place where the titanium root should be implanted, incorrect installation of the implant relative to the level of the alveolar ridge.
- Poor-quality implantation system - the process of osseointegration depends on the quality of the material from which the artificial root is made. Since tissue regeneration is reduced in immunodeficiency, the quality of the implant is of paramount importance for its normal fusion with the bone.
- Failure to comply with doctor's recommendations regarding postoperative care on the part of an HIV-infected patient. With poor hygiene, the risk of developing peri-implantitis and titanium root rejection increases 5-7 times.
- Exacerbation of HIV disease - the immune system cannot cope with its responsibilities, medications have almost no effect, post-operative wounds do not heal well, inflammation develops in the implantation area, and the implant begins to be rejected.
The risk of infection or rejection is also present in healthy patients. But with immunodeficiency it is higher. Difficulties are possible at any stage of treatment. There is no need to plan implantation for HIV infection with complications due to the risk of undesirable consequences.
Routes of transmission of the virus
The greatest likelihood of HIV transmission is from a person who is at the end of the incubation period, at the time of initial manifestation and at a late stage of the disease. The infection in question is classified as a long-term illness. The virus thrives in all human biological fluids (blood, semen, vaginal secretions, breast milk, saliva, tears, sweat, etc.). It is worth noting that the virus is contained in these biological fluids in different concentrations. This determines the difference in their epidemiological significance.
Human biological substrates that are most likely to transmit infection include:
- blood;
- breast milk;
- vaginal discharge;
- sperm and pre-cum.
It is worth noting that HIV infection is caused by pathogens entering the internal environment of the body. We are interested in the question: “Is it possible to become infected with HIV at the dentist?” Therefore, we will consider the only possible method of transmission of infection – through blood.
Proper care of implants
After implantation, careful care is required. All patients need this, but for HIV-positive patients, the implantologist’s recommendations must be followed with triple scrupulousness.
- Brush your teeth twice a day;
- use floss;
- rinse your mouth after eating;
- do not eat solid foods (nuts, grilled vegetables);
- visit the dentist once every six months for professional hygiene.
Be sure to take a course of antibiotic therapy prescribed by your doctor.
Maintain stable CD -4 lymphocyte counts by continuing antiretroviral therapy (as prescribed by your doctor).
HIV prevention in dentistry
It is no secret that cases of infection of patients in medical institutions, manicure salons and other establishments have been recorded. The risk group includes all facilities where services involving surgical or cosmetic procedures are expected to be provided.
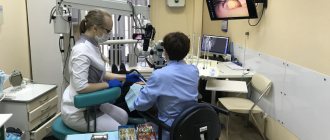
Dental clinics are no exception. A huge number of people visit their offices every day. It is for this reason that it is especially important to comply with all sanitary standards and sterilize dental instruments. Today, every clinic has a plan of preventive measures. By fulfilling all the requirements, both the private dentist and the doctor at the public hospital protect themselves and the patients in their office from infection.
Vacuum of knowledge
However, this issue is regulated by written rules. Thus, the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 18, 2010 N 58 (as amended on June 10, 2016) “On approval of SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities”” indicates that dental handpieces must be sterilized after each patient.
This is also evidenced by modern instructions on the correct and safe processing of dental handpieces. The Kemerovo correspondent for AIDS.CENTER conducted a small experiment: she specifically walked through the city’s dental offices to check how these documents work. It turned out that there was no way. When a woman sat down in a chair and asked uncomfortable questions, the answer, as a rule, in most places was the already familiar “We treated it,” which in practice often meant: they wiped the top twice with a cotton swab containing chloramine.
However, there is no need to panic. Professor of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology of the Moscow State Medical University named after A. I. Evdokimov Irina Shestakova answers a question on our site that it is quite difficult to really assess the likelihood of such an infection. And the risk is not as great as it might seem at first glance.
Possible causes and features of infection in the dental office
We are interested in the likelihood and routes of infection of dental patients. Can you get infected with HIV at the dentist? Theoretically yes. In a medical facility, you can become infected with a single exposure of virus particles to the blood. For example, this can happen during the removal of a dental unit with an insufficiently sterile instrument. Repeated fractional exposure (microinfection) can also lead to the development of the disease in the patient. As a rule, the body, having good resistance, is able to resist viruses. But the mucous membrane cannot always work as a barrier.
When a person is treated in a clinic that has its own sterilization station, there is no risk of infection. The security guarantee is almost one hundred percent. Modern dental clinics in Moscow are almost all equipped to the highest standard. The so-called human factor can only play a cruel joke here. A negligent attitude towards preventing infection of any of the staff is possible. Therefore, the choice of a doctor should be approached with all responsibility.
Implantation methods - are they all suitable?
When using the classic two-stage protocol, the probability of engraftment of the artificial root is low, due to the traumatic nature of the intervention. A weak immune system will not be able to cope with wound healing after the implantation procedure or repeated incision to fix the crown. Therefore, the method of choice is basal implantation.
- The technology involves installing a titanium root through a micro-puncture of the gums with immediate loading of the prosthesis. The operation is performed in one stage; the implant root and abutment form a single structure.
- The use of special models of implants implanted into deep bone layers that are not subject to inflammation and atrophic processes provides high primary stability and rapid osseointegration.
- Titanium roots are implanted into the lateral zones at an angle, bypassing the sinuses, nerve plexuses, and large blood vessels.
- Installation of basal implants is the best option for severe chronic pathologies, including immunodeficiency and hepatitis.
Minimally invasive surgery does not involve cutting the gum, drilling the bone, or placing sutures. Postoperative rehabilitation proceeds quickly, with minimal discomfort for the patient.
The ROOTT Clinic is one of the few dental centers in Russia specializing in dental implantation methods with immediate loading. Our doctors have been working with the basal protocol for many years. Thanks to the combination of protocols in one design, we restore teeth in record time, even in patients with a complicated history.
How do dental clinics in Moscow carry out sterilization?
The virus in question is sensitive to high temperature. Boiling kills it very quickly (60 seconds). The virus is not able to withstand the effects of disinfectants (hydrogen peroxide, chloramine solution, alcohol, ether and acetone).
In order to prevent infection, specialists at a modern clinic always follow sanitary rules. Dental instruments go through several stages of cleaning:
- disinfection;
- Preliminary processing;
- sterilization.
In addition to these manipulations, a procedure is carried out to detect hidden blood on the instrument. The quality of sterilization is also controlled.
Dentistry has long practiced the one-time use of the following devices and protective equipment:
- saliva ejector;
- injection needles;
- dental aprons and aspirators;
- gloves, masks.
Advice for patients
There are several rules that will help you protect your trip to the dentist. For many patients, this event itself is stressful. And if they are also worried about the question: “Is it possible to become infected with HIV at the dentist?”, a trip to the doctor may not take place at all. We offer several ways to kill two birds with one stone.
Firstly, switching attention will work. And this will distract the patient from the fear of dental instruments.
Secondly, a person will feel much calmer when he can control the issue of his own safety.
You must make sure that the doctor has opened the packaging of instruments intended for single use before your eyes.
Before the procedure, you can pay attention to the condition of the instruments, as well as the cleanliness of the room.
Correct actions in unusual situations are the key to safety. For example, anesthesia was administered at the dentist, after which the doctor accidentally pricked himself with a needle. What to do? The specialist should use the Anti-AIDS first aid kit, and not just change gloves and continue treatment.
back side
In February 2022, a doctor from one of the state clinics near Moscow contacted the AIDS.CENTER Foundation. An elderly woman works as a dentist. In winter, a patient came to her complaining of acute toothache. Since she admitted that she had HIV infection, the woman did not dare to use a standard instrument, believing that in such cases it requires some kind of “special” disinfection, and asked the manager to give her one that had been written off and was not used for working with ordinary clients.
While manually cleaning the canals with it, she accidentally pricked her finger, and the patient’s blood got under the glove. “I took off the glove, washed it with running water, put it on and started working again. According to SanPiN, after I finish the tooth, I must warn the head nurse and the manager about the emergency,” says the dentist. - After I released the patient, and she was satisfied, after all, I am a good doctor and did my job conscientiously, I ran to the head doctor, to the office where she sits with the deputy. I say that I had “such” a patient, I was damaged. And she told me: “Go, you are free!” “She screamed, laughed together with the deputy and sent me to the reception.” If the elderly woman had used a standard tool, the damage most likely would not have occurred, the interlocutor agrees. But even after the injury had already happened, no one even thought to inform her about the actions that she should have taken to protect herself in the current situation.
Suddenly, the elderly doctor herself found herself in the patient’s place: after telling her relatives about the incident, she cried all night: “My sister died with her husband, she left three children. Four more are mine, we need to feed them, raise them, my husband and I work together.” Fortunately, one of her colleagues advised her to call the regional AIDS center, whose staff explained: there are medications that, if taken within 72 hours after the incident, can prevent the development of infection.
How the diagnosis could have turned out for her - says another ward of the Foundation, also a dentist near Moscow. After he himself received HIV, the man was immediately fired from the clinic. Only six months later did he manage to find a new place, and only thanks to the fact that, while undergoing a medical commission, he convinced the private clinic that performed him not to paste the blood test results into the card, printing them out on a separate sheet and handing them over (that is, hiding his HIV status from the new employer).
Providing dental care to HIV-infected people
Federal law states that preventing the spread of diseases caused by the immunodeficiency virus in the Russian Federation also involves providing medical care. It is agreed to reduce contact with the patient to a minimum. The doctor is obliged to maintain medical confidentiality. The law provides for disinfection measures. In connection with them, the advisability of placing sick patients in separate rooms was noted. At the same time, they must be equipped with the necessary equipment. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to carry out all therapeutic procedures last (after healthy patients).
Patients with HIV infection can receive full dental care provided that the prescribed safety measures are followed. In turn, people with HIV infection must notify staff of their status.
Education issue
Lebedev states: “It’s enough to ask specialists at some cosmetology seminar: “What is viral load?”, and they won’t answer you. They just don't know this term. Hence the problems. Their knowledge regarding HIV is equal to that of ordinary people who do not have a medical education.” “Now I want to address cosmetologists: don’t you think it would be better not to intimidate patients, not to scare them away from you, but, on the contrary, to form trusting relationships with them so that they do not hide their diagnoses from you? Because it is then that the cosmetologist will be able to guide the patient in the right direction, even if the patient is unfavorable,” the specialist concludes.
According to Lebedev, when a patient comes to him and says that he has HIV, the surgeon clarifies whether he is taking antiviral therapy and what his viral load is. If a patient does not undergo treatment and his viral load is high, Lebedev does not refuse him surgery, but first suggests that he take care of his health and only then come to him. “A patient who wants to improve his appearance is a person who wants to love himself, and we can help him with this. He is not to blame for his diagnosis, it just happened that way, and our task is to help him cope with psychological pressure and alienation, to improve his quality of life,” the specialist sums up.
What to do if you suspect an infection?
In general, experts recommend that all adults periodically get tested for HIV. This can be done using rapid tests, which are sold in pharmacies. The patient will receive more reliable information in specialized rooms. You just need to donate blood and wait for the result.
Unfortunately, early diagnosis of HIV infection is complicated by the fact that the initial symptoms also occur with other ailments. However, you should be wary of unmotivated fatigue, increased sweating at night, and headaches. At the same time, high body temperature and prolonged diarrhea may persist. Symptoms of infection include:
- weight loss;
- furunculosis;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
HIV can be suspected if the following diseases are diagnosed:
- pneumonia (Pneumocystis);
- Kaposi's sarcoma;
- brain toxoplasmosis;
- herpes zoster.
Alternatives
If implantation cannot be performed, the patient is offered alternative options:
- Dental bridges are a reliable method of prosthetics, but require depulpation and grinding of healthy teeth that act as a support for the prosthetic structure.
- Removable dentures are the simplest method of restoring dentition. However, it does have disadvantages. Does not stop bone atrophy, restores chewing function by 60%. Removable dentures cannot be used in the presence of opportunistic diseases of the oral cavity (aphthous stomatitis, exfoliative cheilitis, Kaposi's sarcoma, etc.).
- Mini-implants are characterized by rapid healing, securely fix a removable denture in the mouth, but cannot withstand increased loads during chewing.
ROOTT implantologists recommend mini-implantation and removable prosthetics as a temporary solution during antiretroviral therapy. When stable CD4 cell counts and an undetectable viral load are achieved, basal implantation is performed.