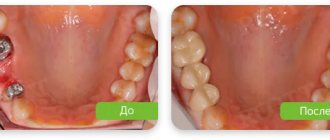
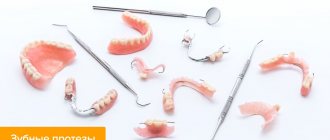
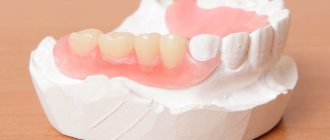
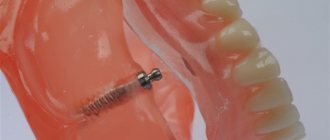
Restoring damaged or lost teeth often takes quite a long time, and it is understandable that patients do not want to experience discomfort from this. To preserve chewing functions and the aesthetics of a smile, they resort to the use of temporary structures.
Temporary (provisional) crowns are a type of dental prosthesis that is installed on a ground tooth or implant while waiting for a permanent crown.
Externally, provisional crowns are similar to permanent ones, but differ in the material from which they are made, strength, stability and service life.
Why are temporary dentures needed?
The main purpose of a temporary prosthesis is to restore chewing function and an attractive appearance; the structures are also designed for the following purposes:
- formation of a prosthetic bed;
- preventing the displacement of healthy teeth;
- helps to reduce the period of adaptation to a permanent prosthesis;
- while wearing it, the correct bite is maintained;
- prevents inflammation and irritation of the gums;
- protects soft tissues from any damage;
- promotes uniform load distribution.
Depending on the situation, temporary removable dentures can be installed for 1-6 months. The maximum wearing period can be up to 5 years, but subject to careful use and proper oral care. Prosthetics are recommended when getting used to implants, re-prosthetics and changing teeth in children.
Call us or 8 (926) 100-10-10
Adaptation to prostheses installed using All on 4 technology
Successful completion of the period of adaptation to prostheses installed using the ALL-ON-4 technology is a necessary condition for obtaining long-term treatment results.
Adaptation (lat. adapto - I adapt) is the process of adapting the body or its individual organs to changing environmental conditions. An adaptive prosthesis is made from dental materials intended for permanent wear. The speed of adaptation varies from person to person, but since the ALL-ON-4 technology ensures that the prosthesis is always in the mouth, adaptation occurs very quickly. From the moment the prosthesis is installed, the adaptation period begins. By adaptation we mean not only simple addiction, when a person forgets that he has a prosthesis in his mouth (we repeat, this happens quickly), but also the whole complex of changes in the body, bones, muscles, and the central nervous system (central nervous system). During the adaptation period (6 months), the doctor, following such changes, modifies the adaptive prosthesis. The prosthesis is designed in such a way that if the load on it is higher than permissible, it can break, which protects the implants during the healing period.
Objectives of an adaptive prosthesis
- Aesthetic and functional rehabilitation during the period of implant integration and correction
- Development and correction of the boundaries of the prosthesis relative to the gums
- Formation of gum relief
- Development of personal hygiene and prosthesis care skills
- Matching the size and shape of teeth for a permanent denture
- Practicing occlusion and bite height, etc.
The following changes occur:
- the appearance, and later disappearance, of postoperative edema;
- the jaw bone is remodeled in the areas of extracted teeth;
- implants are integrated;
- chewing reflexes change, sending information to the central nervous system, etc.;
- antagonist teeth are changed and evaluated.
Schedule appointments with your doctor
The schedule of meetings with an orthopedic doctor can be individual and depends on the implant installation technology, but, as a rule, the following stages go through:
- Day 1 (90′): the doctor installs the prosthesis and monitors the distribution of the load when the teeth are closed.
- Days 10-14 (40′): removal of sutures and control of the prosthesis. Training in hygiene skills with this prosthesis.
- Day 30-40 (60′): removal of the prosthesis in order to fill the gaps and undercuts formed due to the disappearance of swelling and the beginning of remodeling. Control of fixation of multi-units. This period is the most critical for implants and Al-V alloy, since the mechanical fixation of the implants is reduced, and the bone has not yet grown.
- 2nd month (30′): control visit to detect hidden cracks in the prosthesis, as well as assess the quality and quantity of attached gum in the area where the implants emerge. If necessary, the issue of correction of the soft tissues of the gums or deepening of the vestibule is discussed and a day for correction is appointed (the cost of additional surgical procedures is not included in the initial plan).
- 3rd month (15′): follow-up examination.
- 6th month (30′): control x-ray, correction of the prosthesis (if required), polishing the prosthesis, drawing up an epicrisis, issuing recommendations for instructions, getting to know other types of prostheses made from other materials and using other technologies, assessing their advantages.
Using an adaptive prosthesis for more than the period recommended by a doctor can lead to the following consequences:
- Breakage of the prosthesis, since plastic is not a very durable material and is subject to aging.
- Loss of implants due to a hidden crack or breakage of the prosthesis, which will inevitably lead to overload of one of the implants. Breakage of the prosthesis is absolutely painless and the patient may not notice it at an early stage, but will only discover it when the implant becomes loose.
- The possibility of allergic reactions to plastic at the point of contact with the gums.
- Unsatisfactory hygiene, because it is not always possible to tightly install the adaptive prosthesis to the gum (see point 3).
- Incomplete restoration of chewing function, since on an adaptive non-reinforced prosthesis it is impossible to make releases beyond the distant implants without increasing the risk of prosthesis breakage, because the heaviest chewing load on the teeth occurs there.
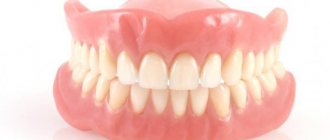
Temporary removable dentures
The price of prosthetics is affordable, the designs are also called “butterflies”, the features include the following:
- plastic is used for manufacturing;
- easy maintenance, since the structures can be removed at any time;
- there is no need to remove dentures at night;
- fastening is performed without grinding the teeth;
- Wearing period is from 3 to 4 months.
Worth knowing! When using acrylic plastic, the patient may experience breakage of the clasps.
Prosthetics
Fixed temporary dentures for front teeth
The plastic crown is fixed with non-permanent cement; the structure can be removed at any time if necessary. Fastening can be performed on a ground tooth, which will later be used as a support for a permanent prosthesis. The entire restoration process is carried out in one visit to the dentist for 2-3 hours.
If you have any questions about the prices and timing of installing temporary dentures on your front teeth, you can always contact our specialists for advice by phone or through the feedback form.
Implantation and prosthetics All-on-4 (methodology)
We talk in detail about the features of the surgical stage in another article, but in short, there are 2 options for the surgical technique. The first option is using an individual surgical template “NobelGuide”, thanks to which the installation of 4 implants will take the implant surgeon only 30-35 minutes. The second option is a classic technique without the use of a template, which requires incisions in the gums and large-scale detachment of mucoperiosteal flaps. Of course, the first option is preferable.
All-on-4 (implant installation stage) –
I would also like to dwell on the choice of implants for the All-on-4 technique, and by far the best choice would be to use original implants. This company has developed not only the “All-on-4” concept itself, but also special types of implants and abutments for it. We are talking primarily about the Nobel Speedy Groovy and Nobel Parallel CC implants, as well as aba (multi-unit), which today are the gold standard for permanent prosthetics of edentulous jaws.
Next we will look at:
- options for temporary fixed prostheses for All-on-4,
- options for permanent fixed dentures on 4 implants.
What happens if you refuse to install temporary dentures?
The main purpose of a temporary prosthesis is to restore the dentition in the oral cavity until a permanent prosthesis is ready or an implant is installed.
For various reasons, this process can take a long time - from two to three weeks or more. During this period, when one or more teeth are missing, there is a high risk of complications:
- pathological change in bite;
- rapid destruction of healthy teeth due to increased load;
- a change in the position of the teeth towards a “gap” - the teeth lose not only their support point, their attachment in the sockets weakens, and all this leads to significant deformations of the dentition;
- without a prosthesis, the exposed area of the jaw will not receive the necessary load during the chewing process, which will provoke changes in the bone tissue - it will become porous, decrease in volume and will be unsuitable for prosthetics;
- The part of the mucosa not protected by the prosthesis is prone to injury when chewing.
And of course, while the prosthesis is being made, the patient should not experience psychological discomfort and be ashamed of his smile. Missing teeth, especially front teeth, is always unpleasant. Installing a temporary denture allows you to safely avoid stress and social maladjustment.
Temporary dentures are much cheaper than permanent ones, and there is no point in saving on them.
The process of addiction
Getting used to wearing temporary dentures depends on the individual’s capabilities.
For some people, this takes a few hours. However, there are also situations when the patient absolutely cannot come to terms with the presence of a foreign element in his mouth.
There should be no pain after temporary prosthetics.
Sometimes patients are concerned about changes in the amount of saliva secreted (increase or decrease). Typically, such a violation indicates poor-quality prosthetics.
To speed up the adaptation to the use of a prosthesis, doctors usually recommend using a special (intraoral) massage.
It is done like this: the index finger clamps the artificial tooth, and the thumb performs massaging movements of the gums (up and down movements, pressing, spiral movement).
Types of temporary dentures
Temporary prostheses are divided into the following types according to their area of application:
- Immediate dentures
This is one of the most affordable types of structures, with which you can restore 1-3 lost teeth in a row. They are only used when defects are enabled.
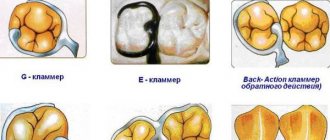
Immediate dentures are also called butterflies. The resemblance to a butterfly is given to the prosthesis by rounded clasp hooks resembling wings. With the help of these hooks, the immediate denture is securely fixed and held on healthy teeth.
The “butterfly” is a removable design that the patient can put on and take off independently. This guarantees an appropriate level of hygiene while wearing the prosthesis.
- Nylon dentures
This is a more versatile option. Nylon dentures are used for inclusionary and terminal defects, to restore an area of the jaw or in the complete absence of teeth.
Nylon dentures are also removable structures. They are fixed using suction cups or special gels and creams, which are recommended by the attending physician.
- Temporary crowns
If the tooth is not completely destroyed or looks unsightly, a crown is installed on it after grinding. And while the permanent prosthesis is being made, a temporary crown is used.
This is a permanent temporary prosthesis that solves the following problems:
- eliminates the aesthetic defect associated with the unsightly appearance of the tooth;
- protects ground teeth from adverse effects and further destruction.
The temporary crown is installed on special temporary cement so that it can be easily removed without damaging the stump.
How long does it take to make a temporary crown on an implant?
Direct method.
The doctor takes an impression using silicone mass, pours a plastic solution into it and puts it all on the implant. Once the resin has cured, the silicone impression is removed and the temporary crown remains on the implant. It is given the required shape, polished and ground, and then secured with special cement.
- Quickly produced.
- Similar to natural teeth.
- Porosity, due to which there is a risk of infection.
- Discoloration due to coloring products.
- Short service life.
- More fragile.
Indirect method.
Based on the casts, a plaster model of both jaws is created in the laboratory, which is used to make a wax crown. A temporary plastic crown is created using the wax model. Sometimes, in the manufacture of plastic crowns, a metal base is used to extend the service life of the products.
- More durable compared to crowns made using the direct method.
- The individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account.
- No.
Making temporary crowns for implants using the direct method in an orthopedist’s office will take no more than an hour. A dental laboratory will make a temporary crown made of plastic in a couple of days.
Preparation and installation of temporary dentures
Installation of temporary prostheses helps solve aesthetic and functional problems while a permanent prosthesis or implantation is being manufactured.
But in order for the prosthesis to meet your expectations, you need to properly prepare for its installation. To do this, you will need to sanitize the oral cavity, eliminate inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane and solve all problems with diseased teeth.
If temporary dentures are recommended by your prosthodontist, do not underestimate their importance to your health and ignore the installation.
Making temporary crowns for implants
Temporary crowns for dental implants are in most cases made of plastic. Please note that metal-ceramics, all-ceramics and zirconium are used to make permanent crowns for implants. If a doctor offers to make a temporary crown, for example, from metal ceramics, think about his honesty and competence. It may happen that the same structure will be installed twice: as a temporary and permanent one. Of course, for a double fee.
Our specialists
Okhotin Dmitry Alekseevich
General practice
Vasiliev Vasily Vyacheslavovich
Surgeon
Minaeva Ekaterina Anatolevna
Pediatric dentist
When are alternative methods required?
There are absolute and relative contraindications for implantation. Absolute ones are those that make implantation impossible in principle. These include:
- various pathologies of bone tissue,
- diseases of the immune system (HIV, AIDS, etc.),
- autoimmune diseases,
- oncology,
- severe infectious diseases (tuberculosis),
- nervous and mental diseases,
- blood diseases (especially bleeding disorders),
- children's age (up to 18 years).
Relative contraindications include problems that are temporary or can be corrected and, after restoration of health, allow implantation. These are states such as:
- pregnancy and lactation,
- rehabilitation period after heart attack and stroke,
- acute viral diseases,
- dental diseases (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, stomatitis, etc.),
- exacerbation of chronic diseases,
- dysfunction of the mandibular temporal joint,
- severe atrophy of the jaw bone,
- malocclusion,
- alcoholism and drug addiction,
- poor oral hygiene.
If you are unlucky and you are one of those who are contraindicated for dental implants (at least in the next few years), then you have to look for alternative methods.