Causes
The organs of the skull are interconnected by a network of blood and lymphatic vessels and cranial nerves. These are the channels through which the infection is transmitted from the ears to the eyes, passes to the throat and back. The symptoms are complex. It is difficult to determine the source of inflammation. But there are several main causes of pain in the ears and eyes.
Neuralgia
With inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, pain spreads to the forehead, temple on one side of the face, and ear. The eye muscle on the affected side, the brow ridge, hurts.
The temperature remains normal. The pain comes in attacks, especially severe at night. The site of inflammation is sensitive to touch.
Causes of neuralgia:
- pathologies of the development of skull bones;
- compression due to tumor;
- traumatic brain injury.
The disease is difficult to diagnose. Treatment consists of pain relief. The sensitivity of the trigeminal nerve increases with the changing seasons. Psychosomatic neuralgia manifests itself as an exacerbation of pain during stress.
Otitis
Inflammation of the middle ear occurs due to the spread of coccus bacteria, which causes a runny nose. Otitis externa and otitis media are distinguished. The auricle becomes covered with boils due to the spread of infection from the ear canal.
A fungal infection also spreads in the middle ear. The fungus appears due to the accumulation of moisture.
The eye is affected by the affected ear. The infection occurs when one bottle of drops is used simultaneously to treat the eyes and ears. The result is lacrimation and redness of the conjunctiva.
Labyrinthitis
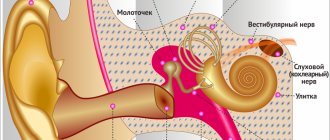
The inner ear consists of a plexus of passages and resembles a labyrinth. Labyrinthitis is inflammation in the inner part of the hearing aid.
Causes of the disease:
- spread of infection from the middle ear;
- tuberculosis;
- fungus;
- mechanical damage.
Symptoms of labyrinthitis appear 2 weeks after recovery from a respiratory infection. The disease causes dizziness and nystagmus - involuntary movement and tremors of the eyeballs.
Migraine
Hemicrania occurs on one side of the head. Throbbing pain is accompanied by photosensitivity. With migraine with aura, the field of vision is lost. Aching ear pain is accompanied by noise and ringing. In severe conditions, a person experiences auditory hallucinations.
Osteochondrosis
Salt deposits in the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine pinch blood vessels. As a result, brain tissue and cranial organs receive little oxygen. There is sand and a burning sensation in the eyes. There is stuffiness and ringing in the ears.
Intracranial pressure
Increased tone of the vessels of the cranium is a consequence of osteochondrosis. Other causes of pressure:
- thrombosis;
- traumatic brain injury;
- tumor;
- hypertension;
- accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
A drawing, throbbing pain is concentrated on one side of the head, covering the eye and ear.
Flu
An acute respiratory infection affects the mucous membranes of the nose and throat. Abundant mucous masses accumulate in the nasal sinuses. Rhinitis develops into sinusitis, inflammation of the inner, middle ear. Obstruction of the nasal passages deprives the tissues of oxygen.
The eyes feel dry, small capillaries burst due to coughing attacks. This creates a complex of symptoms characteristic of various colds. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Tumor
New growths in the brain create compression on surrounding structures. Pressing pain appears as the tumor grows penetratingly. Compression of blood vessels and nerves causes visual and hearing impairment. Symptoms are characteristic of various diseases, so oncological pathology is difficult to establish.
Odontogenic maxillary sinusitis - symptoms and treatment
Often, treatment of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis is carried out using a combination of conservative and surgical methods. The method of treatment and its volume depends on the causative factor and the course of the disease.
For odontogenic sinusitis caused by acute or aggravated periodontitis, treatment often consists of eliminating the causative factor and prescribing drug therapy. To eliminate the cause of inflammation, endodontic treatment of the root canals of a diseased tooth is performed, followed by filling.
In case of extensive destruction of the coronal part of the tooth, its strong mobility, as well as the patient’s refusal to preserve the causative tooth, its extraction (removal) is carried out. If by the time of treatment the patient has developed a purulent form of sinusitis, a puncture of the maxillary sinus is performed with evacuation of purulent contents and daily washing of the sinus with antiseptic solutions. Drug therapy is prescribed. In the catarrhal form of acute maxillary sinusitis, sinus puncture is not required; drug therapy and lavage through the natural anastomosis are prescribed.
Treatment of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis is usually an interdisciplinary problem: the disease is jointly treated by dental therapists, dental surgeons, maxillofacial surgeons and otolaryngologists. The number of specialists depends on the severity of the disease.
For odontogenic cysts of the maxillary sinus, the presence of filling material and other foreign bodies in the lumen of the maxillary sinus without oroantral communication (pathological communication between the sinus cavity and the oral cavity), surgical treatment is indicated. There are several types of operations on the maxillary sinus.
Radical maxillary sinusotomy according to Caldwell-Luc. Under general anesthesia, the mucous membrane and periosteum in the vestibule of the oral cavity are dissected from the canine to the second molar. A raspatory is used to skeletonize (expose) the bone tissue, after which the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus is trepanned (created access). The burr hole is expanded to 1.5*1.0 cm, the mucous membrane of the anterior wall of the sinus is excised and all pathological tissues and fluids are removed from the sinus: pus, polyps, foreign bodies, cyst membrane, blood clots, etc. This type of operation requires extremely careful execution, because it is necessary to remove all pathological tissue in the least traumatic way, without affecting the healthy mucous membrane of the sinus. Also, during the operation, an additional communication is created between the sinus cavity and the nasal cavity, into which tubes are subsequently installed for subsequent rinsing with antiseptic solutions. Afterwards, the postoperative wound is sutured and drug therapy is prescribed. The material obtained during the operation is sent for pathohistological and bacteriological examination. According to the literature, this surgical method has complications in the postoperative period in 80% of cases [18]:
- replacement of ciliated epithelium with scar tissue;
- fusion of the natural anastomosis with the nasal cavity;
- impaired sensitivity of teeth and adjacent soft tissues;
- trauma to the nasolacrimal duct;
- lacrimation;
- osteomyelitis of the upper jaw and zygomatic bone.
With a gentle micromaxillary sinus, an incision of about 8 mm is made in the area of the canine fossa, the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus is trepanned, the hole is widened for the introduction of an endoscope and endoscopic surgical instrument. The maxillary sinus is sanitized (cleansed), foreign bodies and pathological tissues are removed under endoscopic control. This method makes it possible to achieve adequate sanitation of the sinus cavity with minimal trauma.
A more modern surgical intervention is trocar sinusotomy, in which a puncture of the mucous membrane in the area of the canine fossa is performed, followed by trepanation of the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus and insertion of a trocar (an instrument designed to penetrate into the body cavity through the integument) into the resulting hole, through which an endoscope and endoscopic instruments are inserted. instruments for surgical sanitation of the sinus. With micromaxillary sinusotomy and trocar sinusotomy, an additional anastomosis is not applied.
Methods for sanitation of the sinus through the natural anastomosis without punctures and incisions are possible; such treatment methods are carried out by otolaryngologists.
Special attention should be paid to the treatment of perforated forms of maxillary sinusitis, as one of the most common forms. At the moment, there are many ways to close perforation of the floor of the maxillary sinus, many of which only slightly differ from each other in the methodology. All techniques pursue the following goals:
- reliable closure of the perforation hole;
- relapse prevention;
- prevention of the formation of persistent oroantral anastomosis.
The most commonly used are various variations of defect replacement with a cheek flap. The point is the same:
- sampling of the mucous membrane of the alveolar process of the upper jaw;
- formation of a mucoperiosteal flap, its mobilization (creation of mobility) and movement to the palatal surface, followed by suturing.
The obvious disadvantage of this method is that it provides only soft tissue regeneration in the area of the perforation hole [19]. Also, the disadvantages of this method include the loss of attached keratinized gum (an immovable cuff, a barrier that protects the tooth and the bone around it from the traumatic effects of food bolus, penetration of microbes and other factors). In addition, the operation can lead to a decrease in the depth of the vestibule of the oral cavity (the space of soft tissue between the lip or cheeks and the elements of the dentofacial row), which threatens the development of gingivitis, periodontitis, the formation of malocclusion, loosening of teeth and other pathologies.
To preserve the attached keratinized gum and the depth of the vestibule of the oral cavity, a palatal flap on a pedicle began to be used. The disadvantages of this method include extensive trauma and a large wound surface of the hard palate. In this regard, splitting of the palatal mucoperiosteal flap is currently widely used. However, these methods also do not allow restoration of lost bone tissue volume. To restore the bone tissue of the alveolar process in the area of the perforation hole, various synthetic and natural bone replacement materials are used.
Diagnostics
If pain in the ear and eyes occurs, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- if inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is suspected - electroneuromyography;
- to confirm otitis - tympanometry, audiometry, MRI;
- influenza is diagnosed based on the results of a virological examination of a nasal smear;
- increased cranial pressure is determined by MRI and lumbar puncture results.
The degree of damage to the optic nerve is determined using ophthalmoscopy.
Causes of headaches in men
Men are most often bothered by cluster pain. It is localized in the temple area and the eyeball. Pain of varying intensity in men occurs during a respiratory disease, an infectious lesion of the body, after an injury, or during the development of a brain tumor. Headaches localized in the back of the head occur with arterial hypertension, stroke, and traumatic brain injury. Often men experience severe headaches accompanied by nosebleeds. The reasons for the violation may be:
- Diseases of the circulatory system;
- Failure of endocrine organs;
- Cardiovascular diseases;
- Meningitis.
- Stroke;
- Tumors of the brain or nasal cavity;
- Hypertension;
- Overwork.
Expert opinion
Author:
Tatyana Aleksandrovna Kosova
Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, neurologist, reflexologist
90% of the population has experienced headache symptoms at least once in their life. Such data is provided by the World Health Organization. In 20% of cases, the headache is permanent. The ratio in the morbidity structure among men and women is 1:3. Neurologists identify various causes of headaches. The most common etiological factors are migraine and tension headache. Migraine is diagnosed in 20–30% of cases, and tension headaches account for 50–70%.
A headache can be a symptom of a serious illness. Therefore, if a pathological sign appears frequently, as well as in the presence of other symptoms, you should consult a doctor. At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists pay close attention to the treatment of various types of headaches. Diagnosis of possible causes is carried out using x-rays, MRI, CT, EEG, angiography and laboratory tests. If necessary, additional studies are prescribed. Individually selected therapy allows you to stop an acute attack and prevent the re-development of the pathological symptom. The drugs used are verified for quality and safety. Treatment regimens comply with international recommendations for headache therapy.
Treatment
In accordance with the diagnosis, therapy is prescribed:
- for neuralgia, relieve pain with analgesics, lidocaine-based ointment, and drugs for vasodilation;
- antibacterial drops and ointments are used to treat otitis externa;
- drops against inflammation with an analgesic effect - for internal otitis;
- Ear infections are treated with penicillin and amoxicillin antibiotics - orally, by insertion into the ear through a catheter.
For more serious diagnoses, pain is relieved and the primary cause of symptoms is treated.
Treatment methods
At the Clinical Brain Institute, treatment is selected individually. The scheme will include two main stages - getting rid of the main cause of the disease and its symptoms. Depending on the stage of the disease and its clinical manifestations, treatment is carried out at home or in a hospital. Several stages can be assigned, which are combined with each other.
- Drug treatment is the first stage for any disease. For headaches that radiate to the right eye, painkillers and antispasmodics, vitamins, and drugs to improve cerebral circulation are effective. In case of high blood pressure, infectious diseases, metabolic pathologies, you should take specific medications to improve the condition, which are prescribed only by a doctor.
- Physiotherapy is an equally important stage of treatment. It is effective for chronic pain and old inflammatory processes, consequences of injuries. Exposure to heat, magnetic radiation, electrical impulses irritates tissues, stimulates blood circulation and innervation.
- Massage is one of the methods of treating headaches associated with muscle spasms, diseases of the cervical spine, and the consequences of injuries. It is important to contact a specialist who will take into account all the physiological characteristics of the patient and help get rid of painful sensations. For acute inflammation, the method is not used.
- Treatment of eye diseases is prescribed by an ophthalmologist. He may prescribe glasses or contact lenses, which are made individually, depending on the results of the examination. Chronic diseases may require the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and specific groups of drugs.
Surgical treatment methods are rarely used. The need for them arises with tumors and hematomas that compress nerve tissue, as well as with other neoplasms. At the Clinical Institute of the Brain you can get detailed advice on headache treatment methods, undergo examinations and receive competent advice from specialists. It is important to contact early, while diagnosis and treatment can improve your well-being, and not wait for irreversible changes.
Prevention
How to prevent the occurrence and spread of infection:
- treat colds promptly;
- do not overcool your head;
- Dry your ears thoroughly after bathing;
- take vitamins to strengthen the immune system;
- use separate bottles of universal drops for treating eyes and ears;
- Carefully clean the ears with cosmetic sticks so as not to damage the eardrum.
Compliance with the rules of prevention and immediate treatment prevents complications. Independent choice of drops, antibiotics, irregular use of drugs only until the first improvement introduces the disease into a chronic state.
The consequence will be the transfer of infection to the lining of the brain - meningitis.
Headache and tinnitus
Headache and tinnitus are signs of otitis media and sinusitis. In this case, patients' body temperature rises. The pain radiates to the eye, teeth, jaw. Headache in the crown area often occurs for the following reasons:
- After severe stress;
- During a migraine attack;
- As a result of overstrain of the neck muscles;
- After abusing alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- Due to traumatic brain injury.
Cervicogenic headache, the symptoms of which indicate problems with the spine, is a secondary phenomenon. Such pain appears with protrusion of the intervertebral discs and the development of spina bifida in the cervical spine, severe tension in the neck muscles, wear of the vertebrae, and compression of the nerve root. A tumor of the cervical spine also causes severe headaches and tinnitus.
Should I see a doctor?
Note! If such a symptom appeared for the first time, it was managed to stop with the help of an anesthetic and it does not appear again - there is no reason to worry.
But if pain attacks recur regularly and intensify, you need to visit a therapist.
He prescribes diagnostics , which usually includes urine and blood tests, MRI and CT, angiography of cerebral vessels, and then refers the patient to an ophthalmologist or neurologist (depending on what assumptions about the diagnosis arise).
When to contact a specialist
The appearance of a throbbing headache is already a “bell” that you need to see a doctor and get checked. And few people know that there are situations that oblige the patient to contact a specialist to alleviate the condition, and sometimes even save a life.
If you notice that:
- The pain lasts for more than one hour, and medications do not help.
- The pulsation becomes stronger, despite the fact that the patient does nothing.
- Pain in the occipital region appears immediately after a person wakes up or awakening occurs due to unbearable sensations that do not allow doing anything.
- A buzzing sensation is often felt in a certain area of the head.
- The pain causes dizziness, nausea, vomiting, partial paralysis, clouding of consciousness, and inability to speak normally.
- Intense pulsating beats that do not stop for several days.
- Changes in blood pressure, which are accompanied by headaches.
- The nature of the throbbing pain constantly changes.
If you notice any of the above changes, you should immediately consult a doctor or an ambulance, as serious problems may be hidden behind this.
Headache with cervical osteochondrosis
With the development of cervical osteochondrosis, the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord are compressed.
Patients are bothered by neck pain that radiates to the head. The vertebral arteries run along the spine in the neck area. They carry oxygen through the blood to the brain. With cervical osteochondrosis, the blood flow in them is gradually disrupted. This occurs due to compression of the vessel by a displaced spinal disc, a strained muscle, or a bony growth on the vertebra. Without adequate therapy, disorders increase, and vertebral artery syndrome gradually develops. It is manifested by headaches, dizziness, frequent loss of consciousness (especially with sudden turns of the head), severe fatigue and decreased performance.