Herpes
is a viral disease. One of the most well-known manifestations of a herpes infection is small, clear, painful blisters on the lips. Previously, in such a case they said “a cold on the lip popped up”, now they more often talk about “herpes on the lip”.
However, the family of herpes viruses is quite large. There are several types of herpes virus that can infect the human body. The most studied types are:
- herpes simplex virus type 1
(HSV-1). It is he who is responsible for pimples on the lip. HSV-1 primarily affects the mucous membranes of the lips, oral cavity and nasopharynx. Herpetic rashes can also appear within the nasolabial triangle (in particular, on the wings of the nose), less often on the cheeks and other parts of the face. Recently, HSV-1 quite often becomes the cause of herpetic lesions of the genital area, where it is introduced through oral sex; - herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) – genital herpes
. Main manifestations: redness, the appearance in the area of redness of bubbles filled with liquid, tending to merge, the appearance of erosions and crusts at the site of the bubbles, itching, headache and muscle pain, increased urination; - chickenpox virus
(varicella) is a type 3 herpes virus. In people who have already had chickenpox, this type of virus causes herpes zoster. Therefore, this type of herpes is also called Varicella-Zoster; - Epstein-Barr virus
(Epstein-Barr viral infection - EBVI) is a type 4 herpes virus. It is the causative agent of mononucleosis, causes malignant diseases of lymphoid tissue, and is considered the cause of chronic fatigue syndrome; - cytomegalovirus
– herpes virus type 5. The virus poses a threat to children during fetal development. May affect internal organs.
Causes of herpes
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) can be transmitted through household contact. Airborne transmission is also possible.
The airborne route is the main route of infection with the varicella zoster virus.
Genital herpes and cytomegalovirus are transmitted sexually.
You can also become infected with herpes through blood or saliva. The virus can be transmitted through saliva through kissing. Small children who put things in their mouths every now and then are also very vulnerable. If at least one child in a children's group is infected, a rapid spread of the infection can be expected.
Classification of viruses
According to the existing international classification, primary and recurrent genital herpes . The latter, in turn, is divided into typical and atypical clinical forms and asymptomatic viral shedding.
The term “genital herpes” arose at the beginning of the 20th century. to designate the lesion on the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia. With the development of virological research methods, information about “atypical” forms of the disease began to appear. The diagnosis “atypical form of genital herpes” is made by gynecologists to designate a chronic inflammatory process of the internal genitalia (colpitis, vulvovaginitis, endocervicitis, etc.) in the presence of a laboratory confirmed herpetic nature of the disease, in contrast to the “typical” picture of the disease, in which on the mucous membrane These organs have lesions with vesicular-erosive elements. At the same time, herpetic lesions of the urethra, anal area and rectal ampulla fall out of this group, although these organs are anatomically and functionally closely related to the genital area.
Research conducted at the Herpetic Center has shown that diagnosing the HSV virus is now complicated due to the fact that in 65% of cases the disease is atypical.
Herpes symptoms
Currently, most people are infected with some type of herpes virus. It is believed that antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus can be detected in almost every adult (up to 98% of the adult population of the Earth). Antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 are detected in 90% of the adult population of large cities.
However, as a rule, carriage of a herpes infection does not lead to the development of the disease. The herpes virus is activated when the body's defenses decrease. The weaker the immune system, the more likely the virus is to transition from dormant to active.
That is why the herpes simplex virus type 1 is popularly called “cold on the lip.” The appearance of herpetic rashes is usually preceded by a common runny nose, that is, ARVI. The disease weakens the immune system, which is what the herpes virus takes advantage of.
Symptoms of herpes simplex
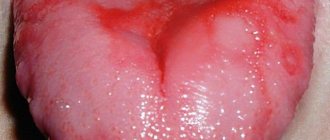
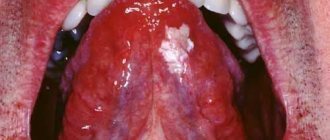
When infected with herpes simplex virus type 1, the incubation period ranges from 1 to 8 days. Typical symptoms: chills, fever up to 39-40°C, headache, general weakness and drowsiness. Then redness appears, in place of which characteristic bubbles form. When the oral mucosa is affected, blisters are usually found on the inside of the lips, tongue, and less often on the palate, palatine arches and tonsils. Bubbles appear at the site where the virus enters the mucous membrane. Subsequently, the bubbles burst, leaving behind painful erosions.
The disappearance of symptoms does not mean complete recovery. The virus remains in the body and after some time (in conditions of decreased immunity) a relapse of the disease is possible. Relapses can occur 1-3 times a year for several years and even decades.
Symptoms of genital herpes
The incubation period of genital herpes lasts from 1 to 10 days, after which itching (burning) may be observed in the areas of future rashes. After which swelling appears, and then groups of bubbles appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. The inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged. The blisters burst and erosions and ulcers form in their place. The process can last from two to five weeks.
Relapse of the disease is possible within two weeks after the initial lesion. Relapses occur in at least half of those who have recovered from the disease.
How does herpes develop?
Herpes has several stages of development:
- at the first stage, unpleasant sensations appear in the lip area, already at this time it is necessary to begin treatment of herpes in order to prevent the transition to the next stage;
- at the second stage, inflammation of the mucous membrane appears, small blisters may appear;
- at the third stage, the blisters enlarge and may burst, leaving small ulcers in their place;
- The fourth stage is characterized by the appearance of scabs at the site of ulcers, which disappear upon healing.
It is important to monitor your body, and if other symptoms appear and your condition worsens, contact the clinic for competent help.
Methods for diagnosing herpes
Diagnosis of herpes is carried out, first of all, on the basis of examination of the patient, since herpetic rashes have a certain specificity. However, your doctor may order laboratory tests. Laboratory tests can detect infection even in the absence of obvious manifestations.
Herpes test
Be prepared that if you suspect a herpes infection, the doctor will write a referral for a blood test, which will determine the presence of antibodies to the herpes virus in the blood. Based on the results of the analysis, it will be possible to judge not only the presence of the pathogen, but also its activity.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
How to treat herpes?
It is impossible to completely destroy a virus that has entered the body. But it is quite possible to suppress its activity so much that it does not bother you. In modern medicine, an integrated approach is used for this. The best results are obtained by combination therapy, which involves the use of antiviral drugs (they are available in the form of drugs for internal use and in the form of external agents), as well as drugs that strengthen the immune system. In some cases, the patient is additionally prescribed local analgesics and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to burn herpes with alcohol? Alas, this method does not affect the virus, but only damages the mucous membranes, so it is better to use special ointments.
What remedies are usually prescribed for herpes on the lips? The table shows a list of the most common medications used to treat the virus.
| Name, dosage form | Description |
| Acyclovir (aka Zovirax). Available in the form of tablets, cream, eye ointments, injection solutions. | An inexpensive antiviral drug that stops the replication of the virus. Addressed to adults and children over 3 years old. Not recommended for use during pregnancy. Antiviral ointment |
| Valacyclovir (aka Valtrex) Available in the form of 500 mg tablets. | One of the best drugs for herpes. It differs from Acyclovir in the method of delivery of the active ingredient. Suppresses the activity of the virus and reduces symptoms. When taking the drug, the risk of infection through contact with other people is reduced. Treatment of herpes in 3 days |
| Famciclovir (aka Famvir) Available in the form of tablets 125, 250 and 500 mg. | Just like Acyclovir and Valtrex, it blocks the replication of the virus. Helps in the treatment of simple virus and the virus that causes chickenpox. Famciclovir is effective against viruses resistant to Acyclovir. Famciclovir |
| Panavir Available in the form of a solution for intravenous injection, as well as in the form of a gel and suppositories (suppositories). | Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drug of plant origin. Increases the body's resistance to infections and has an antipyretic effect. |
| Docosanol (aka Erazaban) Available in the form of a cream for external use. | Has an antiviral effect. Intended for use in adults and children over 12 years of age. Pregnant women are prescribed with caution. |
| Proteflazid Available in the form of drops. | Antiviral agent for systemic use. Intended for the treatment of herpes simplex in children and adults. Used in pediatric practice (including in children under 1 year). |
| Flavoside Available in the form of syrup. | Effective in the treatment of herpes simplex, as well as in the treatment and prevention of influenza. Used in pediatric practice (including in children under 1 year). |
The presented list of drugs is far from complete - the doctor, depending on the characteristics of a particular patient, may recommend other drugs. For example, in some cases antibiotics cannot be avoided (if there is a risk of contracting other infections).
Treatment methods for herpes
Treatment of herpes is aimed at suppressing viral activity, as well as increasing immunity. Oral and topical medications may be prescribed.
The selection of drugs is carried out by a doctor depending on the type of disease (type of infection), as well as on the location of the lesion.
It is impossible to completely eliminate the herpes virus from the body. That is why it is important to always maintain the body’s defenses at a sufficiently high level, and also to prevent re-entry of the virus.
Prevention of herpes
If a person close to you has manifestations of herpes (“a cold has popped up on the lip”), try to ensure compliance with the following hygiene rules:
- use an individual towel and personal hygiene products (soap, toothbrush, etc.);
- be careful with cosmetics: do not use lipstick of a sick person;
- If you have genital herpes, avoid sexual intercourse.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Which doctor's help might be needed for herpes?
With the questions “what causes herpes to constantly appear on the lips” and “I’m tormented by herpes - what to do?” You can contact your therapist first. He will subsequently refer you to an infectious disease specialist or dermatologist (if we are talking about an oral virus). Patients with a genital infection should see a gynecologist (women) or a urologist (men). Since the pathology may be associated with diseases of the internal organs, you may need to consult a gastroenterologist, hepatologist or pulmonologist.
Reminder in case of illness
It must be remembered that when a rash appears, a person becomes acutely contagious. Moreover, not only those around him can suffer, but also the sick person himself. For example, from a lesion on the lips with dirty hands, the herpes virus can be carried into the eyes or genitals.
Therefore, it is important to follow the following rules
- Do not touch lips affected by rashes. If you touch them, wash your hands thoroughly.
- Use your own towel and utensils.
- If your lips are affected, do not squeeze the blisters or pick off the scabs. This may cause additional skin infection.
- Refrain from kissing and oral-genital contact.
- If you wear contact lenses, do not wet them with saliva to moisten them.
- Apply antiviral cream to your lips not with your fingers, but with cosmetic sticks.
What is herpes and what types does it happen?
Herpes is an infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. It is transmitted during any contact. This can be touching, kissing, petting and any type of sex. Herpes is also classified as a sexually transmitted infection. Sometimes it’s enough to use someone else’s chapstick and the virus will be passed on to you.
It looks like a blistering rash on the skin or mucous membranes. Herpes usually appears on the face, lips or genitals. Elsewhere it is rare and occurs mainly in people with weakened immune systems. Herpes in Greek means “creeping”, and it’s not just that: you can become infected through sexual contact, and the virus will appear on the face, this is its peculiarity.
Causes
There are many provoking factors leading to exacerbation of the disease. In addition to the weakening of immune forces, there are a number of other reasons:
- Emotional stress, physical fatigue, stressful situations.
- Long-term insolation.
- Surgical interventions.
- Taking immunosuppressive drugs.
- Hormonal imbalances.
In addition, there may be a combination of several negative factors leading to the activation of infection in the body. During illness, it is important to isolate yourself from others.
I often get “colds” on my lips. Is there any way to get rid of herpes once and for all?
Once you get infected with the virus, you will become inseparable. Once the virus enters the body, it continues to live in the body for the rest of its life, perhaps asymptomatically or with relapses. It penetrates the nervous system and settles in the nerve ganglia.
Even our ancestors suffered from herpes
The herpes virus could not be identified until 1940. But it turns out that people had it 6-7 million years ago. It was probably transmitted to humanity by monkeys. Scientists even found the hominid species that was the first to become infected. It is believed that he ate the meat of a monkey infected with the virus and became the first carrier.
Herpes viral infection: placing emphasis.
– The next, very relevant topic is “Herpesvirus infection”. And I am pleased to give the floor to Andrey Viktorovich Ignatovsky.
Andrey Viktorovich Ignatovsky , Candidate of Medical Sciences:
– Good afternoon, dear colleagues. We continue our conversation about infectious agents. Today, herpesvirus infection remains one of the most pressing problems for doctors of almost all specialties. We very often discuss the negative impact of herpes virus infection in relation to the impact on the reproductive tract - this problem is extremely interesting to obstetricians-gynecologists and urologists. I think that this presentation will show the relevance of this problem for general practitioners and general practitioners.
We usually talk about herpes simplex viruses - the first and second types, and the third type virus - this is the varicella zoster viral infection. And, of course, I would like to start today with the varicella zoster viral infection, because this infection, probably, in the aspect of general medical practice, has an incredible number of interesting and important aspects.
So, type 3 herpes virus. You see that the first encounter with the third type of herpes virus leads to the development of chickenpox. This is a primary infection caused by a type 3 virus. A certain important aspect is that in this case, with a primary infection, the encounter occurred for the first time, the patient does not have antibodies, and the patient is not protected against this infectious agent. Hence, a rather frivolous attitude towards chickenpox can result in fatal cases, which we periodically see in Russia and which are recorded. And, of course, looking at almost all cases, we see that the patient received standard therapy for a mild form, and it was not taken into account that the patient was not protected, and there are etiotropic drugs that were not used in almost all fatal cases prescribed by a doctor. Further, the virus in patients who have had chickenpox remains in the spinal ganglia, and relapses of herpesvirus infection occur in the form of herpes zoster.
For whom is a patient with herpes zoster dangerous? It is dangerous for those patients who have not had chickenpox or have not been vaccinated against it. Today there is vaccination, and we know that we can prevent the occurrence of chickenpox. As for clinical understanding, I would like it to be the same for type 3 virus. We call the primary infection “chickenpox”, the first encounter with the virus – there are no antibodies. But the reactivation of the herpes virus from the dorsal ganglion is already called herpes zoster or herpes zoster, or herpes zoster. This is a slide from one of the conferences where fatal cases were analyzed, and the lecturers presented, among other things, our frivolous attitude towards herpes virus infection caused by the third type virus. Indeed, it seems that it is easier to get over it if there is an outbreak of chickenpox in a children's group - it may be better to take children there who have not been sick, many parents believe. A child exposed to the virus will get sick. I would caution against such reckless tactics. It is better to vaccinate the child in this case, and carefully monitor those children who have chickenpox in order to promptly determine the indications for prescribing systemic etiotropic antiviral drugs. Professor Tatochenko said, in my opinion, a very beautiful and correct phrase: “Infection is always a risk. The doctor’s task is to reduce it to a minimum.” As for chickenpox, as for viral infection, today we can do this in a number of cases and completely avoid severe complications and sometimes deaths.
It must be remembered that etiotropic antiviral drugs that are effective against the first and second type of virus, that is, against the herpes simplex virus, are almost as effective against varicella zoster viral infection. There are differences, I think we will have time to talk about them today, between the effects of acyclovir and penciclovir on the herpes virus of the first, second and third types. But, nevertheless, these drugs are etiotropic in relation to the herpes virus of the first, second and third types.
What danger should expect pregnant women who have chickenpox? The situation is probably not so common, but this leads to a lot of problems. We always discuss this rather large block of issues with obstetricians and gynecologists at our round tables. But it is important for a general practitioner to remember that the risk of chickenpox pneumonia is about 10%.
Returning to the further course of herpes virus infection, it is necessary, of course, to touch upon the issue of herpes zoster. The traditional idea, which many remember from their student days, is that herpes zoster appears in the area of the chest dermatomes, thoracic segments. Of course, yes, but we must remember that almost the entire human body is divided into dermatomes, and we can see the reactivation of a herpes virus infection in the form of herpes zoster in the area of any dermatome.
Here are the traditional clinical manifestations - this is a chest dermatome. Classic manifestations are erythema, edema and grouped microvesicles, blistering rash. But we must remember that if we see lesions in the area of several dermatomes, then, of course, we are talking about the fact that the herpes virus infection is acquiring, or in this case the patient has, a severe course. Dermatomes can be in different localizations, in particular, genital localization can be, these can be manifestations in the sacral area, and here it is necessary to differentiate these manifestations with the zosterophoric course of herpesvirus infection, which can be caused by the herpes simplex virus, but of the second type.
If we are talking about severe, atypical forms, then, of course, we must remember that the third type of virus also has such forms. And here we see the patient’s blisters filled with hemorrhagic contents. This is a hemorrhagic form. There may be typical rashes, but in the breast area. If the patient is not examined completely and does not see this linearity of the rash, then one might think that she has some manifestations on the mammary gland. However, a complete examination of the patient gives an idea and allows for a correct and timely diagnosis.
I would point out that previously the occurrence of herpes zoster in elderly patients was considered traditional. However (and we even wrote an article at our department, observing patients at the Ott Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology), the patient population has just become younger. We also saw young women, just in the period of pregnancy, in the period of feeding.
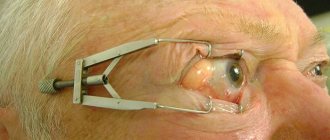
We must not forget about special localizations, which are extremely dangerous, primarily due to life-threatening conditions. This is ophthalmoherpes. Ophthalmoherpes is dangerous because the path of development of this inflammatory process affects both the blood vessels and the membranes of the brain. And here the risk of complications is enormously higher. Starting from acute retinal necrosis and ending with stroke. That is why, having met such a patient, a doctor of almost any specialty should not redirect him, playing the role of some kind of “switchman,” but take over the initial stage of patient management, and then attract specialists of the required profile - ophthalmologists, neurologists. But an etiotropic antiviral drug should be prescribed as soon as the patient comes to your appointment. You can consider this an emergency.
The initial manifestations are very interesting. It is always erythema, swelling. There may be no microvesicles, but the fundamentally important point is that (we can go back to the previous slide and look at this slide) clearly half of the face is affected, as if a lesion was drawn along a ruler. But the apex of the nose is always involved if it is affected in the patient. And here we clearly see a unilateral lesion, which makes it easy to make a diagnosis. Neither the allergic process will proceed like this, clearly delineated, nor any other.
It must be remembered that in 10% of patients with normal immunity with herpes zoster, hematogenous spread of the infection with the development of a disseminated form is possible, which should also alert the doctor and make him especially attentive to such patients. We must remember that clinical manifestations are not only rashes, but also pain. It usually accompanies this process and is present in different forms. We will also talk to you about pain options today.
Postherpetic neuralgia is considered one of the most dangerous complications among all the main groups; we see that there are many of them: skin, visceral, neurological, and ocular complications. But postherpetic neuralgia is most difficult to treat with medication. Sometimes, even with correct and timely prescribed therapy, it is impossible to avoid such a complication.
What is postherpetic neuralgia, and who is at higher risk? These are elderly and older patients. The area of the rash matters: the maximum risk is the area of the trigeminal nerve and brachial plexus. Other areas have a moderate or lesser risk, but this does not exclude the occurrence of such pain syndrome. Of course, pain in the prodrome, preceding the rash, and a pronounced rash.
We must remember that the older the patient is, the higher the risk of developing postherpetic neuralgia. What do we mean by postherpetic neuralgia? Perhaps, this Dworkin classification is the most acceptable, and it most correctly shows us that we can consider postherpetic neuralgia to be pain that lasts four months or longer. Everything up to four months is divided into either acute herpetic neuralgia or subacute herpetic neuralgia. A fundamentally important point in this classification is the therapeutic approaches. They are different. At the initial stage of the disease, along with inflammatory pain caused by the influence of the virus, neuropathic pain also arises. The fundamental difference is that we can effectively control inflammatory pain with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. But unfortunately, we cannot influence the pain, which is called neuropathic, with anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics, and over time, just by the fourth month, the significance of inflammatory pain practically decreases, but the significance and role of neuropathic pain increases enormously. That is why for patients who have been ill for a long time, whose pain persists after suffering from herpes for four months or more, the prescription of analgesics is useless; completely different classes of drugs must be prescribed, involving a neurologist for consultation. Without a neurologist, competent treatment of such a patient is impossible.
You see that the types of pain can be completely different - this is both acute and tearing pain. Sometimes it can be allodynia - pain with a light touch. But, nevertheless, all this causes extreme suffering to our patients. How to avoid this pain? How to avoid postherpetic neuralgia? Early appointment – up to 72 hours. Doctors often misunderstand 72 hours. The patient came back after 74 hours, but he has rashes, there is activity of the process - we must still prescribe such therapy. We are talking about ideal conditions - the sooner such therapy begins, the better results we will get. Of course, the prescription of highly effective antiviral drugs, I am primarily talking about famciclovir, adequate pain relief in the acute stage. Quite good preliminary results have been obtained on the effectiveness of vaccination. What treatment principles exist today for herpes virus infection? Of course, this is etiotropic therapy. It must be remembered that nucleoside analogues are the drugs of choice today for the treatment of all forms of herpesvirus infection. Immunomodulatory therapy is pathogenetic therapy. We can do without her. It is not included in any protocol - international or domestic. Symptomatic therapy, of course, has a certain value.
And, of course, you need to remember that etiotropic drugs are acyclovir, its valino- and fervalocyclovir and famciclovir. (00:12:30) Symptomatic therapy will most likely be required for a patient with herpes zoster. These are analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and, at the stage of pain control, physiotherapy, but not ultraviolet radiation. It must be remembered that ultraviolet radiation is an aggressive, damaging factor. Tanning is a protective function of the skin.
When choosing a drug, you must remember that the most sensitive to acyclovir - the herpes simplex virus of the first and second types, varicella zoster - is more than 20 times, and cytomegalovirus is 470 times less sensitive to acyclovir than the herpes simplex virus of the first type. If we talk about drugs, then, of course, we need to remember that today both acyclovir drugs (acyclovir and valacyclovir, and famciclovir) differ in bioavailability. The bioavailability of drugs is different, due to their pharmacokinetic characteristics and, above all, accumulation in certain structures. And it is important for us, when speaking and discussing herpes virus infection caused by herpes simplex virus and herpes virus type 3, accumulation in Schwann cells, because the spread of the virus from the spinal ganglion occurs perineurally, periaxonally and, precisely, along Schwann cells. The concentration of penciclovir - the active substance famciclovir - is many times higher than the concentration of acyclovir.
And one more important point - we say that abnormal nucleosides become active under the influence of the enzymes of the herpes virus itself and accumulate only selectively in infected cells. We must remember that all acyclovir drugs (this applies to acyclovir, valacyclovir) are intracellular for less than an hour or about an hour. If we are talking about famciclovir, then you see, based on the table, which, in fact, is based on data from numerous studies, that the varicella zoster virus allows the drug to remain in the infected cell from 7 to 11 hours.
The route of elimination is the kidneys. We must now remember this very important aspect, because at the end of my presentation I will show questions, and we will touch upon the issues of medicinal safety of the use of these drugs. If we talk about comparative analysis and dosages of drugs, then, undoubtedly, such studies have also been conducted. And you see in this diagram the comparative dosages of famciclovir at a dose of 250 mg three times a day, 500 mg three times a day. And a comparison with acyclovir - the traditionally known dose of 800 mg five times a day.
We see, of course, that acyclovir is lagging behind. Its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties differ from famciclovir. And, of course, the powerful effect with a more modern form of famciclovir provides better therapeutic indications, which is why today it is considered the number one drug for the treatment of herpes virus infection, caused, in particular, by the herpes virus type 3.
If you and I are discussing indications, then, of course, in this case herpes zoster is important to us. We have already discussed accumulation in Schwann cells. And the dosages will vary: in patients with normal immunity, the dosage is 250 mg three times a day, or 500 mg twice a day. The only difference, when the dosage will need to be doubled or increased, is ophthalmoherpes. Essentially, we have to say that in immunocompromised patients the dosages will always be doubled. And patients with ophthalmoherpes, even with normal immunity, still require high dosages. This is a dosage of 500 mg three times a day. If we are talking about herpes zoster in patients with reduced immunity, then famciclovir is also prescribed in double dosage, and the duration of therapy is 10 days.
Pay attention to this slide - this is a patient with ophthalmograpes. Here the dosage should also be 500 mg three times a day. Undoubtedly, it is necessary to involve a neurologist and an ophthalmologist for consultation.
Speaking about immunocompromised patients, with insufficient immunity, we must, of course, not forget about patients with the immunodeficiency virus. The thing to remember here is that famciclovir is the only drug approved by the FDA to treat both herpes zoster and genital herpes in HIV-positive patients.
If we touch on the issue of treating postherpetic neuralgia, it should be noted that drugs such as gabapentin and pregabalin will be effective in influencing neuropathic pain. And, we discussed this aspect, it is imperative to involve a neurologist. It is he who should prescribe such drugs. They may be given concomitantly with famciclovir or another abnormal nucleoside, or may be given soon after. That is, in fact, there is no need to wait for the development of postherpetic neuralgia and such a diagnosis. Recent studies have shown that the earlier we prescribe such drugs, the better the effectiveness in treating this condition. You see that there are drugs for second-line treatment, and, of course, there are certain approaches. First of all, we focus on the visual analog pain scale. And, understanding that we received or did not receive the effect of the therapy, we can adjust this therapy. This means that you need to understand that therapy is not straightforward. It is difficult for the patient, its tolerance is not always easy and simple. This requires special attention, and, I repeat once again, it is better to prevent it - by early adequate prescription of an etiotropic antiviral drug.
In the second block I would like to discuss herpes virus infection caused by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Traditionally, we have divided: conventionally, we believed that the first type of virus affects the upper part of the body, localizing in the area of the face and lips. And the second herpes virus was considered genital. However, laboratory diagnostics are improving, and today we know that these viruses no longer have the clear anatomical connection that we previously distinguished.
We must, of course, remember that we distinguish between primary herpes and recurrent forms of herpes virus infection. Clinical features: acute onset of primary infection, symptoms of intoxication, enlargement of regional lymph nodes - these are, in fact, the main clinical signs. And the laboratory results will be an increase in the level of antibodies. More often we encounter primary infection in children. And this form is herpetic gingivostomatitis, herpetic manifestations in the lip area - labial herpes. If we are talking about genital localization, about the period when a person did not encounter this virus in childhood, but, having already begun sexual activity, received the virus - in this case, of course, primary genital herpes develops. Other manifestations are also possible.
If we talk to you about the symptoms of relapse, they are well known. Prodromal phenomena in the form of pain, itching, burning, discomfort in the rash area, and later clinical manifestations. They may not always be in the form of erythema and edema; both typical and atypical forms may appear. In the case of an atypical course, we will not see bubbles, as we discussed, either these bubbles will be filled with hemorrhagic contents, or they may even be blisters.
Of course, it is necessary to distinguish between degrees of severity - mild, moderate and severe. It is this aspect that will determine the doctor’s approach, planned activities and, of course, the aspect of patient consultation. If we talk about clinical manifestations, they are well known. However, it is necessary to clarify whether this is a primary herpesvirus infection or a relapse. Clinical manifestations may be somewhat similar; only laboratory tests will allow us to distinguish between primary infection and relapse. In the event of a complication, as you see on this slide, a discussion will be required regarding the use of topical or perhaps even systemic antibacterial drugs.
In the case of herpetic glossitis - a lesion of the oral mucosa - topical drugs, of course, cannot be used, and only systemic etiotropic antiviral drugs will necessarily be discussed here. Well, in this case, one should, of course, not forget that there is a risk of developing ophthalmoherpes, developing herpetic keratitis, and here an extremely important issue will, again, be a discussion not only of the use of eye drops that have an antiviral effect, but also necessarily in the prescription of systemic etiotropic antiviral drugs.
Speaking about treatment strategies for herpesvirus infection, you need to remember that there is treatment, it differs in dosage, primary infection of relapse and two options for suppressive therapy - episodic suppressive therapy in anticipation of medical manipulations and long-term suppressive therapy to prevent relapses and prevent transmission to a partner. What is important? It is important that the use of external forms today should be limited. European guidelines for the management of patients with genital herpes in 2010, citing previously published work, showed that the use of topical drugs contributes to the development of resistance to this drug. Therefore, it is necessary to limit the use of topical forms. If we are talking about the use of the drug for primary infection, here I will say what differs today is the dosage. For famciclovir they remained 250 mg three times a day, but for valacyclovir the CDC since 2010, and the World Health Organization increased the dosage since 2003. This dosage for the treatment of primary infection is 1000 mg twice daily. If we are talking about the use of valacyclovir and acyclovir, we must remember that the active substance remains the same acyclovir. By combining with the amino acid valine, a complex is obtained, which, yes, is well absorbed, but the active ingredient remains acyclovir. The dosages used to treat recurrent infections are presented on the slide. Famciclovir has the smallest dosage - it is 125 mg twice a day, for valacyclovir this dosage is 500 mg twice a day, for acyclovir this dosage can vary, ranging from 200 mg to 400 mg per single dose, and the number of such doses is from three until five.
The new dosage for famciclovir, registered in the instructions, is short courses. In fact, the whole world is fighting for such short courses. The use of the drug in case of frequent relapses contributes to the rapid relief of symptoms, while the level of antibodies increases, which further contributes to an easier course of the herpes virus infection. And this three-day treatment regimen is quite convenient for our patients. It is necessary, of course, to remember the difference in drugs, because the development of acyclovir-resistant strains today will probably slowly take one of the leading leading positions.
How do the drugs work? So, the virus has entered the cell, and then the assembly of viral DNA begins under the influence of two viral enzymes - viral thymidine kinase and viral polymerase. And the drugs that enter the cell - acyclovir and penciclovir - are similar to guanosine, one of the components of viral DNA. Next, the thymidine kinase of the virus makes acyclovir active, and this acyclovir molecule remains, relatively speaking, alone. If we are talking about penciclovir, then the situation is as follows: the thymidine kinase of the virus also activates penciclovir, but the thymidine kinase of the virus has a hundred times greater aggregation of penciclovir, and the number of penciclovir molecules is many times higher intracellularly. And then the viral polymerase mistakenly integrates penciclovir into the terminal sections of DNA, since they are abnormal, there is no complementary tail and, accordingly, the assembly of viral DNA stops. Thus, the drugs only work in those cells where the virus is present. Where there is no virus, where the virus does not replicate, the drug will not work. This is extremely important. Well, the concentration of penciclovir on the left graphs is high and stable and does not decrease over time. But acyclovir triphosphate, unfortunately, leaves the plasma very quickly, and its therapeutic concentrations quickly fall.
Speaking about labial herpes, concluding our conversation, it must be said that there is a short single-dose regimen - three tablets of 500 mg, a convenient pulse regimen, and we must, of course, not miss this opportunity, because labial herpes is often a start for some patients development of complications from the nervous system. This must be remembered.
And in conclusion, I would like to cite the work that was published in 2008. It struck me with its abstract - we don’t often pay attention to side effects and drug safety issues, but the abstract is quite interesting. The instructions for acyclovir preparations indicate that it is necessary to ensure adequate hydration of the patient even in tablet forms. But, please note, this article discusses issues when patients were given intravenous acyclovir, high dosages were required due to the severity of this process, and complications in the form of acute renal failure were obtained. What causes such complications? First of all, the molecular structure of acyclovir. It has a crystalline structure, and these crystals can damage the tubular apparatus of the kidney and, in fact, lead to the development of acute renal failure. These patients were subsequently switched to famciclovir and recovered successfully. Just the same, when using acyclovir preparations, you need to remember that both when administered intravenously and when prescribing tablet forms, it is necessary to provide the patient with good hydration.
Thank you for attention.
Precautionary measures
In order for the disease to pass in a mild form and its complications to appear, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Rule #1. Avoid touching your face with your hands, especially in the area of blisters. Otherwise, you risk spreading the infection to a larger area of skin.
- Rule #2. During illness, be especially careful about your personal hygiene.
- Rule #3. Isolate yourself and try to avoid close contact with people, especially the elderly and children.
Is herpes contagious? Should I now avoid kissing and sex if I have a flare-up?
Herpes is contagious and spreads from person to person. But in general, there is nothing wrong with this - the disease is not dangerous for most healthy people.
If you are afraid of infecting your partner with herpes or becoming infected yourself, always use a condom during vaginal, oral and anal sex. And during cunnilingus, create a barrier between the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals using a special latex napkin - a rubber dam. But remember, such protection still does not provide a 100% guarantee that you will not become infected.
If you do not want to use a condom, and your relationship with your partner is long and monogamous, then a healthy partner can take a course of antiviral drugs to prevent the disease. This is advice from the Herpes Virus Association. In this way, you can reduce the risk of transmitting herpes, but you need to consult a general practitioner about treatment. He will tell you which pills to take, for how long and in what dosage.
During the period of exacerbation of herpes, it is better to avoid sex and close contacts. As soon as you have a burning and tingling sensation on your lips, blisters around your mouth or on your genitals, the virus is in an active reproduction phase. From now on until the rash and crusts disappear, it is better to refrain from close contact.