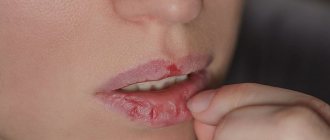
There can be many reasons why lips stick together and the skin around the mouth dries out. When dealing with such a problem, it is very important to determine the source of its occurrence and eliminate it. Only after this the treatment will be successful and quick. You should not engage in independent treatment; it is better to trust professionals, since it is important to accurately diagnose and prescribe competent therapy.
Non-pathological causes
Various factors can provoke white plaque on the lips:
- insufficient oral care;
- an unbalanced diet when it does not provide the body with sufficient vitamins and minerals;
- wearing dentures;
- taking certain medications;
- depression;
- bad habits, in particular smoking.
To get rid of unwanted manifestations in such cases, it is enough to eliminate the provoking factor.
If the problem occurs only in the morning, most likely the white coating is dried saliva that flows out randomly during sleep. When such manifestations are observed occasionally, and the plaque itself does not have an unpleasant odor, there is no need to worry. The film will disappear after hygiene procedures.
Preventive actions
To minimize the risk of unpleasant symptoms and deterioration of skin condition, you must follow simple rules:
- eat a balanced diet;
- observe drinking regime;
- treat underlying diseases in a timely manner;
- protect skin from ultraviolet exposure;
- control your habits and actions - do not lick or bite your lips; make sure that the child does not do this;
- cope with stress;
- use hypoallergenic, high-quality cosmetics for lip care.
Chief author and editor-in-chief: Makarskaya S.E., 29 years of experience.
Last revision: 01/10/2019
Pathological causes
If plaque appears regularly even after oral hygiene, this may indicate a more serious pathology, namely:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- scarlet fever;
- respiratory tract diseases;
- lichen planus;
- stomatitis;
- diabetes mellitus, in which you constantly feel thirsty;
- exacerbation of herpes infection.
An undesirable symptom may also appear in the morning due to dental diseases (caries, periodontal disease).
Candidiasis: manifestations of infection and its danger
Separately, it is worth highlighting such an infectious disease as candidiasis. Fungi of the genus Candida are present in almost every organism. Under favorable conditions (decreased immunity, taking antibiotics, oncology, hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, etc.), they are activated and cause candidiasis of the oral mucosa. The disease most often affects infants and older people.
One of the main signs of the disease is a white, loose coating on the tongue and lips. It may also cover the inner surface of the cheeks, less commonly affecting the palate and gums. The plaque is easily scraped off, the tissue underneath turns red and sometimes bleeds. Other symptoms of candidiasis:
- unpleasant taste;
- dry mouth;
- burning sensation;
- formation of cracks on the lips and redness in the corners of the mouth;
- pain and difficulty swallowing;
- discomfort with normal tongue movements.
The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. The first of them is more common. The second can manifest itself in smokers, as well as in carriers of HIV infection. As each form of the disease progresses, other undesirable symptoms may appear.
If the acute form of candidiasis is not treated, it will become chronic. In this case, the patient feels severe discomfort. In places where plaque is localized, wounds appear that bleed and fester. Thrush quickly spreads to other parts of the mouth, making it difficult to chew food. The infection eventually affects the pharynx and tonsils. Then it descends into the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, liver and causes irreparable harm to them.
Why do lips become sticky?
Lack of vitamins
The cause of this mouth problem is an acute deficiency of vitamin substances in the body. This condition negatively affects the condition of the skin. It can dry out and lose elasticity. Most often, negative effects are observed with a lack of the following vitamins:
- Vitamin A or retinol. An acute lack of this vitamin in the body makes itself felt by certain unpleasant signs, which include: loss of elasticity of the epidermis, increased dryness.
- Vitamin E or tocopherol is responsible for the normal regulation of water balance in the epidermal layer. If this substance is contained in the body in minimal quantities, unpleasant symptoms such as peeling, roughness, dryness and stickiness of the skin occur.
- B vitamins are the main link in the metabolic processes that occur in the cells of the epidermis. If these elements are not enough, the lips become cracked, inflamed, rashes, dryness and stickiness appear on them.
- Vitamin C is very important for healthy looking skin. With a lack of this vitamin, collagen synthesis in the dermal cells is disrupted. This is characterized by such signs as dryness, pallor, loss of elasticity.
If vitamin deficiency is diagnosed, any medications should be prescribed only by a doctor, especially if this concerns children.
Allergy
When in contact with various irritants, stickiness may appear on the lips due to the development of an allergic reaction. At the same time, such a problem can be provoked by either a single contact with an allergen or prolonged exposure to it. The most common irritants include:
- Ultraviolet radiation, intense wind. Often the lips stick together in the spring of those people who do not use protective cosmetics.
- Dental substances that are used by doctors to fill teeth.
- Ingredients that make up lip cosmetics. Especially if the lipstick or balm is expired.
- Using toothpaste with a high fluoride content increases dryness and stickiness of lips.
- Citrus products, salty, spicy foods.
- Smoking. For many heavy smokers, substances present in cigarettes react with the skin, causing unpleasant symptoms.
If an allergy is diagnosed, exclusion of the potential irritant and treatment with antihistamines will be necessary.
Other reasons
Other reasons for this condition include constant lip licking, especially in strong winds or cold. As a result, redness, dryness, and the formation of pale yellow or grayish scales appear on the epidermis. After their removal, a red border is visible. Many experts are convinced that if a person constantly licks his lips, he is susceptible to frequent stress, so in this case, a mandatory component of complex therapy is to reduce the negative impact of stressful situations.
The habit of holding various objects in the mouth is often observed in children than in adults. The child gets acquainted with the world around him, constantly tries to explore the surface, taste toys and other objects. This is fraught with the penetration of bacteria into microdamages on the skin, the development of an inflammatory process and unpleasant symptoms, including increased dryness and stickiness of the skin.
Sometimes sticky lips are a sign of an infectious disease:
- infectious - bacterial, candidiasis or herpes cheilitis;
- infectious dermatitis.
Other reasons for a sticky mouth include:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- general dehydration of the body;
- anemia;
- diseases of the urinary system;
- development or exacerbation of diabetes mellitus;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
If these are symptoms of disease, a thorough diagnosis must be carried out before prescribing treatment.
Localization Features
The cause of plaque can be determined by taking into account its location.
| Localization | Most likely causative factors |
| Corners of the mouth |
|
| Outer lips |
|
| Inner lips |
|
A sticky coating on the surface of the lips in the morning indicates a pathology of the stomach or esophagus.
How is treatment carried out when plaque appears in the oral cavity?
To prescribe effective treatment, the doctor must first determine why plaque appears on the lips. The faster and more accurately he makes a diagnosis, the easier the therapy will be. Treatment will differ in each individual case. A universal technique is to rinse the mouth with soda and potassium permanganate.
Treatment of candidiasis can be local and systemic. Suitable therapy is selected taking into account the stage of development and form of the disease. Local treatment of the affected areas is carried out using antifungal and antiseptic drugs - sprays, rinses, gels, etc.
Systemic treatment of candidiasis is carried out in the chronic form of the disease and its spread to other organs. It involves taking special polyene antibacterial drugs, which are active against most fungi and some protozoa, or antimycotic substances. The following remedies are often prescribed:
- "Nystatin" is a polyene antibiotic characterized by moderate toxicity;
- Fluconazole is a highly effective antimycotic drug;
- "Nizoral" is an antifungal agent that copes with candidiasis in a few days.
An addition to the main therapy can be rinsing the mouth with decoctions of sage, chamomile, and yarrow. To eliminate an undesirable symptom, it is important to adjust your diet, drink enough fluids, and humidify the air in the room. It is also necessary to sanitize the oral cavity and constantly maintain its hygiene at a high level.
On average, treatment takes three weeks. It is carried out until the symptoms disappear completely and then extended for another week.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Patients are advised to avoid eating too hot and too cold food, staying in cold and high humidity conditions, and applying decorative cosmetics. They use medicinal and non-medicinal methods. Treatment tactics are determined by the cause of lip swelling:
- Mechanical damage
. For bruises and hematomas, apply cold; for burns and abrasions, apply ointments with an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect. - Allergy
. Antihistamines are used. In severe cases, general glucocorticosteroids are indicated. - Cheilitis
. Depending on the type of disease, sedatives or anti-inflammatory drugs, protective creams, hormonal ointments, and vitamin preparations are prescribed. - Herpes
. Antiviral ointments are applied to the affected area 5-6 times a day. - Erysipelas
. Antibiotics from the group of macrolides or penicillins are recommended, treatment of the affected area with antiseptics, and subsequent application of ointments.
Among the physiotherapeutic methods for some pathologies, UVB, ultrasound, and laser therapy can be used. For diseases that occur due to decreased immunity, immunocorrectors, general tonics, and multivitamin preparations are prescribed.
Surgery
Surgical interventions for lip swelling are rarely required. Taking into account the pathology, the following operations are performed:
- Mechanical damage
: primary surgical treatment of maxillofacial wounds, plastic surgery after burns. - Dental diseases
: opening of a subperiosteal or submucosal abscess, tooth extraction during periostitis, removal of salivary gland stones. - Tumors
: lip resection.
In the postoperative period, antibiotics, analgesics are prescribed, and dressings are performed.