Symptoms of teething in infants - how to recognize and respond correctly
Among the important moments in a child’s development, special attention should be paid to the period when the baby is cutting teeth; signs of teething often worry both the baby and his parents. The child begins to cry and worry often, there is often an increase in temperature, and sometimes the child suffers from digestive system disorders. This time will be easier to bear if parents know how the process of teething occurs and what needs to be done to alleviate the child’s condition.
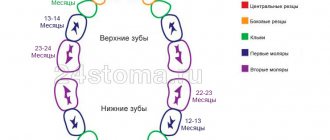
Sequence of teething in children
A newborn child has 20 follicles of primary teeth in the lower and upper jaws, as well as 16 rudiments of permanent teeth (later another 16 rudiments form in the jaws, increasing the number of permanent teeth to 32).
The teeth on the lower jaw begin to appear first. The tooth enamel of children contains more pores and fewer microelements in comparison with the already formed enamel of adults, which contains a large amount of minerals. Therefore, children have a high risk of dental caries, which can be avoided by maintaining hygiene and proper diet, treating teeth with special protective varnishes that will accelerate the mineralization process.
Sequence of baby teeth eruption in children
- 6-10 months – lower central incisors;
- 8-12 months – upper central incisors;
- 9-13 months – upper lateral incisors;
- 10-16 months – lower lateral incisors;
- 13-19 months – upper first molars;
- 14-18 months – lower first molars;
- 16-22 months – upper canines;
- 17-23 months – lower canines;
- 23-31 months – lower second molars;
- 25-33 months – upper second molars.
Timing of permanent teeth eruption
- 6-7 years – upper and lower first molars, lower central incisors;
- 7-8 years – upper central and lower lateral incisors;
- 8-9 years – upper lateral incisors;
- 9-10 years – lower canines;
- 10-11 years – upper first premolars;
- 10-12 years – upper second premolars and lower first premolars;
- 11-12 years – upper canines and lower second premolars;
- 11-13 years – lower second molars;
- 12-13 years – upper second molars;
- 17-21 years old – lower and upper third molars (wisdom teeth).
Deviations during teething in infants
Delayed eruption may occur in a baby due to previous illnesses or illnesses suffered by the child’s mother during pregnancy. Such diseases cause deformation of the jaws and lead to a lack of space for another tooth or teeth to appear.
Treatment in this case is selected individually after examining the child’s teeth and jaws, as well as analyzing an x-ray.
Early eruption is also considered a deviation from the norm. Teething before 4 months is considered a violation, but this is not any pathology for the baby. An extreme form of early teething is when a baby is born with a set of baby teeth.
Deviation from the order of teeth eruption and asymmetry of teeth eruption are considered the most significant symptom of possible deviation from the norm than early or late eruption. Despite this, often this disorder is not the cause of any pathologies in the baby’s body, and may be the norm for a particular child.
Enamel hypoplasia can be determined visually: on newly emerged teeth you can see spots (white, brown or dark brown), horizontal grooves or stripes, and minor depressions (pits). This pathology is associated with abnormalities that arose during pregnancy or childbirth.
Why does a tooth bleed?
The situation when a tooth bleeds is familiar to everyone. According to WHO, 100% of adults have caries, and 15-20% are diagnosed with severe periodontal diseases. The cause is not always pathological, but it is impossible to identify it on your own. If your gums are inflamed or your teeth are bleeding, the dentist will determine the treatment. Doctors at Dr. Granov’s clinic not only relieve tooth pain and bleeding, but also eliminate its cause.
Reasons why a tooth bleeds
Droplets of blood appear when brushing with a brush that is too hard, when injured with sharp objects, even while taking certain medications, such as aspirin. But these reasons are related to the gum, and not the tooth itself. Often, already at the appointment, the patient complains of tooth bleeding, but the doctor sees that the source of concern is the gums.
But in some cases, the cause is actually inside the tooth, which is bleeding due to:
- granulations - loose bleeding tissue that fills the carious cavity and gum pocket;
- inflamed pulp - connective tissue inside the tooth, penetrated by nerves and blood vessels.
Diseases that cause teeth to bleed
Bleeding manifests itself as a complication of caries. It accompanies the following pathologies:
- periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth and holding it in the socket, accompanied by the formation of granulations;
- chronic pulpitis - inflammation of the pulp of tissues in which blood vessels and nerves pass;
- dental abscess - the formation of a purulent cavity in it, which destroys the vessels of the pulp.
Timely treatment of inflamed tissues prevents their further destruction.
If overgrown bleeding areas of the pulp or periodontal tissue are left unattended, the inflammation spreads to the bone or even provokes the development of a tumor.
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
By leaving a request on the site, you consent to the processing of personal data
Make an appointment
Periodontist consultation
500 rub.
Teeth are bleeding: what to do
It is impossible to independently determine the cause of bleeding. All the more dangerous are attempts at self-medication. Trauma or cauterization of inflamed areas sometimes becomes an impetus for the formation of a tumor. Therefore, when a tooth or gum bleeds, all manipulations must be carried out by a dentist.
At Dr. Granov’s clinic, doctors use instrumental and hardware methods to diagnose any pathologies of the teeth and periodontium - the tissues that support it in the socket.
Signs of teething in children
Often, during the process of teething, children experience general malaise. One of the obligatory symptoms of teething is excessive drooling, which usually occurs at 5-7 months of age. The child cannot yet control the secretion of saliva. Over time, its amount will begin to decrease due to the development of reflexes. Excessive salivation is a sign that the nerves of the gums are irritated, which means that the child will soon erupt his first tooth.
Pain is the surest and most unpleasant sign of teething for a baby. Pain in the gums bothers the child, especially when the tooth approaches the surface of the gums. Often during this process the child’s temperature rises to 37.5 degrees.
Dysfunction of the digestive system is often observed during teething. Symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, and regurgitation can occur due to an increase in the volume of liquid that the child consumes during the day. However, there is a risk of not noticing an acute intestinal infection, the likelihood of which is quite high, since a teething child puts various objects in his mouth, which are not always clean. It is recommended to take your child to the doctor if the above symptoms appear.
Gum inflammation is one of the most common signs of teething in a baby. Redness and inflammation of the gums occur, and they begin to swell. These signs indicate that the tooth is already approaching the surface. However, the process of teething is quite long, and this does not mean that if the child has gum inflammation, the first tooth will appear the very next day. The tooth first passes through hard bone tissue, then breaks through the gum mucosa, and only after that can you see a white bump on the surface of the gums, which is a sign that the tooth is about to appear.
Sometimes children experience bad breath during teething. This may be a consequence of the inflammatory process. The oral cavity provides good conditions for the emergence and proliferation of bacteria that cause this symptom. To get rid of bad breath, you should pay special attention to the oral hygiene of a teething child. You can gently massage the gums with a soft brush, and give your child water to drink more often.
Rashes sometimes appear on the body. Due to increased salivation, the rash most often appears on the chin. Also, a rash can occur on various parts of the skin; redness of the child’s face or cheeks is observed.
Due to infection in the mouth, the child may develop stomatitis. Small but painful ulcers may form in the baby's mouth. With this disease, children begin to refuse food and an increase in temperature is observed. In this situation, even though the child will be in pain, it is necessary to examine the baby’s mouth and find out if there are any areas affected by infection.
Reasons for the development of gingivitis in children
The abundance of causes of the disease can be divided into two large groups.
Common reasons include:
- colds, especially if they occur frequently;
- sore throat and chronic sinusitis;
- hormonal disorders;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
Among the local reasons it is worth highlighting:
- poor-quality fillings, which, when destroyed, injure soft tissues;
- caries (infection from the cavity quickly enters the gums);
- crowded teeth;
- violations during the installation of braces;
- Tight lips that interfere with quality teeth cleaning.
Separately, it is worth noting the most important reason, since all of the above are only a catalyst for the development of the disease. So, the main reason why gingivitis begins to develop is poor oral hygiene, which can manifest itself both in improper brushing of teeth and in incorrectly selected toothpaste and brush.
Symptoms of the disease
Gingivitis has quite a few characteristic signs by which one can guess the onset of the disease:
- bleeding gums;
- pain during cleaning;
- swelling of the gums;
- severe redness of the gums in the case of an acute phase of inflammation;
- when the disease becomes chronic, the gums may acquire a bluish tint.
Often with the naked eye you can notice a large amount of accumulated plaque and tartar, and there may also be many teeth affected by caries.
In addition, gingivitis can be caused by diseases that have nothing to do with the oral cavity:
- heart and vascular diseases;
- disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases.
The above factors reduce immunity, as a result of which the gums lose their ability to resist toxins formed in plaque.
What is the best way to treat?
As was said a little above, gingivitis occurs due to accumulated soft plaque, so the first thing you need to do is get rid of it. Plaque can be removed using ultrasound - this is a simple and absolutely painless procedure. Using a special attachment, the dentist touches dental plaque, which is destroyed by ultrasound. By the way, ultrasound allows you to get rid of not only soft plaque, but also hardened formations on the teeth.
It is necessary to understand that plaque can be effectively removed, especially if inflammation has begun, only with ultrasound: rinsing with various means, using special toothpastes and gels with the addition of antibiotics can temporarily remove the symptoms of gingivitis, but these methods are not able to eliminate its cause. As soon as you stop using these medications, bleeding will return and the disease will continue to progress. Therapy aimed at reducing the inflammatory process is justified only after the deposits have been removed.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is usually prescribed as follows:
- Rinse with Chlorhexidine solution. The maximum duration of use of the drug is 10 days. Rinsing should be done twice a day for at least 30-40 seconds per procedure. The solution, which has a bitter taste, which not all children will like, has no contraindications based on the child’s age.
- Rinse with Miramistin (prescribed after the child reaches the age of 3 years). You need to rinse three times a day. The drug is inferior in its effectiveness to Chlorhexidine and is significantly higher in price.
- Rinse with infusions of chamomile or sage (it is not recommended to use oak bark).
In addition to rinses, many doctors prescribe ointments and gels. It is believed that the gel is more effective than ointment because, due to its consistency, it has the ability to remain on the gums for a long time, which promotes better absorption. In addition, the medicinal substances contained in the product penetrate much better into the tissues from the gel than from the ointment.
The most effective and proven gels on the positive side are the following:
- Cholisal is a drug that simultaneously has two effects: analgesic and anti-inflammatory. It is used for gingivitis and the beginning of teething (the drug is rubbed directly into the place where the tooth is emerging). There are no age restrictions. The gel can be used for a maximum of one and a half weeks, twice a day. After applying the product, it is recommended to eat within two, or preferably three, hours.
- Metrogil Denta. Used after 6 years. Apply directly with your finger or a cotton swab to the gums near all teeth; there is no need to rinse off the gel.
Many parents often decide to treat their child on their own, not wanting to see a dentist. But you need to understand that the use of anti-inflammatory drugs will have no effect if you do not get rid of the deposits, so you will still have to set aside time to visit the dentist. If you ignore the advice, then:
- symptoms of bleeding will disappear, but will reappear after completion of the course of therapy;
- gingivitis can become chronic, causing periodontitis.
In addition to anti-inflammatory therapy, oral cavity sanitation and silvering are carried out - a method that does not require drilling, but has a lot of disadvantages.
How to avoid the occurrence of gingivitis?
The following remedies will help prevent gum bleeding:
- High-quality oral hygiene. Parents should instill in their children oral care skills from an early age. Not all adults know that hygiene measures must begin before the first tooth begins to erupt.
- Using the right paste. If the child does not have gingivitis, then you can use any paste designed for children. If your child does not brush their teeth well enough, you can purchase a paste with amino fluoride.
- Stick to your diet - avoid snacking, limit the consumption of fast carbohydrates (carbonated drinks, sweets). Of course, you don’t need to completely deprive your child of sweets, but you can give them only immediately after the main meal, after which you should brush your teeth.
How to make teething easier
In order to make the difficult process of teeth appearing easier for your child, you should pay special attention to the child’s oral hygiene and follow the necessary regimen:
- Until 1-1.5 years of age, it is necessary to wipe the baby’s teeth with a special silicone brush;
- From the age of 1.5 years, start using a special children’s brush;
- From the age of 2, teach your child to rinse his mouth after eating.
When the child reaches one year of age, it is necessary to visit the dentist.
It is also necessary to remember that children pay special attention to the behavior of their parents, especially their mother. You can make the teething period easier by giving your child as much attention as possible. It is recommended to carry the baby in your arms more often, talk to him, and distract him with toys.
Babies who are breastfed try to contact their mother's breast as much as possible when teeth appear. During this period, you should not adhere to a strict feeding schedule for the child: the child should be fed as often as he asks for it. This will reduce the infant's irritability.
During the appearance of the first teeth, the child also needs teethers. This helps relieve gum irritation. Sometimes children refuse special teethers, preferring a regular toy. In this situation, you should be especially careful to ensure that the toy is always clean, without sharp corners or small parts, to avoid infection or accident.
Various medications or folk remedies can also help alleviate the symptoms of teething, which can be used in consultation with a doctor. In addition, it is necessary to frequently wipe away the saliva that accumulates near the mouth. If a teething baby experiences vomiting or diarrhea, the baby should be given liquid pureed food and drink enough liquid.
The following folk methods should not be used when cutting a baby’s first teeth:
- Press on the gums with your finger, while applying force. This will cause increased pain and irritation for the child.
- Giving your baby dried bread or cookies: there is a risk of choking on crumbs. In this case, it is better to use safe teethers.
- Treat the gums with undissolved soda or try to free the tooth yourself: in this case, there is a high risk of infection, which will only harm the child.
Main causes of bleeding
Lack of proper oral hygiene. Injury to the gums and the formation of bruises can be caused by a hard toothbrush. Improper flossing can also cause injury.
Plaque and tartar, the accumulation of many microorganisms contribute to the rejection of teeth from the gums. The resulting gap fills with blood. In order not to provoke such a problem, you should brush your teeth thoroughly and regularly visit the dentist for preventive purposes.
A risk factor is changes in hormonal levels, including during pregnancy, disruption of the internal systems of the body, or simply with age. The result is looseness of the walls of blood vessels and their slight injury.
Infectious diseases of the oral cavity that develop as a result of the accumulation of harmful microorganisms and bacteria. The reason is poor oral hygiene, lack of timely treatment and professional cleaning. The result is bleeding from the tooth canal.
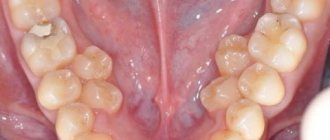
Eruption of the first teeth in infants: photos of gums and possible difficulties
In rare cases, the eruption of baby teeth is not accompanied by obvious discomfort.
All parents are looking forward to these first and quite serious changes in the life of their beloved baby with impatience and excitement.
It is important to know what symptoms accompany this process and how to identify changes occurring in the gums.
What does the gums look like when the baby’s first teeth erupt (there are many photos of infants’ gums in the article)? What should parents do if her color turns white, blue or black?
Should I consult a doctor if there is a bruise or hematoma, swelling, inflammation or even blood before eruption?
Hematoma during the eruption of primary teeth, normal or pathological?
Teething is a physiological process, which, however, can cause a lot of trouble for the baby and sleepless nights for parents.
For some lucky people, teeth pop up like mushrooms after rain, quickly and imperceptibly; to the delight of mom and dad, grandparents. Just a couple of days and your baby is smiling happily, proudly showing off his new tooth! But more often than not, the eruption of a baby tooth causes discomfort for the baby and anxiety for parents. Suddenly, the smiling baby begins to act up for no apparent reason, and may even develop a fever. Temperatures can vary from 37 to 38 degrees and above. The parents' concern is understandable; what if the little one gets sick? It is natural to want to help a child and alleviate suffering. What to do in such a situation?
Our recommendations.
- Examine the child's oral cavity. You may immediately see an area of swollen gum mucosa or an already erupting tooth.
- Assess your baby's salivation. The already increased salivation in a 1-2 year old child at the time of the eruption of a new tooth intensifies even more. Transparent nozzles may appear. If drool flows like a river, then this is another confirmation that the cause of the whims lies in the new tooth!
- The absence of ARVI symptoms, improvement in the child’s condition and mood after taking an anesthetic also confirms that the “culprit” of the trouble is a new tooth.
- What is the best way to help your baby survive this stage? Firstly, these are special gels and teethers. You shouldn’t get carried away with gels; they don’t have the most beneficial composition for a developing body. The gel alleviates the condition for a very short period of time, thanks to a component that has a local anesthetic effect. Secondly, painkillers and antipyretics (for example, Nurofen (suppositories or syrup), again if necessary, no more than once every 6-8 hours. Do not forget that children tolerate fever much easier than adults.
The most important thing in alleviating the symptoms of teething is the patience and care of the family around the baby, the ability to distract and entertain the child.
Even a eruption hematoma (as in the photo),
There is no reason to panic and visit the dentist in person, especially now, during the COVID-19 pandemic.
All you have to do is take a photo and send it to us by email. We will remotely provide individual recommendations and reassure parents. According to observational statistics, only 0.05% of cases require dental intervention. The hematoma does not need to be smeared with anything (it will not help), or opened (at home there is a risk of infection, in the office it is at least useless). Just calm down and be patient, as soon as the tooth erupts, the hematoma will go away (like an ordinary bruise). May 21, 2022
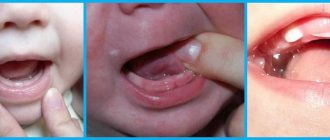
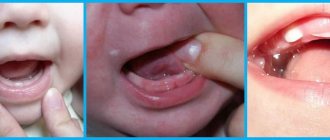
What gums look like
Long before the first incisors appear , significant changes in muscle tissue can be observed - the main sign of changes in the child’s body.
The color of the tissue structures in the gum area changes: they become more loose.
In the area where the cobs appear, there is swelling and a slight increase in size of the mucous membrane.
The inflamed gum becomes reddish , but it is also possible that it may acquire bluish, burgundy or purple hues, which becomes a serious cause for concern on the part of parents.
As the cutter approaches the surface, the white spot becomes more distinct and noticeable. The final stage is the release of the cobs from the tissue structures.
The very first harbinger of long-awaited changes in the oral cavity is severe itching in the gum area .
To eliminate unpleasant and uncomfortable sensations, the baby constantly tries to scratch this area with his hands and begins to put toys in his mouth.
What does the swollen upper gum look like during and before the eruption of the first teeth in children, photo:
Swollen gums when the lower teeth erupt in an infant, photo:
Teething symptoms
What are the symptoms of teething in a one-year-old child? What are the symptoms of teething in children? Typically, symptoms of teething in children under one year old include:
- Profuse salivation. It may cause coughing and hoarseness, as well as a rash in the mouth and chin.
- Swelling, redness and soreness of the gums
- Itchy gums. Babies often try to relieve it by chewing almost anything they can get their hands on.
- Decreased appetite or complete absence of it, as well as refusal to eat
- Temperature increase
- Sleep disturbance
- Increased excitability
- Changing the stool
- Runny nose
It is important to understand that when teething in children, the symptoms can be different and it is not at all necessary that the child has everything on the list. Symptoms of teething in children after one year are very often similar to those present before one year. Even when molars erupt in children, the symptoms may be similar, but everything, of course, is purely individual.
Problems and solutions
Swelling and redness of the gums when incisors and molars appear is considered normal and should not cause concern to parents. This process is not always accompanied only by the described symptoms.
Parents are faced with blueness of muscle tissue, the appearance of hematomas and bruises, which causes panic.
To minimize possible complications , it will be useful for caring parents to become familiar with the etiology of deviations from the norm and ways to eliminate them.
Why does pulpitis of permanent teeth occur in children and how to treat it? Details are in this material.
You can learn about the symptoms of pityriasis rosea in children from this publication.
Is it possible to bathe a child with roseola? Our article will answer the question.
Swelling
If a baby under the age of one year has swelling of muscle tissue , then we are most likely talking about the eruption of baby teeth.
The first milk teeth begin to erupt when the baby reaches six months of age. Sometimes - several months earlier, and in some cases - much later.
Other signs also indicate that a child’s gums are swollen during teething. This is an increase in temperature, loss of appetite, general malaise, worsening mood.
Swelling of the gums is a natural process that should simply be endured, providing the baby with proper care and attention.
To alleviate the condition, traditional healers recommend using compresses with infusions based on chamomile , which has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Swollen or swollen gums when the first upper teeth erupt in infants, photo:
blue tint
When cutting through the incisors, you may encounter the appearance of cyanosis - acquiring a blue tint .
Did your baby's gums turn blue when teething? The cause of the symptoms is associated with ruptures of small blood vessels located in the gum, through the tissue structures of which the baby tooth erupts.
Small incisions may be necessary as large amounts of fluid and blood will most likely have accumulated there.
THE WEBSITE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION!!!
Teething in children: timing, symptoms, possible complications
At the age of five to six months, a difficult period begins in the life of the child and his parents. Teething syndrome in children is a special physiological condition, which is accompanied by characteristic symptoms : fever , swelling and pain in the gum tissue, loose stools, loss of appetite and other unpleasant symptoms . At this point the child becomes capricious, loses activity, and often cries.
However, some parents, during the period of eruption of the first milk teeth in infants , ignore the baby’s , preferring to simply use painkillers instead of seeking medical advice. Such a mistake can be costly, because by attributing all disorders to a natural physiological process, parents risk ignoring the signal that the child is sick. The process of teething in a baby is a serious reason to go to see a doctor, because it is not for nothing that this syndrome was separately included in the international classification system of diseases ICD 10 , under the index K00.7. Only an experienced and qualified specialist will be able to distinguish the symptoms of the eruption of the first teeth in a six-month-old baby from the manifestations of more serious pathologies that may threaten the child’s health. Professional and timely diagnosis in a medical institution is the only guarantee that treatment of a dangerous disease will begin at an early stage and be successful. And even if there is only a natural physiological stage of the child’s development, the doctor can determine how the process is proceeding and whether any deviations from the norm are observed. And if necessary, an experienced specialist will prescribe effective medications and ointments to relieve teething pain or relieve other symptoms that bother the baby .
Features of the teething process, timing and order of appearance
The statistical norm for the appearance of the first baby teeth in a baby is six months. However, modern medical practice confirms the existence of a tendency to speed up this process. Signs of teething can be observed in children aged five months and, in rare cases, four months. By the first year of life, up to eight incisors can already be observed in a child’s mouth, and by about three years the rest appear. It is worth noting that the dynamics of manifestation and growth depend on many indicators: the sex of the child, heredity, diet, indicator of physical activity, degree of development of organs and systems.
There is no universal data on this issue, but there is a conditional table that reflects the approximate timing and order of teething in children :
- The lower incisors begin to appear very first, this process lasts until nine months of age;
- The upper incisors grow between seven and ten months;
- Lateral incisors from 9 to 12 months, parallel above and below;
- The eruption of the front molars in children will begin from one year to nineteen months, the second ones appear much later - almost at the age of two years;
- The upper canines range from 16-20 months, and the lower ones - up to 22 months.
Symptoms of teething in children and signs of disruption of this process
The first symptom that parents most often pay attention to is fever. Deviations from the norm are usually not too significant - within 37.5 - 38 degrees. It is worth monitoring not only the magnitude, but also the duration. A natural increase in temperature is usually easily relieved with antipyretic drugs. A persistent increase in temperature above 38 indicates that teething syndrome occurs with complications. At this age, the primary immune system is just forming in the child’s body, and inflammatory or even infectious processes can develop in the oral cavity and intestines.
The second important sign that can help the doctor during the eruption of baby teeth is the nature of the mucous discharge. Swelling of the nasal cavity and gums is a natural process during the growth of fangs and incisors of the upper jaw; the mucus is watery in nature. Thick and colored discharge is a sure sign of an ENT disease.
One of the symptoms of teething in babies is also loose stools. In this case, the consistency becomes only slightly thinner than usual. Do not confuse the signs accompanying tooth growth with diarrhea. If a child has a serious intestinal disorder for several days, and eating is accompanied by vomiting, then you should urgently go to the hospital, where an infection will most likely be diagnosed.
But most often, parents turn to doctors with complaints about gum replenishment. Teething is a process in which soft tissue is torn, causing pain . A qualified professional will prescribe topical anesthetics to relieve discomfort and recommend massage techniques to speed up the process. Under no circumstances should you select medications on your own.
Recommendations for parents
Teething causes discomfort not only for the baby, but also for parents who want to ease the child’s well-being.
To reduce disturbing symptoms, you can use:
- drugs that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
teethers , accelerating the appearance of the baby tooth on the surface. These are toys that contain gel or water inside.
The child will chew on the teethers and eliminate itching and soreness in the gum area;
antipyretics for gums, which are given when the temperature rises during teething.
Immediately before taking any medications, consult your pediatrician to rule out intolerance to the components of the substance;
traditional medicine (use mint, chamomile, lemon balm, lavender, sage).
Medicinal plants have an anti-inflammatory effect, and decoctions based on them can be used to treat gums with signs of inflammation.
Complications for which you should not hesitate to visit a doctor include the formation of large hematomas, an increase in temperature above 38 degrees, the formation of ulcers, frequent bouts of vomiting or stool disorders, severe cough or the appearance of a runny nose, accompanied by greenish mucus discharge.
Is a diet necessary for giardiasis for children and what should it be like? Our publication will tell you about this.
What does prickly heat look like in children in the photo, what treatment is required? You will find answers to your questions in this material.
Read about the causes of urticaria in children in this article.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
During this period, it is important to ensure peace for the baby . It is worth temporarily avoiding visiting noisy companies, traveling, and stress, which can aggravate the process.
Vomiting and regurgitation should not be frequent companions. Their appearance is acceptable at high temperatures, but the baby should be shown to a doctor.
To massage the gums, you can use a moistened, rough cloth, or do it with a massage toothbrush. It is important to perform the procedure carefully, without damaging the child’s mucous membranes.
About children's first teeth:
Now you know what gums look like when the first teeth erupt (see photo), how gums swell and swell and why.
Most often, the eruption of baby teeth occurs without serious complications . Parents are required to carefully monitor the condition of the baby’s oral cavity in order to promptly identify and prevent the development of dangerous pathologies.
What to expect
The first teeth appear at about 6 months of age. It may take 2 months from the moment the first signs appear until the tooth appears.
The following symptoms will help you understand that your baby is teething:
- before the teeth emerge, the gums look inflamed and swollen;
- salivation increases;
- the child begins to put all objects and toys into his mouth;
- eats poorly;
- sleep becomes interrupted, often wakes up crying.
The baby's behavior during teething also undergoes changes. The baby becomes capricious, excitable, and often asks to be held.
Does not tolerate harsh sounds or bright light. There are sudden changes in mood: from apathy to an increased desire to be paid attention to.
Signs of teething that resemble the onset of a cold and bowel dysfunction:
- frequent regurgitation;
- the temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- bowel disorder (constipation or diarrhea);
- runny nose;
- cough;
- rash on cheeks.
It is not necessary that all these symptoms will be detected immediately. Some babies may only experience diarrhea, while others may simply drool. When the upper teeth come in, the temperature often rises.
During teething, especially the upper ones, the gums are injured. Therefore, you can see blood on it. It can change the smell of your mouth.
Timing of eruption
All children get their first teeth at different times. But already from the 1st month growth begins inside the gums. Teeth can come out early - at 3 months, or they can appear late - at 10-11 months. Most often, the first tooth can be seen at 6 months.
The early appearance of teeth in infants (3 months) is associated with the intake of vitamins and minerals during pregnancy. If teeth appear before 3 months, the child needs to be examined. This may be the cause of endocrine diseases.
Normally, by the age of one year there should be at least 1 tooth. In cases where the teeth do not come out for a long time, the child should be shown to a doctor to rule out developmental pathologies.
Reasons why babies teeth erupt late:
- rickets;
- weakened immune system;
- endocrine disorders;
- unbalanced diet, late complementary feeding;
- premature birth;
- edentia – absence of the rudiments of baby teeth.
The pattern by which the upper teeth erupt in most children is as follows:
| Name of teeth | Appearance time |
| Central incisors | 8–12 months |
| Lateral incisors | 9–13 months |
| Fangs | 16–22 months |
| First molars | 13–19 months |
| Second molars | 2–3 years |
The pattern of teething of the lower row of teeth in many children is as follows:
| Name of teeth | Appearance time |
| Central incisors | 6–10 months |
| Lateral incisors | 10–16 months |
| Fangs | 1.5–2 years |
| First molars | 1.5 years |
| Second molars | 2–3 years |
In some children, the pattern of teeth appearing changes, for example, the canines rather than the incisors emerge first. This is an individual feature that does not bring anything bad.
Consultation with a dentist is necessary when the pairing of eruption is disrupted: one tooth of the pair has appeared, but the other has not, while other teeth are being cut. This may indicate a congenital malformation.
Unpleasant symptoms and pain accompany the period when fangs come out. This is due to the fact that these teeth have sharp, wide and jagged edges.
The upper teeth are often accompanied by a runny nose. This occurs due to the spread of swelling and inflammation of the nasal mucosa. By the age of 3, babies should have 20 baby teeth.
Preventative dental checkups should not be ignored. First visit – at 1 year. Only a specialist can identify oral problems in a timely manner.
Complications during teething
It is important to monitor the symptoms of a child’s first teeth erupting in order to predict complications. Complications may include:
- Early teething. The norm is 6 months, but it may be that the child’s teeth begin to erupt at 2 months
- Too late teething. It is possible that even at 8 months the child has not yet erupted teeth. The consequence of this situation can be edentia - this is the complete or partial absence of teeth in the oral cavity.
- Incorrect teething sequence
- Abnormal tooth formation or dental anomalies
- Tooth growth abnormalities
- Enamel hypoplasia. It is a lesion of tooth enamel that occurs in children under 10 months of age.
- Aphthous ulcers or aphthous stomatitis. It is the process of small purulent ulcers appearing in the mouth
- Gum hematoma. May occur when a blood vessel is damaged
At the INTAN implantation and dentistry centers you can provide a wide range of pediatric dentistry services. All services are provided only by highly qualified dentists who have a special approach to children and knowledge of how to carry out treatment so that the little patient likes it.
Giving help
You can alleviate the symptoms of teething with increased attention and affection. You need to pick up the child more often, play with him, talk to him, read books. This is how the baby feels cared for and is distracted.
Adults need to know what activities will help alleviate the condition:
- Proper diet. Avoid sweet foods. It is worth including products such as cottage cheese, cheese, cauliflower.
- As soon as the first teeth appear, they need to be properly cared for. You need to buy a special brush with soft rubber bristles. Your baby should brush his teeth without toothpaste.
- The child should be offered rubber toys, teethers (corrugated or with water).
- Massage the gums with an adult's finger. Be sure to wash your hands with soap before the massage!
- For local anesthesia, gels and ointments are used (Kalgel, Cholisal, Kamistad).
- Antipyretic drugs based on ibuprofen or paracetamol (Nurofen, Panadol).
- You can use decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, lemon balm, mint, sage). They have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. The decoction is taken orally or applied to the gums.
- A solution of soda helps relieve inflammation. To do this, add 1 teaspoon of baking soda to a glass of boiled water. Gauze is wrapped around the finger and moistened with the solution. You can treat your gums several times a day.
- During the period of teething in infants, preventive vaccinations should be excluded.
Problems that arise with the first teeth
The color of the first teeth can tell about the child's health.
- If the base has a blackish tint, this indicates that you are taking iron supplements. This color can be observed in chronic inflammatory diseases.
- A yellowish-brown tint indicates that the mother took antibiotics during pregnancy, or the child himself during the appearance of teeth.
- A yellowish-green tint indicates blood disorders.
- The red tint appears during a congenital disorder of porphyrin pigment metabolism.
When teeth are being cut, parents can help their child. The main thing is to understand the signs in time and consult a doctor. Care and attention are the best medicines for a baby at this time!
{SOURCE}