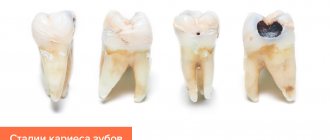
Dry mouth is an unpleasant sensation that can be a symptom of serious illnesses. If dry mouth occurs constantly or frequently, it is necessary to understand the cause that is causing it and, if necessary, begin treatment. Elimination of dry mouth, as a rule, is achieved only as a result of treating the underlying disease, which should be the true goal. In any case, the feeling of dry mouth is another reason to pay attention to your health.
Dry mouth is caused by insufficient hydration of the oral mucosa, mostly due to insufficient saliva production. In medicine, dry mouth caused by a cessation or decrease in saliva production is called xerostomia.
.
Quite often, dry mouth occurs in the morning or at night (that is, after sleep).
Symptoms associated with dry mouth
Dry mouth in most cases manifests itself as a complex of symptoms described as:
- "viscosity" or "stickiness" in the mouth;
- thirst;
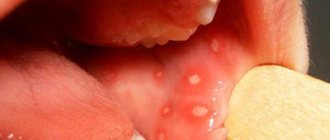
- irritation of the oral mucosa (burning and itching), the appearance of a bright border of the lips, cracks on the lips and in the corners of the mouth;
- dry tongue. The tongue turns red and becomes rough. It becomes more difficult to speak, chew and swallow. Decreased taste perception;
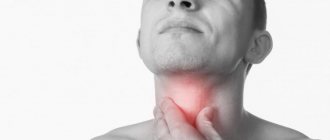
- dry throat. The voice becomes hoarse and more hoarse;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Poor oral hygiene
Poor hygiene is a common cause of xerostomia in healthy people. Dry, rough gums, sometimes itchy and red, are the result of excessively intense brushing, the use of too aggressive mouth rinses, or an allergy to toothpaste.
In this case, you should make care more gentle or replace hygiene products with better ones. Especially if you use alcohol-based rinses. Alcohol dries out mucous membranes.
A good option for careful hygiene would be products from the Asepta series. For example, a rinse based on xylitol, potassium citrate and herbal extracts - it soothes the gums, prevents inflammation and prevents tooth decay. For people with sensitive teeth, ASEPTA SENSITIVE toothpaste is suitable.
Causes of dry mouth that are not pathological
In some cases, dry mouth is not associated with a medical condition. For example:
- Dry mouth can occur in the morning and at night due to intoxication. This is a typical situation after drinking too much the night before.
- When nasal breathing is impaired, a person breathes through his mouth during sleep. The mouth is slightly open, and the oral mucosa dries out faster. Nasal breathing can be impaired due to a runny nose, nasal polyps, or a deviated nasal septum. A similar situation occurs with snoring. The cause of snoring in most cases is a decrease in the tone of the soft palate. Muscle weakening develops with age. This is why older people snore more often, and their oral mucosa becomes dry. This reason explains dry mouth in the morning in the elderly in most cases.
- If you don't drink enough fluids in hot weather, you shouldn't be surprised by dry mouth. A similar effect can be caused by eating highly salted foods.
- Many medications can cause dry mouth.
- Smoking is another common cause of dry mouth.
- Dry mouth can be one of the symptoms of menopause.
Pathogenesis
The female body responds to most adverse conditions by changing the balance of hormones. This is especially noticeable during adolescence, during pregnancy or menopause. But sometimes, due to chronic pathologies, the endocrine glands and organs of the reproductive system produce secretory fluid unevenly.
If estrogen levels drop, biochemical, histological and functional changes begin in the urethra and vagina. The hormone is responsible for the production of collagen, which is involved in maintaining sufficient quality of vaginal tissue. If there is not enough of it, the stratified epithelium becomes thinner, smaller, and less elastic.
Diseases that may cause dry mouth
Dry mouth can be caused by high fever and intoxication due to various infectious diseases (flu, sore throat, etc.). Diseases associated with large loss of fluid as a result of vomiting or diarrhea (cholera, dysentery) can also cause dry mouth. In such cases, dry mouth is one of many symptoms and does not attract special attention.
If dry mouth is combined with diarrhea, flatulence, belching, nausea and pain in the left side of the abdomen, then this may indicate pancreatitis.
Dry mouth in combination with a bitter taste, heartburn, white or yellow coating on the tongue can indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract such as gastritis, duodenitis, cholecystitis.
Dry mouth can also occur with:
- diseases of the salivary glands;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis);
- neoplasms of the oral cavity (benign and malignant);
- damage to nerve endings that contribute to the functioning of the salivary glands;
- anemia;
- vitamin A deficiency;
- systemic diseases (scleroderma, Sjogren's disease, cystic fibrosis).
Treatment
The course of treatment is always individual, it depends on the causes of the disease and the characteristics of your body.
In cases where xerostomia is caused by a malfunction of the salivary glands, the doctor may prescribe a special massage that improves blood flow and restores fluid production. A more serious problem is blockage of the channels that remove saliva. In this case, you will need to clean them under local anesthesia. If the blockage is caused by a stone, surgical intervention is needed.
If the cause of xerostomia is an allergy or a side effect of drugs, what caused the reaction is excluded, and the drugs are replaced. The patient is advised to add vegetable oils to his food, drink vitamins and eat more fish.
If erosion or cracks have already appeared on the mucous membrane, they must be treated with special disinfectants. Rinsing with herbal decoctions also helps, but never with salt.
Sources:
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Prevention of recurrence of localized periodontitis in young A.K. YORDANISHVILI, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov, Military Medical Academy named after. CM. Kirov, International Academy of Sciences of Ecology, Human Safety and Nature.
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- putrid odor from the mouth is a direct consequence of the intensive proliferation of bacteria;
- burning tongue - it appears with fungal diseases of the oral cavity;
- pimples and dry lips are formed due to a lack of vitamins in the body.
Eliminate dry mouth
If dry mouth is caused by drinking alcohol and smoking, then it can only be eliminated by getting rid of the bad habit. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of salty and sweet foods. Pay attention to how you breathe - through your nose or mouth. If nasal breathing is difficult, the cause must be diagnosed and nasal breathing restored. To do this, you will have to see a doctor. It is also important to monitor the humidity in the room.
Dry mouth can be the first symptom of many diseases. Therefore, if you often experience a feeling of dry mouth, it is necessary to understand its nature, determine the cause and, if necessary, consult a doctor and begin treatment for the disease that caused this symptom.
Deadly pregnancy complication: who is at risk
Monitoring the course of pregnancy is 50% highly artistic pasting tests into a card, and 50% - performing completely routine procedures: weighing, measuring the abdomen with a centimeter tape, examining the limbs and measuring blood pressure (BP). On two hands. Necessarily. From an early date.
Once upon a time, the USSR managed to significantly reduce maternal mortality rates in a simple but surprisingly effective way.
A midwife was stationed in every small settlement who could measure a pregnant woman’s blood pressure and independently boil a portion of urine in order to find protein in it.
Simple midwives in the USSR and highly educated obstetrician-gynecologists in modern Russia are doing the same thing - persistently looking for signs of impending preeclampsia - a formidable and deadly complication of pregnancy.
What is preeclampsia?
This is a serious complication of pregnancy, in which the functioning of the entire body is seriously disrupted. In addition to the increase in blood pressure, a large amount of protein appears in the urine, the number of platelets in the blood decreases, the functioning of the liver and kidneys suffers, epigastric pain, visual disturbances, and severe headaches appear.
The condition can rapidly progress and lead to convulsions with loss of consciousness - eclampsia.
Preeclampsia begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. The sooner, the more dangerous. Preeclampsia that develops before 32 weeks of pregnancy is considered early; pregnancy always ends prematurely, because attempts to preserve it can kill both mother and child.
Sometimes preeclampsia develops in the postpartum period, which is why obstetrician-gynecologists never relax.
Why is this happening?
Science still cannot give an exact answer to this question, despite the fact that the pathogenesis of the disease is well studied.
In some cases we can predict the development of the disease, but almost never we can prevent it.
At risk:
- primigravida;
- women who had preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy;
- preeclampsia in relatives (mother, sister);
- women who suffered from arterial hypertension before pregnancy or experienced an increase in blood pressure for the first time before 20 weeks;
- women with a history of kidney disease;
- women with diabetes mellitus, autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, antiphospholipid syndrome), thrombophilic conditions;
- obese women;
- women aged 40+ (another hello to all fans of the idea of delayed motherhood);
- multiple pregnancies;
- pregnancy after IVF
What is the child's risk?
Preeclampsia may require emergency delivery at any stage of pregnancy. This is often the only way to save the mother's life.
Severe prematurity in a newborn is a heavy burden that can affect the rest of a person’s life. Despite the breakthrough successes of modern neonatology, which has made it possible to nurse 500-gram babies, the mortality rate among premature babies is very high.
What does a woman risk?
Women who experience preeclampsia are likely to experience the condition in each of their pregnancies, with subsequent preeclampsia always more severe than the previous one.
Despite the fact that preeclampsia goes away with pregnancy, the risks of developing cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, stroke and heart attack remain.
Without adequate help, you may develop eclampsia, a severe seizure disorder similar to epilepsy. Acute renal failure, pulmonary edema are rapidly increasing, stroke or myocardial infarction, placental abruption, sudden intrauterine fetal death, retinal detachment with loss of vision can occur.
What is HELLP syndrome?
HELLP syndrome was first described in 1954. This is an abbreviation made up of the first letters: hemolysis - intravascular destruction of red blood cells (Hemolysis), increased activity of liver enzymes (Elevated Liver enzymes) and thrombocytopenia (Low Platelet Count).
This serious and potentially fatal condition is accompanied by severe blood clotting disorders, necrosis and rupture of the liver, and cerebral hemorrhages.
Dangerous symptoms
You should immediately consult a doctor if swelling appears on the face and hands, headaches that do not go away after taking conventional medications, blurred vision - blurred vision, “veil and fog”, flashing “spots” before the eyes.
Preeclampsia can manifest itself as pain in the epigastric region, right hypochondrium; nausea and vomiting in the second half of pregnancy, difficulty breathing are dangerous. A sudden weight gain (3-5 kg per week) may be a warning sign.
Preeclampsia is not mild
The most difficult thing for an obstetrician-gynecologist is not to panic ahead of time. Sometimes the situation allows you to delay time a little to allow the fetal lungs to ripen.
Up to 34 weeks, corticosteroids are administered to prevent respiratory distress syndrome. Sometimes the situation quickly worsens and requires immediate action and delivery.
How to prevent preeclampsia?
Unfortunately, doctors can predict many obstetric complications, but cannot prevent them. Over the years of research, a long list of disappointments has accumulated. The bed-rest regimen (resting in a lying position during the day), limiting table salt, fish oil or taking garlic tablets will definitely not help prevent the development of preeclampsia.
Neither taking progesterone medications, nor using magnesium sulfate, nor taking folic acid, nor using heparins, including low molecular weight ones (Clexane, Fraxiparin) is not a preventive measure. However, all of these drugs can be used during pregnancy for other purposes.
If the risk of preeclampsia is high, your doctor may suggest taking acetylsalicylic acid daily after the 12th week of pregnancy.
Pregnant women with low calcium intake (<600 mg per day) are advised to take supplemental calcium in the form of medications.
The best thing you can do is take care of prevention before pregnancy. Hypertension should be well controlled before conception.
Obesity requires weight loss, diabetes requires compensation and reliable control. Unfortunately, this is the right but difficult path.
Most often, women come into pregnancy with a whole bunch of problems that require urgent solutions.
Obstetricians and gynecologists around the world continue to measure blood pressure. On two hands. On every visit. And they ask you not to forget to regularly take a general urine test. This is a life-saving strategy.
Oksana Bogdashevskaya
Photo depositphotos.com
The opinion of the author may not coincide with the opinion of the editors
Which doctor should I contact for dry mouth?
If you complain of dry mouth, you can contact your dentist or general practitioner (GP or family doctor). After identifying the cause that caused the feeling of dryness, you may be redirected to an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist or rheumatologist.
Most likely, you will need to undergo various tests (general blood count, general urinalysis, blood test for thyroid hormones, biochemical blood test, serological test), and, if necessary, undergo some instrumental studies (ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography).
Diagnostics
It is important for the gynecologist not only to determine the degree of dryness and other symptoms, but also to find out the causes of the anomaly. The doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, finds out her lifestyle, the quality of the menstrual cycle and other nuances. On the examination chair he conducts a detailed examination.
To determine the anomaly, the gynecologist prescribes colposcopy, during which he uses a colposcope: assesses the condition of the mucous membrane, its color, thickness, and integrity. Next, he moves on to specific tests that determine pH, glycogen levels and other parameters. Immediately take a smear for microflora and cytology. Colpocytological examination helps to determine the degree of maturity of the squamous epithelium.
A blood test for hormones and other laboratory tests of biological substances are required.