Pain in the throat and ear is a clinical manifestation of a number of otolaryngological diseases, and much less often - neoplasms of a malignant nature. Most often it is one-sided and signals the presence of inflammatory processes occurring in the sinuses, tonsils, lymph nodes and larynx. Treatment of chronic sore throat is aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes and pain symptoms. For this, the otolaryngologist prescribes medications.
The otolaryngology department of CELT offers diagnosis and treatment of chronic ear pain. Our multidisciplinary clinic has been operating in the paid medical services market in Moscow for almost thirty years. Our specialists operate with international treatment standards and have everything necessary for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment in accordance with them.
At CELT you can consult an otorhinolaryngologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Causes of chronic pain in the throat and ear
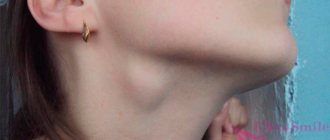
Pain in the throat and ear, without or with fever, is one of the most common complaints of patients visiting an otolaryngologist. On average, about 15% of patients seek professional help. As already mentioned, most often the pain occurs on one side; There are also cases when it covers both sides.
The reasons for this phenomenon lie in pathological processes affecting several anatomical structures, but not necessarily. There are often cases when the pain radiates to the ear when the throat is affected. The features of human anatomy are such that the ear, throat, mouth and nose form a communicating system, interconnected by channels.
When inflammation develops in any of the organs, the process spreads through these channels, affecting other structures of the system - the organs of hearing and the pharynx - which provokes pain in the throat and ear. The patient may complain of a sore throat radiating to the ear - or, conversely, the appearance of pain in the organ of hearing and spreading to the throat. It also happens that the patient cannot accurately determine the source of pain.
Symptoms in the form of pain are characteristic of a wide range of pathological conditions, which you can learn about by reading our tables presented in the following sections.
A little about the ear itself
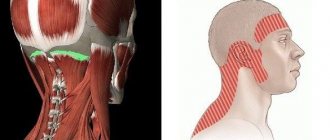
To understand exactly what departments and problems we are talking about, you need to carefully study the structure of the ear. This is a rather complex organ, including three sections:
- Outer ear . This zone includes everything that can be seen without any additional devices. This is the concha and the visible ear canal.
- Middle ear . The invisible part, consisting of the tympanic cavity and the auditory ossicles. This section is protected by the temporal bone.
- Inner ear . The most complex section, consisting of bone canals. It ensures the conversion of incoming sounds into impulses that are transmitted to the brain and recognized there. In addition, the vestibular apparatus is located here, which is responsible for human coordination and balance.
Diseases of the throat and ear, in which pain in the throat radiates to the ear
| Pathology causing symptoms | What is it characterized by? |
| Lymphadenitis | Inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes due to damage by bacteria or viruses. It can occur in acute or chronic form and manifests itself:
|
| Rhinitis | Inflammatory processes of the nasal mucosa, which can develop due to viral lesions. They appear:
|
| Sinusitis | Inflammation that covers the paranasal sinuses, developing when they are damaged by bacteria, viruses or fungi. Depending on the localization of pathological processes, sinusitis is divided into sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, and ethmoiditis. Their clinic provides for increased body temperature, headaches, sore throat, radiating to the organ of hearing. |
| Tonsillitis | Inflammatory lesion of the tonsils, developing as a result of damage by pathogenic microorganisms. The pain during the disease is acute and radiates to the ear, and in the chronic form it is sticky. The patient's throat has a burning sensation and soreness, and a reflex cough develops. |
| Otitis | Inflammation that affects the external, middle or internal parts of the hearing organs, and occurs in acute or chronic form. Pain with it is accompanied by a significant deterioration in well-being. Often otitis media occurs along with tonsillitis, causing a sore throat. |
| Pharyngitis | Inflammatory damage to the mucous membrane of the pharynx due to damage by bacterial or viral agents. Very often it occurs together with tonsillitis and, in addition to pain in the ear and throat, is manifested by the following symptoms:
|
Diagnostics
It is necessary to conduct a general and biochemical blood test to determine the presence of infection, a microbiological analysis of a smear from the ear and nasopharynx. An ENT doctor examines the level of hearing and the patency of the auditory tube. X-rays and MRIs can determine the presence of inflammatory diseases, lesions of joint tissue or neoplasms; An ultrasound is performed to determine the condition of the hearing organs. In case of hypertension, blood pressure and ECG measurements are required. In the absence of physiological changes leading to tinnitus, consultation with a psychotherapist is necessary.
Common diseases that cause pain in the throat and ear
| Pathology | What is it characterized by? |
| Diphtheria | An acute infectious disease that develops as a result of exposure to bacterial agents. It is manifested by the development of fibrinous inflammatory processes in the area where the latter is introduced. Most often these are the upper respiratory tract, bronchi or oropharyngeal mucosa. |
| Measles | An acute infectious viral disease, manifested by the appearance of a rash on the skin, fever and pain in the throat, radiating to the ear. Its complication is often otitis media, which also causes pain. |
| Scarlet fever | Acute infectious processes that begin with a sore throat and are characterized by primary damage to the oropharynx, as well as pronounced intoxication. |
Treatment
It is clear that due to various reasons for the appearance of noise, treatment methods can vary significantly in each case. If the clicking in the ears is caused by the presence of wax plug, it is removed in a hospital setting. In the presence of infection, complex antimicrobial therapy is carried out - antibacterial or antifungal drugs, antihistamines (Diazolin, Suprastin, Loratadine) and vasoconstrictors (Otrivin, Naphthyzin, Polydexa), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Ibuprofen). In case of severe muscle spasm, muscle relaxants (Drotaverine, No-Shpa) are prescribed. For lesions of the jaw joints, it is recommended to take chondroprotectors (Glucosamine, Chondroitin).
The accumulation of fluid in the inner ear requires the prescription of antipsychotics (Aminazin, Triftazin) to normalize the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and diuretics (Diacarb, Veroshpiron) to reduce the level of edema. Pneumomassage of the eardrum, performed by an otolaryngologist, is also indicated. Tinnitus with hypertension requires treatment of the underlying disease. To normalize blood pressure, beta-blockers (Anaprilin, Metoprolol), sedatives (Persen, Novo-Passit), ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Lisinopril, Ceronapril), calcium blockers (Nifedipine, Manidipine), diuretics are prescribed.
If tinnitus reduces the patient’s quality of life, along with drug therapy, the use of psychological techniques may be recommended to reduce the severity of subjective perception of noise.
The reception is conducted by specialists
Kirillov Evgeniy Sergeevich
Audiologist, otoneurologist
Cost of services
Initial consultation with an audiologist
1200₽
Repeated consultation with an audiologist
1000₽
Other causes of sore throat and ear pain
In addition to sore throat and ear pain, all of the above inflammatory pathologies have one more common symptom: increased body temperature. However, there are other reasons for which pain symptoms occur, and they are not associated with inflammation. Therefore, there is no elevated temperature with them or occurs only when the process is neglected.
| Initiating factor | What is it characterized and manifested by? |
| Traumatic injuries to the mucous membrane | Pain can occur due to a burn (thermal or chemical), ingress of a foreign body, or mechanical impacts. |
| Neoplasms of benign and malignant etiology | Benign and malignant neoplasms of the larynx are a fairly rare phenomenon that can make it difficult to eat and cause pain. Requires seeking professional medical help. |
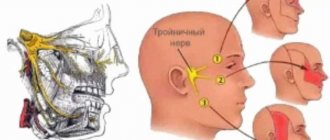
Ear pain with pathologies of other organs
When ear pain is directly related to diseases of the hearing organ, diagnosing and treating ear pain in adults is usually not difficult. It is much more difficult to help adults with ear pain if there are no visible pathologies upon examination. In such situations, we talk about otalgia - a condition when there is ear pain, but there is no inflammation.
Diseases that cause otalgia include:
- mastoiditis;
- This is an inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone, located behind the auricle; as a rule, the disease develops as a complication after otitis).
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint located behind the auditory canal;
- This joint can be subject to pathologies such as arthritis, arthrosis, dislocations, which leads to pain in the hearing organ.
- dental diseases;
- problems with the spine;
- inflammation of the pharynx (acute tonsillitis, pharyngitis, peritonsillar abscess);
- oncological diseases of the pharynx;
- sinusitis;
- neuralgic pathologies;
- intracranial tumors.
Treatment of sore throat and ear
To relieve a patient of a sore throat, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause that provokes it. CELT specialists conduct comprehensive diagnostic studies that eliminate the risk of error. For this, the patient is prescribed to undergo general laboratory tests, bacterial culture, X-ray and pharyngoscopy. Treatment tactics are developed based on the results obtained and the patient’s individual indications.
| Pathology | Treatment |
| Lymphadenitis | The acute form is treated conservatively: taking antibiotics and vitamins, as well as UHF. The purulent process is opened and drained. The chronic form requires elimination of the underlying disease, which provokes inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes and pain. |
| Rhinitis | The acute form is treated with medications, heat treatments and antibiotics if a bacterial agent is identified. As for chronic, it requires the use of astringents, antibacterial ointments, instillation of antiseptics and UHF. According to indications, cauterization of the nasal mucosa or cryodestruction is performed. |
| Sinusitis | Treatment is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and ensuring the outflow of purulent masses from the paranasal sinuses. The latter allows you to eliminate pain. The patient is prescribed antibacterial or antiviral drugs, and a maxillary sinusotomy is performed according to indications. |
| Tonsillitis | Treatment tactics are selected depending on the form and stage of the disease and provide an integrated approach. In the process, local procedures and drug treatment with the use of immunostimulants and immunocorrectors are used, which reduces pain and improves the general condition of the patient. Surgical treatment is aimed at removing the tonsils and is carried out according to indications if lymphoid tissue has been replaced by connective tissue. |
| Otitis | Treatment depends on which part of the hearing organ is affected. It is possible to use antiseptics that are injected into the ear canal. In addition, warm compresses, physiotherapeutic procedures, and the use of topical anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended. If the above does not give the desired result, the eardrum is pierced to ensure the drainage of pus. This automatically reduces pain and the patient feels relief. |
| Pharyngitis | It is important to eliminate the factors that provoke the disease. The patient should avoid consuming foods that can cause irritation to the mucous membrane. If a bacterial agent is detected, antibiotic therapy is administered. Local treatment involves rinsing with antiseptics and inhalation. |
Having decided to undergo a course of treatment for chronic pain in the throat and ear at CELT, you will have an appointment with doctors of the highest category and candidates of medical sciences. They will help you get rid of unpleasant symptoms by eliminating the cause of their development. You can make an appointment with them online or by contacting our operators.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Otitis
Do people's ears often hurt?
Inflammation of the middle ear - acute otitis media (AOM) - occurs in up to 62% of children already in the first year of life!!! During the first five years of life in the United States and Western Europe, more than 90% of children experience at least one NDE, which means we need to know how to help ourselves and our children with the development of such a frequent and unpleasant disease.
What is the reason?
No doctor will tell you with certainty what is the cause of otitis media. It is believed that this is more often an infectious disease that can be caused by a virus, bacteria or fungus. This can also be a manifestation of an allergic reaction and occur for other reasons. Otitis is a frequent companion to acute respiratory infections, especially with a severe runny nose. Snot, flowing down the back wall of the pharynx, carries the infection into the auditory tubes, and through them it enters the middle ear. This is how inflammation occurs.
Has your ear blown?
It is a common belief that your ear can hurt if you blow into it! Can't inflate in the ear. Otitis is not a contagious disease and does not occur from wind and cold. It cannot be prevented by regularly wearing a hat or wrapping the ear. The middle ear is completely isolated from the external environment by the eardrum, which does not allow air or bacteria to pass through. The infection enters the middle ear from the nasopharynx, since the middle ear is connected to the nasal cavity by a hollow cartilaginous tube - the Eustachian tube.
Different otitis media: AOM or ESO?
Normally, the Eustachian tube opens when swallowing, and through it mucus from the inner ear flows into the nasopharynx (have you heard the clicking sound in your ears when swallowing? - the tube opens!). When there is inflammation in the nose, the mucous membrane of this tube swells and blocks the exit of mucus from the middle ear, the ear is bursting with accumulated mucus and sharp pain is observed, there is dizziness, vomiting, high (up to 40) temperature and even decreased hearing. But this is not yet acute otitis media, it is called acute exudative otitis (ESO), sometimes this otitis is called tubootitis or eustacheitis. It lasts on average 48 hours. It may go away on its own, or if the accumulated mucus becomes infected, it may be complicated by acute otitis media.
Are we eating antibiotics?
Otitis media is one of the leading reasons for the prescription of antibiotics, often unjustified. In France, more than 3 million and in the United States about 30 million prescriptions for antibiotics are written annually for acute otitis media.
But is it necessary to take antibiotics if otitis media occurs?
Not always. There are publications showing that antibiotics have no effect at all on recovery from otitis media. And why, one might ask, poison the body? But in a real situation, it is necessary to take into account the likelihood of developing complications of otitis, and these complications are as follows: perforation (that is, a hole) of the eardrum, adhesion (gluing) of the auditory ossicles or their destruction, brain abscess, meningitis. That is why it is impossible to unequivocally refuse antibiotics for otitis media.
But you need to know that:
Antibiotics are indicated only for AOM, but should not be used for EOM (tubo-otitis), that is, in the first 48 hours after the onset of the disease, if a person has a viral disease, i.e. ARVI, then antibiotics are even harmful, they will weaken the immune system and cause allergization. The diagnosis of AOM requires confirmation of the presence of effusion in the middle ear, that is, if, during examination by an ENT doctor, a hyperemic and bulging eardrum is noticed, in combination with acute local manifestations (severe pain) and general symptoms (dizziness, vomiting, temperature), then this is truly acute otitis media and here you need to take antibiotics (not for otitis, but for possible complications!)
We treat ourselves
How can we help ourselves or our child with acute pain in the ear when otitis suddenly begins? Firstly, you need to provide the child with bed rest and rest, especially if he has a fever. It is necessary to lay the child with the sore ear up and drop a few drops of Otipax there (if there was no perforation of the eardrum before!), give the child an anesthetic (Panadol, Efferalgan or Nurofen in syrup for children, in a dose appropriate to the age and body weight of the child ( according to the instructions), drop a few drops of a diluted solution of “dolphin” or aqua-maris into the nose (the previously fashionable vasoconstrictor drops give a temporary and not radical effect, and after them there is often a “recoil” effect - the nose becomes even more stuffy, so these remedies are without It is better not to use urgent doctor's recommendations!) and give the child to chew the child's orbit. Yes, yes, give him chewing gum! Let him chew it 4-6 times a day during the entire illness with otitis media. This will lead to the opening and cleansing of the auditory tubes, possibly and to a quick recovery. Chewing gum is so useful for runny nose and otitis media that there may be talk of an alternative to antibiotics! Xylitol (xylitol), a natural 5-hydroxy alcohol contained in chewing gum, has been shown to inhibit in vitro the growth of bacteria Streptococcus mutans and S. pneumoniae. Using chewing gum (5 times a day) with xylitol reduces the incidence of acute otitis media in children by 1/3! And of course, the child must be shown to an ENT doctor. After all, it is he who can, upon direct examination, determine what kind of otitis media a patient has - exudative or already moderate?! And better, earlier. If a doctor is not available, Otipax drops should be instilled every 15 minutes 3 times, and then every 2-3 hours, and then less often, 3 times a day. These measures often save you from otitis media in 1-2 days than waiting a long time for the doctor to come or for you to get an appointment with him. It is also useful to have a blue glass lamp at home (a regular blue light bulb 60-75 W) and screw it into a table lamp instead of the usual one to warm the child’s sore ear 1-2 times a day from a distance of 15-20 cm for 5 minutes for 7-8 days in a row. . If the measures indicated in this booklet do not help within 48 hours after the onset of acute pain, a doctor should definitely see the child! He will probably still have to take an antibiotic or undergo some kind of medical procedure.
How to avoid getting otitis media?
To avoid getting otitis media at all, you must not get a runny nose! Neither removal of enlarged adenoids (proven by research) nor antibiotic prophylaxis can prevent otitis media. Most often, otitis media occurs from improper nose blowing!
How to blow your nose correctly?
How to blow your nose incorrectly: they pressed a handkerchief over the child’s nose and said, “Blow!” He will blow, but only the entire infection will fly into the ears through the Eustachian tube. How to blow your nose correctly: do not pinch your child’s nostrils! No need to press the wings of your nose! Let him blow his nose once or twice like this (and just keep the handkerchief next to your nose, don’t touch your nose at all, wipe anything that might get a little dirty, gently wipe it off, for irritation under the nose for a long-term runny nose, use baby cream), and then you can blow your nose like this: one nostril was pressed, the child took in air with his mouth and blew his nose into the free nostril, then change the nostril. And if you immediately pinch the nostril or even press the wings of the nose, as many parents like to do when the child blows his nose, then he will probably suffer from otitis media.
An excursion into psychology
The human body, like a finely tuned musical instrument, sensitively reacts with every cell to changes in the psychological atmosphere around it. Children especially experience stressful moments in life with all their being. And there is an opinion that in those families where the child hears what he does not want to hear (swearing and screaming of parents, extremely emotional arguments between relatives, insults and insults, even “jokingly” inflicted on him or his mother, obscene expressions, swearing) Children suffer from ear diseases more often and more severely. Take care of your children, watch your speech and what the child hears. Don’t wrap your child up, toughen him up, develop him physically, teach him to keep his mouth closed, learn to rinse his nose yourself at home, and use antibiotics only as a last resort when it’s really necessary. Do not shift the concern about your future to the doctor, think about the health of your children yourself, and you will succeed!
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS - YOU MUST CONSULT A DOCTOR
First aid
If an adult’s ear hurts, then at home you need to relieve the acute pain yourself. Regardless of the intensity of the pain, the patient must insert a cotton pad soaked in boric alcohol. The following tactics are:
- Take painkillers if the pain is unbearable. Paracetamol or ibuprofen will do.
- Topical corticosteroids are used in the nose to relieve swelling of the mucous membranes and normalize ventilation of the ear canals. The condition improves after 10-20 minutes.
- If the pain does not go away, you can put ear drops in each ear, regardless of which ear hurts. The product is first warmed up in the palms.
It is necessary to avoid drafts, not to go outside unless absolutely necessary, and to avoid contact with water when washing your hair. Important to remember! You cannot make compresses, instill ear drops with an antibacterial effect, or warm up the area of inflammation if there is any discharge from the ear.