Pain in the jaw when opening the mouth, localized anterior to the ear canal (anterior to the ear) is one of the main signs of problems with the temporomandibular joint (see “TMJ dysfunction”), which provides a mobile connection between the lower jaw and the skull.
Pain in the jaw joint can have varying degrees of severity, intensify when opening and closing the mouth, and be accompanied by difficulty and sometimes impossibility of opening the mouth. May be accompanied by various “noise effects” in the joint area: clicking (see “Clicks when opening the mouth”), grinding, creaking (see “Crunching when opening the mouth”). And also tinnitus. But all these signs, if left unattended, can soon have quite unpleasant consequences for the patient.
During a direct examination by a specialist, you will be able to find out your exact diagnosis, as well as receive a referral for diagnosis or a treatment plan.
Table: how to figure out who to contact
| What's troubling? | Which dentist should I contact? |
| Bleeding gums/Teeth sensitivity | Hygienist or periodontist |
| Missing teeth | Orthopedist |
| Have crooked teeth/bad bite | Orthodontist |
| Tooth hurts / The wall has broken off / There is caries | Therapist |
| The wisdom tooth is painfully erupting / Swelling has appeared on the side of the cheek | Surgeon |
All dentists conduct an examination, consultation, draw up a treatment plan and perform a thorough diagnosis of the entire oral cavity. In modern dentistry, an integrated approach to each clinical situation is valued, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Diagnostics
On average, a diagnosis by an orthodontist takes 30 to 40 minutes, but can take several days. It all depends on the patient’s desire to take certain photographs. Standard procedures included in the diagnostic list:
- visual inspection;
- a panoramic photograph that allows you to see the full view of the jaws, including the roots of the teeth, wisdom teeth, and tooth buds;
- teleroentgenogram (TRG). It allows you to determine the cause of the anomaly, see the relationship of the jaws, and draw a conclusion about what treatment methods will be required;
- 3D scanning or taking impressions of the jaws, with the help of which the exact dimensions of the jaw are determined;
- photographing. It allows you to assess changes in the patient’s appearance and the dynamics of treatment;
- 3D analysis or computed tomography (CT). Required if the doctor suspects a non-standard tooth tilt or other complex problems;
- video recording that allows you to record functional disorders in movement.
Dentist-therapist
The main field of activity of this doctor: treatment and prevention of caries and its complications. What manipulations does:
- treatment of caries;
- endodontics (work in root canals) for pulpitis, periodontitis;
- root canal retreatment;
- chipped fillings, tooth walls;
- carrying out treatment using a microscope (treatment of caries, work in canals);
- providing assistance for acute toothache.
The therapist also conducts a thorough examination and can refer the patient to related specialists if he notices any pathology.
Causes of jaw pain not related to dental disorders
Neuralgia
When the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for the sensitivity of the face and oral cavity, is damaged, the pain is strong, sharp, reminiscent of the pain of pulpitis. Often patients with trigeminal neuralgia undergo unnecessary dental treatment with depulpation or tooth extraction, but the pain syndrome persists.
Sialolithiasis
Salivary stone disease is characterized by the formation of stones in the ducts of the large salivary glands. Since the salivary glands are located in the mouth, pain during their inflammation also affects other nearby organs of the oral cavity, in particular the jaw.
Sinusitis
When the mucous membrane of the maxillary cavity becomes inflamed, increasing swelling and accumulation of exudate cause pain spreading to the upper jaw area from the side of the affected sinus.
Otitis
Sometimes the symptoms of otitis media are similar to toothache. With inflammation of the middle ear, pain often radiates to the jaw. The pain is sharp, shooting, aggravated by chewing and swallowing.
Submandibular lymphadenopathy
Enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes is observed in diseases of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, stomatitis, and oncological tumors. Pain under the jaw is often accompanied by limited range of motion - it is difficult for the patient to bend and turn his head, or open his mouth wide.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Irradiation of pain into the lower jaw can be observed during an attack of angina and myocardial infarction. A characteristic symptom of coronary heart disease is burning, pressing pain behind the sternum. But with an atypical course of a heart attack, retrosternal pain may be completely absent, only reflected pain comes to the fore: in the left arm, in the neck, in the face, in the jaw.
Dental hygienist
A dental hygienist has a secondary professional medical education. A prerequisite for working as a hygienist is to successfully complete the course “Preventive Dentistry”. What does a dental hygienist do:
- professional oral hygiene;
- treatment of gums with the Vector device;
- whitening;
- provides training in proper oral hygiene;
- selection of personal hygiene products;
- deals with the prevention of gum disease in adults and children.
In short, the main area of work of a dental hygienist is the removal of dental plaque (tartar, plaque). It is important to see a hygienist every six months to maintain oral health.
Orthopedic dentist
Dental services include dental prosthetics. It is the orthopedic dentist who deals with all types of dental restoration using orthopedic structures. These include:
- crowns;
- bridges;
- veneers, lumineers;
- inlays, overlays;
- mouthguards, splints;
- temporary structures for long-term orthopedic treatment;
- removable and fixed dentures;
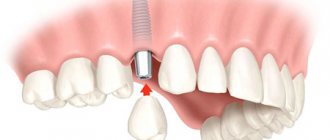
- prosthetics on implants.
How to treat arthrosis of the jaw?
Treatment for arthrosis of the jaw joint varies depending on the causes of the disease. Its purpose is:
- restoration of mobility of the lower jaw;
- suppression of degenerative and dystrophic processes in the joint.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes analgesics and recommends wearing a splint - an elastic, removable mouth guard that distributes the load on the jaw. The selection of an individual splint (based on an impression), palatal plate or other orthodontic device for arthrosis of the jaw joint is carried out for relaxation in case of muscle hypertonicity or maintaining a healthy position of the TMJ. If the splint is not enough, a specialist may prescribe a Botox injection. Then permanent dentures are created for the patient, which help support the joint affected by arthrosis and correct the bite. Also, with arthrosis of the lower jaw, selective grinding of teeth can be performed.
Treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint involves a moderate change in habits. Patients should avoid eating solid foods, frequent vocal exercises, and chewing gum. Therapy for arthrosis of the jaw joint requires lifelong limitation of mechanical loads and regular visits to the dentist or gnathologist. Preventive courses of physical and pharmacotherapy are carried out at least 2 times a year. It is important to minimize stress and physical strain. The further the disease progresses, the softer the food should be - until the patient switches to purees, cereals, soups and juices.
It is considered optimal to start treatment at stage 1 or 2. In advanced cases of arthrosis of the jaw joint, only surgical intervention can help the patient.
Osteoarthritis of the jaw joint - which doctor should I contact?
The first step if you suspect arthrosis of the jaw is to consult an orthodontist or gnathologist. They will give the patient a referral for an x-ray, and will also determine whether there are any malocclusions or dental contact problems. You may also need to consult a prosthodontist.
If the cause of the disease is primary diseases, in parallel with a specialized doctor, narrow specialists participate in the treatment of jaw arthrosis - for example, a rheumatologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, psychotherapist or otolaryngologist.
Drug treatment of jaw arthrosis
Treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint with medications is usually carried out in a hospital setting. At home, patients can take painkillers, use warming and analgesic local drugs, and also take chondroprotectors.
To relieve inflammation and improve jaw mobility, patients take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) intravenously or orally - for example, ketoprofen, ibuprofen, paracetamol, nimesulide. For topical use, ointments and gels are recommended - finalgon, nicoflex, voltaren, butadione and indomethacin. In the absence of allergies, preparations based on medical bile and bee venom are used. Muscle relaxants, such as mydocalm, help relieve spasm in arthrosis of the jaw joint.
For severe pain, in addition to glucocorticosteroids (hydrocortisone), injections of opioid analgesics are prescribed - for example, tramadol, trimeperidine.
If there are injuries or foci of infection in the body, treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint is accompanied by antibiotic therapy in the form of injections of cefazolin, metronidazole, cefuroxime.
For better regeneration of cartilage and synovial fluid, it is recommended to take chondroprotectors - for example, artracam, Dona or Movex.
Drug therapy for arthrosis of the jaw joint is carried out 2-3 times a year as prescribed by a doctor. The administration of drugs is often combined with physiotherapeutic techniques - for example, in the form of electrophoresis with novocaine, lidase and iodine, Trilon ointment.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of jaw arthrosis
Physiotherapy in combination with properly selected medications and orthodontic devices helps eliminate pain without surgery, even at the 3rd stage of arthrosis. Therefore, the following physiotherapeutic techniques are used to treat arthrosis of the jaw joint and rehabilitate patients.
- ultrasound (10-20 sessions);
- laser therapy (14 sessions);
- microwave therapy (UHF - 10-12 sessions);
- electrophoresis (10-12 sessions);
- phonophoresis;
- mud therapy;
- myogymnastics;
- massage of masticatory muscles;
- balneotherapy (including paraffin therapy and ozokerite);
These procedures improve nutrition of the affected joint, normalize metabolism and activate the processes of natural regeneration of bone and cartilage tissue. With fibrotic changes in tissues, physical therapy helps to soften them and increase the range of motion of the jaw. Also, this type of treatment relieves inflammation, has an analgesic effect and serves to prevent complications of arthrosis of the jaw joint.
Therapeutic exercise for arthrosis of the jaw joint
Therapeutic exercises for arthrosis of the lower jaw help maintain facial mobility, speech intelligibility, improve innervation of the affected area and reduce the impact of the disease on other organs and systems. With hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, it helps to stretch the ligaments and relax the jaw, and also strengthens the jaw apparatus. This promotes proper distribution of the load, and therefore slows down the progression and reduces the symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw joint. Myogymnastics does not replace wearing a mouthguard, but significantly enhances its effect.
- Press your tongue against the hard palate and allow your jaw to drop freely as you relax the muscles in your lower face.
- Place your thumb on the affected joint (in front of your ear) and, keeping your tongue against the roof of your mouth, place your index finger on your chin. Lower your jaw halfway, overcoming the gentle resistance of your index finger. Shut your mouth. Repeat 6 times, and then begin to lower your jaw completely (also 6 times).
- Raising your shoulders and chest, tuck your chin in so that a “double chin” forms under it. Hold for 3 seconds, then repeat (10 times).
- Place your thumb under your chin and gradually open your mouth completely, against the gentle resistance of your finger. Then grab your chin with your thumb and index finger and repeat the exercise - this time closing your mouth (10 times).
- With the tip of your tongue in the center of your palate, open and close your mouth.
- Grasp a small object with your front teeth and slowly move your jaw from side to side. Then repeat the exercise with back and forth movements. As your range improves and the exercise becomes easier, increase the thickness of the object.
Pediatric dentist
Treatment and extraction of teeth for patients under 18 years of age is carried out by a pediatric dentist. When working with young patients, the primary task is to find contact with the child and get him ready for treatment, because almost all children enter any medical office with fear. In addition, the children's doctor needs to tell the child's parents how to carry out home oral hygiene for the baby, what products to use, when the physiological change of teeth occurs, etc.
Maintaining dental health from a very early age is necessary for the normal formation of the dental system.
Maxillofacial surgeon
This specialist is needed for those whose bite pathology requires surgery. Usually this is a pronounced mesial bite or a combination of several disorders, especially with a pathological narrowing of the jaw. The operation itself is only one of the stages of treatment; in preparation for it and after it, you still need to wear braces to stabilize the occlusion (closing of the teeth) and improve the aesthetics of the smile.
Surgical correction of the bite: the jaws are given the correct shape, but the teeth still need alignment
Gnathologist
Not everyone has heard of this doctor, and this is no accident. This profession is very rare.
This specialist deals with pathologies of the temporomandibular joint. If the patient is bothered by clicking in the joint, pain when opening the mouth, tooth wear, discomfort in the joint when chewing, then it is necessary to contact a gnathologist to eliminate the pathology.
- Pavel
October 7, 2022 at 08:17Thank you for your article, I learned a lot of new things. I had never had any problems with my teeth in my life, so there was no need to understand the areas of dentistry. And now the situation has changed, the first signs of dental ill health have appeared, we have to figure it out. First, I’ll go to my city free dentistry, then maybe I’ll go to a private clinic. Thank you for the clarification
Administrator
October 10, 2022 at 01:37 pm
Hello, Pavla! We are glad that you found the information useful. We invite you to see our specialists if you need dental care.
Conclusions. Expert advice
After reading the material, you understand who an orthodontist-dentist is and why you need to visit him regularly. If we summarize what has been said, we can draw the following conclusions:
- the sooner you see a doctor with a problem, the better;
- It is not necessary to prepare for the visit, but if you tell your child in advance about which specialist you are going to, this will simplify the visit to the orthodontist and make it easier for the child;
- Treatment almost always takes a lot of time, but it gives results.