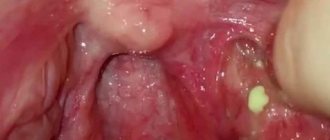
Tonsillitis is an infectious disease characterized by inflammation of the tonsils. The disease can have both acute and chronic forms. Chronic tonsillitis is diagnosed in 15% of children and 10% of adults. Another name for tonsillitis is tonsillitis, which literally translated from Latin means “squeezing”, “suffocation”. Indeed, the main symptom of a sore throat is a sore throat and discomfort when swallowing. The term "angina" is often used by both medical professionals and patients.
Classification of forms of tonsillitis (tonsillitis)
- I catarrhal form (the inflammatory process is manifested by redness and swelling of the tonsils).
- II follicular form (yellowish purulent dots appear on the surface of the tonsils - festering follicles).
- III lacunar form (liquid pus or purulent-caseous plugs form in the lacunae).
- IV fibrinous form (characterized by the formation of a single continuous plaque of a whitish-yellow color, which can extend beyond the tonsils, often occurs in people with reduced immune system function).
- AIDS, blood diseases, hunger, old age.
- V herpetic form (most often caused by adenoviruses, herpes simplex viruses, characterized by vesicular rashes on the back of the pharynx or soft palate, predisposed to ulceration).
- VI phlegmonous form (intratonsillar abscess) is a complication of acute tonsillitis (lacunary, catarrhal, follicular) or chronic tonsillitis, which is an acute purulent inflammation of the peritonsillar tissue.
- VII ulcerative-necrotic form (gangrenous form) - characterized by the formation of yellow-white blisters (ulcers) on the tonsils, in some cases the spots spread to the entire oral cavity and throat.
- VIII mixed forms (a variant of the disease in which colonization of lymphoid tissue occurs by several pathogens at once, as a result of the addition of a secondary infection or with a severe decrease in immunity).
Acute tonsillitis (common name - sore throat)
an infectious disease with local manifestations in the form of acute inflammation of the components of the lymphatic pharyngeal ring, most often the palatine tonsils, caused by streptococci or staphylococci, less often by other microorganisms, viruses and fungi. Sore throat is also called exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
The most common are vulgar (ordinary, banal) tonsillitis: catarrhal, lacunar, follicular, fibrinous, phlegmonous, herpetic and ulcerative membranous. In recent years, all types of tonsillitis have been called acute tonsillitis.
Catarrhal
Catarrhal tonsillitis develops acutely, the patient complains of a burning sensation in the throat, dryness, soreness, and then there is slight pain when swallowing. A clinical picture of astheno-vegetative syndrome is observed. The temperature is usually low-grade. Upon examination, the tonsils are hyperemic, somewhat enlarged in size, and in some places may be covered with a thin film of mucopurulent exudate. The tongue is dry and coated. There is a slight increase in regional lymph nodes. Typically, clinical manifestations disappear within 3-5 days.
Follicular
Follicular tonsillitis begins with an increase in body temperature to 38-39 °C. And the occurrence of severe pain in the throat when swallowing, often radiating to the ear. Depending on the severity of intoxication, headache, lower back pain, fever, chills, and general weakness occur. Most often, the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and their palpation is painful. There is hyperemia of the soft palate and tonsils, on the surface of which numerous round, somewhat raised yellowish or yellowish-white dots are visible. The duration of the disease is 5-7 days.
Lacunarnaya
Lacunar tonsillitis occurs with symptoms similar to follicular tonsillitis, but more severe. With it, yellowish-white plaques appear against the background of the hyperemic surface of the enlarged tonsils. The duration of the disease is 5-7 days.
Fibrinous
Fibrinous tonsillitis is characterized by the formation of a single continuous plaque of a whitish-yellow color, which can extend beyond the tonsils. This type of sore throat can develop from lacunar or proceed independently with the presence of a continuous film already in the first hours of the disease. In the latter case, an acute onset is characteristic with high fever, chills, severe symptoms of general intoxication, sometimes with signs of brain damage.
Phlegmonous (intratonsillar abscess)
Phlegmonous tonsillitis is relatively rare. Its development is associated with purulent melting of the tonsil area. The defeat is usually unilateral. The tonsil is enlarged, hyperemic, its surface is tense, and painful on palpation. On examination, a forced position of the head and enlarged regional lymph nodes, painful on palpation, are characteristic. Complaints of sore throat when swallowing, talking; headache, increased body temperature to 39-40 °C, symptoms of general intoxication. Pharyngoscopy: the tonsil is enlarged, hyperemic, its surface is tense, and painful on palpation. Characterized by trismus of the masticatory muscles, asymmetrical pharynx due to displacement of the uvula and tonsil to the healthy side. The mobility of the soft palate is limited.
Herpetic
Herpetic sore throat often develops in childhood. Its causative agent is the Coxsackie A virus. The disease is highly contagious and is transmitted by airborne droplets and rarely by the fecal-oral route. Herpetic sore throat debuts acutely, fever appears, the temperature rises to 38-40 ° C, sore throat occurs when swallowing, headache, muscle pain in the abdomen; There may be vomiting and diarrhea. Small reddish bubbles are visible in the area of the soft palate, uvula, palatine arches, tonsils and posterior wall of the pharynx. After 3-4 days, the blisters burst or resolve, and the mucous membrane takes on a normal appearance.
Ulcerative-membranous
The causative agent of ulcerative membranous sore throat is considered to be a symbiosis of a spindle-shaped bacillus and an oral spirochete, which often live in the oral cavity of healthy people. Morphological changes are characterized by necrosis of the surface of one tonsil with the formation of an ulcer. The patient complains of a feeling of awkwardness and a foreign body when swallowing, putrid odor from the mouth, and increased salivation. Body temperature, as a rule, is not elevated. There is moderate leukocytosis in the blood. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged on the affected side. The duration of the disease is from 1 to 3 weeks, sometimes lasting several months.
In more than 50%[1] cases of angina, the main etiological role belongs to group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, adenoviruses, herpes virus, Coxsackie Enterovirus, Vincent's spirochete, and Candida fungi.
Predisposing factors: local and general hypothermia of the body, decreased local and general immunity, trauma to the tonsils, the state of the central and autonomic nervous system, impaired nasal breathing, chronic inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, nose and paranasal sinuses[1].
Clinical manifestations
In acute primary tonsillitis, the clinical picture is manifested by symptoms of damage to the tonsils - varying degrees of pain in the throat when swallowing, signs of general intoxication, hyperemia, swelling of the tonsils, fibrinous-purulent plaque at the mouths of the lacunae, grayish-yellow plaque, under which superficial low-painful ulcers are found, regional lymphadenitis.
A sore throat begins with a sore throat and a sharp increase in body temperature to 39–40 °C (sometimes up to 41 °C). Sore throat is usually severe and sharp, but can also be mild. Lymph nodes enlarge. They can be easily felt under the lower jaw and cause pain. Sore throat can also occur at lower body temperatures - from 37 to 38 ° C, but with greater damage to the throat.
Sore throat often occurs with ARVI, especially of adenoviral origin, but enlarged lymph nodes are relatively rare.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic technique for recognition is examination of the pharynx - pharyngoscopy, as well as assessment of complaints and medical history. Also, to determine the type of infection, a smear of mucus or pus is taken from the tonsils. The biomaterial is sent for various types of tests according to the decision of the attending physician.
Complications
The most common complications of tonsillitis are acute otitis media, acute laryngitis, laryngeal edema, neck phlegmon, peripharyngeal abscess, and acute cervical lymphadenitis.
Treatment
Basic recommendations: bed rest in the first days of the disease, a non-irritating, soft and nutritious diet, vitamins, and drinking plenty of fluids.
In the treatment of sore throat, the choice of drug depends on the type of microbe that caused the disease. The type of drug, dosage and method of administration are determined by the attending physician.
- In the treatment of bacterial sore throats, various types of antibiotics and antimicrobial drugs of synthetic origin are used (depending on the sensitivity of the microbe and the patient’s response to medications), various local antiseptics, which are available in the form of a spray or aerosol, as well as tablets, lozenges and lozenges.
- In the treatment of fungal tonsillitis (this disease is provoked mainly by a fungus from the genus Candida), antifungal drugs are used. Fungal tonsillitis often occurs after long-term treatment with antibiotics.
- Treatment of viral tonsillitis involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as symptomatic drugs.
Often, for sore throat of any origin, the otolaryngologist prescribes various antiseptic and cleansing solutions for gargling, which are prescribed for use hourly. Recently, experts believe that gargling does not speed up the healing process, but may make you feel better.
At temperatures above 38 degrees, you can take antipyretics. For bacterial etiology of sore throats, in many cases an antibiotic is prescribed that is active against coccal flora (streptococci and staphylococci), the course is carried out for at least 7 days,
Prevention
To prevent tonsillitis, timely sanitation of foci of chronic infection (carious teeth, chronic tonsillitis, purulent lesions of the paranasal sinuses, etc.) and elimination of the causes of impaired nasal breathing are necessary.
Sore throat can be contagious (especially with scarlet fever), so the patient should be placed in a separate room, often ventilated and wet cleaned, and children and the elderly should not be allowed near him. A special container is provided for the patient, which is boiled or doused with boiling water after each use.
Gargling solutions:
- Furacilin solution (ready-made pharmaceutical solution does not need to be diluted)
- Chlorhexidine solution (for adults – without dilution, for children, one part of chlorhexidine is 2 parts of water)
- Chlorophyllipt alcohol solution (one teaspoon per 100 ml of water)
- Pharmaceutical propolis tincture (5-10 drops per 100 ml of water)
- Herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula, sage in a mixture or separately)
To ensure that rinsing is effective:
- The solution must be warm
- One rinsing episode should be at least 30 seconds in duration.
- After rinsing, it is advisable to refrain from drinking or eating for an hour.
It is necessary to gargle with a course (at least 3 times a day for 5 days)
- Fennel fruits -10.0
- Mint leaves – 30.0
- Chamomile flowers – 30.0
- Sage leaves - 30.0
Use 1/2 cup as a warm infusion to rinse for laryngitis, tonsillitis, and sore throats.
Infectious disease doctor Milena Krinitsina
UZ "22 - Yagorodskaya Polyclinic"
Complications of tonsillitis (tonsillitis)
Sore throat is one of those diseases that cannot be endured “on your feet”.
Indifference to your health if you have a sore throat is criminal; hoping for help from “folk remedies” and medicines from the home medicine cabinet of your friends and acquaintances is, to say the least, short-sighted. The question of treating sore throat is precisely the correct treatment. If the patient receives inadequate therapy for tonsillitis, complications may include various heart defects, kidney disease, joint damage, the transition of the inflammatory process to surrounding tissues with subsequent formation of abscesses, otitis (inflammation of the middle ear), laryngitis (inflammation and swelling of the larynx), as well as others diseases (tonsil abscess, paratonsillitis, phlegmon, meningitis, mediastinitis, purulent lymphadenitis, tonsillar sepsis, etc.).
Treatment of sore throat at GUTA CLINIC
Treatment of tonsillitis in our clinic is carried out comprehensively, drug therapy is prescribed individually, both antibacterial and immunomodulating, decongestants, antihistamines are used, as well as physiotherapy (rinsing, washing, irrigating the tonsils with various medications).
Treatment of abscesses is only surgical followed by rehabilitation therapy. Otorhinolaryngologists at GUTA CLINICS recommend that at the first symptoms of tonsillitis - difficulty swallowing, pain and discomfort in the throat, redness of the tonsils, fever, changes in sense of smell, taste, voice - contact a specialist. Don't let your sore throat progress and stay healthy!
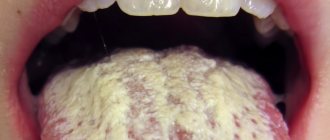
When should you see a doctor if you have a white coating on your tongue?
White coating on the tongue is a symptom, not a disease, so it is necessary to find out the cause of plaque formation from a specialist (especially if it is accompanied by discomfort, pain and burning in the mouth, the plaque persists for more than several weeks, ulcers form, chewing and swallowing are difficult), and undergo diagnostics and treatment of the disease causing such symptom. Depending on the problem, the doctor will prescribe antifungal drugs, local glucocorticosteroid therapy, antibiotic therapy and other treatment methods.
Often, a white coating on the tongue goes away on its own (for example, caused by ARVI) within a few weeks. Don’t forget to take proper care of your oral cavity: brush your teeth regularly with a soft-bristled brush, use a special scraper on your toothbrush to clean your tongue, floss, mouthwash, drink plenty of water, try to eat healthy and balanced, give up bad habits, eat regularly Visit your dentist for preventive examinations (at least once every six months) and treatment.