From this article you will learn:
- Temperature after tooth extraction
- Why does the temperature rise after tooth extraction?
- In what other cases does hyperthermia occur?
- Are fevers associated with tooth extraction dangerous for children?
- How long does the temperature last after tooth extraction?
- How to help yourself at home with a hyperthermic reaction
- When you really can’t do without a doctor
- How to prevent your temperature from rising
- What is the role of the clinic in the prevention of hyperthermic conditions?
Tooth extraction in an adult or child is stressful, an operation, and unpleasant sensations before and after the procedure. And when it seems that everything is over, the patient discovers that he has a fever. Reaction – fear, repeated stress, worries.
Heat
Hyperthermia can be a natural reaction to surgery and a sign of a pathological condition. What should a patient do and when should he urgently seek medical help?
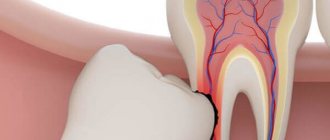
Why does the temperature rise after tooth extraction?
Hyperthermia is a natural reaction of the body to the action of pathogenic flora and viruses. They die at elevated temperatures. And the reason for visiting the dentist is precisely the infection of the oral cavity with pathogenic flora. The doctor’s task is to identify the causes of inflammation and stop its source.
Removal of a tooth
Reasons for tooth extraction:
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment of periodontitis;
- impassable root canals;
- mobility of the dentition in periodontal diseases;
- damage to dental canals;
- purulent processes - abscess, phlegmon.
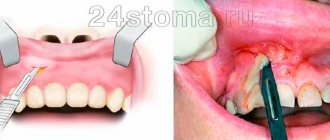
All diseases for which tooth extraction is one of the treatment methods cause infection with pathogenic flora. It is transmitted throughout the body by hematogenous route. Therefore, during treatment, and even more so during the removal of a molar, incisor or canine tooth, the wound may become infected.
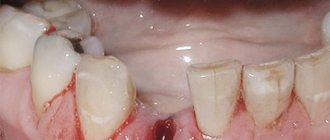
If a wisdom tooth has been extracted, it is usually accompanied by a large wound. Stitches are required. Due to the weakness of the walls of the blood vessels, a hematoma can form. Before the procedure, the surgeon must warn the patient about this.
Therefore, an increase in temperature is a normal reaction to injury. But only if hyperthermia lasts 1–2 days after surgery and does not rise above 38 degrees. If the temperature increases and additional symptoms are added, then this is a reason to consult a doctor and find out the causes of this condition.
If there is bleeding
After difficult removal of the figure eight, bleeding may occur. It needs to be installed, but it is not always possible to do this in a short time. In severe cases, the dental surgeon places sutures on the postoperative wound and performs tamponade. Then the patient is recommended to apply a cold compress to the cheek for some time. It helps stop bleeding and quickly relieve swelling.
It is very important to understand what causes bleeding after surgery. Among the most common reasons:
- arterial hypertension or a sharp one-time increase in blood pressure;
- the use of anesthetics containing adrenaline (such drugs help dilate blood vessels);
- injury to the wound with the tongue or foreign objects;
- taking medications that reduce blood clotting;
- performing heavy physical work shortly after the intervention.
If bleeding continues throughout the day, this is abnormal. In such a situation, it is recommended to make an appointment with a doctor.
In what other cases does hyperthermia occur?
A visit to a maxillofacial surgeon and surgery is a stressful situation. The temperature can rise even against the background of emotional experiences.
Possible reasons for the increase in temperature after molar extraction:
- ARVI, acute respiratory infections, relapse of tonsillitis - intervention in the oral cavity causes a decrease in immunity. Therefore, surgery can be a provoking factor in chronic sore throats, making the patient more susceptible to pathogenic flora. Rhinorrhea, sneezing, coughing, and pain when swallowing are added to hyperthermia.
- Alveolitis is an infection of the tooth socket. After its removal, a blood clot forms in the socket.
- Its task is to prevent wound infection. If the doctor's recommendations are not followed - eating, chewing on the operated side, frequent rinsing - the clot detaches and the wound becomes infected. The result is inflammation, pus, severe pain and an increase in temperature to pyretic values.
- Mistakes by a dental surgeon when removing a tooth include excessive tissue trauma, leaving fragments and parts of the root in the socket.
If any unpleasant symptoms appear after removal of a molar, incisor or molar, you should contact an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Are fevers associated with tooth extraction dangerous for children?
Extraction of a molar, incisor or canine for children is carried out if the baby tooth interferes with the growth of the permanent one or when it is completely destroyed. But this is a simple removal, since baby teeth are not held tightly and, often, pain relief is not even required. The wound is small and does not bleed.
Fever after tooth extraction
An increase in temperature to 37–37.5 degrees is a normal reaction of the body. If the readings on the thermometer are higher, then you need to consult a dentist. If pathologies in the oral cavity are excluded, you should undergo an examination by a pediatrician.
When is elevated temperature normal?
Very often, after a tooth is pulled out, a person experiences various unpleasant symptoms. They are due to the fact that the figure eight has long and winding roots. It is also far away and always difficult to get to. In the absence of free access to the crown, removal always turns out to be quite traumatic.
In the first two days after extraction of the unit, the following phenomena are considered normal:
- increase in body temperature to 37-38°C;
- swelling and redness of the socket;
- pain in the wound area;
- general weakness.
If healing proceeds without complications, these symptoms disappear within one to two days. Of course, swelling and soreness take longer to go away, but body temperature should not remain elevated for a long time.
How to help yourself at home with a hyperthermic reaction
After extraction of a molar, canine or incisor, the surgeon will give recommendations and explain possible reactions of the body. Therefore, the patient must follow the rules of oral care:
- Do not consume food or drinks for 2 hours after the procedure. Do not chew on the affected side of the jaw.
- Take antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor, rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions.
- If your temperature rises, you need to monitor your condition. It is allowed to take antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen as prescribed by a doctor. For adults - in tablet form, for children - in the form of syrups in dosages according to age or suppositories at night or during daytime sleep.
- Drinking plenty of fluids and rest are recommended. The patient should be in a ventilated area. There is no need to wrap yourself up or do any thermal procedures.
What you can and cannot do after tooth extraction
If the temperature does not subside on its own or the condition worsens, you should contact a medical facility. If it rises to 39 degrees or higher, call an ambulance.
When you really can’t do without a doctor
Any hyperthermia lasting more than 3 days is a reason to consult a doctor.
Symptoms after tooth extraction
Symptoms for immediate examination by a dental surgeon:
- increased pain 1–2 days after molar extraction;
- swelling of the gums, cheeks;
- gum hyperemia;
- discharge of blood and pus from the wound cavity;
- bad breath;
- enlarged lymph nodes under the lower jaw, behind the ears.
The dentist will conduct an examination. According to indications - cleaning and washing the wound, removing tooth fragments or roots, applying antibacterial drugs to the wound, suturing the wound.
After cleaning the wound, the inflammation subsides and the temperature drops. The doctor will prescribe additional treatment - a visit to wash the wound and apply antibacterial dressings, take antibiotics, rinse with antiseptics.
Inflammation of a wisdom tooth
The most problematic for most people are the third molars of the lower dentition, which are commonly called “wisdom teeth.” The upper “eights” relatively rarely become a source of serious problems, but the lower ones are a real headache not only for people, but also for dentists. Their correct treatment or removal requires the doctor to have a lot of experience, skill and, to some extent, wisdom, which once again confirms the accuracy of the popular name for eights.
Lower third molars: history of the problem
Why are the third lower molars so problematic, why does inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth occur in almost every second inhabitant of the planet? This is our payment for a comfortable lifestyle, in particular, for changed eating habits. Modern food is very different from what our ancestors ate even a few hundred years ago. Heat treatment made the food soft, making long chewing unnecessary. Children often swallow food without chewing it properly.
What is the result? As a result, the lower jaw does less work, and for the body this becomes a signal that its development can be slowed down, because there is no need for a massive mandibular bone. As a result, it becomes smaller than nature intended. The number eight, which is the last to erupt, has no room left for normal growth and development. Hence the typical problems - retention, dystopia, gum inflammation, almost inevitable pain during teething.
Alarming symptoms
The eruption of the figure eight is often accompanied by pain. But what exactly does a person hurt? Dental tissue, gums near the wisdom tooth, bone tissue of the lower jaw? Or do neighboring elements of the dentition hurt, on which the problematic third molar puts pressure?
The gums near the wisdom tooth hurt. The area of gum that covers the third molar has its own name. It is commonly called the gingival hood. Very often the molar cannot overcome the resistance of the hood and a problem arises. The wisdom tooth does not fully erupt (in this case it is called impacted), and the gums above it become inflamed. Inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth is called pericoronitis.
Pain is the first and main symptom of inflammation, but it is far from the only one. In many patients, the gums become swollen, and along with it, the nearby soft tissues of the cheek swell. As a result, the entire middle third of the face on the side of inflammation becomes swollen. Pain often occurs when swallowing and chewing food.
Redness of the gums is another clinical sign that unmistakably indicates the development of an inflammatory process. If you wait too long to seek help from a specialist, purulent inflammation develops, which indicates an infection. Discharge of pus from under the gingival hood and bad breath are symptoms of a purulent-inflammatory process. In the future, the infection can spread to neighboring tissues, including the jawbone.
Treatment Options
If your gums near your wisdom tooth are inflamed, it is better to immediately contact the nearest dental clinic or medical center where you will receive the necessary assistance. The first step should be x-ray diagnosis. If your dentist plans to treat you without an x-ray, consult another specialist.
An x-ray will show exactly how the third molar is growing and erupting. If it grows at an angle in the direction of the second molar, if it “lies” and literally crashes into the adjacent element of the dentition, it needs to be removed. Otherwise, there is a high probability of developing malocclusion, destruction of enamel and carious lesions of the second molar, as well as other problems with the lower dentition and the dental system as a whole.
It should be said that the situation described above with dystopia (abnormal position and direction of growth) is not uncommon. Dystopia of the figure eight occurs very often. If left unattended, sooner or later it will lead to other more serious problems requiring expensive, lengthy and tedious dental treatment.
Is it possible to do without deletion? Certainly. If the molar is growing in the right direction and is not pressing on its neighbor, there is no need for extraction. In this case, the dentist will choose the following algorithm of actions:
- Prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers and antihistamines to reduce gum swelling.
- The area of gum above the figure eight is removed to facilitate its eruption. Important! Removal is possible only if there is no infection.
- With the development of a purulent-inflammatory process, antibiotics are prescribed.
- In case of infection, the gingival hood is not removed, but dissected to improve the outflow of pus. After suppressing the pathogenic flora, gum excision is performed.
The cost of therapeutic treatment of gum inflammation near a wisdom tooth is low - about 2,500 rubles. Hood dissection is a painless procedure performed using local anesthetics. After a visit to the dentist, it is enough to follow his recommendations: take medications prescribed by the doctor, regularly rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions, apply dental gels with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects to the inflamed area of the gums.
Wisdom tooth removal
If the position and direction of growth are abnormal, removal of the third molar is indicated. Since it is a vestigial organ, its absence will not in any way affect the function of the dental system, while abnormal growth can lead to malocclusion and other serious problems.
Removing a wisdom tooth is a complex procedure. The figure eight has a powerful root system and is firmly anchored in the jaw bone. The roots are often curved, making the extraction process more difficult. However, dentists have an expression that a good doctor turns a complex extraction into an easy procedure for the patient, but an inexperienced dentist makes a simple extraction difficult and painful. It is very important to contact a qualified specialist!
The presence of a well-developed root system requires special preparation for removal. It involves drilling or crushing the area of bone that holds the roots. A good tactic is sawing the crown; fragments are much easier to remove than the entire tooth.
The cost of complex extraction of impacted and dystopic wisdom teeth varies from 6 to 12 thousand rubles. This price includes anesthesia benefits. The procedure is performed under conduction or infiltration anesthesia; most often, local anesthetics based on articaine (Ultracaine, Ubistezin) are used for these purposes. The extraction lasts 15-20 minutes, but if the doctor does not have the proper experience, the process can even take a couple of hours.
Is it painful to have a third molar removed? According to most patients, it is a little scary, but not painful at all. Psychological discomfort, of course, is present, but there is no pain. Patients who are terrified of dental procedures may be offered sedation or anesthesia, but this is extremely rarely necessary.
After removal
After the procedure, you must follow a few simple rules. First, you should abstain from eating for three or four hours. Smokers must abstain from smoking during this time. You can drink water within an hour and a half after the operation.
In the future, you need to eat soft food for one or two days. Food should not be hot or cold, ideally its temperature should be close to body temperature. Chew food on the healthy side to avoid washing out the blood clot. Formation of a blood clot in the socket is an important part of the healing process. To speed up the healing dynamics, ask your dentist to place one or two sutures on the gum above the hole before extraction. It doesn't hurt, but it's very effective.
Pain after removal cannot be completely avoided; it will make itself felt after the anesthetic wears off. Fortunately, postoperative pain is not severe and can be easily relieved with conventional analgesics. Doctors often prescribe Ketanov or its analogues in injection form to patients. Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection; this is especially true in the presence of a purulent-inflammatory process.
Regular rinsing with antiseptic solutions will help suppress the vital activity of pathogenic microflora. Chlorhexidine, which is sold in any pharmacy, is well suited for these purposes. Gels or creams with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects should also be applied to the surface of the gums. Please note that you need to rinse your mouth carefully so as not to provoke the blood clot to be washed out of the hole. The procedure is more similar to baths than to the usual rinses.
The body temperature remains elevated after removal. A normal reaction to surgery is weakness and general malaise. There is no need to worry about minor bleeding from the wound. After three to five days, the condition returns to normal, the bleeding stops, and the pain no longer bothers you.
You can learn more about the treatment of inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth by consulting a medical dentist.
How to prevent your temperature from rising
- After extraction of a molar, incisor or molar, the doctor’s recommendations should be followed. How to behave as a patient:
- do not eat or drink for the first 2 hours;
- do not chew on the affected part of the jaw;
- do not smoke – preferably for several days and definitely on the first day after the procedure;
- do not rinse your mouth without a doctor’s prescription - this helps wash out the blood clot;
- Until recovery, refrain from visiting public places - baths, saunas, procedures with a cosmetologist;
- do not touch the wound with your fingers or a toothbrush;
- take prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- come for examination at the appointed time;
- do not heat or rinse your mouth with alcohol-containing preparations, vodka, or alcohol.
A day or two after removal, the doctor will prescribe baths with antibacterial drugs. The liquid should be collected and held, but not rinsed.
When to sound the alarm
- It happens that removal turns out to be difficult. Then the doctor warns the patient in advance about possible complications and tells him to come for a follow-up appointment in the coming days. You should sound the alarm if:
- Symptoms of a viral disease are observed. Then the fever persists for longer than three days. Cough, runny nose, and throat congestion appear. Efficiency decreases.
- After one or two days the temperature does not decline, but on the contrary, begins to rise. If it stays at 38.5-39 degrees throughout the day, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
- Signs of inflammation in the oral cavity have become more pronounced. The gums are more swollen, accumulations of pus are visualized in the socket area, and there is no blood seal. This indicates complications.
Dry socket is especially dangerous. They talk about it if a dense blood clot does not form at the site of the pulled out tooth. The wound remains open to infection, which means that regenerative processes do not proceed correctly.
What is the role of the clinic in the prevention of hyperthermic conditions?
The clinic’s task is to create all conditions for the patient’s recovery and prevent the development of complications. What is required for this:
- The operation is performed under aseptic conditions by an experienced doctor in compliance with all standards and treatment protocols.
- The surgeon must explain to the patient the sequence of his actions, the rules of behavior after removing an incisor, molar or canine. Prescribe treatment and conduct follow-up examinations. If necessary, adjustment of prescriptions.
- If complications develop, provide high-quality and timely medical care.
Recovery after surgery depends on the quality of the surgeon’s work and the patient’s compliance with his recommendations. Hyperthermia after tooth extraction is a normal reaction of the body. You shouldn't be afraid of her. If the temperature has risen above pyretic values - from 38 degrees and above, then you need to urgently contact the clinic for examination and treatment correction.