Modern dentistry uses the latest technologies in the treatment of certain pathologies. Recently, electroodontodiagnosis (EDD) , with the help of which it is possible to determine the current state of all the nerve elements of the pulp of any tooth. The basic principle is based on the use of weak electric current. It should be emphasized that EDI gives an idea not so much about the state of the dental pulp itself, but rather characterizes the integrity and functionality of its sensitive nervous system. As is known, during various pathological processes in the hard tissues and pulp of the tooth, not only the histological structure and hemodynamic processes in the pulp change, but also degenerative processes occur in the nerve receptors, which is manifested by a change in their electrical excitability. At the same time, it must be remembered that changes in EOM indicators can occur under various pathological conditions of the periodontal tissues and sensory nerves of the maxillofacial region.
The use of electric current is based on the well-known fact that every living tissue is characterized by excitability, or the ability to become excited under the influence of a stimulus. The minimum strength of stimulation that causes excitation is called threshold. The use of electric current for diagnostic purposes has become most widespread, since its strength and duration are easily dosed, and it can be used repeatedly without fear of causing damage.
There are a number of basic rules when using EDI:
- all physiotherapeutic procedures should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor, who will actually write out the prescription;
- you must strictly follow all the requirements and instructions of the doctors that precede the first procedure;
- as a rule, EDI cannot be performed on a full or empty stomach; the best option would be 40-60 minutes after a meal;
- During the entire procedure, the patient is prohibited from talking, moving, sleeping, reading, etc.;
- After completing the diagnosis, the patient must rest for 30-40 minutes.
When is an electroodontometric study necessary?
Electroodontometry in dentistry is prescribed in the following cases:
- differential diagnosis of caries depth;
- diagnosis of pulpitis;
- identification of tumors on the roots of the tooth;
- injury to the maxillofacial region;
- inflammatory process of the maxillary sinus;
- inflammatory destructive bone disease;
- chronic focal or hematogenous anaerobic infection;
- jaw tumors of various origins;
- inflammation and damage to peripheral nerves;
- radiation damage to tissues;
- treatment with orthodontic appliances.
Technique and methodology of electroodontodiagnosis
1. Prepare the device for operation:
- connect the active and passive electrodes to the corresponding keys “A” and “P”;
- ground;
- connect to the network;
- press the “On” key (the signal light lights up) “50 or 200”.
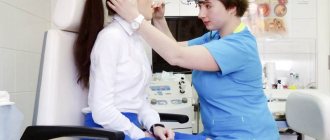
2. Prepare the patient for the procedure:
- make you sit comfortably;
- explain possible sensations during electroodonto diagnostics;
- put a rubber mat on the floor to isolate the patient’s and doctor’s chairs;
- prepare the tooth for examination.
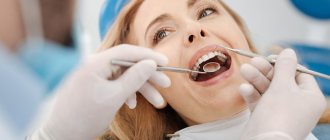
For examination, the tooth must be isolated from saliva and dried with a cotton ball in the direction from the cutting edge to the equator (alcohol or ether cannot be used). If there are dental deposits, they must be removed. If the teeth are carious, then it is necessary to remove the softened dentin and dry the cavity. For accurate diagnosis, if an amalgam filling is present, it is removed, because An amalgam filling is a good conductor of electric current, through which the electric current ramifies well. To avoid current leakage when testing the excitability of a tooth with a filling in contact with an adjacent filling, it is necessary to insert a celluloid plate smeared with Vaseline between them. Arrange the electrodes depending on the device used. Thus, when working with the OD-2m device, the passive electrode is placed together with a moistened pad on the back of the hand and fixed with a bandage; when working with the EOM-1 device, it is given to the patient’s hand.
The active electrode is placed on sensitive points:
- the middle of the cutting edge of the front teeth;
- the tip of the anterior tubercle at the premolars;
- the tip of the anterior buccal cusp at the molars;
- from the bottom of the carious cavity at 3-4 points.
3. Carry out the procedure:
— press the “50-200” keys (switching ranges), and the “50” or “200” signal light lights up. Start research on the 50 µA range. When working with the EOM-3 device, after placing the electrodes on the patient, the nurse smoothly and slowly moves the potentiometer handle to the right until a sensation appears in the tooth (warmth, burning, jolt), which the patient notifies with the sound “A-A”. The nurse registers the threshold current strength and releases the potentiometer knob, turning off the “Network” key.
When working with the EOM-1 device, after placing the electrodes, the patient presses the switch button and the pulses enter the patient circuit (the doctor’s hand holding the active electrode must be in a rubber glove). When minimal sensations appear in the tooth, the patient removes his thumb from the button and opens the circuit (before each study, the arrow returns to zero). The doctor records the threshold current on a milliammeter scale. Electrical excitability studies cannot be carried out from a filling adjacent to the gum; care must be taken to ensure that the active electrode holder does not come into contact with the mucous membrane. During the procedure, the teeth are periodically dried, because they are moistened by breathing.
The dental branch of medicine is developing quite actively; new technologies are constantly appearing for the treatment and diagnosis of certain pathologies. Recently, EDI has become increasingly popular in dentistry. This technique allows you to accurately diagnose and prescribe effective treatment. Let's figure out what electroodontodiagnosis (EDD) is, in what cases its use is indicated and whether there are contraindications to the procedure.
The essence of the procedure
This technique has been known in dentistry for more than 60 years, but recently its popularity has been increasing.
The method is based on measuring the level of resistance of oral tissues to electric current. The higher the indicators, the deeper the inflammatory process has penetrated inside.
This method uses the property of nerve tissue to be excited under the influence of electric current. During the procedure, the threshold excitation of the tooth receptors is determined.
The current at the moment of passing through the pulp does not damage it, as it is strictly dosed. Therefore, to carry out it is necessary to have the necessary knowledge. Normally, we can talk about the following indicators:
- For teeth with formed roots, electrical excitability ranges from 2 to 6 μA.
- For baby teeth, the indicators are within the same limits.
- At the moment of eruption of permanent teeth and the formation of their roots, electrical excitability is either greatly reduced or completely absent, and can amount to 200-150 μA.
- When the root is fully formed, the reading is around 2-6 µA.
EDI values in dentistry, compared with the norm, make it possible to judge the development of the pathological process.
For example, with the development of caries, electrical excitability drops to 20-25 μA; when the pulp is affected, the values are in the range of 7-60 μA.
If the reaction is 61-100 μA, then we can say that the death of the coronal pulp is observed, and the inflammatory process moves to the root part of the tooth.
For more accurate results, the doctor usually first sends the patient for X-ray diagnostics in order to know approximately the area with pathological changes. But this study does not give a complete picture of what is happening, so electroodontic diagnostics will be much more effective.
Rules for using EDI
Since the procedure involves the use of electric current, there are several rules for its use:
— Only a doctor writes out a referral for EDI and the entire procedure is carried out under his strict supervision and control.
— The patient must strictly comply with all recommendations and requirements of the doctor.
— Before the first procedure, thorough instructions must be given.
— EDI in dentistry is not recommended to be performed immediately after meals or on an empty stomach. The optimal time is 40-60 minutes after eating.
— During the procedure, you cannot get up, move or talk. Any movements may lead to errors in the results.
— To prevent electric shock, do not touch the device or try to independently adjust the dose of current.
— If during the procedure you feel severe pain, burning, or dizziness, you must inform your nurse or doctor.
— After the procedure is completed, the patient needs to rest for 40 minutes.
The purpose of electroodontodiagnosis
A doctor may refer you for EDI for the following purposes:
- Conduct differential diagnostics. EDI in dentistry indicators
- Determine the localization and severity of the pathological process.
- Choose a therapy method and monitor its effectiveness throughout treatment.
Indications of EDI in dentistry
The procedure is indicated in the presence or suspicion of the following pathologies:
- Caries of any location and degree of development.
- Periodontitis.
- Pulpitis of varying degrees.
- Periodontitis.
- Sinusitis.
- Neuritis of the trigeminal or facial nerve.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Actinomycosis.
- Neoplasm on the jaws.
- Injury to teeth or jaws.
- Radiation damage.
- Orthodontic therapy.
- Radicular cyst.
It can be noted that almost all pathologies of the dental system require the use of EDI in dentistry for an accurate diagnosis and prescription of effective treatment.
Contraindications for EDI
Any research and electroodontodiagnostics is no exception; they have their own contraindications for use.
They can be divided into relative and absolute.
The first category includes nervous agitation of the patient, which can lead to inaccurate results.
The presence of factors that lead to current leakage in the oral cavity:
- This is possible in the presence of pins, crowns, amalgam, or perforation of the wall of the memorized canal.
- If there is an obstacle to the passage of current, for example, an inlay or a plastic crown on the teeth.
- Incorrectly configured or faulty device for carrying out the procedure.
- The thickness of the contact layer is small.
- The procedure is carried out incorrectly.
Absolute contraindications include:
- The patient has a pacemaker.
- Mental disorders.
- Children's age up to 5 years.
- It is impossible to achieve complete dryness of the tooth.
- The patient cannot tolerate electric current.
Pros and cons of the technique
EDI (electroodontic diagnostics of the tooth) has its advantages:
— Ease of use.
— Availability of the method.
- Excellent information content.
— The doctor has the opportunity to carry out the procedure directly in his office.
But there are also disadvantages:
— It is important to carry out the procedure correctly.
— Take into account the individual pain threshold of patients.
— The procedure should be carried out taking into account age.
— We must take into account the characteristics of the device.
— Take into account the degree of root formation.
— The technique requires both material and time costs.
EDI device
Dentistry in its practice uses both domestic and foreign equipment.
Among the newest models, the following brands are the most popular: Gentle Plus. Digitest. Vitapulp. Pulptester.
There are popular Russian models: EOM-3. EOM-1. IVN-01. OD-2.
The first of the presented Russian models is not used very often, since an assistant is required to carry out the procedure, and not all doctors have their own nurse.
Preparing the device for the procedure
Before the procedure begins, the device must be prepared for use.
This stage includes the following manipulations:
— First of all, the active and passive electrodes are connected to the corresponding keys.
— Perform grounding.
— Connect the device to the network.
— Press the “On” button, when the device starts working, the signal light will light up.
After this, you can assume that the device is ready for use.
Preparing the patient for the procedure
After preparing the device, you need to deal with the patient:
Make him sit comfortably in a chair.
Explain what he may feel during the procedure.
For insulation, be sure to place a rubberized mat on the floor.
Prepare the diseased tooth for examination.
Tooth preparation is as follows:
- Dry the tooth using a cotton swab. Alcohol or ether should not be used for these purposes.
- If there are deposits on the teeth, they should be removed.
- If there is caries in the teeth, it is necessary to remove the soft dentin and dry the cavity.
- If there is an amalgam filling, it must be removed, since this material is a good conductor of current.
Place the electrodes in the required location. The passive electrode is attached to the back of the hand and fixed. The active electrode is fixed on sensitive points.
Methodology of the procedure
Once the device and patient are ready for EDI, the procedure begins.
Current is applied and the strength is gradually increased until the patient feels pain, tingling or burning.
The nurse or doctor records the threshold current and turns off the device.
EDI in dentistry is quite informative. The indicators allow you to accurately determine the pathology.
To check the accuracy of the results, a healthy tooth is also checked.
It is necessary to take into account during the procedure that there must be a closed circuit between the device, the patient and the doctor, otherwise you can get not entirely reliable results.
The specialist should not wear gloves during the procedure.
To obtain reliable results, measurements are made several times and the average value is taken. If the patient’s reaction changes slightly, then the results are reliable, but with large deviations, a false positive or false negative reaction can be suspected.
Read more on FB.ru: https://fb.ru/article/312484/chto-takoe-eod-v-stomatologii-kak-provoditsya-eod
The main reasons for false-positive reactions during EDI
1. Contact of the conductor/electrode with an extensive metal restoration (bridge, class II filling) or with the gum, allowing current to pass through the periodontium.
2. The patient's anxiety when he has not been correctly explained what to expect. An agitated, nervous or fearful patient may raise their hand as soon as they think the device is on or when asked if they feel anything.
3. Wet (colliquation) necrosis of the pulp. (Current may pass through the periodontium and the patient may slowly raise his arm at near maximum readings.)
4. Lack of isolation from saliva.
Electroondometric diagnostic procedure
Before the electroodontic diagnostic procedure, the doctor must explain to the patient the essence of the method and the purpose of its use, warn about possible unpleasant sensations and describe the technique. The patient must understand what actions he needs to perform when a pain signal occurs. An important condition for using the device is its disinfection and sterilization.
Electroondometry stages:
- Preliminary cleaning of teeth from plaque and stones to obtain a more accurate result.
- Attaching a neutral electrode to the patient. It may take the form of a part of a diving apparatus hose. The electrode does not touch the area being analyzed.
- Drying the tooth with cotton swabs and separating it from saliva with napkins or gauze.
- Applying a conductor gel to the active electrode for better contact with tooth enamel. A cap can act as a conductor, which must first be moistened.
- Place the electrode on sensitive teeth and turn on the current supply. Monitoring by the doctor to ensure that the mucous membrane does not come into contact with the active electrode.
- If pain occurs, the patient gives a hand signal to the dentist. At this moment, the current supply stops, and the result obtained is recorded.
- Repeat the procedure to obtain the most accurate data.