An ordinary light filling, which a dentist places on a treated tooth, performs three important functions at once: it restores the shape and damaged surface of the tooth, protects it from destruction and penetration of dirt, bacteria and food debris, and, finally, restores its aesthetic appeal. The ideal filling is strong and invisible, matching the enamel.
Therefore, staining a filling is the same defect as losing it, that is, it requires going to the dentist and replacing the filling, or polishing and cleaning it. Let's consider under what circumstances the filling is painted, and in which cases what needs to be done.
Reasons for color change
Have you noticed that the filling on your tooth has darkened? Several factors could have contributed to the color change.
- Consumption of coloring products. A newly placed filling can become darkened by strong tea, black coffee, chocolate, red wine, grapes, and concentrated fruit juices. The composite can also become colored when consuming carrots, beets, blueberries, cherries, and carbonated drinks with dyes.
- Smoking. Tobacco smoke causes resins, plant alkaloids, and organic acids to settle on restored teeth, causing them to acquire a yellowish or brown tint.
- High levels of fluoride in water and food. Drinking low-quality water and foods high in mineral content can cause multiple stains on your teeth.
- Insufficient oral hygiene. If you don't clean your teeth well, stains will remain on them and bacterial plaque will accumulate. This can lead to secondary caries.
What to do if the filling is evenly colored
If, some time after treatment and filling of a tooth, you suddenly discover that the filling has changed color - it has become pinkish or yellowish, or simply darkened - in most cases this means one thing: you forgot about the doctor’s instructions and still ate some kind of coloring eating too early. A newly installed filling, unfortunately, is susceptible to staining, and if you dined on something with a high content of dyes, it may change color.
How to fix:
Contact a dentist who will polish and clean the filling. Most often, the top stained layer will be sanded and the filling will become lighter again.
In addition, old fillings can also become stained, but for a different reason. Modern fillings are made from a composite material that is most suitable for dental purposes in composition and function. It has only one drawback: due to frequent temperature changes (consumption of hot and cold food), this material expands and contracts again. These are microscopic changes, we don’t feel or see them, but microbes and dyes can still get inside the filling this way.
How to fix:
The dentist, depending on the situation, will suggest either replacing the filling (if it is very old and no longer performs basic functions), or will be able to polish it. But replacement is a more suitable option.
Types of darkening of restorations
Most often, fillings on teeth darken evenly. Fresh fillings may become stained in the first hours after placement if you consume coloring products. Old restorations are also subject to uniform discoloration:
- due to the effects of low and high temperatures,
- narrowing or expansion of the filling.
Less commonly, composite restorations darken around the perimeter. This occurs due to the fact that the filling material has not completely filled the carious cavity. Pathogenic microorganisms and food particles penetrate into a small crack, which leads to darkening and destruction of the filling.
Associated symptoms
In addition to blackening of the enamel, other symptoms may develop:
- The appearance of erosions, gouges, black spots or spots on the enamel.
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Mobility of the filling.
- Pain when pressing, tapping or chewing.
- Inflammatory process in the gums around the filling, bleeding of the mucous membrane, swelling. The appearance of bumps or gumboil in an advanced stage.
Changes in tooth color should not be ignored. This is a clear sign of a pathological process.
Why does the tooth turn black?
Crowns help restore the integrity of the dentition and maintain the structure of periodontal tissue. If before prosthetics the color of the unit was natural, and the transformation occurred subsequently, then the reasons for the darkening of the tooth may be
:
- Imperfect processing and unskilled treatment of a decaying tooth before prosthetics.
- Ignoring a crack in a ceramic crown. Especially from the reverse side, when there is no violation of visual aesthetics.
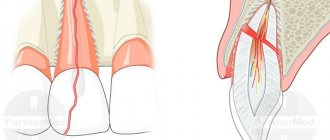
- Formation of a pocket between the gum and crown. Radical caries begins, bacteria and food debris get under the crown.
- The appearance of a gap between the crown and the ledge formed during tooth processing. Why does this happen? Perhaps the impression was taken incorrectly or the technician made an error. Or the patient refused a temporary crown, and minor deformation of the ledge occurred between treatment and installation.
Sometimes a patient has a metal-ceramic crown, and he is worried because of a dark stripe in the root zone of the chewing tooth. It is worth visiting a doctor, but for the most part, the reason is that the frame below is not covered with a sufficient layer of ceramics and over time begins to show through. The integrity of the prosthesis is not threatened. The defect is only aesthetic.
Another point:
the front teeth or molars may be over-prepared, under the gum. Soft tissues may react with recession, part of the enamel between the gum and the denture will be exposed and the process of destruction will begin.
Also the cause may be somatic ailments, metabolic disorders, chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
Can a dead tooth hurt?
- Added 11/12/2019
- Dental treatment
- No comments yet
With age, almost every person can find a dead tooth in their dentition, which, logically, should no longer provoke pain. In practice, it often turns out that over time, discomfort or pain of varying intensity appears. Can a dead tooth hurt, what to do in such cases, how to deal with the problem that has arisen - specialists can answer all these questions in detail.
Which tooth is called dead
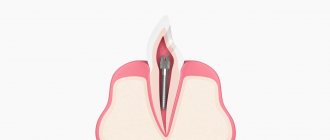
This concept appears more in the speech of ordinary people rather than specialists. Dentists call such an incisor, canine, molar or premolar pulpless. The pulp is a collection of nerve endings and blood vessels that carry nutrients that maintain the normal condition of bone tissue.
Pulp loss occurs in three ways:
- Planned during treatment. This is necessary if a pathological process occurs inside the pulp, the only solution to which is to remove the nerve. Using local anesthesia, the dentist opens the pulp cavity, removes the soft contents and fills it with filling material, after which the tooth is sealed again.
- Before installing a crown. In this case, depulpation is sometimes carried out even in the absence of direct indications. This is done to eliminate the risk of future crown removal for root canal treatment.
- The nerve and blood vessels decomposed after prolonged inflammation that was not treated. In such cases, a person periodically takes painkillers so that the tooth stops hurting, and after a while, when the nerve is already dead, the pills are no longer needed, because the pain stops.
You should not think that removing the pulp is a guarantee that nothing in this tooth will ever hurt again. The absence of a nerve and the supply of nutrients gradually lead to a deterioration in the condition of the dentin; it becomes not as dense and strong as it was before. The enamel does not receive the necessary minerals, which are normally transferred from the blood, which affects its condition. All this makes the dead element of the dentition more vulnerable to various diseases.
When to eat mono after filling?
People who have ever had a filling installed know that you can eat no earlier than two hours later. This time is enough for the material to acquire the required hardness and be well fixed in the tooth crown.
Modern materials differ from classical composites, so the question of whether it is possible to eat after a light filling is relevant. Dentists have different opinions regarding how long after a light filling can be eaten without the risk of damage. Some experts are of the opinion that after a light filling you can eat immediately. This is explained by the properties of photopolymers. The material hardens under the influence of ultraviolet rays, which means that after the procedure is completed, the filling should not be exposed to external influences.
However, the risk is not completely excluded. For complete confidence in the readiness of the material, and most importantly, its reliable fixation in the tooth. For this reason, most experts, when asked “how long not to eat after installing a light filling,” recommend refraining from eating and drinking for at least 2 hours.
A filling fell out: special reasons for women
In addition to the above factors, the destruction of fillings in women can accelerate for two reasons:
- menopause - due to impaired calcium absorption, bones and teeth lose strength;
- expecting a child - all nutrients are used for the development of the fetus, so pregnant women often lose fillings, and then their teeth very quickly collapse.
The fact that pregnant women cannot have their teeth treated is an unacceptable misconception. On the contrary, expectant mothers need to eliminate all foci of infection, including caries. The anesthetics used do not harm the child, the treatment is completely painless. However, it is advisable to carry out dental treatment in the second trimester of pregnancy.
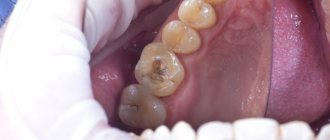
How is caries under a filling diagnosed?
When treating diseases of the teeth and gums, dentists often need to take x-rays. Unfortunately, when studying an x-ray, not every doctor pays attention to the condition of previously filled teeth and existing fillings.
Meanwhile, it is the X-ray data that allows:
- identify pathological changes in the area of contact between the walls of the treated carious cavity and the filling material;
- assess the degree of their development.
Recently, in Moscow clinics, the condition of fillings is assessed using a modern and even safer technique of visioradiography. Digital X-ray equipment increases the information content of diagnosing the condition of dentin under a filling and allows you to view all the details on a computer monitor. The examination is accompanied by significantly less radiation exposure to the patient compared to traditional radiography.
Primary, secondary, tertiary prevention of caries
Primary, secondary and tertiary prevention of caries refers to a number of measures aimed at preventing and correcting the consequences of the disease at various stages. This classification is also relevant in the case of dental caries under a filling.
| Prevention of caries | Description |
| Primary prevention of caries | Preventing caries before the disease spreads. This includes taking vitamins, correcting nutrition and maintaining a healthy lifestyle (all together this is endogenous prevention). Another subtype of primary prevention is exogenous. This includes professional hygiene with a doctor, the use of products to strengthen enamel and teeth, and undergoing fluoridation and fissure sealing procedures. |
| Secondary prevention of caries | Primary and secondary prevention of caries differ in that in the second case we are dealing with a formed carious cavity. Secondary prevention of dental caries is a complex of therapeutic and endodontic manipulations aimed at eliminating caries and preserving the tooth. |
| Tertiary caries prevention | Restoring a tooth that has been irreversibly damaged by caries using prosthetics or implantation. |
A filling fell out: what to do before visiting a doctor
- Make an appointment with your dentist.
- Brush your teeth twice a day, especially on the damaged side.
- Chew on the opposite side.
- After each meal, use mouthwash or rinse your mouth with warm water. You can use chamomile decoction or an antiseptic (furacilin, chlorhexidine).
- Do not touch the resulting cavity with a toothpick.
- Do not try to seal the “hole” with cotton wool or gum.
- For pain, take Nurofen (can be used for pregnant women and children) or another analgesic.
- There is no need to try to fill the cavity with a fallen filling.
Diagnostics
The task of diagnosis is to determine why the filling material and the dental elements underneath have turned black. Professional techniques will help identify the presence of caries and the extent of damage in order to make a final decision on removal or treatment.
Diagnosis consists of a visual examination, as well as an x-ray examination. If concomitant diseases of the oral cavity are suspected, additional diagnostic methods can be used.
What to do
You should not ignore the symptom in the form of pain from a dead element, as the pathology will only get worse. This can lead to tooth loss or even more serious complications. The patient should go to the dental clinic as soon as possible.
Before visiting the clinic, severe pain should be relieved with pills. Sometimes rinsing with a soda-salt solution at room temperature helps. Warming the affected area is strictly prohibited, as this will only increase the progress of inflammation and worsen your health.
After a detailed examination and questioning, the doctor will prescribe further examination. Most often, it is necessary to take an x-ray of the area where the discomfort is concentrated in order to view the condition of the pulp, canals, and detect internal carious cavities. Particular attention is paid to the condition of the root and the presence of microcracks in it, since such cracks always become a concentration of bacteria. Treatment may require removal of a filling or crown removal. In difficult cases, the tooth will have to be removed to get rid of the pathology, which can spread throughout the bone tissue and cause dangerous complications, such as osteomyelitis.
If the cause of the pain is deposits in the periodontal pocket that have led to periodontitis, the patient will undergo professional cleaning and a long course consisting of injection therapy, tablets, ointments, etc. In case of false pain, the doctor will refer the person for further examination to another specialist. This doctor will have to conduct a diagnosis, identify the cause and prescribe therapy that will relieve the patient of unpleasant phenomena.
False pains
In addition to the cases described above, there is so-called referred pain. This means that the source of the disease is not in the oral cavity, but sensations are transmitted through nerve endings to this place. At the same time, the brain forms the feeling that a dead canine, incisor, molar or premolar was starting to hurt.
Most often, reflected painful feelings arise from inflammation of the maxillary sinus, focusing in the area of the upper molars, premolars or canines. During the examination, an experienced dentist will immediately ask the patient a question about sinusitis.
A child's fillings fall out of his baby teeth
The destruction of fillings on baby teeth is associated with the following factors:
- Enamel and dentin in children are much weaker than in adults.
- The skills of proper brushing of teeth are not sufficiently developed.
- Frequent dental problems associated with dirty hands.
- Fidgets injure their teeth by falling and chewing hard objects.
- Children love to drink cola. With constant consumption of a drink containing phosphoric acid, teeth are destroyed and fillings fall out.
- Parents mistakenly refuse to install an inlay or crown on a badly damaged tooth for their child; instead, they insist on building it up.
What to do if a child’s baby tooth filling falls out? Re-filling is required. Tooth extraction is not advisable, as problems with bite may arise in the future. Leaving a damaged tooth without a filling is also not worth it. Repeated caries will negatively affect the condition of the rudiments of permanent teeth.