Plaque on the tongue itself is not a disease, it is a symptom that reflects what is happening in the body. There are types of plaque on the tongue that indicate a disorder in the functioning of internal organs. These types of plaque are called pathological.
Author:
- Sadykhov Rahim Agalarovich
ENT pathology expert
3.64 (Votes: 14)
Plaque on the tongue itself is not a disease, it is a symptom that reflects what is happening in the body. In this regard, the statement that language is a mirror of our health is quite true. A slight transparent or whitish coating is normal for a healthy adult. It is usually noticeable after sleep and can be easily cleaned with a toothbrush. However, there are other types of plaque that are not so harmless and indicate a disorder in the functioning of internal organs. These are pathological types.
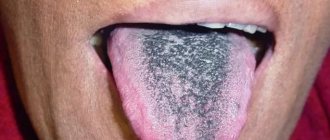
Pathological plaque can be different: the color ranges from thick white to black, dense and sticky in consistency, and has a bad odor. The structure of the language itself may also change. This is the first signal about the onset of the disease, so if you notice uncharacteristic changes in the appearance of your tongue, consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis. Indeed, in this case it is necessary to identify the root cause of this unpleasant manifestation and quickly begin to treat the underlying disease.
Properties of plaque
In order to competently organize independent monitoring of the condition of the tongue to identify signs of incipient diseases on its surface, you need to know what factors and indicators you need to focus on.
Blue coating on the tongue - reasons
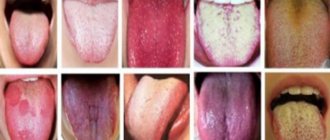
- The color has a fairly wide range of variations: transparent, white, yellowish, brown, gray. A red, green, crimson, or black tint may also appear. In children, it often turns out that the bright color was caused by a felt-tip pen that was in the mouth. It could be a caramel cockerel, a drink, or chewing gum. Therefore, before you panic, trying to understand why the child has a blue tongue, it is necessary to analyze the diet preceding this event. Adults experience color changes after drinking coffee, and smoking also contributes to this.
- There are several different types of plaque depending on the texture:
- dry;
- homogeneous;
- wet;
- oily;
- dense;
- loose.
- Sediment thickness is one of the key parameters. If upon visual examination it turns out that the plaque has increased in intensity and the pinkish lingual surface is practically not visible through it, control over the condition of the body should be strengthened. If the picture persists for 24 hours, it is advisable to apply for an appointment for examination.
- Localization of a spot of clearly defined deposits on a certain area of the tongue makes it possible to determine the location of the pathological focus in the body.
- The ease of removing plaque shows the degree of its pain. The normal translucent layer is peeled off during morning hygiene measures and does not appear throughout the day. Deposits that appear due to malfunctions in the functioning of specific systems are not completely removed, but after some time they become even thicker and acquire a color tone characteristic of the underlying disease.
The plaque in a healthy person is transparent and whitish in color. It does not block the view of the tissue of the tongue, is easy to clean, and has no odor. May be slightly yellowish in winter.
Associated symptoms of pathology
If the organ necessary for conversation acquires a specific tone, then most often the baby will additionally exhibit the following symptoms:
- Swelling in the mouth and face;
- Specific secretions;
- The presence of cracks, weeping ulcers;
- Soreness in the mouth when talking or eating;
- There are pimples, growths, and bumps on the surface.
If, when sticking out your tongue, not only a blue tone is visible, but also additional signs of illness, such as an unpleasant odor, then it is recommended to immediately consult a pediatrician. There is no need to prolong the baby’s condition until it becomes critical. It is better to start treatment at the first symptoms.
Reasons for the formation of blue plaque
It is advisable to collect and analyze all cause-and-effect manifestations that allow us to solve the problem of why a person’s tongue is blue, in order to notice important signals in time. This shade may appear if there is trouble in the heart area. The localization of this color on the lower surface indicates circulatory disorders aggravated by cardiopulmonary failure.
What to do if a blue coating appears on the tongue
A bluish tint on the tongue appears with scurvy. It may also reflect insufficient blood circulation. For a specialist, this may be evidence of poisoning by mercury or other heavy metals. If a blue coating on the tongue suddenly appears on the edges of the tongue located in front of the pharynx, the reasons lie in the kidney area. This kind of indicator can warn of a serious illness. Blue-black spots disappear only after the functioning of the adrenal glands in producing hormones is normalized.
The bluish upper plane becomes an accurate sign of the onset of the development of cardiovascular failure without the presence of other symptoms such as pain, a feeling of oppressive heaviness, and weakness. This will allow you to carry out a set of preventive measures to prevent a heart attack.
Diamond-shaped glossitis
With a disease such as rhomboid glossitis, the posterior portion of the mucous membrane of the tongue is affected. In this case, there is a slight compaction and a change in the color of the affected area to bluish. The disease is usually asymptomatic, more often in middle-aged male smokers.
Symptoms of a disease such as anemia (lack of iron, folic acid, vitamin B12 in the blood) are a blue tongue and pale skin.
With cyanosis, which causes a bluish tint of the skin and mucous membranes due to a reduced level of oxygen in the blood, a change in the normal color of the mucous membrane of the tongue to blue is also observed. There are two types of cyanosis:
- Central. Bluish discoloration of the lips, tongue, conjunctiva.
- Peripheral cyanosis. Bluish discoloration of the skin of the hands or feet, as well as nails.
Peripheral cyanosis is a local change, while central cyanosis indicates the presence of diseases of internal organs, such as cor pulmonale (changes in the right parts of the heart - their increase due to increased blood pressure), hypoxemia (low oxygen content in the blood due to circulatory disorders).
These diseases are caused by chronic disorders of the respiratory system, which increases or provokes heart failure.
In addition, blue tongue can occur in patients with renal failure (pathology of the kidneys with impaired formation and excretion of urine).
As you understand, you should not self-medicate and you must promptly seek help from your attending physician, who will make the correct diagnosis and select treatment for you.
Types of plaque that appears on the tongue
The variety of plaques that appear on the lingual surface has its own explanation, based on their characteristic outlines, color shades, and localization.
- The entire tongue is covered with a dense whitish coating with a simultaneous increase in temperature - an infectious disease.
- White deposits appeared in the middle of the tongue with the simultaneous appearance of cracks on the sides - pathological changes in the intestines or stomach. At the first manifestations, it is advisable to follow an easily digestible diet without fatty and salty foods. If you feel pain, you should immediately undergo an examination and obtain medical advice.
- Deposits with a white tint in the anterior area are pathological manifestations in the respiratory system, one of the causes of which may be smoking.
- White spots of deposits all over the tongue are a fungal infection that occurs from the development of dysbacteriosis. Often a consequence of uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- The presence of a spotted plaque of red and white color is an alarming signal, since the symptoms of scarlet fever often appear. Modern medicine has effective methods for curing this insidious disease; the main thing is to seek help in time.
- The yellowish tint of deposits in small quantities should not cause concern. But with their significant thickness and intensity, we can draw a conclusion about possible inflammatory foci of the gallbladder. If at the same time you begin to worry about pain on the right side under the ribs, you should be examined to diagnose cholecystitis.
- A gray tint of plaque indicates problems in the gastrointestinal system, including increased acidity due to malfunctions that lead to dehydration and disruption of the microflora.
- The transformation of plaque into a brown crust can warn of food poisoning. If there are few deposits, it is worth analyzing the diet to identify products that can color them brownish (chocolate, coffee, cocoa, strong tea). A non-disappearing plaque like this may indicate dysbacteriosis.
The black color of the deposits should alert you, as this may be a sign of the disease entering a critical phase.
Visit to the veterinarian
At the appointment, the veterinarian examines the four-legged animal, listens to its chest and checks its heart function. To do this, he uses the following research:
- auscultation, detecting extraneous noise;
- pulse oximetry, which measures the degree of oxygen saturation in the blood;
- urine and blood tests to detect concomitant disorders;
- ECG, which determines heart rhythm;
- Ultrasound and x-rays that reveal pathological changes inside the lungs and heart.
The doctor may supplement the standard list with pleural puncture, bronchoalveolar lavage, or other studies. The final amount depends on the difficulty of identifying the main cause of the ailment.
Causes of plaque in a child
Daily examination of the internal lining of the oral cavity should become a mandatory procedure. A light thin whitish layer on the tongue that disappears after hygiene procedures or eating is normal. If the whiteness does not disappear during the day, and the layer of plaque thickens, it can be assumed that the baby has a common fungal infection, usually called thrush.
Why is there a blue coating on the tongue?
If this disease is not treated promptly, painful ulcers will develop, which will make the child worry and cry. Whitish rashes also appear during colds, disappearing after recovery. Indigestion and vomiting paralleled by a whitish coating should alert parents and prompt them to immediately obtain a qualified medical opinion, as this could be gastritis.
A child’s blue tongue requires special attention, one of the key indicators that can reflect a number of pathological problems in various important sectors of the body:
- respiratory system;
- heart (angina pectoris, arrhythmia);
- circulatory system;
- kidneys
Babies who cannot yet speak cannot express the discomfort that arises from incipient diseases, and parents do not always know how to correctly identify the child’s crying as a consequence of the pain experienced. Therefore, any signal should serve as the beginning of close observation and, if deviations are detected, immediate contact with doctors. Often, a blue tongue in an infant is associated with disorders of the nervous system, accompanied by convulsions and disruptions in the functioning of the cerebral circulation.
Therapeutic diet
Regardless of what the cause of the cyanotic organ of taste is, the first thing you need to do is normalize your diet. The following should be excluded from the diet:
- food from fast foods,
- fatty meats (lamb, pork, duck),
- spicy and salty,
- marinades and smoked meats,
- carbonated drinks,
- alcoholic drinks,
- flour and sweet,
- mushrooms.
You need to eat often, but little by little. Make sure that the intestines are emptied in a timely manner. You need to drink at least two liters of still water per day.
The diet menu should include the following products:
- vegetables (except legumes),
- lactic acid,
- vegetarian soups,
- porridge (wheat, rice, buckwheat),
- non-sour fruits and berries,
- dietary meat (rabbit, turkey, chicken breast).
Ways to cleanse your tongue
To clean the surface of the tongue from the plaque that forms, it is not necessary to use complex techniques. Regular, affordable devices will do.
- The toothbrush may not have a special rough lining on the inside, oriented to directly carry out a thorough cleansing of thin normal deposits while simultaneously massaging the tongue. It is enough to walk with medium soft bristles with or without antibacterial paste in the direction from the root to the lips, as well as across the tongue to grab the side surfaces.
- You can purchase a special scraper. It is usually made of plastic, although metal or wood products are also available. Some scrapers are supplemented with special brushes.
If necessary, use reasonably accessible devices, for example, a teaspoon. You can take a bandage, wrap it around your finger, or use a clean towel or textile napkin.
Tongue hygiene is carried out only after teeth have been brushed. The movements of the scraper are directed only from the root of the tongue to its tip. First, the side with the brush is used, and then massage procedures are performed with the hard part of the device.
Blue coating on the tongue - reasons
Blue coating on the tongue
What to do if a coating appears on the tongue
Blue surface on the tongue What to do if a blue coating appears on the tongue
Dark coating on the tongue Why is there a blue coating on the tongue
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
It is recommended to avoid foods that are too hot, cold, hot or spicy. You should eat soft foods that do not injure the tongue, preferably stewed, boiled, steamed. The best option is a diet that includes purees, slimy porridges, pureed soups. Before and after meals, you need to rinse your mouth with weak solutions of chlorhexidine and potassium permanganate or a solution of furatsilin. For severe pain, the surface of the tongue can be lubricated with local anesthetics.
Conservative therapy
An important part of the treatment is the sanitation of the oral cavity, and, if necessary, the replacement of dentures and orthodontic structures. The list of therapeutic measures is determined by the nature of the pathology:
- Glossitis
. Rinses and applications with anesthetics are indicated. For intense pain, lubrication with a mixture of glycerin and anesthesin is effective. Plaque is removed with a swab containing proteolytic enzymes. Treat with antiseptics. Local healing drugs are used. - Phlegmon and tongue abscess
. For superficial abscesses, rinse with antiseptic solutions, prescribe antibacterial agents, and if ineffective, surgical interventions are performed. For deep abscesses and phlegmons, conservative therapy is an auxiliary treatment method, carried out against the background of operations, and includes antibiotics, analgesics, antihistamines, and anti-inflammatory drugs. - Candidiasis
. Alkalinizing rinsing solutions are used as local remedies. The oral cavity is lubricated with antifungal ointment and treated with solutions of iodinol, lugol, fucorcin. The therapeutic regimen also includes general antifungal drugs and, in severe cases, immunotherapy. - Glossalgia
. It is recommended to take light tranquilizers, motherwort, and valerian. A good result is achieved with trimecaine blockades of the lingual nerve and injections of B vitamins. Unpleasant sensations are eliminated through oral baths and applications with anesthetics. The main pathology and neurotic disorders are treated. - Xerostomia
. It is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcohol, use soft-bristled toothbrushes, drink frequently to moisturize the mouth, and suck on sugar-free lollipops to stimulate saliva production. The oral cavity is lubricated with a solution of vitamin A. Novocaine blockade of the salivary glands is performed, vibration massage, medicinal electrophoresis, and galvanotherapy are prescribed. - Neuralgia
. Anticonvulsants, non-narcotic analgesics, and vitamin complexes are used. For severe pain, antidepressants, sleeping pills, sedatives, and antipsychotics are recommended. Therapeutic blockades are carried out. Lubricate the tongue with a solution of cocaine. Patients are given a referral for SMT, galvanization, and diadynamic therapy. - Anemia
. In case of iron deficiency anemia, treatment of the underlying disease, nutritious nutrition with a high content of heme iron, and ferrous preparations are required. In case of pernicious anemia, the provoking pathology is corrected and vitamin B12 is prescribed.