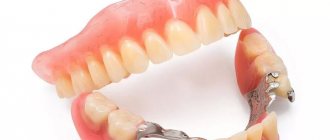
The design of the clasp prosthesis consists of the following main components:
- Metal frame-arc
- Support-retaining elements
- Artificial teeth attached to an arch
The metal arch, which runs along the palate of the upper jaw or under the tongue, is an important component of the clasp denture, as it combines two bases on which artificial teeth are installed.
Base - an element of the prosthesis, including artificial teeth and connected to the branches of the metal parts of the supporting prosthesis. With the help of locks (connecting elements), the base is installed and secured to the supporting teeth, while resting against the alveolar process.
The base is made of plastic reinforced with metal mesh.
Prosthetics using clasp
Modern dentistry allows you to use this type of removable prosthetics, such as a clasp denture, when several teeth are lost.
Most experts believe that there is no alternative to it today: the advantage lies in the comfort of wearing and the even distribution of the load when chewing between the remaining teeth and gums.
Prosthetics using a clasp makes it possible to replace any part of the teeth.
Advantages
They are distinguished by the presence of a cast metal frame in the form of a thin arc - a clasp. The plastic base and artificial teeth are fixed on this thin frame.
Dentures are installed in cases where it is impossible to use permanent structures in the form of a bridge. The thin arch in clasp dentures makes wearing them comfortable - it does not cover the palate, making it possible to feel the taste of food.
Clasp denture on the lower jaw
If a prosthesis is installed on the lower jaw, the metal arch does not allow it to fall out and does not interfere with the movement of the tongue. In addition, diction does not deteriorate during a conversation. Thanks to the clasps, the service life of dentures increases to 5 years; for plastic options, this period is 2.5 years.
It has been established that bone tissue and gum tissue atrophy over time when wearing prostheses, their shape changes and no longer coincides with the shape of the prosthesis. Discomfort, pain appears, and fixation worsens. Under clasp dentures, such atrophy occurs much more slowly - this allows you to increase the period of wearing them.
Features of the clasp
A clasp denture is a conditionally removable structure that fully restores teeth and all their functions. It is fixed in the oral cavity to the supporting crowns in several ways: clasps, crowns, locks.
The prosthesis consists of a metal frame, a plastic base with artificial crowns. The frame consists of an arch, saddles (for crowns) and support-retaining components. The size and location of the arch depend on the defect in the dentition, the jaw, the shape of the alveolar process, the individual anatomical features of the patient’s oral cavity, and the condition of the mucous membrane. On the upper jaw it has a width of 8-10 mm and is flatter. On the bottom – 4-6 mm and semi-convex shape. This form ensures convenient use and quick adaptation to the design.
Due to the presence of the arch, the prosthesis has a very small base, the patient’s palate remains open - the taste and thermal perception of food is not disturbed. The prostheses are quite lightweight, but very durable and easy to use.
A big advantage is the possibility of using it for diseases of periodontal tissue and mobility. Unlike other structures, it does not loosen, but strengthens and splints the supporting teeth. The components of the structure correctly distribute the chewing load across the jaw. For high-quality clasp prosthetics, you need at least 5 healthy teeth for support.
Splinting prosthesis
A feature of clasp dentures is the possibility of their use in prosthetics of moving teeth (lateral and anterior). Often, with loose teeth, this method of prosthetics is the only one.
The splinting method is used for chronic inflammatory and degenerative processes (periodontal disease, periodontitis), when teeth become painful and mobile.
Fixation of mobile teeth in the case of installation of clasps occurs due to a thin arc located on the inner surface of the teeth and repeating their shape. This additional arch holds the teeth in the desired position and helps stabilize their health.
Indications and contraindications for use
Clasp dentures are used for treatment in the following clinical situations:
- Dental defect in the anterior or lateral part of the jaw;
- Loss of several teeth in a row;
- Lack of teeth, which is combined with periodontal diseases, abrasion of dental tissues;
- Mobility;
- Unilateral or bilateral root defects.
Prostheses are not installed in the following cases:
- Absence of all teeth;
- Presence of less than 5 supporting teeth;
- Low height of clinical crowns;
- Poor hygienic care of the oral cavity;
- Severe periodontal tissue diseases;
- Acute inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- Dental diseases;
- Deep bite;
- Diseases of the temporomandibular joint;
- Allergy to materials used;
- Serious pathologies of the body;
- Period of exacerbation of diseases.
Fixation methods
The properties of the clasp, as well as service life, cost, and comfort of use depend on the method of fixation in the oral cavity. The dentist is faced with the task of reliably installing the structure so that it remains stable during functions - eating, talking. And also choose a fastener that will not have a negative effect on the teeth, gums, and mucous membranes.
Clasp fixation
The most affordable is the clasp denture. The elements are small but very durable hooks made of metal or plastic. The clasps cover the supporting crowns and thus securely hold the prosthesis. There are various support-retaining clasps, which differ in shape, type, and location.
The most important thing for high-quality prosthetics is to choose the right type of clasp. To do this, the dentist and technician carry out special methods for examining jaw models. The condition of the dentition, the number of missing teeth, the route of insertion of the prosthesis, the location of the defect and the boundary line, the presence of antagonist teeth, occlusal contacts, etc. are taken into account.
Clasps are a simple and reliable method. The disadvantage is the lack of aesthetics. In the anterior part of the jaw (in the smile area), the hooks may be noticeable.
Locking system
During the treatment process, special locks are used - attachments. The products consist of two parts - internal and external. One part is installed in the prosthesis, and the second in an artificial crown on the supporting tooth. When dressing, the mechanism clicks into place. Locks provide reliable fixation and stabilization of the structure by attaching to natural teeth, roots or implants. The method has many advantages:
- Excellent aesthetics;
- The castles are completely hidden from others;
- The smile looks beautiful and natural;
- Reliability and strength;
- Possibility to replace the lock;
- Long service life.
The disadvantage is the need to cover the supporting teeth with artificial crowns, strict requirements, complex manufacturing process, and relatively high cost.
- Telescopic crowns
The most aesthetic, high-quality and expensive treatment method is the use of clasp on telescopic crowns. The products are a special system of two crowns, one of which is placed on the supporting tooth, and the second is located in the frame of the prosthesis. These crowns precisely match each other and snap into place when the product is put on. Stabilization of the structure is ensured by the vertical walls of the crowns.
During use, chewing pressure is evenly distributed over the jaw, which prevents atrophy. Telescopic crowns are invisible to others, so the prosthesis is very aesthetic.
Beam fixation
Another reliable fastening method is the beam system. It consists of 2 parts: a fixed beam and a metal matrix in the prosthesis frame. The beam is attached to the crowns of the supporting teeth, and the matrix completely repeats the shape of the beam. When applying the clasp, the structure snaps into place, fixation and stabilization are ensured.
Clasp dentures with clasps
Your “clasps” can be fixed to the jaws using metal clasp hooks. Clasps are selected according to the individual characteristics of the size and shape of the teeth. They are usually cast along with the frame and are highly durable and strong. Clasp fasteners are budget-friendly and usually cost patients slightly less than other types of fasteners.
Despite their advantages, many people do not like such fastenings due to the fact that the hooks are often visible when opening the mouth or talking. However, the extraordinary strength of such retainers and the ease of their use attracts many elderly patients who are relaxed about dental aesthetics to hook-based structures.
The distribution of food load when using hooks occurs in a ratio of 1:3. In this case, one third of the load goes to the teeth, and the rest of it falls on the gums, which is important for patients with bad teeth.
In some cases, specialists themselves may insist on fastenings in the form of clasps in cases where the use of other fasteners is impossible.
Advantages and disadvantages
With high-quality prosthetics, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient, the clasp has many advantages:
- Excellent functional properties;
- Full restoration of functions;
- Strong fixation;
- Possibility of treatment in the absence of varying numbers of teeth;
- Possibility of prosthetics for diseases of periodontal tissues, mobility;
- Protection of periodontal tissue from unwanted load;
- Splinting;
- Elimination of horizontal pressure and proper distribution of chewing load;
- Support-retaining fixation elements prevent subsidence of the prosthesis;
- During use, prevention of alveolar ridge atrophy occurs;
- Possibility of prosthetics for location anomalies (tilting, rotation of teeth);
- Excellent fixation and stabilization;
- There is no need to prepare the abutment teeth;
- With the help of a prosthesis (onlays, splinting), you can change the height of the bite;
- Good aesthetics and appearance of the structure;
- The clasp takes up little space in the oral cavity;
- Tactile, taste or temperature sensitivity is not impaired;
- Quick habituation process;
- Simple hygienic care;
- Long service life;
- The prosthesis can be adjusted;
- The strong position of the clasp gives self-confidence to each patient, the use of the design is psychologically comfortable.
The disadvantage of the clasp is the complex manufacturing technology, which requires the skills of a doctor, special equipment, and materials from a dental technician.
How is prosthetics performed?
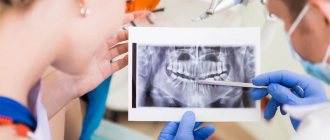
Prosthetics using a clasp design is quite lengthy and complex, but justified by excellent results. The first stage of treatment is a thorough clinical examination. The dentist conducts an examination, assesses the topography and size of the dentition defect, the condition and position of natural teeth. The type of occlusion, interalveolar distance, nature of teeth closure and other factors that may affect the success of treatment are determined. The patient is prescribed additional research methods (radiography, CT).
At the next visit, the specialist makes an accurate diagnosis and selects a suitable clasp prosthesis. The patient is informed about fixation methods and chooses the desired one. The dentist takes individual impressions of the jaws and passes them on to the dental technician.
In the dental laboratory, jaw models are cast, examined, and the future design is modeled. Several oral fittings are required during the manufacturing process. The finished structure is handed over to the dentist. The doctor tries on the prosthesis in the mouth and tells the patient how to put it on and take it off. Gives recommendations for use and hygienic care.
Types of fastenings
All orthopedic prostheses in dentistry are divided into groups:
- removable;
- fixed;
- partially removable.
Clasp structures belong to the third group, since removal is carried out only to perform hygienic procedures. Patients easily cope with this task with one movement of the hand. There is no need to remove the denture at night.
When chewing food, emotional conversations and expressions of joy (laughter), there is no need to worry about the reliability of the fixation. The prosthesis is firmly held by fastenings.
Care
The clasp denture on the teeth must be removed periodically. Not every day, but 1-2 times a week, the product must be removed from the mouth and thoroughly cleaned.
You can take care of your teeth as usual – 2 times a day with a brush and toothpaste. After each meal you should rinse your mouth with water. Before going to bed, you should use a irrigator or clean the interdental spaces with floss. Every 6 months it is recommended to visit the dentist for professional hygiene, preventive examination of the prosthesis and oral organs.
We can conclude that clasp dentures are an excellent method of prosthetics. They perform all their functions and give a beautiful smile.
Higher medical education
- Abdominal surgery
- obstetrics and gynecology
- Allergology and immunology
- Angiosurgery
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology and resuscitation
- Bacteriology
- Biochemistry
- Valeology
- Laboratory doctor
- Gastroenterology
- Hematology
- Geriatrics
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- Hirudotherapy
- Homeopathy
- Dermatovenereology
- Dermatocosmetology
- Pediatric abdominal surgery
- Pediatric allergology and immunology
- Pediatric anesthesiology and resuscitation
- Pediatric gastroenterology
- Pediatric hematology
- Pediatric gynecology
- Pediatric dermatology
- Pediatric cardiology
- Pediatric cardiology interventional
- Pediatric cardiac surgery
- Pediatric combustiology
- Children's physical therapy
- Children's drug addiction
- Pediatric neuropathology
- Pediatric neurosurgery
- Pediatric nephrology
- Pediatric general surgery
- Pediatric oncology
- Pediatric otorhinolaryngology
- Pediatric ophthalmology
- Pediatric pathological anatomy
- Pediatric plastic surgery
- Child psychiatry
- Child psychology
- Child psychotherapy
- Pediatric pulmonology
- Pediatric rheumatology
- Pediatric X-ray surgery
- Pediatric LUTS
- Children's dentistry
- Pediatric dentistry therapy
- Pediatric dentistry-surgery
- Children's forensic drug testing
- Child forensic psychiatric examination
- Pediatric audiology
- Pediatric toxicology
- Pediatric thoracic surgery
- Pediatric traumatology-orthopedics
- Pediatric transplantology
- Pediatric urology and andrology
- Pediatric physiotherapy
- Pediatric phthisiology
- Pediatric maxillofacial surgery
- Children's extracorporeal detoxification
- Pediatric endocrinology
- Pediatric endoscopy
- Pediatric infectious diseases
- Dietetics
- Immunology
- Infectious diseases
- Cardiology
- Interventional cardiology
- Cardiac surgery
- Clinical laboratory diagnostics
- Clinical pharmacology
- Combustiology
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging
- Resortology
- Physiotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Mammalogy
- Manual therapy
- Emergency and disaster medicine
- Medical biology
- Medical genetics
- Medical psychology
- Medical physics
- Medicinal chemistry
- Healthcare management
- Methodology
- Narcology
- Neuropathology
- Neurosurgery
- Neonatological surgery
- Neonatology
- Nephrology
- General practice
- general surgery
- Oncologist-gynecologist
- Oncology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
- Pathological anatomy
- Pediatrics
- Perfusionology
- Plastic surgery
- Proctology
- Occupational pathology
- Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Rheumatology
- Radiology
- X-ray surgery
- Reflexology
- Sexopathology
- Ambulance and emergency medical care
- Social hygiene and health care organization
- Sports medicine
- Statistics
- Dentistry
- Dentistry-orthodontics
- Dentistry-orthopedics
- Dentistry-therapy
- Dentistry-surgery
- Sujok therapy
- Forensic drug testing
- Forensic psychological and psychiatric examination
- Audiology
- Therapy
- Therapy for teenagers
- Toxicology
- Thoracic surgery
- Traumatology-orthopedics
- Transplantology
- Transfusiology
- Urology
- Physiotherapy
- Phytotherapy
- Phthisiology
- Functional diagnostics
- Cytology
- Maxillofacial Surgery
- Expert histologist
- Expert thanatologist
- Extracorporeal detoxification
- Electrocardiography
- Endocrinology
- Endoscopy