Development of teeth before eruption
The health of your baby’s teeth needs to be taken care of long before they erupt. It is useful for expectant mothers to know that the rudiments of baby teeth are formed already at the 7-8th week of intrauterine development, and permanent ones - at the end of 4 months. Not only the timing of teething, but even the level of mineralization of the enamel of both milk and molars depends on how pregnancy proceeds. Therefore, it is so critical that a woman receives all the vitamins and microelements and is as healthy as possible.
But it’s not just nutrition that’s important. Research results have shown that in the presence of industrial harmful substances in the environment of the expectant mother during pregnancy and numerous stressful situations, the formation of all dental tissues in the child is disrupted and the timing of the appearance of baby teeth is shifted. Among children born to women with high blood pressure, late eruption of primary teeth was observed in 56.7%. In approximately a third of the examined children born to mothers with heart defects, late eruption of primary teeth was detected, as well as deviations in the pairing and sequence of their eruption. The length of pregnancy also plays a role. There is a pronounced dependence of the timing of the eruption of the first teeth on the degree of prematurity: the earlier the baby is born, the later the first teeth erupt [1, 2].
How to help your baby when he is teething
Teeth are breaking through - it even sounds painful. Indeed, when a baby starts teething, it is often painful. Many children sleep poorly, often cry, and some even develop a fever. But there are other symptoms that indicate your baby is going through the baby teething period. The first signs of teething and, above all, what to do when teeth appear and how to reduce pain will be discussed in a conversation with first category pediatrician Ekaterina Borisovna Bulavina.
— Ekaterina Borisovna, please tell us when do babies usually start teething?
— The timing of teething varies quite widely. On average, the first teeth emerge at 5-7 months, but the process can begin earlier (at two or four months) or take up to a year. And some babies are born with teeth. Everything is very individual and depends on many factors, such as heredity, sufficient calcium intake in the body, the gender of the child, and the climate in the place of residence.
— How quickly will teeth be cut after the first one appears?
— In both boys and girls, the process of complete eruption of the primary dentition usually takes 2.5–3 years. The upper incisors appear 2-3 months after the appearance of the lower ones, then at the age of 9-13 months the upper and lower lateral incisors erupt. From one year to one and a half years, the upper and lower first molars alternately appear, then, by 20 months, the upper and lower canines, and by 2-2.5 years, the second molars. However, the order and timing when babies start teething are very arbitrary.
Table and chart by month: what time do children start teething?
How can you tell if your baby is teething?
— The appearance of teeth, although physiological, is a real test for the child and his mother and father. Only recently have we experienced colic, a feeding and sleeping schedule has been established, when suddenly the baby becomes restless again, is capricious, refuses to eat, or, on the contrary, often and greedily grabs the breast or bottle, sleeps poorly and puts everything in his mouth. These are sure signs that teething has begun.
Some lucky people endure the entire process completely painlessly, and only a casual tap on the gum with a spoon reveals the first tooth that has already erupted. But sometimes the moment of teething is so difficult for the baby that it is easy to confuse it with the onset of the disease.
Only a doctor can determine the real cause of the child’s anxiety, and you should definitely contact him if the temperature rises to febrile levels, severe lethargy, weakness or, conversely, severe excitability of the baby, as well as if signs of infection occur, such as a runny nose, cough, frustration digestion, vomiting, loose stools.
— Ekaterina Borisovna, parents are waiting for the appearance of the first incisors with caution. What symptoms characterize the process besides pain?
— When teeth are cut, the symptoms are very diverse, and everything is individual. In this case, the symptoms may differ depending on the location of the cutting teeth. Usually the most unpleasant sensations accompany the appearance of only the first teeth. All subsequent ones erupt more calmly, and the child practically stops paying attention to this process. When chewing teeth appear, pain may resume, but it is not as intense as at the very beginning of eruption. The appearance of the upper teeth is often accompanied by a runny nose: this is due to the proximity of the location and the single network of blood supply to the upper jaw and nasal cavity.
| First symptoms of teething | Features of the child’s condition and behavior |
| Swelling and redness of the gums |
|
| Excessive salivation |
|
| Decreased appetite or complete refusal to eat |
|
| Increased moodiness |
|
| Temperature |
|
| First symptoms of teething : Swelling and redness of the gums | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Excessive salivation | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Decreased appetite or complete refusal to eat | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Increased moodiness | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
| First symptoms of teething Temperature | Features of the child’s condition and behavior
|
— When is it better to lower the temperature during teething?
— Typically, antipyretic therapy is prescribed when the temperature rises above 38.5 degrees. Low-grade fever, up to 38 degrees, should always be brought down in children with organic damage to the central nervous system, with the threat of seizures, as well as with pronounced changes in the general condition of the child.
— Why do you need to carefully monitor your baby’s health during teething? Does teething affect the immune system?
— Teething is a rather complex process in which all systems of the child’s body are involved. The immune system is no exception. When the tooth moves, traumatic damage to the gums occurs and, as a result, inflammation occurs in the tissues. Immune cells rush to the inflammatory focus, trying to eliminate it, which somewhat weakens the local protective reaction. In addition, in abundantly secreted saliva, the content of the enzyme lysozyme is reduced, and it loses its protective properties. In addition, during this period the child puts everything into his mouth, trying to scratch the itchy gums, which increases the risk of infection and injury to the mucous membrane.
— How can parents distinguish teething from other problems, such as a cold?
— It is sometimes difficult even for a specialist to distinguish a viral infection from teething syndrome: very often the two conditions occur simultaneously. With eruption syndrome, the temperature rarely exceeds 38-38.5 degrees, the discharge from the nose is copious, mucous in nature, often transparent. The cough is superficial and occurs more often in a horizontal position. All symptoms are accompanied by profuse salivation. The child's general condition rarely deteriorates; the child is capricious, whiny, but not lethargic or apathetic.
Teething can also be accompanied by symptoms of dyspepsia, such as regurgitation, and sometimes even vomiting, and loose stools. Unlike an intestinal infection, regurgitation and vomiting are episodic and occur when there is an excessive accumulation of saliva.
Liquefied stools may be associated with increased motility due to an increase in temperature - swallowing large amounts of saliva and intense chewing movements. Stool 1-2 times a day, normal color and smell, without pathological impurities, but softer consistency.
If any symptoms appear that do not fit into the picture of teething, you should definitely consult a doctor.
— Does all children experience pain during teething?
— Each child has his own pain sensitivity threshold. The intensity of inflammatory reactions is also different for everyone, so each baby experiences teething differently. If one continuously cries all night, the other may behave in a completely normal way. It depends both on genetics and on the baby’s temperament.
— When teeth are being cut, how can you help your baby? What medications are allowed to be given to relieve pain?
— Pain-relieving gels are widely used. However, you should remember the rules for their use. They have a short-term effect, about 20-30 minutes, but it is not recommended to use them more than five times a day. The gel is applied in a thin layer to avoid an overdose of the drug. And, as is the case with any medicine, do not forget about a possible allergic reaction in the baby.
You can quickly and permanently relieve pain only with anti-inflammatory drugs. And there are a lot of BUTs here. Any drug is unsafe, especially if given for the first time. Only a doctor can assess the child’s condition and prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy if necessary, taking into account the risk-benefit ratio.
Medicines from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed internally. The dosage is calculated by the doctor depending on the weight of the child. Gels with local anesthetic and antiseptic effects are used on the mucous membrane.
— Is it possible to relieve pain and other symptoms with folk remedies?
— Treatment with folk remedies is very popular in our country, although the global scientific community questions its effectiveness. Only exposure to cold has proven effectiveness, so it is recommended to give your child chilled pacifiers and teethers to chew on. Cold causes vasospasm, reduces swelling and inflammation in the gums, and, as a result, pain temporarily subsides. The effect is short-lived, but it still exists. Massaging the gums with a fingertip or soft brush is also helpful.
— Ekaterina Borisovna, tell us in more detail how pacifiers or toys that can be chewed help with toothache, and how to choose a pacifier and a special teether for a child.
— Gum massage helps the baby cope with unpleasant sensations. During the massage, itching decreases, gum tissue softens, and it is easier for the tooth to make its way. But constantly massaging a child’s gums is a very tedious task. He may well engage in self-massage, especially since during this period he himself happily puts everything into his mouth.
Special pacifiers or teethers will be excellent massage assistants. They differ from regular pacifiers in their greater rigidity and textured surface, and are made of latex or silicone. Many models of teethers are equipped with a cooling function - there is a liquid inside that can be cooled. Teethers are also made from plastic, wood or even textiles. But, in my opinion, they do not meet safety standards. It’s worth choosing brands that have been widely represented on the children’s goods market for a long time.
— What techniques can be used to distract a child from toothache?
- In this case, there is only one method - to surround the baby with care and attention as much as possible, pick him up more often, put him to the chest if the child asks. Next to the parents, the baby feels safe and calms down. Children react very sensitively to the behavior and emotions of adults, so it is important for parents to be calm and friendly, to distract the kids with a toy, song, or kind words. You can play finger games with older children. Relaxing massages and long walks are helpful.
Unfortunately, there are no absolutely effective methods. Parents can only help the child cope with the problem that has arisen. But there are some tips that will help you survive this difficult period.
— Please share them with our readers.
— The rudiments of teeth are formed long before birth. Therefore, during pregnancy, mothers should carefully monitor their diet. A sufficient supply of calcium is especially important for the formation of healthy teeth in a baby. But even after birth you shouldn’t forget about calcium. When breastfeeding, the mother's diet should include dairy products or calcium supplements in case the baby is intolerant to cow's milk proteins.
Hardening from birth is the key to good immunity. There is no need to wrap your child in a hundred clothes and be afraid to ventilate the rooms. Walk in any weather and for a long time, use a light contrast shower. And then the baby won’t be afraid of any cold.
Also, avoid public places, especially during the teething period. The baby is very vulnerable at this moment. Postpone visits from relatives, shopping trips and visits to closed playgrounds for a while - thereby you will reduce the risk of infection for your child.
It is also especially important to maintain optimal temperature conditions in the room during this period. Heat and dry air will only increase discomfort.
Teething is a difficult stage in a child’s life. If the process causes severe discomfort, is accompanied by the appearance of alarming symptoms, or high fever, then you should contact a specialist for help as soon as possible. Otherwise, surround your baby with care and attention, select pacifiers, teethers, toys that relieve itching, and use medications with the doctor’s permission. The main thing during this period is to be there and help the baby cope with the pain in every possible way.
Pediatrician Ekaterina Borisovna Bulavina
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
Why are baby teeth needed?
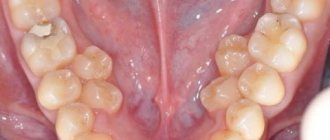
Nature has designed the correct order and timing of teething in children. Evolutionarily, this is due to the need to form the bite and jaw bones for chewing and speech. Over the years, the bones grow, and baby teeth, which at the beginning of their appearance were tightly adjacent to each other, diverge by the age of 6-7 years, forming wide interdental spaces that are natural for this period - tremata and diastemas.
There are only 20 teeth in the primary dentition. This is explained by the fact that they must be correctly placed in the small child’s jaw in the first years of the baby’s life, and eliminates the crowding of teeth that provokes dental diseases. The last of the baby teeth are replaced at the age of 10-12 years. However, they are very important for the physiological formation of the jaw bones and the permanent bite.
Proper growth and health of baby teeth helps:
- rebuild the body from lactophoric to mixed type of nutrition;
- reserve space for the normal location of future molars;
- form a mixed bite.
There is a misconception that if baby teeth become infected with caries, they can not be treated, but can be removed immediately. But modern dentists are against such tactics. Early removal is fraught with displacement of adjacent baby teeth and the appearance of problems with an adult bite. Therefore, it is so important to maintain the presence and health of all baby teeth until the permanent teeth erupt on their own [3].
Formation of the dentition
The article tells how to understand that a child is teething, and about ways to help him with pain and inflammation of the gums. But first, a few words about the process of dentition formation.
The formation of absolutely all teeth occurs in the fifth month of intrauterine development. They remain in a “frozen” state and begin to grow immediately before eruption. Therefore, if a child has no teeth by 9-12 months, radiography is prescribed - a study that allows one to evaluate their formation and location.
Timing of baby teeth eruption
Teething is a genetically programmed event that occurs at a certain period.
Physiological teething is characterized by three main features: certain timing, pairing and sequence of eruption “Characteristics of exogenous and endogenous factors influencing the eruption of primary teeth in children” Dr. med. Galaktionova M. Yu.
Children's baby teething rates vary depending on their ethnicity. But as research shows, in general, in the world there is a reduction in the time from birth to the moment when the first tooth appears. This is due, according to most researchers, to the global acceleration of human development [1]. How and when baby teeth erupt is one of the indicators of a child’s physical development.
The reasons for violation of the order and timing of teething in children can be:
- heredity;
- climatic conditions;
- nature of feeding;
- some diseases, for example, rickets.
The standards for the eruption of primary teeth according to the American Dental Association are presented in the table.
| Baby teeth | Upper jaw eruption / month. | Lower jaw eruption / month. |
| Central incisor | 8-12 | 6-10 |
| Lateral incisor | 9-13 | 10-16 |
| Fang | 16-22 | 17-23 |
| First molar | 13-19 | 14-18 |
| Second molar | 25-33 | 23-31 |
The indicated periods are average indicators, varying depending on individual and family characteristics [4,5]. But the sequence of appearance of teeth is significant, and it is better to track and record it. From a physiological point of view, the correct order of eruption of baby teeth in children is important for the formation of occlusion .
Signs of the appearance of the first teeth
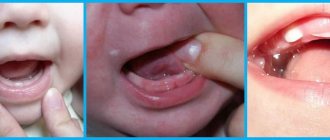
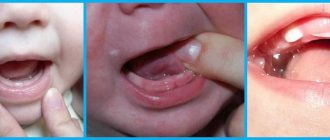
It happens that the growth of units is not accompanied by pain. True, this rarely happens. Many children do not tolerate the birth of chewing organs well, especially when they are not fed rationally. After all, their body does not receive enough useful microelements and vitamins, which complicates growth. Sometimes it happens that the rudiments are cut with carious lesions due to a deficiency of calcium, phosphorus, fluorine, potassium, and magnesium. What is the behavior of a child when teething?
- There is swelling, swelling of the gum tissue, mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, and difficulty breathing. The gums begin to hurt.
- Saliva production increases significantly.
- The child begins to become capricious.
- He loses his appetite and refuses to eat.
- Due to itching, his fingers are constantly in his mouth.
- The temperature rises slightly for 1-2 days.
- Diarrhea may begin, bowel movements become watery, but not too frequent. This condition usually lasts from 1 to 3 days.
- Sometimes there is a mild runny nose with clear, runny mucus. Duration – 2-3 days.
In addition, a symptom such as a wet cough that occurs in a horizontal position and lasts no more than 3 days may appear. There may even be a slight reddening of the throat, as there is increased blood flow in the gums. During this period, the future tooth is visible under the mucous tissues. The main thing for parents is not to miss the moment when serious diseases can form. If in doubt, you should consult a doctor.
Helping your baby with teething
The appearance of baby teeth is not an easy process not only for the children themselves, but also for their parents. The most common symptoms of teething:
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- increased salivation;
- itching and desire to keep hands and toys in the mouth;
- child's capriciousness;
- sleep disturbance;
- refusal to breastfeed, bottle or complementary foods;
- temperature increase;
- bowel disorders;
- runny nose.
The following will help you get through this period as comfortably as possible:
- special teething rings that relieve itching, especially with a cooling effect;
- dental gels with local anesthetic effect;
- antipyretic and painkillers;
light massage with a silicone fingertip, which will bring relief and calm the baby [6]
The first "bells"
The first signs of rapid teething are quite vague, but after observing the child for several days, you can notice changes in his well-being and behavior. Most babies begin to act restless, wake up more often at night, and eat less milk or formula about 4 weeks before the central incisors (these teeth appear first in children) erupt.
During this period, behavioral changes can be noted, listed in the table below.
Table. Changes in behavior during teething.
| Action | Why does the child behave this way? |
| This is explained by severe itching in the place where the tooth should appear: the top of the tooth rests on the gum, trying to break through the mucous tissue, and injures it, causing severe irritation. | |
| Such behavioral changes are especially pronounced in breastfed children due to stronger emotional contact with their mother. For an infant, the breast is not only a source of food, but also a means of comfort, therefore, when experiencing pain and discomfort, the child instinctively looks for an object that he associates with positive emotions. For bottle-fed babies or mixed-fed babies, this item can be a bottle of milk or a pacifier. | |
| The explanation for the temporary refusal of foods introduced into the children's diet is due to physical discomfort and unpleasant sensations when the gums touch a spoon or other cutlery. If you give your child a raw apple or carrot during this period, most likely he will try to chew them with pleasure, since such movements provide gum massage and help soothe pain. This method must be used strictly under adult supervision due to the risk of accidental inhalation of small pieces! |
Changes during this period also affect children's sleep. Most babies fall asleep well, but begin to wake up frequently at night to breastfeed. It is impossible to fight this phenomenon - sleep returns to normal after the eruption of the frontal incisors and canines, which are the most painful. To relieve pain, you can use special gels with analgesic properties, for example, “Kamistad Baby” or “Kalgel”. They will also help reduce inflammation caused by trauma to the gums from the sharp tip of an erupting tooth.
Important! If during a night's sleep a child wakes up too often, cannot fall asleep for a long time, and each rise is accompanied by a bout of severe crying, it is necessary to consult a doctor to rule out pathologies of the digestive system and other internal organs.
Caring for baby teeth
As soon as your first tooth comes through, don’t put off going to the dentist. Make a schedule of visits (at least once every 3-4 months). And after the first birthday, it is advisable to also see an orthodontist. If there are no problems, visits to him should be repeated once a year [7,8]
It is important to provide proper care at home.
- An ultra-soft toothbrush with a small head is suitable for baby teeth
- Children's mouth rinses are used from about 4 years of age or from the time the child learns to spit out liquid.
- Parents should supervise the brushing of preschool children's teeth and, if necessary, help and finish cleaning missed areas.
- Adults need to teach their child to rinse their mouth after eating from a very early age.
- Until the child has learned to spit on his own, toothpaste should not contain fluoride.
- A timer in the bathroom or a favorite song helps you keep your teeth brushing to 2 minutes.
- Solid food should be included in the diet daily in sufficient quantities to properly form the bite and stimulate the gums.
These simple recommendations help maintain the health of baby teeth from the very beginning until their natural replacement with permanent ones.
How to help your baby during this period
The time of birth of milk rudiments is an important period in the life of a newborn. Since it is accompanied by difficulties and pain, every parent should pay more attention to their child, take care of him, and calm the crybaby. If a child has severe gum inflammation, it should be shown to a doctor. Care and affection will help compensate for the baby's discomfort. You shouldn’t start weaning your baby these days, because it’s additional stress for him. It is better to distract the child from difficulties by keeping him busy with an interesting game, which causes a positive mood. And:
- Unpleasant sensations in the mouth are alleviated by special rings, rubber elastic toys that the child chews, thereby scratching the gums.
- Chewing a bagel or bread crust relieves itching.
- You can use gels such as Kamistad, Kalgel, Cholisal, which must be prescribed by a doctor. Applying and rubbing drugs into mucous tissues will eliminate pain. The medicine contains antiseptics and analgesics. The drug has a calming effect.
- Saliva flowing from the mouth should be blotted with a soft cloth to prevent irritation of delicate skin.
- Dentists recommend using local anesthetics such as Dentol. The basis of the drug is benzocaine.
- Tablets of Ibuprofen, Paracetamol or baby suppositories and syrups may be prescribed.
- The child's condition will be eased by a gentle massage of the gum tissue. It is performed with a finger dressed in a sterile fingertip. You can use a special nozzle equipped with silicone bristles.
It is important that parents do not miss dangerous symptoms. You should definitely visit a doctor if the color of the crowns changes. Blackish areas in the area of the tooth neck indicate a chronic inflammatory process. With a yellowish-greenish tint, disturbances in bilirubin metabolism can be suspected. A reddish color indicates metabolic disorders of pigment such as porphyria. We must not allow ulcers, stomatitis, or damage to the mucous membrane to appear in the mouth. It is forbidden to use aspirin and alcohol solutions, or to lick your baby’s pacifier or spoon, so as not to introduce pathogenic bacteria. Even with a typical picture of the appearance of chewing organs, a visit to the doctor will not be superfluous.