Timing of teething
The wait is especially long after the removal of chewing temporary teeth, which are usually the first to suffer from caries and its complications. Often, parents frivolously insist on removing molar baby teeth, blithely declaring: permanent ones will grow in!
But the process of changing bites develops according to strict laws. Follicles (buds) of temporary and permanent teeth are located in two rows in each jaw of a newborn, going through successive stages of formation and mineralization before eruption. It is impossible to speed up these stages by any means.
The milky roots gradually dissolve, and permanent follicles are pushed out in their place by the coronal part. And only after the formation is completed, permanent teeth appear above the surface of the gum. The first to erupt is the so-called “sixth tooth” - the first molar, which parents often mistake for temporary, and therefore do not treat its carious lesions. This tooth has an important function - it determines the height of the permanent bite and the place of the other “brothers” in the dentition.
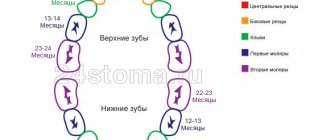
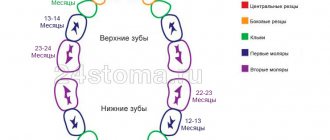
We give approximate dates for the appearance of permanent teeth to make it easier for parents to navigate the normality of the change process:
- first incisor - 6-7 years;
- second incisor - 7-8 years;
- fang - 9-11 years;
- first small root - 8-10 years;
- second small root - 11-12 years;
- first major molar - 6 years;
- second major molar - 13-14 years.
Small molars replace primary chewing teeth. If a temporary tooth was removed at the age of 6-7 years, which is not uncommon, then the child is deprived of the ability to fully chew food for as long as 5-6 years. Therefore, it is so important to promptly treat caries of milk precursors.
When do the first teeth usually appear?
At birth, a child's teeth are in a state of maturation within the jaw bones. There is a complete set of baby teeth in various stages of growth and hardening (mineralization). The front teeth form earlier than the others and begin to emerge into the oral cavity, cutting through the gums, already when the child reaches the age of six months. With the normal and correct development of a child, teeth continue to erupt on time and in pairs - one on each side, and a full set of twenty milk teeth appears by the age of three.
Teething symptoms
Consequences of early destruction of primary teeth
After the early removal of a baby tooth, the gum in its place becomes overgrown, and the permanent one is deprived of its natural landmark. This leads to phenomena such as:
- dystopia - eruption of a permanent tooth outside the dental arch;
- retention - the occurrence of a formed tooth in the thickness of the jaw bone.
If the baby tooth does not receive treatment, and the inflammatory process spreads to its roots, then the permanent follicle located under them is damaged. In this case, the permanent one may die, and then its place in the dentition will remain empty. The absence of a tooth is confirmed by radiography.
What types of delayed eruption are there?
Currently, doctors talk about two main types of delayed eruption.
The first is retention. Pathology is diagnosed in 1-7% of cases, and retention can be associated with both baby teeth and permanent teeth. The essence of the disorder is that the teeth have already formed, but have not yet erupted. The pathology can be caused by various anomalies: improper formation of buds, inflammatory processes, hematomas. In many children, the canines of the upper jaw are susceptible to retention.
The causes of adentia are not fully understood
The second type is edentulous. This is a more dangerous pathology in which the absence of teeth (complete or partial) is detected. The absence of all teeth is extremely rare, and the reasons for such an anomaly are not fully understood. Usually we are talking about problems with the formation of tooth germs in the prenatal period, and this, in turn, is provoked by various external factors (infections and inflammations, poor lifestyle of the mother, complicated pregnancy, deficiency of nutrients). In case of edentia, an x-ray is prescribed, during which it is determined whether there are any rudiments of milk teeth in the jaw. If they are present, the reason why teeth are not erupting is determined.
Problems when changing bites
Sometimes a situation arises that a child “grows a tooth under a tooth” - the permanent one has already appeared above the gum, and the temporary one is firmly held in its place. This happens when the resorption process of one or more milky roots is disrupted. This is also a reason to contact pediatric dentistry - after all, no one can say in how many days a loose baby tooth will fall out, and its “stubbornness” leads to the dystopia of a permanent one.
Dental doctors remove even such semi-loose teeth with anesthesia, so as not to cause discomfort to children. Only a specialist can decide what to do when changing the bite. Regular monitoring by the dentist during such an important period will help to avoid the formation of an abnormal relationship of the dentition, which will require further treatment by an orthodontist.
If a child’s baby tooth is loose, then you shouldn’t guess how long it will take for it to fall out; it’s better to consult a doctor without delay for qualified advice.
At the Shifa clinic, children are treated with modern equipment using the latest materials. The center has all the conditions for an accurate diagnosis of the condition of primary and permanent dentition, and this is the key to correct medical tactics. The dentists of the Shifa clinic find an approach to every child and master the most advanced methods of assistance, constantly improving their professionalism in Russia and abroad. Contact the best doctors who will help solve any dental problem!
7 questions about changing baby teeth
Parents worry when their child doesn’t have teeth for a long time, and then when they appear. They worry if there are few of them or, conversely, too many. We collected the most important questions about the timing of the replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones, as well as about possible deviations from the norm, and asked them to the winner of the competition for pediatric dentists in Russia, Yulia Selyutina.
1. What to do after a child’s baby tooth falls out - is it necessary to stop the bleeding somehow? You don't need to do anything special. After a tooth falls out, a blood clot forms in the socket within about 5 minutes. It promotes rapid wound healing. But there is no need to treat it with ointments or heat the cheek. It is also important not to rinse your mouth with anything, otherwise the clot can be accidentally removed - and then healing will take longer. By the way, it is precisely in order for this clot to form that the doctor, after removing the tooth, applies a sterile gauze swab to the wound. It must be kept in the mouth until the bleeding stops. Some children, after a tooth falls out, constantly “check” the socket with their tongue. There's nothing wrong with that. But make sure that they do not put foreign objects into their mouths. After a tooth falls out, it is better not to eat anything for an hour. You can give your child something to drink, but not anything hot. And it is advisable not to chew or bite food on the side that “lost” the tooth for a couple of days. The remaining teeth should be brushed as usual with toothpaste and a brush, morning and evening.
2. Tested remedy: a baby tooth is loose - tie a string to it and pull. Is it always good? The baby tooth begins to loosen due to the fact that its roots are dissolving. This is a natural process and in most cases the rope method can be used. Of course, provided that the child himself is not afraid to part with a tooth in this way. In addition, not all teeth are so mobile that ordinary floss can remove them. In some cases, additional effort may be required. If the baby tooth is mobile, and the child is not averse to loosening it, it does not hurt him, then he may well remove the tooth in this way. The main thing is that the child’s hands are clean during the “procedure”. If there is no result for a long time, the loose tooth has not fallen out for two weeks, it bothers the child, and he is afraid or does not want to remove it himself, then it is better to consult a doctor. The doctor can handle this one or two times. Sometimes even anesthesia is not required, or it is enough to anoint the gums with an anesthetic gel or spray with a spray.
3. Why do baby teeth not fall out on schedule? Is there something wrong with the child? The timing of the change of baby teeth indicated in various tables is arbitrary and highly averaged. Deviations in one direction or the other occur very often, and this is not a pathology or a sign of a disease. The main thing that influences the timing of the eruption and replacement of baby teeth is heredity. But no connection has yet been found between any general somatic diseases and earlier or later change of baby teeth. There is an additional research method - orthopantomogram. This is a panoramic photograph of all the teeth of both jaws at once. Having done it, you can determine the number of all the rudiments of permanent teeth, understand how the process of resorption of the roots of baby teeth is progressing, and make predictions. It is not at all necessary to conduct such a study, because it does not affect the timing of teeth change. However, an orthopantomogram can reassure parents or indicate a possible problem. For example, the absence of one or more permanent tooth buds.
4. The baby tooth has fallen out, but the permanent one is in no hurry to replace it. When is it time to worry? There are no critical deadlines. Sometimes you have to wait quite a long time for a permanent tooth to appear. For example, due to the fact that there is simply no room for it in the child’s jaw. A permanent tooth may not erupt at all if the child’s rudiment has not formed. You can take a picture of the area where the tooth is supposed to appear and find out what is causing the delay. If the tooth germ has formed and there is enough space in the jaw, be patient. Otherwise, consult an orthodontist. He will draw up a treatment plan that the child may need in the future.
5. The child lost almost all of his baby teeth in elementary school. Will his permanent ones fall out faster? Early change of teeth is quite common, it is not a pathology, not a violation of the “norm”. And it certainly doesn’t mean that permanent teeth should fall out, especially early. Unlike baby teeth, which sooner or later fall out on their own, we lose permanent teeth for some reason. For example, due to the diseases “periodontitis” or “periodontal disease”. With them, the tissue of the jaw bones dissolves and the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth is destroyed. If this happens, the teeth may become loose and even fall out. But this practically never happens in children. Even if they had “bad” baby teeth, this does not mean that there will be problems with their permanent teeth. It is important to care for them and clean them. Sometimes the use of additional means, for example, an irrigator, is simply necessary even when the teeth are still baby. Ideally, of course, your child’s oral care products should be selected by a dentist.
6. The baby tooth has not yet fallen out, it is not even loose, but the permanent one is already growing behind it. What to do? I believe that in such a situation the baby tooth should be removed by a dentist. Then ask your child to try to push the permanent tooth in the desired direction with his tongue. This is where parents' help comes in handy. Lubricate your finger with vegetable oil and perform massage movements, pushing the tooth in the desired direction. It is enough to give this mini-massage a couple of minutes a day.
7. Is it worth correcting a milk bite? Undoubtedly. Problems with bite during the period when a child has baby teeth can affect the appearance of pathologies when permanent teeth erupt. Practice shows that the sooner you start dealing with this problem, the better the results will be in the distant future. Correction or prevention of the formation of malocclusion can begin when the child turns 5-6 years old and all 20 baby teeth have erupted.
© Asya Gasimova